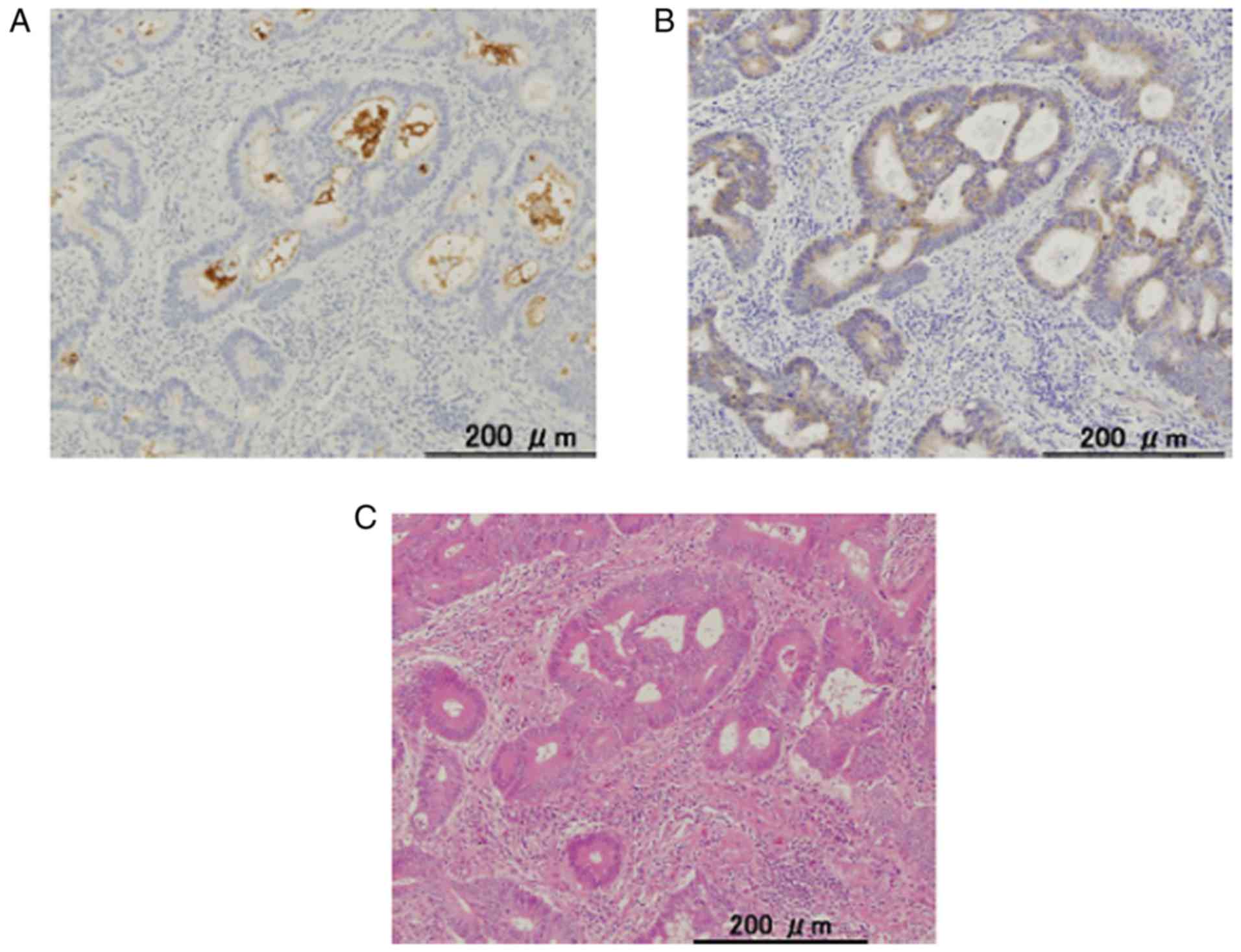
|
1
|
Bosset JF, Collette L, Calais G, Mineur L,
Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L, Daban A, Bardet E, Beny A and Ollier
JC: EORTC Radiotherapy Group Trial 22921: Chemotherapy with
preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
355:1114–1123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tomono A, Yamashita K, Kanemitsu K, Sumi
Y, Yamamoto M, Kanaji S, Imanishi T, Nakamura T, Suzuki S, Tanaka K
and Kakeji Y: Prognostic significance of pathological response to
preoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced
rectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 21:344–349. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hamburger AW and Salmon SE: Primary
bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 197:461–463. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Espersen ML, Olsen J, Linnemann D, Høgdall
E and Troelsen JT: Clinical implications of intestinal stem cell
markers in colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:63–71.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carmon KS, Gong X, Lin Q, Thomas A and Liu
Q: R-spondins function as ligands of the orphan receptors LGR4 and
LGR5 to regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:pp. 11452–11457. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P,
van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H,
Peters PJ and Clevers H: Identification of stem cell in small
intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 449:1003–1017.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xi HQ, Cai AZ, Wu XS, Cui JX, Shen WS,
Bian SB, Wang N, Li JY, Lu CR, Song Z, et al: Leucine-rich
repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 is associated with
invasion, metastasis, and cloud be a potential therapeutic target
in human gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:2011–2020. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McClanahan T, Koseoglu S, Smith K, Grein
J, Gustafson E, Black S, Kirschmeier P and Samatar AA:
Identification of overexpression of orphan G protein-coupled
receptor GPR49 in human colon and ovarian primary tumors. Cancer
Biol Ther. 5:419–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Michelotti G, Jiang X, Sosa JA, Diehl AM
and Henderson BB: LGR5 is associated with tumor aggressiveness in
papillary thyroid cancer. Oncotarget. 6:34549–34560.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang L, Tang H, Kong Y and Xie X, Chen J,
Song C, Liu X, Ye F, Li N, Wang N and Xie X: LGR5 promotes breast
cancer progression and maintains stem-like cells through activation
of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cells. 33:2913–2924. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu XS, Xi HQ and Chen L: Lgr5 is a
potential marker of colorectal carcinoma stem cells that correlates
with patient survival. World J Surg Oncol. 10:2442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Q, Zhang X, Li WM, Ji YQ, Cao HZ and
Zheng P: Prognostic value of LGR5 in colorectal cancer: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1070132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han Y, Xue X, Jiang M, Guo X, Li P, Liu F,
Yuan B, Shen Y, Guo X, Zhi Q and Zhao H: LGR5, a relevant marker of
cancer stem cells, indicates a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
patients: A meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
39:267–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saigusa S, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y,
Matsushita K, Kawamura M, Okugawa Y, Hiro J, Uchida K, Mohri Y and
Kusunoki M: Clinical significance of LGR5 and CD44 expression in
locally advanced rectal cancer after preoperative
chemoradiotherapy. Int J Oncol. 41:1643–1652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma S: Biology and clinical implications of
CD133(+) liver cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 319:126–132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Long H, Xie R, Xiang T, Zhao Z, Lin S,
Liang Z, Chen Z and Zhu B: Autocrine CCL5 signaling promotes
invasion and migration of CD133+ ovarian cancer stem-like cells via
NF-κB-mediated MMP-9 upregulation. Stem Cells. 30:2309–2319. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shien K, Toyooka S, Ichimura K, Soh J,
Furukawa M, Maki Y, Muraoka T, Tanaka N, Ueno T, Asano H, et al:
Prognostic impact of cancer stem cell-related markers in non-small
cell lung cancer patients treated with induction chemoradiotherapy.
