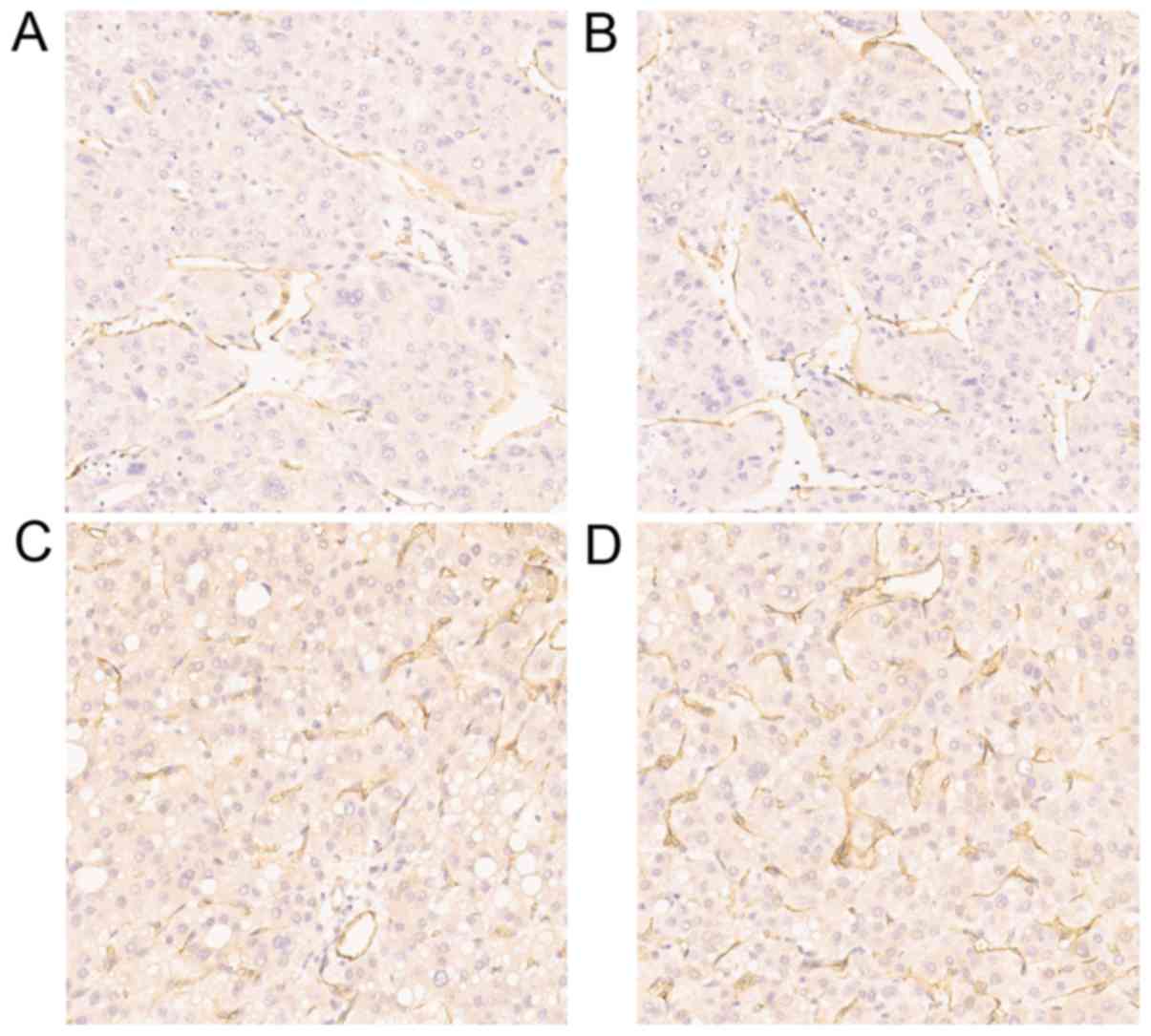
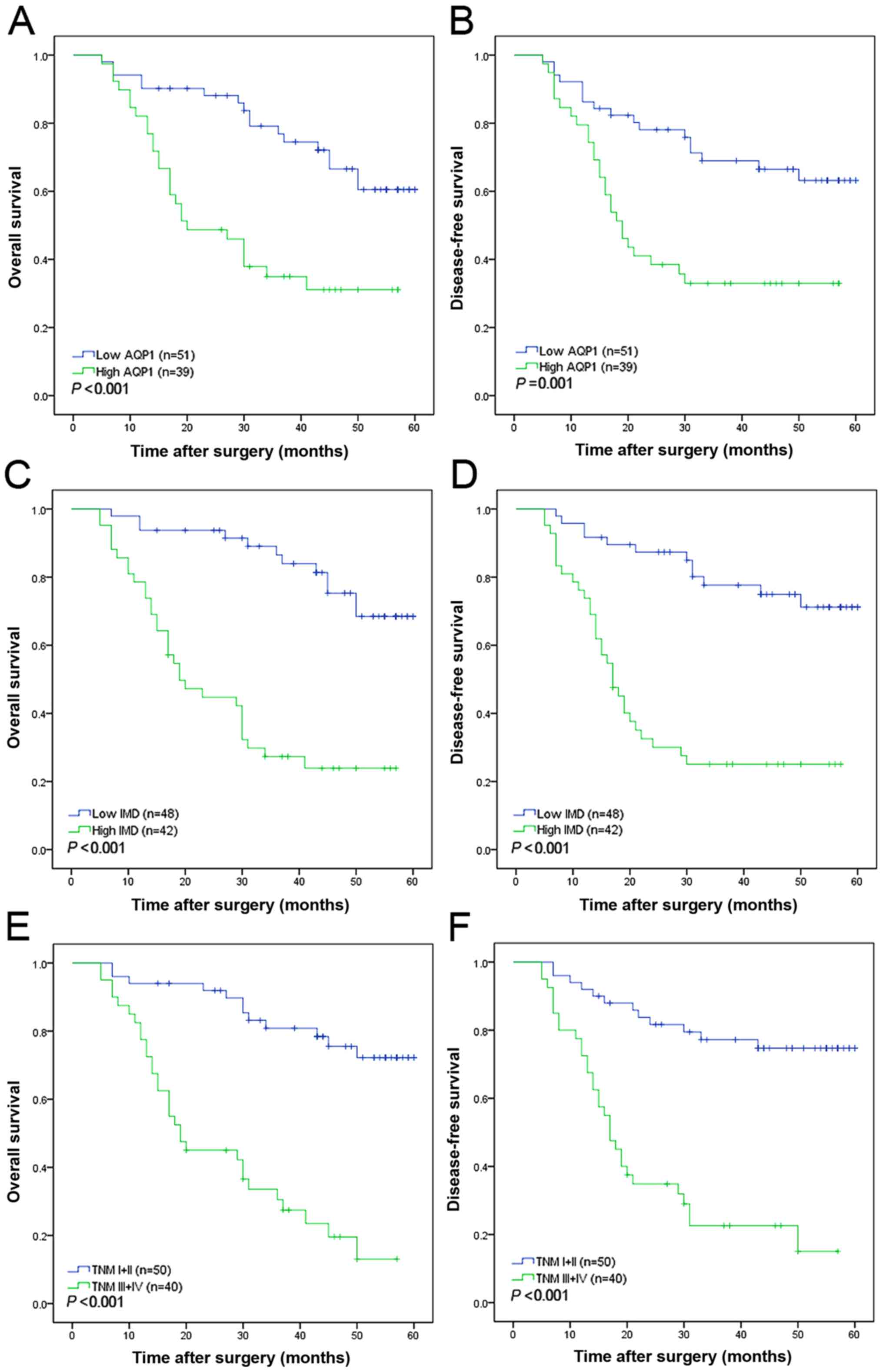
|
1
|
Llovet JM: Updated treatment approach to
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterology. 40:225–235. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bruix J, Sala M and Llovet JM:
Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
127 5 Suppl 1:S179–S188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gish RG, Marrero JA and Benson AB: A
multidisciplinary approach to the management of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 6 3 Suppl 6:1S–16S.
2010.
|
|
4
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gomaa AI, Khan SA, Leen EL, Waked I and
Taylor-Robinson SD: Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:1301–1314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ayyappan AP and Jhaveri KS: CT and MRI of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Exp Rev Anticancer Ther.
10:507–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Park YN, Kim YB, Yang KM and Park C:
Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and
angiogenesis in the early stage of multistep hepatocarcinogenesis.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 124:1061–1065. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roncalli M, Roz E, Coggi G, Di Rocco MG,
Bossi P, Minola E, Gambacorta M and Borzio M: The vascular profile
of regenerative and dysplastic nodules of the cirrhotic liver:
Implications for diagnosis and classification. Hepatology.
30:1174–1178. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Poon RT, Ng IO, Lau C, Zhu LX, Yu WC, Lo
CM, Fan ST and Wong J: Serum vascular endothelial growth factor
predicts venous invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective
study. Ann Surg. 233:227–235. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao DF, Wu XH, Zhu Y, Shi GS, Dong ZZ, Yao
DB, Wu W, Qiu LW and Meng XY: Quantitative analysis of vascular
endothelial growth factor, microvascular density and their
clinicopathologic features in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 4:220–226. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun HC, Tang ZY, Li XM, Zhou YN, Sun BR
and Ma ZC: Microvessel density of hepatocellular carcinoma: Its
relationship with prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 125:419–426.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murakami K, Kasajima A, Kawagishi N,
Ohuchi N and Sasano H: Microvessel density in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Prognostic significance and review of the previous
published work. Hepatol Res. 45:1185–1194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu C, Jiang Z, Bazer FW, Johnson GA,
Burghardt RC and Wu G: Aquaporins in the female reproductive system
of mammals. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 1:838–871. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC,
Krishna S and Bell BA: Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in
oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
72:262–265. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mobasheri A, Airley R, Hewitt SM and
Marples D: Heterogeneous expression of the aquaporin 1 (AQP1) water
channel in tumors of the prostate, breast, ovary, colon and lung: A
study using high density multiple human tumor tissue microarrays.
