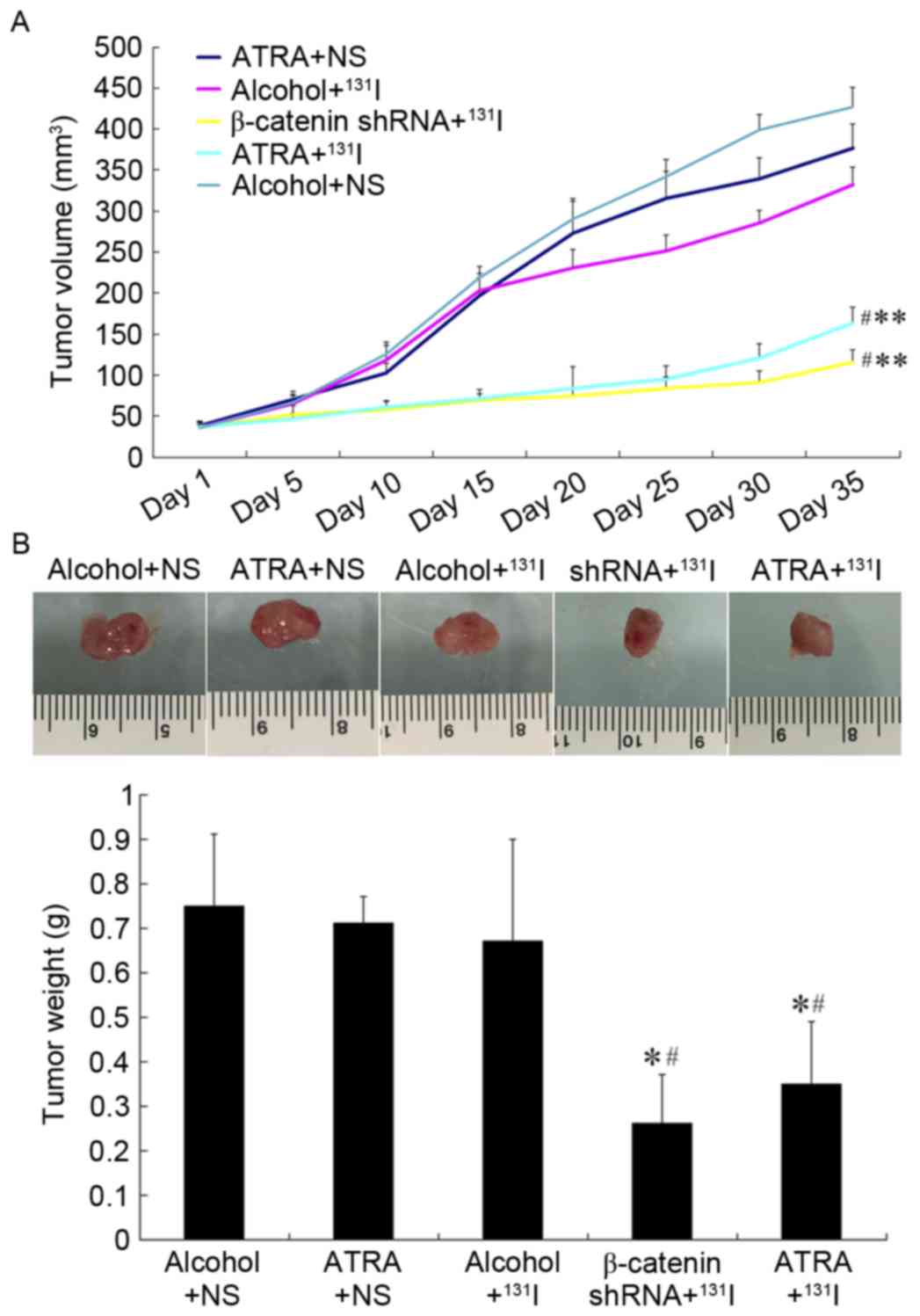
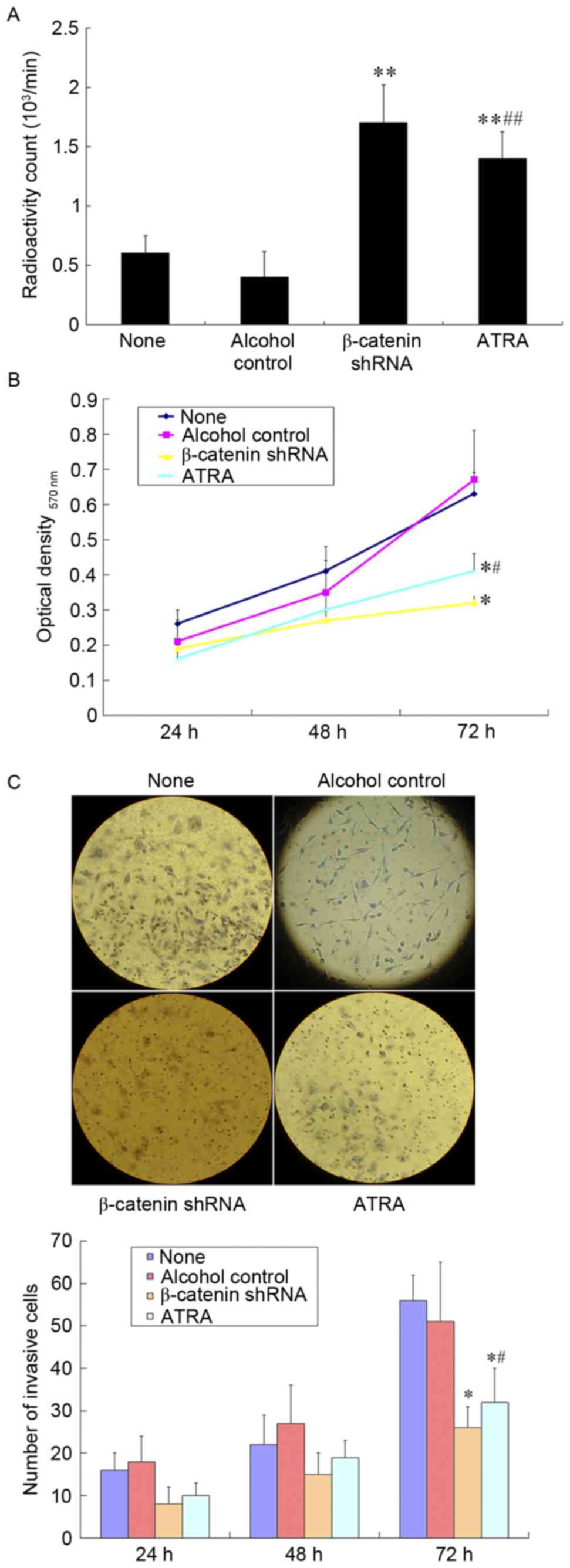
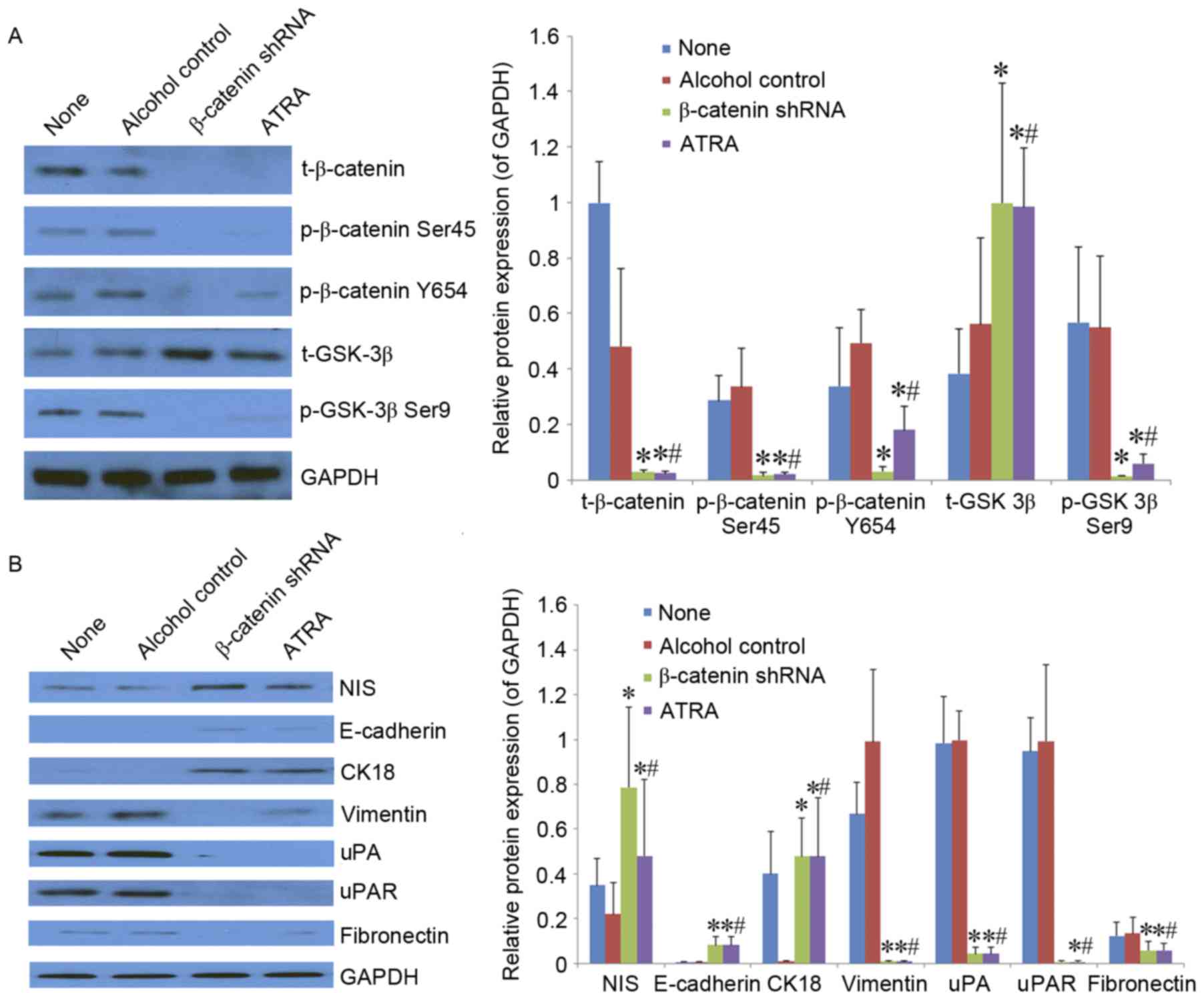
|
1
|
Kojic KL, Kojic SL and Wiseman SM:
Differentiated thyroid cancers: A comprehensive review of novel
targeted therapies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:345–357. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smallridge RC, Ain KB, Asa SL, Bible KC,
Brierley JD, Burman KD, Kebebew E, Lee NY, Nikiforov YE, Rosenthal
MS, et al: American Thyroid Association guidelines for management
of patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 22:1104–1139.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Glaser SM, Mandish SF, Gill BS,
Balasubramani GK, Clump DA and Beriwal S: Anaplastic thyroid
cancer: Prognostic factors, patterns of care, and overall survival.
Head Neck. 38 Suppl 1:E2083–E2090. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schenk T, Stengel S and Zelent A:
Unlocking the potential of retinoic acid in anticancer therapy. Br
J Cancer. 111:2039–2045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gutierrez-Mazariegos J, Schubert M and
Laudet V: Evolution of retinoic acid receptors and retinoic acid
signaling. Subcell Biochem. 70:55–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leelawat K, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K,
Mahidol C and Tanaka M: All-trans retinoic acid inhibits the cell
proliferation but enhances the cell invasion through up-regulation
of c-met in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 224:303–310.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu SM, Chen W and Wang J: Distinguishing
between cancer cell differentiation and resistance induced by
all-trans retinoic acid using transcriptional profiles and
functional pathway analysis. Sci Rep. 4:55772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tari AM, Lim SJ, Hung MC, Esteva FJ and
Lopez-Berestein G: Her2/neu induces all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)
resistance in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 21:5224–5232. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang M, Guo R, Xu H, Zhang M and Li B:
