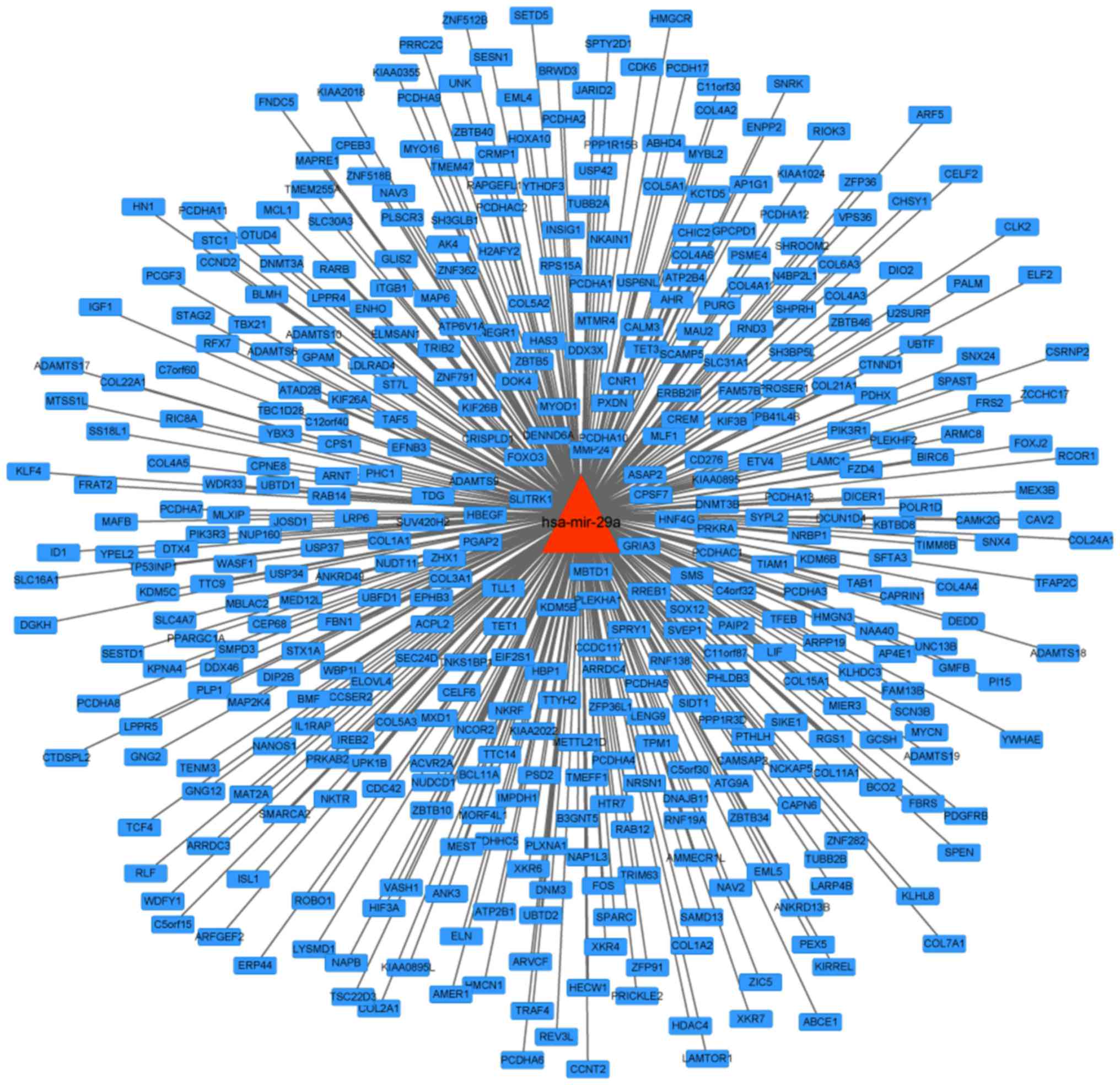
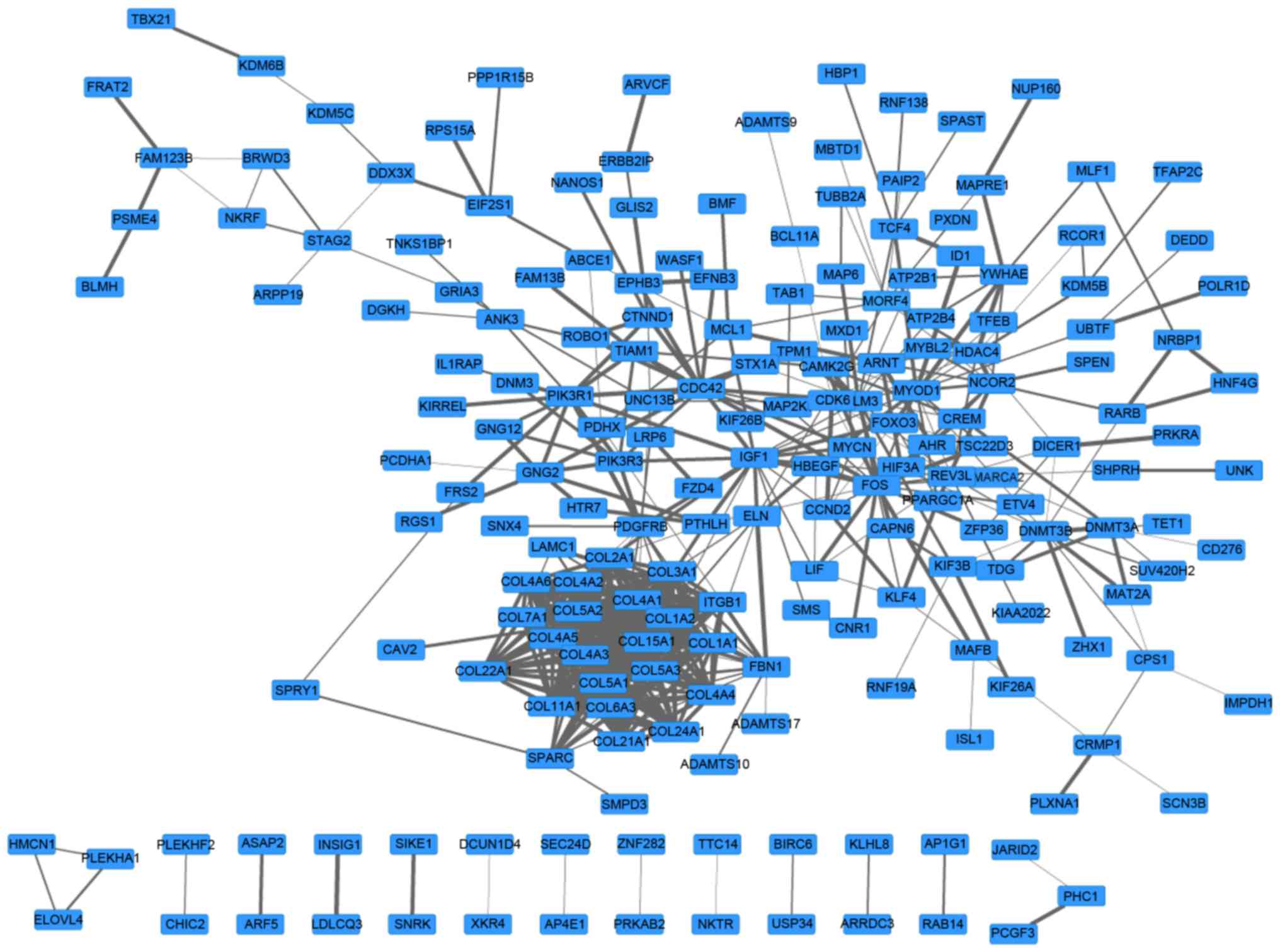
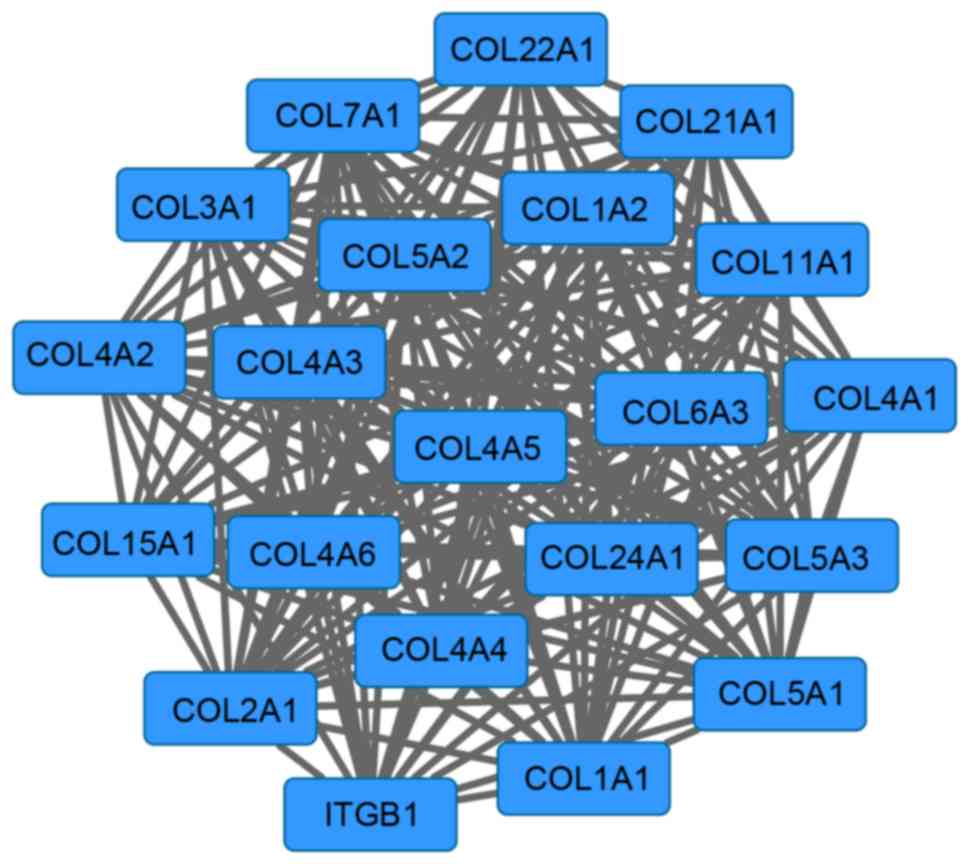
|
1
|
Ploeg M, Aben KK and Kiemeney LA: The
present and future burden of urinary bladder cancer in the world.
World J Urol. 27:289–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kauffman EC, Ng CK, Lee MM, Otto BJ, Wang
GJ and Scherr DS: Early oncological outcomes for bladder urothelial
carcinoma patients treated with robotic-assisted radical
cystectomy. BJU Int. 107:628–635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wright JL, Black PC, Brown GA, Porter MP,
Kamat AM, Dinney CP and Lin DW: Differences in survival among
patients with sarcomatoid carcinoma, carcinosarcoma and urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol. 178:2302–2307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi Z, Wei Q, Zhang M and She J: MicroRNAs
in bladder cancer: Expression profiles, biological functions,
regulation, and clinical implications. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.
