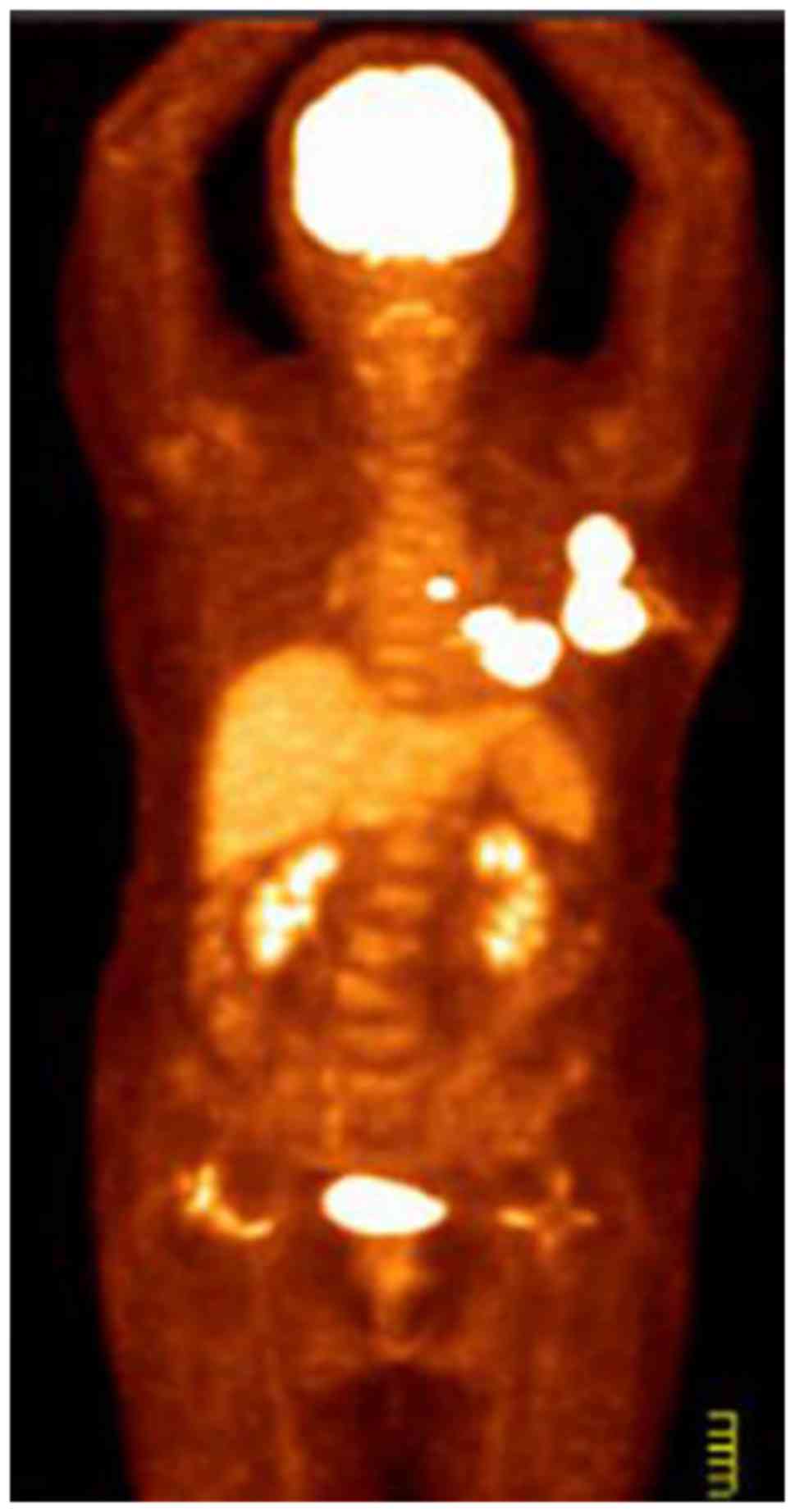
