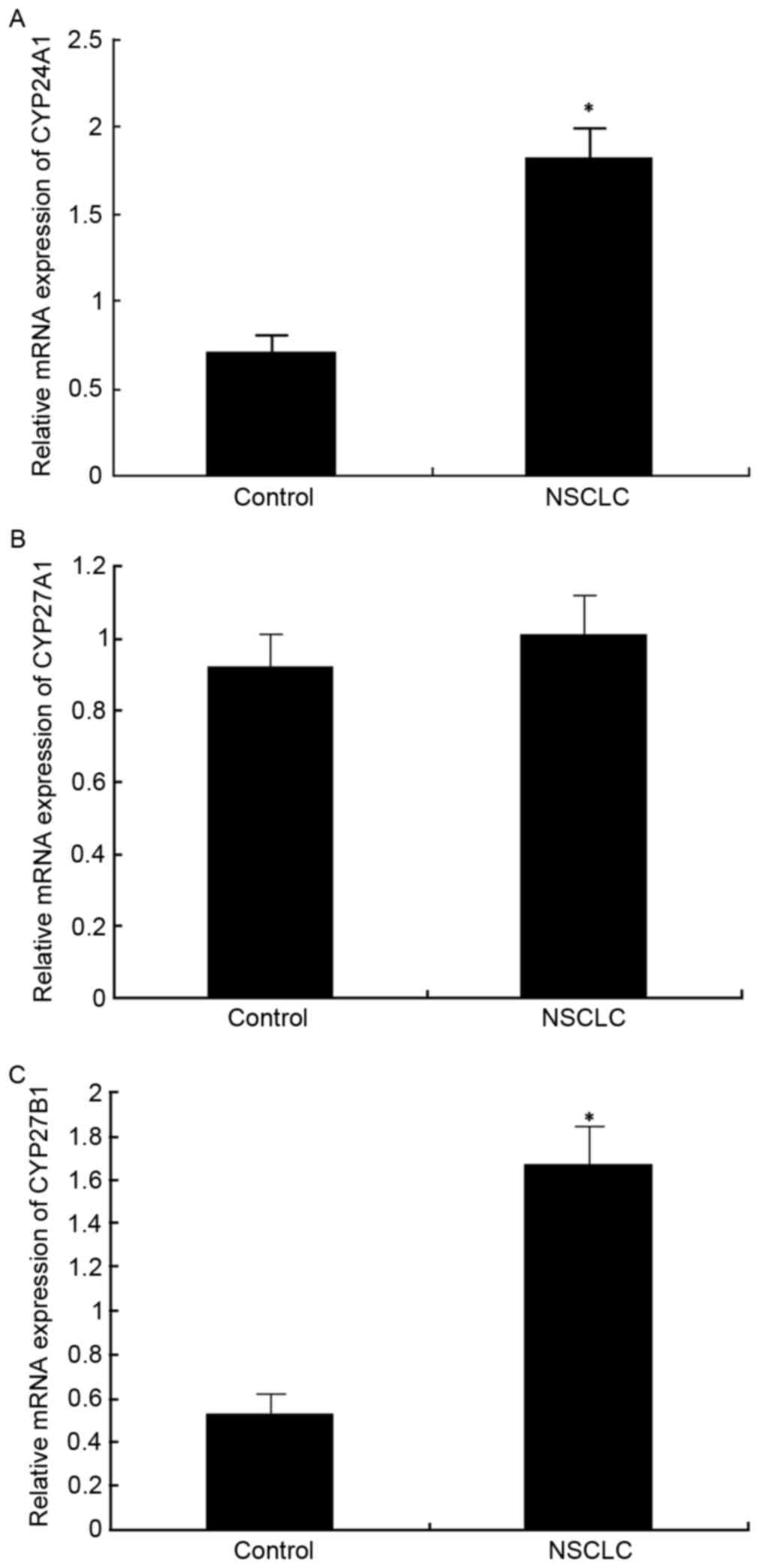
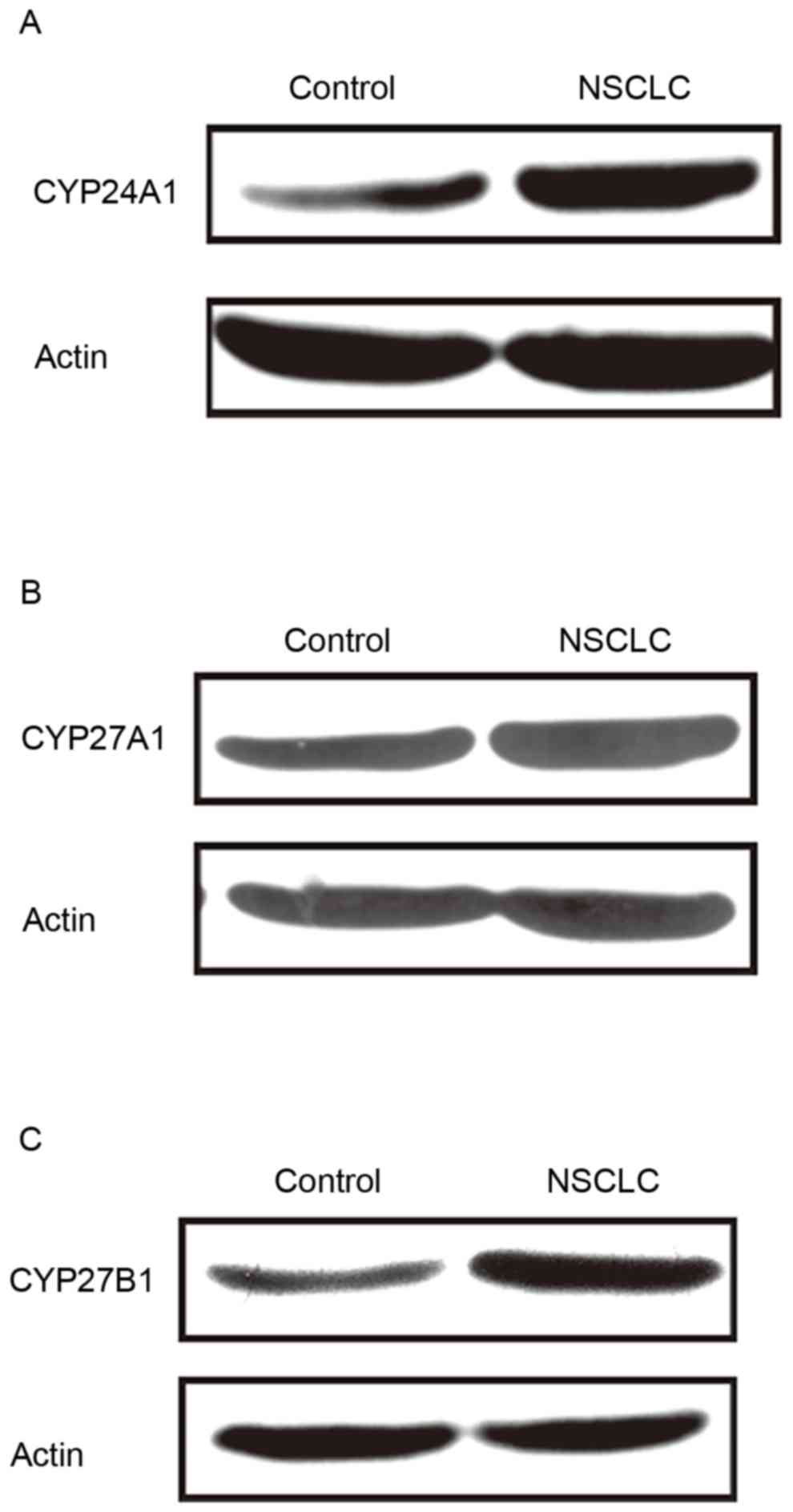
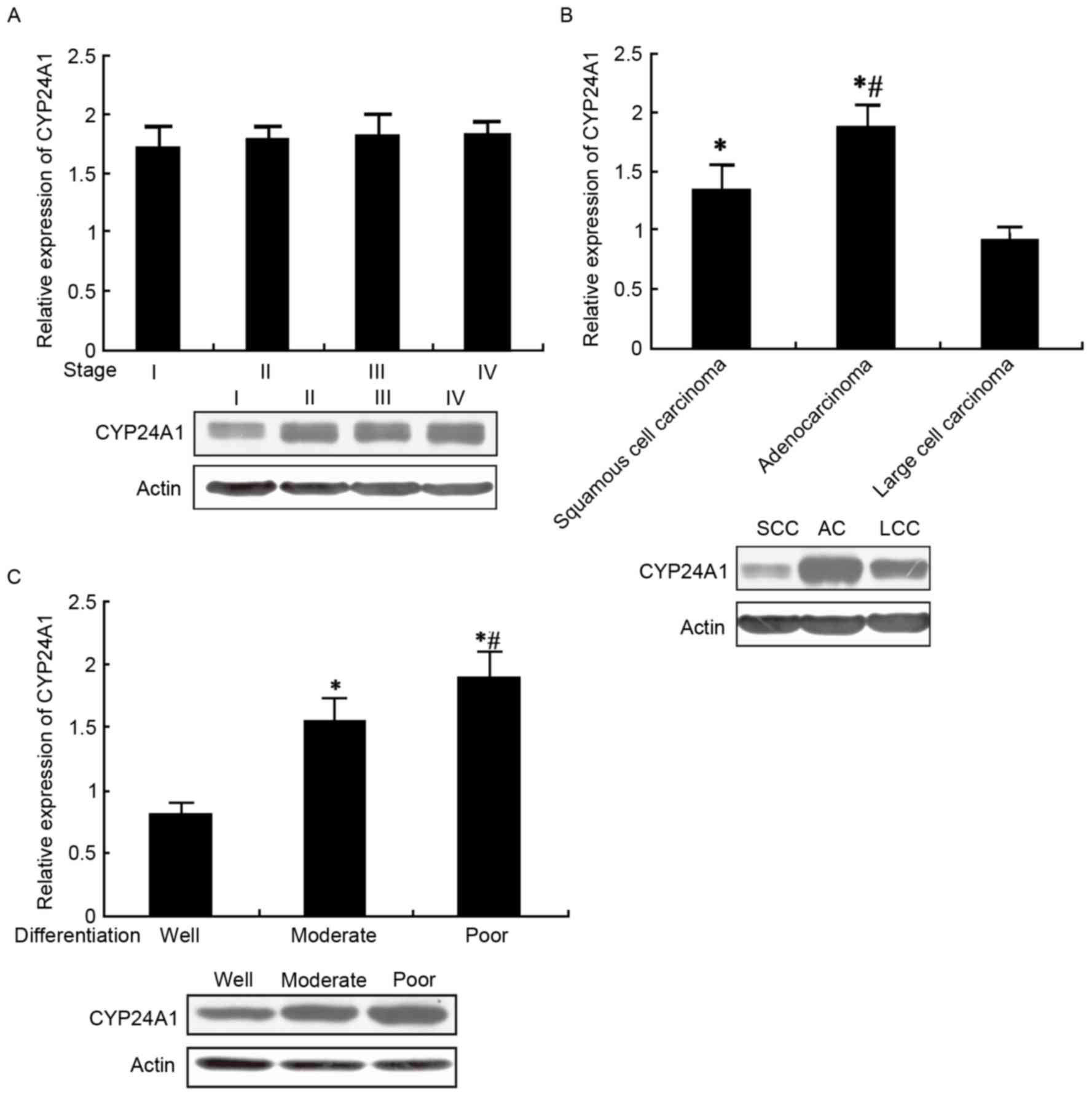
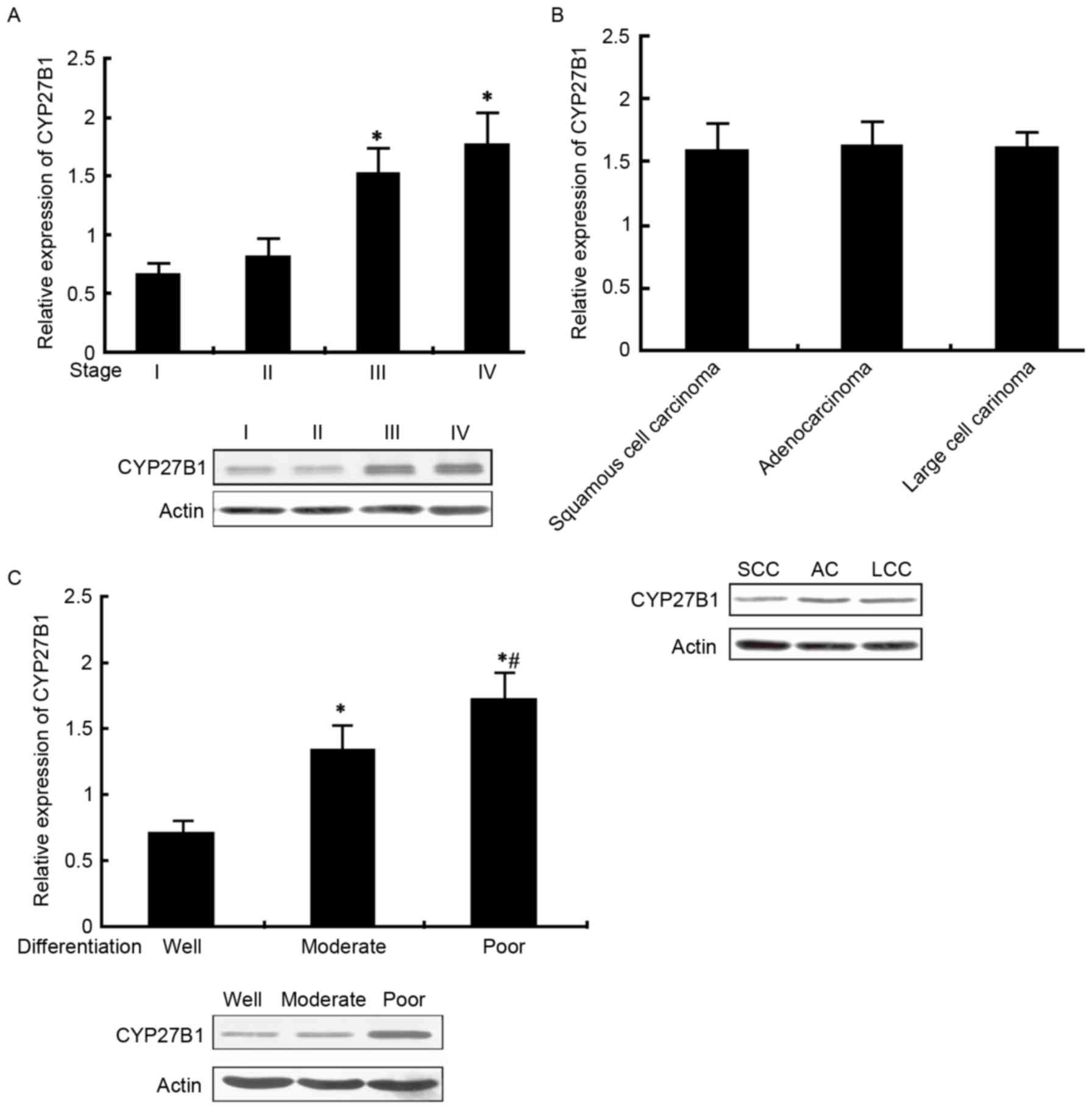
|
1
|
Gudala S, Khan U, Kanungo N, Bandaru S,
Hussain T, Parihar M, Nayarisseri A and Mundluru HP: Identification
and pharmacological analysis of high efficacy small molecule
inhibitors of EGF-EGFR interactions in clinical treatment of
non-small cell lung carcinoma: A computational approach. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 16:8191–8196. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia M, Duan ML, Tong JH and Xu JG: MiR-26b
suppresses tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
directly targeting COX-2 in lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:4728–4737. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paz-Ares L, Hirsh V, Zhang L, de Marinis
F, Yang JC, Wakelee HA, Seto T, Wu YL, Novello S, Juhász E, et al:
Monotherapy administration of sorafenib in patients with non-small