24:55–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wszolek MF, Rieger-Christ KM, Kenney PA,
Gould JJ, Neto Silva B, Lavoie AK, Logvinenko T, Libertino JA and
Summerhayes IC: A MicroRNA expression profile defining the invasive
bladder tumor phenotype. Urol Oncol. 29:794–801.e1. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Soini Y, Haapasaari KM, Vaarala MH,
Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Kärjä V and Karihtala P:
8-hydroxydeguanosine and nitrotyrosine are prognostic factors in
urinary bladder carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 4:267–275.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, Li R, Yuan J, Yang
Y, Zhu X, Chen B, Wu J and Li M: miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to
augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5402–5415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cathomas R, Rothermundt C, Klingbiel D,
Bubendorf L, Jaggi R, Betticher DC, Brauchli P, Cotting D, Droege
C, Winterhalder R, et al: Efficacy of cetuximab in metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer might depend on EGFR and PTEN
expression: Results from a phase II trial (SAKK 08/07). Clin Cancer
Res. 18:6049–6057. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thogersen VB, Sørensen BS, Poulsen SS,
Orntoft TF, Wolf H and Nexo E: A subclass of HER1 ligands are
prognostic markers for survival in bladder cancer patients. Cancer
Res. 61:6227–6233. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, Qi W, Nicoloso M,
Arora A, Calin G, Wang H, Siefker-Radtke A, McConkey D, et al:
miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth
factor receptor therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5060–5072. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yun SJ, Jeong P, Kim WT, Kim TH, Lee YS,
Song PH, Choi YH, Kim IY, Moon SK and Kim WJ: Cell-free microRNAs
in urine as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of bladder cancer.