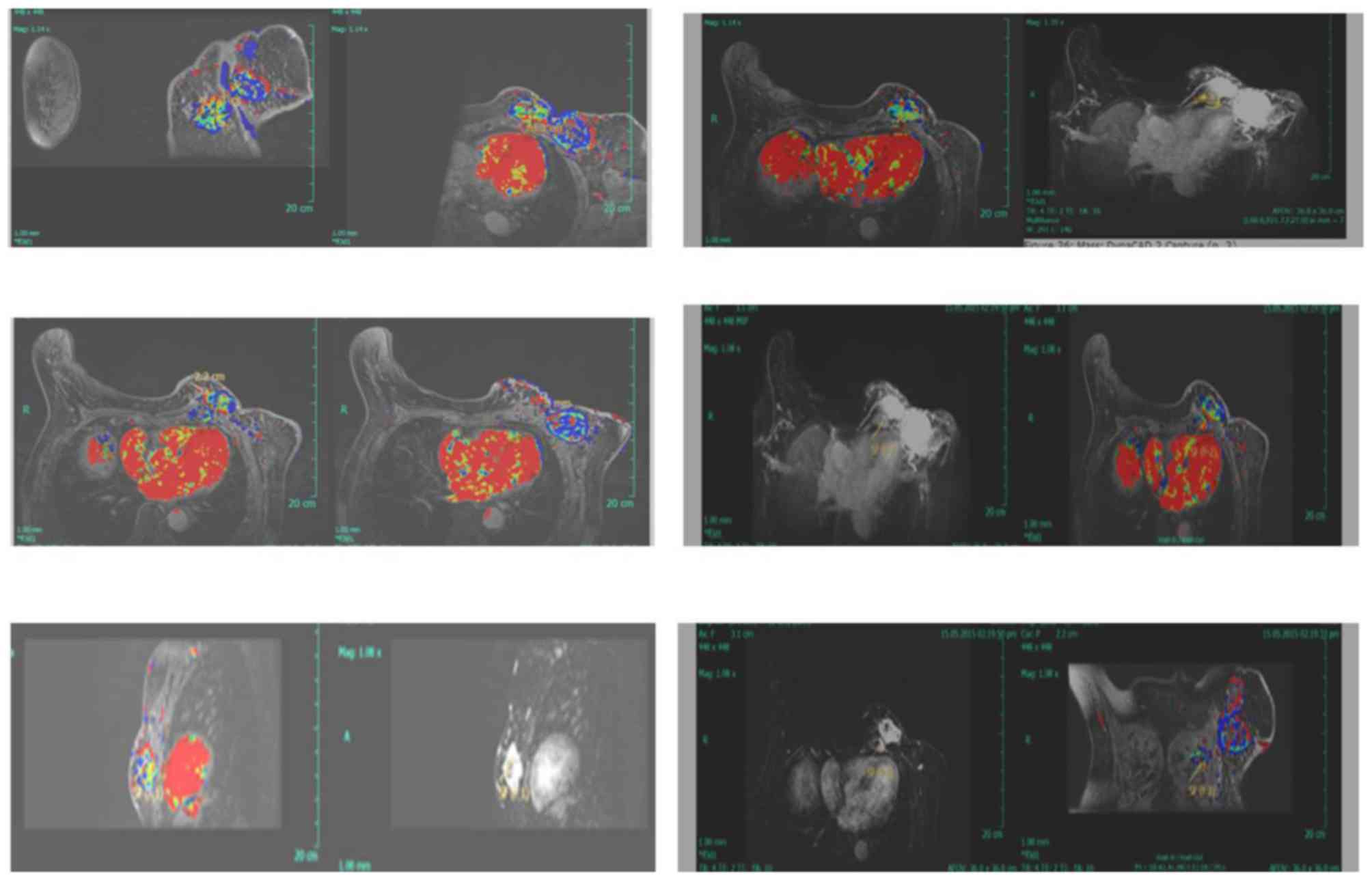
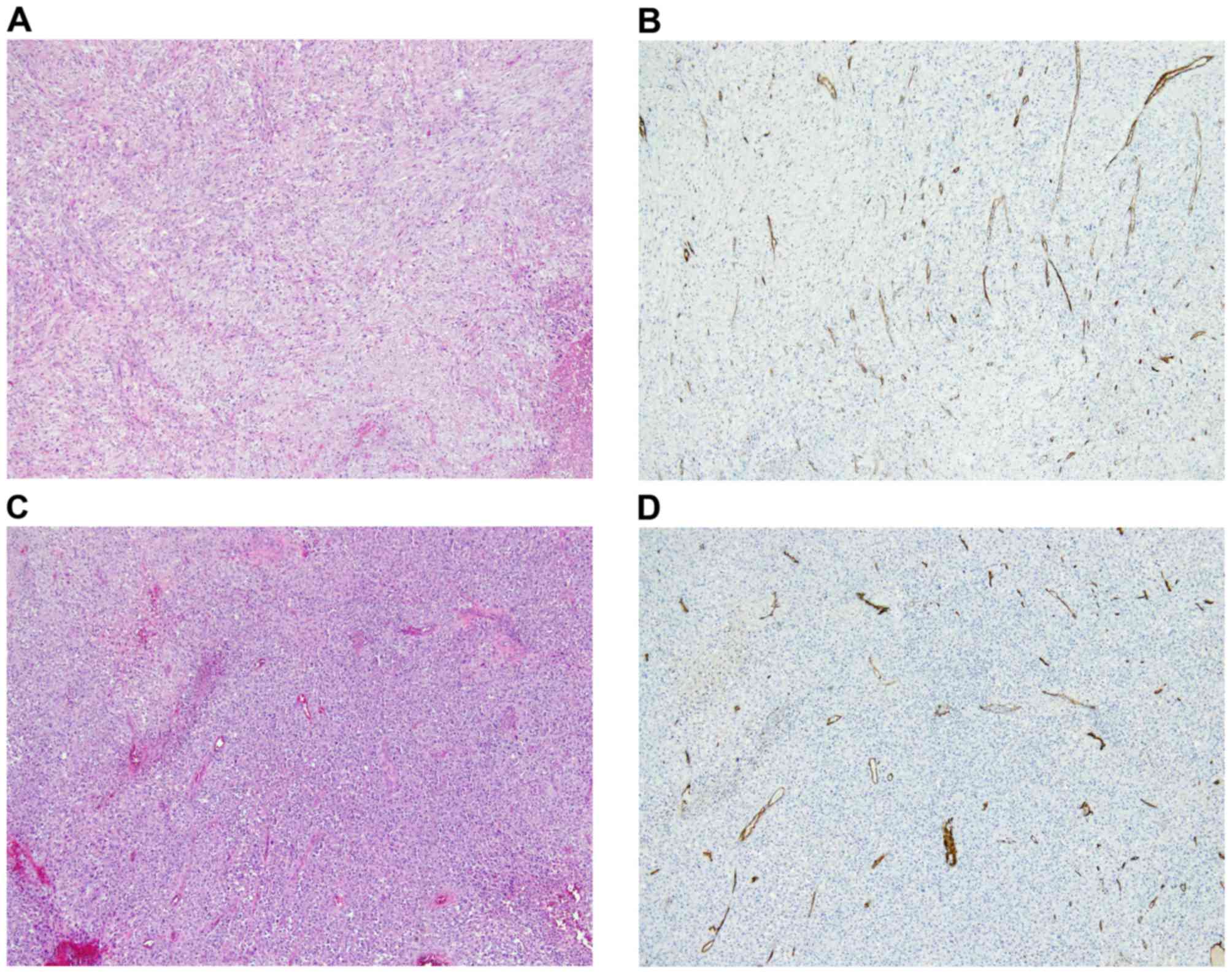