cell lung cancer (MISSION) trial: A phase III, multicenter,
placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib in patients with relapsed or
refractory predominantly nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer
after 2 or 3 previous treatment regimens. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1745–1753. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guerrera F, Tabbò F, Bessone L, Maletta F,
Gaudiano M, Ercole E, Annaratone L, Todaro M, Boita M, Filosso PL,
et al: The Influence of tissue ischemia time on RNA integrity and
patient-derived xenografts (PDX) engraftment rate in a non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC) biobank. PLoS One. 11:e01451002016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tai CJ, Wang CK, Tai CJ, Tzao C, Lien YC,
Hsieh CC, Hsieh CI, Wu HC, Wu CH, Chang CC, et al: Evaluation of
safety and efficacy of salvage therapy with sunitinib, docetaxel
(Tyxane) and cisplatinum followed by maintenance vinorelbine for
unresectable/metastatic nonsmall cell lung cancer: Stage 1 of a
simon 2 stage clinical trial [Corrected]. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e23032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Robinson AG, Young K, Balchin K, Owen T
and Ashworth A: Reasons for palliative treatments in stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer: What contribution is made by
time-dependent changes in tumour or patient status? Curr Oncol.
22:399–404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sasaki S, Yoshioka Y, Ko R, Katsura Y,
Namba Y, Shukuya T, Kido K, Iwakami S, Tominaga S and Takahashi K:
Diagnostic significance of cerebrospinal fluid EGFR mutation
analysis for leptomeningeal metastasis in non-small-cell lung
cancer patients harboring an active EGFR mutation following
gefitinib therapy failure. Respir Investig. 54:14–19. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kepka L and Socha J: PET-CT limitations in
early stage non-small cell lung cancer: To whom more aggressive