Retinoic acid and tributyrin induce in-vitro radioiodine uptake and
inhibition of cell proliferation in a poorly differentiated
follicular thyroid carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun. 32:605–610. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Muhlbauer M, da Silva AC, Marassi MP,
Lourenço AL, Ferreira AC and de Carvalho DP: Retinoic acid
modulation of thyroid dual oxidase activity in rats and its impact
on thyroid iodine organification. J Endocrinol. 205:271–277. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang M, Hou YL, Kang QQ, Chen XY, Duan LQ,
Shu J, Li SL, Hu XL and Peng ZP: All-trans-retinoic acid promotes
iodine uptake via up-regulating the sodium iodide symporter in
medullary thyroid cancer stem cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:1859–1862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dohan O, De la Vieja A, Paroder V, Riedel
C, Artani M, Reed M, Ginter CS and Carrasco N: The sodium/iodide
symporter (NIS): Characterization, regulation, and medical
significance. Endocr Rev. 24:48–77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Furuya F, Shimura H, Suzuki H, Taki K,
Ohta K, Haraguchi K, Onaya T, Endo T and Kobayashi T: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors restore radioiodide uptake and retention in
poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer cells by
expression of the sodium/iodide symporter thyroperoxidase and
thyroglobulin. Endocrinology. 145:2865–2875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sastre-Perona A and Santisteban P:
Wnt-independent role of β-catenin in thyroid cell proliferation and
differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 28:681–695. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lan L, Deng W, Chen HL, Huo L, Deng L,
Zhang G and Luo Y: Nuclear translocation of β-catenin represses
membrane localization of NIS in human thyroid cancer cells.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:891–896. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haberkorn U, Altmann A, Jiang S, Morr I,