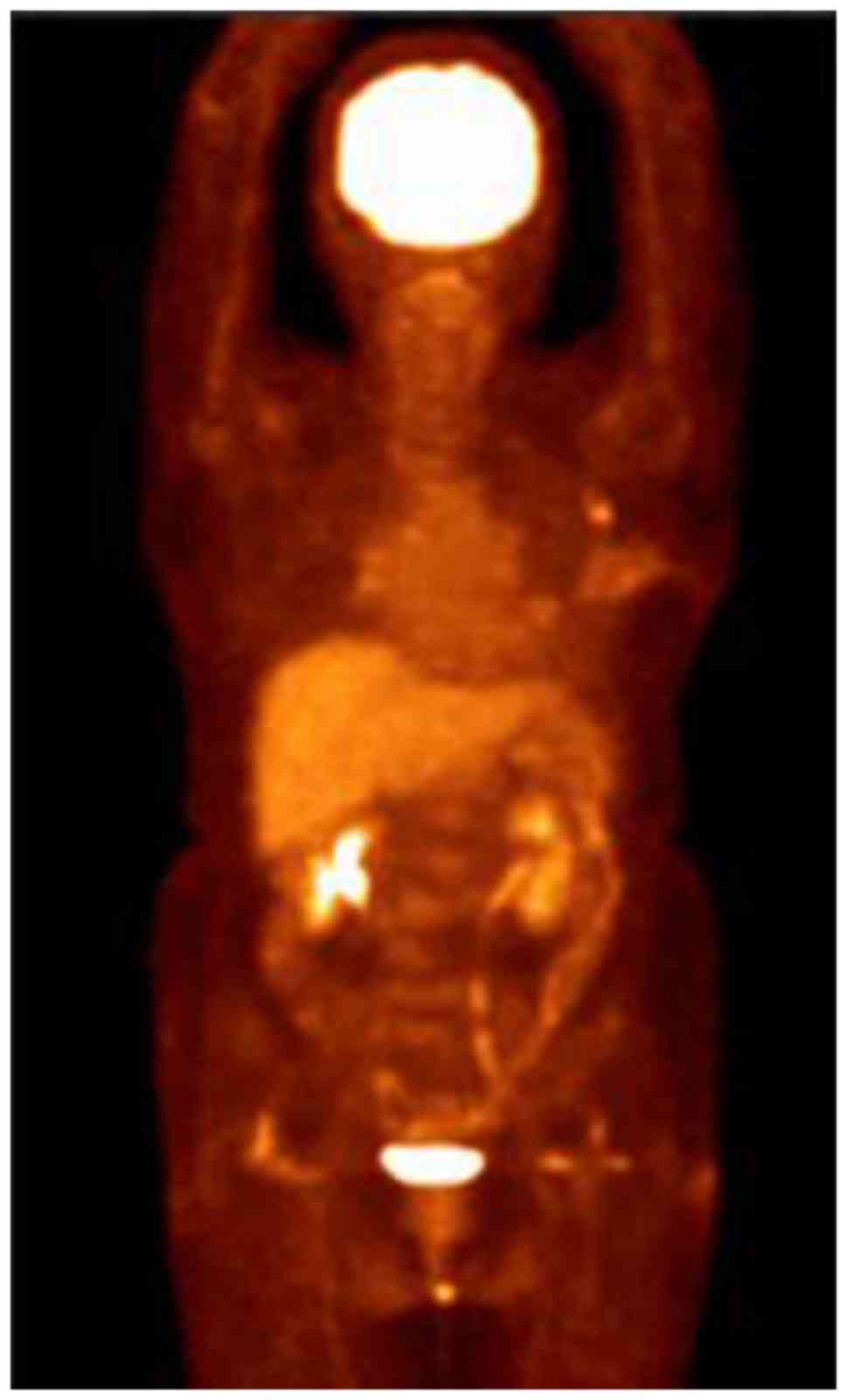