approach in radiotherapy and surgery should be directed? J Thorac
Dis. 7:1887–1890. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Piotrowska A, Wierzbicka J, Nadkarni S,
Brown G, Kutner A and Żmijewski MA: Antiproliferative activity of
double point modified analogs of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D2 against human malignant melanoma cell lines. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:pii: E76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aguirre M, Manzano N, Salas Y, Angel M,
Díaz-Couselo FA and Zylberman M: Vitamin D deficiency in patients
admitted to the general ward with breast, lung, and colorectal
cancer in buenos aires, argentina. Arch Osteoporos. 11:42016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wen Y, Da M, Zhang Y, Peng L, Yao J and
Duan Y: Alterations in vitamin D signaling pathway in gastric
cancer progression: A study of vitamin D receptor expression in
human normal, premalignant, and malignant gastric tissue. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13176–13184. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vashi PG, Edwin P, Popiel B and Gupta D:
The relationship between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and
survival in newly diagnosed advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
BMC Cancer. 15:10122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christakos S, Dhawan P, Verstuyf A,
Verlinden L and Carmeliet G: Vitamin D: Metabolism, molecular
mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects. Physiol Rev.
96:365–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khayatzadeh S, Feizi A, Saneei P and
Esmaillzadeh A: Vitamin D intake, serum Vitamin D levels, and risk
of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Res Med
Sci. 20:790–796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hibler EA, Molmenti Sardo CL, Dai Q,
Kohler LN, Anderson Warren S, Jurutka PW and Jacobs ET: Physical
activity, sedentary behavior, and vitamin D metabolites. Bone.