Mahmut M and Eisenhut M: Iodide uptake in human anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma cells after transfer of the human thyroid peroxidase
gene. Eur J Nucl Med. 28:633–638. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang Y, Zhao J, Wu C, Luo Y and He D:
Construction and identification of shRNA eukaryotic vector
targeting human β-catenin. Acad J Second Milit Med Uni. 30:965–967.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nakamoto Y, Saga T, Misaki T, Kobayashi H,
Sato N, Ishimori T, Kosugi S, Sakahara H and Konishi J:
Establishment and characterization of a breast cancer cell line
expressing Na+/I-symporters for radioiodide concentrator gene
therapy. J Nucl Med. 41:1898–1904. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sastre-Perona A and Santisteban P: Role of
the wnt pathway in thyroid cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
3:312012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ryan J, Curran CE, Hennessy E, Newell J,
Morris JC, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM: The sodium iodide symporter (NIS)
and potential regulators in normal, benign and malignant human
breast tissue. PLoS One. 6:e160232011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheong SJ, Jang D, Jeong HJ, Lim ST, Sohn
MH, Katzenellenbogen JA and Kim DW: Reduction of stimulated sodium
iodide symporter expression by estrogen receptor ligands in breast
cancer cells. Nucl Med Biol. 38:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SJ, Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm SH,
Choi MG and Yoo HJ: Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on
sodium/iodide symporter and CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein-homologous protein under condition of endoplasmic reticulum
stress in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Horm Metab Res. 43:331–336. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beyer S, Lakshmanan A, Liu YY, Zhang X,
Wapnir I, Smolenski A and Jhiang S: KT5823 differentially modulates
sodium iodide symporter expression, activity, and glycosylation