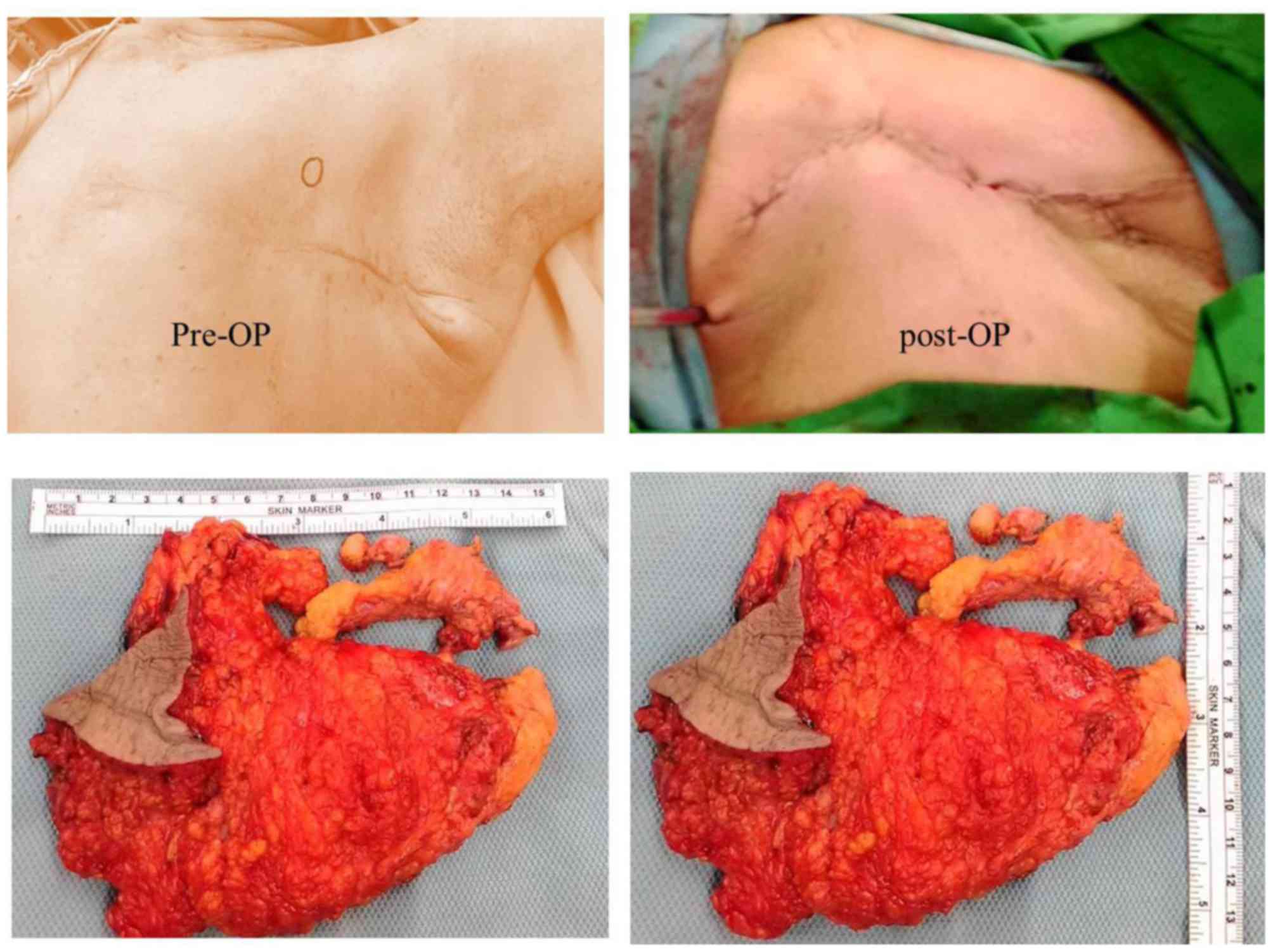
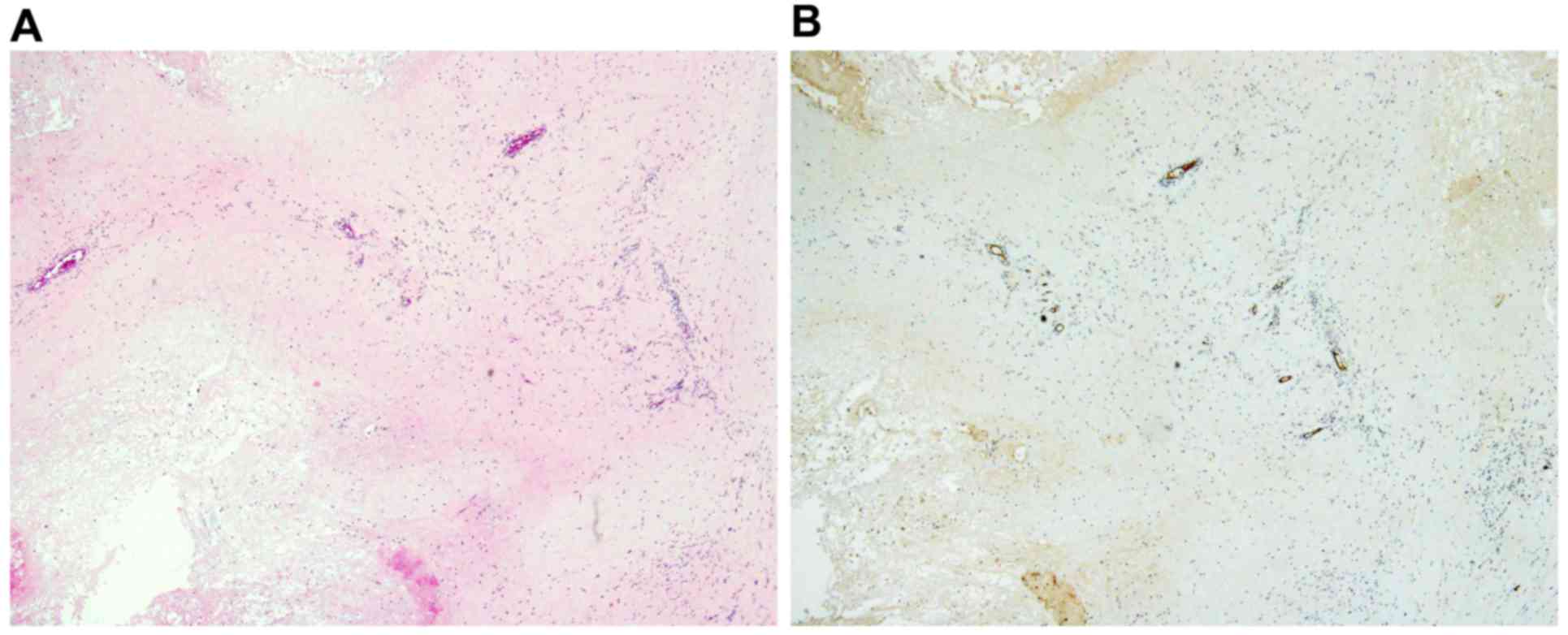