83:248–255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang Z, Yi X, Luo B, Zhu J, Wu Y, Jiang
W, Chu H, Yang Z, Li S, Zhu H, et al: Induced sputum deposition
improves diagnostic yields of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: A
clinicopathological and methodological study of 17 cases.
Ultrastruct Pathol. 40:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ortakoylu MG, Iliaz S, Bahadir A, Aslan A,
Iliaz R, Ozgul MA and Urer HN: Diagnostic value of endobronchial
ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in various lung
diseases. J Bras Pneumol. 41:410–414. 2015.(In English,
Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin K, You Y, Swier V, Tang L, Radwan MM,
Pandya AN and Agrawal DK: Vitamin D protects against
atherosclerosis via regulation of cholesterol efflux and macrophage
polarization in hypercholesterolemic swine. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 35:2432–2442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fedorova OV, Zernetkina VI, Shilova VY,
Grigorova YN, Juhasz O, Wei W, Marshall CA, Lakatta EG and Bagrov
AY: Synthesis of an endogenous steroidal na pump inhibitor
marinobufagenin, implicated in human cardiovascular diseases, is
initiated by CYP27A1 via bile acid pathway. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
8:736–745. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gascon-Barré M, Demers C, Ghrab O,
Theodoropoulos C, Lapointe R, Jones G, Valiquette L and Ménard D:
Expression of CYP27A, a gene encoding a vitamin D-25 hydroxylase in
human liver and kidney. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 54:107–115. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adams JS and Hewison M: Extrarenal
expression of the 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1-hydroxylase. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 523:95–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mast N, Lin JB and Pikuleva IA: Marketed
drugs can inhibit cytochrome P450 27A1, a potential new target for
breast cancer adjuvant therapy. Mol Pharmacol. 88:428–436. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brożyna AA, Jochymski C, Janjetovic Z,
Jóźwicki W, Tuckey RC and Slominski AT: CYP24A1 expression
inversely correlates with melanoma progression: Clinic-pathological
studies. Int J Mol Sci. 15:19000–19017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Horváth HC, Lakatos P, Kósa JP, Bácsi K,
Borka K, Bises G, Nittke T, Hershberger PA, Speer G and Kállay E:
The candidate oncogene CYP24A1: A potential biomarker for
colorectal tumorigenesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 58:277–285. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anderson MG, Nakane M, Ruan X, Kroeger PE
and Wu-Wong JR: Expression of VDR and CYP24A1 mRNA in human tumors.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 57:234–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Whitlatch LW, Young MV, Schwartz GG,
Flanagan JN, Burnstein KL, Lokeshwar BL, Rich ES, Holick MF and
Chen TC: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-1alpha-hydroxylase activity is
diminished in human prostate cancer cells and is enhanced by gene
transfer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 81:135–140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Kim SH, King AN, Zhao L, Simpson
RU, Christensen PJ, Wang Z, Thomas DG, Giordano TJ, Lin L, et al:
CYP24A1 is an independent prognostic marker of survival in patients
with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:817–826. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shui IM, Mondul AM, Lindström S, Tsilidis
KK, Travis RC, Gerke T, Albanes D, Mucci LA, Giovannucci E and
Kraft P: Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium Group:
Circulating vitamin D, vitamin D-related genetic variation, and
risk of fatal prostate cancer in the national cancer institute
breast and prostate cancer cohort consortium. Cancer.
121:1949–1956. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee WR, Ishikawa T and Umetani M: The
interaction between metabolism, cancer and cardiovascular disease,
connected by 27-hydroxycholesterol. Clin Lipidol. 9:617–624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kong J, Xu F, Qu J, Wang Y, Gao M, Yu H
and Qian B: Genetic polymorphisms in the vitamin D pathway in
relation to lung cancer risk and survival. Oncotarget. 6:2573–2782.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jacobs ET, Van Pelt C, Forster RE, Zaidi
W, Hibler EA, Galligan MA, Haussler MR and Jurutka PW: CYP24A1 and
CYP27B1 polymorphisms modulate vitamin D metabolism in colon cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 73:2563–2573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|