between thyroid and breast cancer cells. Endocrinology.
152:782–792. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Willhauck MJ, Kane ODJ, Wunderlich N, Göke
B and Spitzweg C: Stimulation of retinoic acid-induced functional
sodium iodide symporter (NIS) expression and cytotoxicity of
131I by carbamazepine in breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 125:377–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang HJ, Youn YK, Hong MK and Kim LS:
Antiproliferation and redifferentiation in thyroid cancer cell
lines by polyphenol phytochemicals. J Korean Med Sci. 26:893–899.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Malehmir M, Haghpanah V, Larijani B,
Ahmadian S, Alimoghaddam K, Heshmat R, Ghavamzadeh A, Adabi K and
Ghaffari SH: Multifaceted suppression of aggressive behavior of
thyroid carcinoma by all-trans retinoic acid induced
re-differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 348:260–269.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lan L, Cui D, Luo Y, Shi BY, Deng LL,
Zhang GY and Wang H: Inhibitory effects of retinoic acid on
invasiveness of human thyroid carcinoma cell lines in vitro. J
Endocrinol Invest. 32:731–738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dutta A, Sen T and Chatterjee A: All-trans
retinoic acid (ATRA) downregulates MMP-9 by modulating its
regulatory molecules. Cell Adh Migr. 4:409–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vasko V, Espinosa AV, Scouten W, He H,
Auer H, Liyanarachchi S, Larin A, Savchenko V, Francis GL, de la
Chapelle A, et al: Gene expression and functional evidence of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in papillary thyroid carcinoma
invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 2803–2808. 2007,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jang GB, Kim JY, Cho SD, Park KS, Jung JY,
Lee HY, Hong IS and Nam JS: Blockade of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
suppresses breast cancer metastasis by inhibiting CSC-like
phenotype. Sci Rep. 5:124652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|