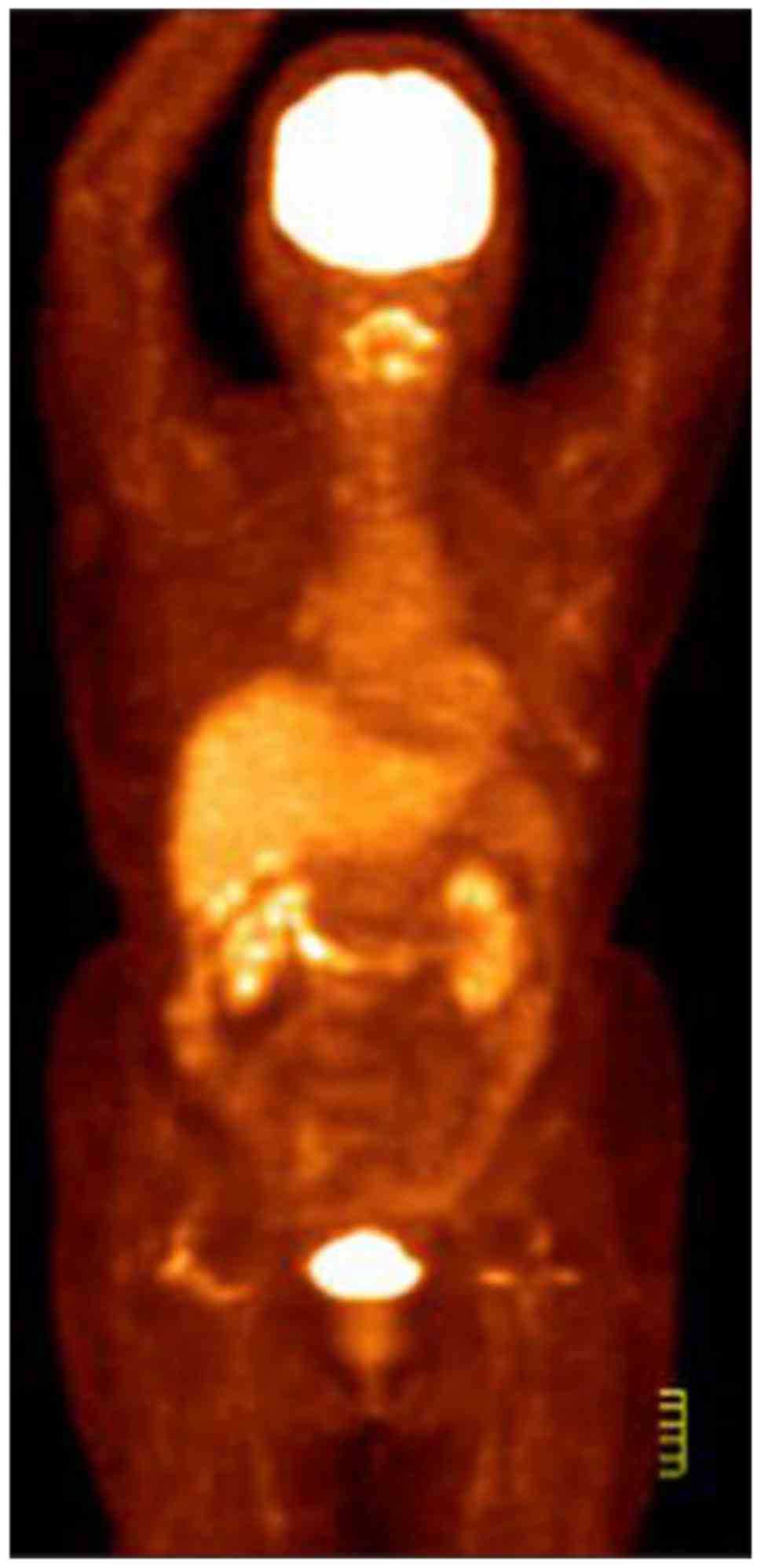