Int J Oncol. 26:1149–1158. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oshio K, Binder DK, Liang Y, Bollen A,
Feuerstein B, Berger MS and Manley GT: Expression of the
aquaporin-1 water channel in human glial tumors. Neurosurgery.
56:375–381. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mobasheri A and Barrett-Jolley R:
Aquaporin water channels in the mammary gland: From physiology to
pathophysiology and neoplasia. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
19:91–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoshida T, Hojo S, Sekine S, Sawada S,
Okumura T, Nagata T, Shimada Y and Tsukada K: Expression of
aquaporin-1 is a poor prognostic factor for stage II and III colon
cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:953–958. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Endo M, Jain RK, Witwer B and Brown D:
Water channel (aquaporin 1) expression and distribution in mammary
carcinomas and glioblastomas. Microvascular Research. 58:89–98.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Hara-Chikuma M
and Verkman AS: Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by
targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature. 434:786–792. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vacca A, Frigeri A, Ribatti D, Nicchia GP,
Nico B, Ria R, Svelto M and Dammacco F: Microvessel overexpression
of aquaporin 1 parallels bone marrow angiogenesis in patients with
active multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 113:415–421. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weidner N: Current pathologic methods for
measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma
and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 36:169–180. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Bai DS, Huang XY, Shi GM, Ke AW,
Yang LX, Yang XR, Zhou J and Fan J: Prognostic Significance of
Capn4 overexpression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e546192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kiriyama S, Uchiyama K, Ueno M, Ozawa S,
Hayami S, Tani M and Yamaue H: Triple positive tumor markers for
hepatocellular carcinoma are useful predictors of poor survival.
Ann Surg. 254:984–991. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tanigawa N, Lu C, Mitsui T and Miura S:
Quantitation of sinusoid-like vessels in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Its clinical and prognostic significance. Hepatology. 26:1216–1223.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D and Hanahan
D: Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia
to neoplasia. Nature. 339:58–61. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liotta LA and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tumor
invasion and metastasis: An imbalance of positive and negative
regulation. Cancer Res. 51 18 Suppl:5054s–5059s. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen ZY, Wei W, Guo ZX, Lin JR, Shi M and
Guo RP: Morphologic classification of microvessels in
hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with the prognosis after
resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:866–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Messerini L, Novelli L and Comin CE:
Microvessel density and clinicopathological characteristics in
hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 57:867–871. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang WQ, Liu L, Xu HX, Luo GP, Chen T, Wu
CT, Xu YF, Xu J, Liu C, Zhang B, et al: Intratumoral α-SMA enhances
the prognostic potency of CD34 associated with maintenance of
microvessel integrity in hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e711892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moon C, Soria JC, Jang SJ, Lee J, Hoque
Obaidul M, Sibony M, Trink B, Chang YS, Sidransky D and Mao L:
Involvement of aquaporins in colorectal carcinogenesis. Oncogene.
22:6699–6703. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan F, Leunig M, Huang SK, Berk DA,
Papahadjopoulos D and Jain RK: Microvascular permeability and
interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth)
liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res. 54:3352–3356.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC,
Bell BA and Krishna S: Increased aquaporin 1 water channel
expression in human brain tumours. Br J Cancer. 87:621–623. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
El Hindy N, Bankfalvi A, Herring A,
Adamzik M, Lambertz N, Zhu Y, Siffert W, Sure U and Sandalcioglu
IE: Correlation of aquaporin-1 water channel protein expression
with tumor angiogenesis in human astrocytoma. Anticancer Res.
33:609–613. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qin F, Zhang H, Shao Y, Liu X, Yang L,
Huang Y, Fu L, Gu F and Ma Y: Expression of aquaporin1, a water
channel protein, in cytoplasm is negatively correlated with
prognosis of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 16:8143–8154.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Papadopoulos MC and Verkman AS: Potential
utility of aquaporin modulators for therapy of brain disorders.
Prog Brain Res. 170:589–601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma B, Xiang Y, Li T, Yu HM and Li XJ:
Inhibitory effect of topiramate on Lewis lung carcinoma metastasis
and its relation with AQP1 water channel. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
25:54–60. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|