Int J Oncol. 41:1871–1878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Diez D: Survival analysis in R.
2012.https://folk.ntnu.no/bo/TMA4275/Download/R.tutorialDiez.pdfAugust
11–2014
|
|
15
|
Therneau TM and Grambsch PM: Modeling
survival data: Extending the Cox model. Springer-Verlag; New York,
NY: 2000
|
|
16
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D105–D110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X and El Naqa IM: Prediction of both
conserved and nonconserved microRNA targets in animals.
Bioinformatics. 24:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toivonen R, Onnela JP, Saramäki J, Hyvönen
J and Kaski K: A model for social networks. Physica A: Statistical
Mechanics and its. Applications. 371:851–860. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Li C and Li MC: Package
‘iSubpathwayMiner’. 2013.http://ftp.cs.pu.edu.tw/network/CRAN/web/packages/iSubpathwayMiner/iSubpathwayMiner.pdfAugust
11–2014
|
|
28
|
Schmidbauer J, Witjes F, Schmeller N,
Donat R, Susani M and Marberger M: Hexvix PCB301/01 Study Group:
Improved detection of urothelial carcinoma in situ with
hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy. J Urol. 171:135–138.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan XJ, Xu J, Gu ZH, Pan CM, Lu G, Shen Y,
Shi JY, Zhu YM, Tang L, Zhang XW, et al: Exome sequencing
identifies somatic mutations of DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT3A
in acute monocytic leukemia. Nat Genet. 43:309–315. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 15805–15810. 2007,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Thatcher JE,
DiMaio JM, Naseem RH, Marshall WS, Hill JA and Olson EN:
Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a
role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
13027–13032. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pradhan S, Bacolla A, Wells RD and Roberts
RJ: Recombinant human DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase. I.
Expression, purification, and comparison of de novo and maintenance
methylation. J Biol Chem. 274:33002–33010. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gowher H and Jeltsch A: Enzymatic
properties of recombinant Dnmt3a DNA methyltransferase from mouse:
The enzyme modifies DNA in a non-processive manner and also
methylates non-CpG [correction of non-CpA] sites. J Mol Biol.
309:1201–1208. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mato JM, Corrales FJ, Lu SC and Avila MA:
S-Adenosylmethionine: A control switch that regulates liver
function. FASEB J. 16:15–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Roje S: S-Adenosyl-L-methionine: Beyond
the universal methyl group donor. Phytochemistry. 67:1686–1698.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Main PA, Angley MT, Thomas P, O'Doherty CE
and Fenech M: Folate and methionine metabolism in autism: A
systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 91:1598–1620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ioachim E, Michael MC, Salmas M, Damala K,
Tsanou E, Michael MM, Malamou-Mitsi V and Stavropoulos NE:
Thrombospondin-1 expression in urothelial carcinoma: Prognostic
significance and association with p53 alterations, tumour
angiogenesis and extracellular matrix components. BMC Cancer.
6:1402006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chakraborty A, White SM and Lerner SP:
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signals for
beta1-integrin expression and adhesion in bladder cancer. Urology.
63:177–183. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lopez-Beltran A and Cheng L: Histologic
variants of urothelial carcinoma: Differential diagnosis and
clinical implications. Hum Pathol. 37:1371–1388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|