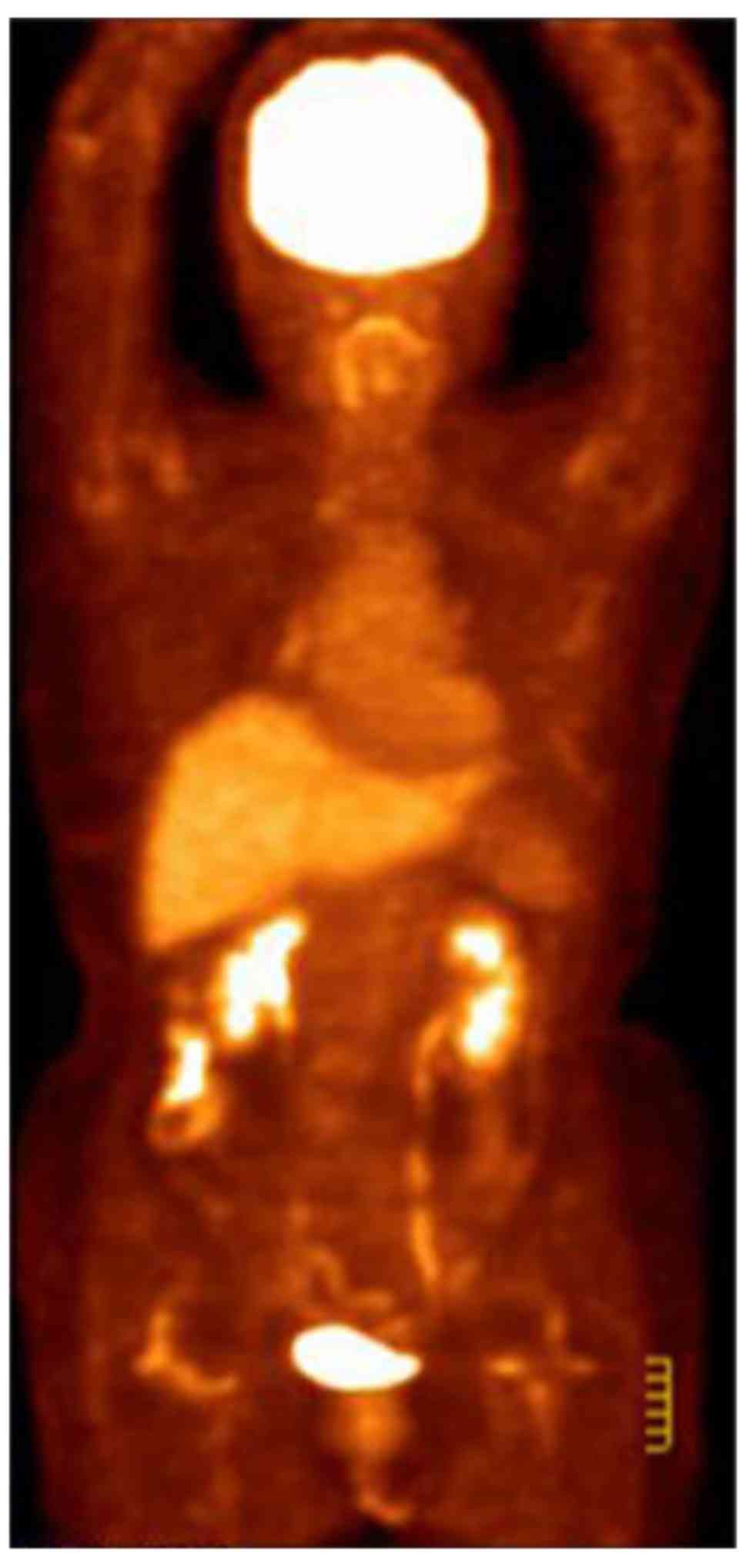
|
1
|
Nathan Roberts* and Dianne M: Runk:
Aggressive malignant phyllodes tumor. Int J Surg Case Rep.