Lung Cancer. 77:162–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou F, Mu YD, Liang J, Liu ZX, Chen HS
and Zhang JF: Expression and prognostic value of tumor stem cell
markers ALDH1 and CD133 in colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
7:507–512. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen S, Song X, Chen Z, Li X, Li M, Liu H
and Li J: CD133 expression and the prognosis of colorectal cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e563802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang K, Xu J, Zhang J and Huang J:
Prognostic role of CD133 expression in colorectal cancer: A
meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 12:5732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hongo K, Kazama S, Sunami E, Tsuno NH,
Takahashi K, Nagawa H and Kitayama J: Immunohistochemical detection
of CD133 is associated with tumor regression grade after
chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Med Oncol. 29:2849–2857. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kawamoto A, Tanaka K, Saigusa S, Toiyama
Y, Morimoto Y, Fujikawa H, Iwata T, Matsushita K, Yokoe T, Yasuda
H, et al: Clinical significance of radiation-induced CD133
expression in residual rectal cancer cells after chemoradiotherapy.
Exp Ther Med. 3:403–409. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Yokoe T,
Okugawa Y, Koike Y, Fujikawa H, Inoue Y, Miki C and Kusunoki M:
Clinical significance of CD133 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α gene
expression in rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy.
Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 23:323–332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maeda S, Shinchi H, Kurahara H, Mataki Y,
Maemura K, Sato M, Natsugoe S, Aikou T and Takao S: CD133
expression is correlated with lymph node metastasis and vascular
endothelial growth factor-C expression in pancreatic cancer. Br J
Cancer. 98:1389–1397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Saigusa S, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y,
Kawamura M, Okugawa Y, Okigami M, Hiro J, Uchida K, Mohri Y and
Kusunoki M: Significant correlation between LKB1 and LGR5 gene
expression and the association with poor recurrence-free survival
in rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 139:131–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hirsch D, Barker N, McNeil N, Hu Y, Camps
J, McKinnon K, Clevers H, Ried T and Gaiser T: LGR5 positivity
defines stem-like cells in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:849–858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chao C, Carmical JR, Ives KL, Wood TG,
Aronson JF, Gomez GA, Djukom CD and Hellmich MR: CD133+ colon
cancer cells are more interactive with the tumor microenvironment
than CD133-cells. Lab Invest. 92:420–436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu YM, Li XF, Liu H and Wu XL:
Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated downregulation
of CD133 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and
migratory ability of liver cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep.
34:2977–2986. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu YS, Hsu HC, Tseng KC, Chen HC and Chen
SJ: Lgr5 promotes cancer stemness and confers chemoresistance
through ABCB1 in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
67:791–799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Yokoe T,
Okugawa Y, Kawamoto A, Yasuda H, Morimoto Y, Fujikawa H, Inoue Y,
et al: Immunohistochemical features of CD133 expression:
Association with resistance to chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer.
Oncol Rep. 24:345–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lim SH, Jang J, Park JO, Kim KM, Kim ST,
Park YS, Lee J and Kim HC: CD133-positive tumor cell content is a
predictor of early recurrence in colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 5:447–456. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Planutis AK, Holcombe RF, Planoutene MV
and Planoutis KS: SW480 colorectal cancer cells that naturally
express Lgr5 are more sensitive to the most common chemotherapeutic
agents than Lgr5-negative SW480 cells. Anticancer Drugs.
26:942–947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi S, Yamada-Okabe H, Suzuki M,
Natori O, Kato A, Matsubara K, Chen Jau Y, Yamazaki M, Funahashi S,
Yoshida K, et al: LGR5-positive colon cancer stem cells
interconvert with drug-resistant LGR5-negative cells and are
capable of tumor reconstitution. Stem Cells. 30:2631–2644. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|