8:161–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Norat F, Dreant N, Riah Y and Lebreton E:
Extraordinary case of malignant phylloid tumor of the breast:
Surgical reconstruction treatment. Ann Ital Chir. 80:475–478.
2009.(In Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matar N, Soumani A, Noun M, Chraibi T,
Himmi A, el Mansouri A, Aderdour M and Bekkay M: Phyllodes tumors
of the breast. Forty one cases. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod
(Paris). 26:32–36. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Belkacémi Y, Bousquet G, Marsiglia H,
Ray-Coquard I, Magné N, Malard Y, Lacroix M, Gutierrez C, Senkus E,
Christie D, et al: Phyllodes tumor of the breast. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 70:492–500. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guillot E, Couturaud B, Reyal F, Curnier
A, Ravinet J, Laé M, Bollet M, Pierga JY, Salmon R and Fitoussi A:
Breast Cancer Study Group of the Institut Curie: Management of
phyllodes breast tumors. Breast J. 17:129–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
EI Ochi MR, Toreis M, Benchekroun M,
Benkerroum Z, Allaoui M, Ichou M, El Khannoussi B, Albouzidi A and
Oukabli M: Bone metastasis from malignant phyllodes breast tumor:
Report of two cases. BMC Clin Pathol. 16:42016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sazuka T, Matsuzaki H, Kanada Y, Tohnosu
N, Yoshiwara C, Aruga T, Iwata K, Sasahara N, Kobayashi H, Yokoyama
M, et al: A case of malignant phyllodes tumor effectively treated
by radiation therapy as a palliative medicine. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
42:1698–1699. 2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hashimoto K, Mimura H, Arai Y, Doi M,
Kojima Y, Tsugawa K and Nakajima Y: Successful preoperative
chemoembolization in the treatment of a giant malignant phyllodes
tumor. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 39:1070–1075. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barth RJ Jr: Histologic features predict
local recurrence after breast conserving therapy of phyllodes
tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 57:291–295. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeng S, Zhang X, Yang D, Wang X and Ren G:
Effects of adjuvant radiotherapy on borderline and malignant
phyllodes tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Clin
Oncol. 3:663–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gnerlich JL, Williams RT, Yao K, Jaskowiak
N and Kulkarni SA: Utilization of radiotherapy for malignant
phyllodes tumors: Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base,
1998–2009. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:1222–1230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen WH, Cheng SP, Tzen CY, Yang TL, Jeng
KS, Liu CL and Liu TP: Surgical treatment of phyllodes tumors of
the breast: Retrospective review of 172 cases. J Surg Oncol.
91:185–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khosravi-Shahi P: Management of non
metastatic phyllodes tumors of the breast: Review of the
literature. Surg Oncol. 20:e143–e148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arjaans M, Schröder CP, Oosting SF, Dafni
U, Kleibeuker JE and de Vries EG: VEGF pathway targeting agents,
vessel normalization and tumor drug uptake: From bench to bedside.
Oncotarget. 7:21247–21258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao L, Yao GY, Liu MF, Chen LJ, Hu XL and
Ye CS: Neoadjuvant bevacizumab plus chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone to treat non-metastatic breast cancer: A
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoS One.
10:e01454422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|