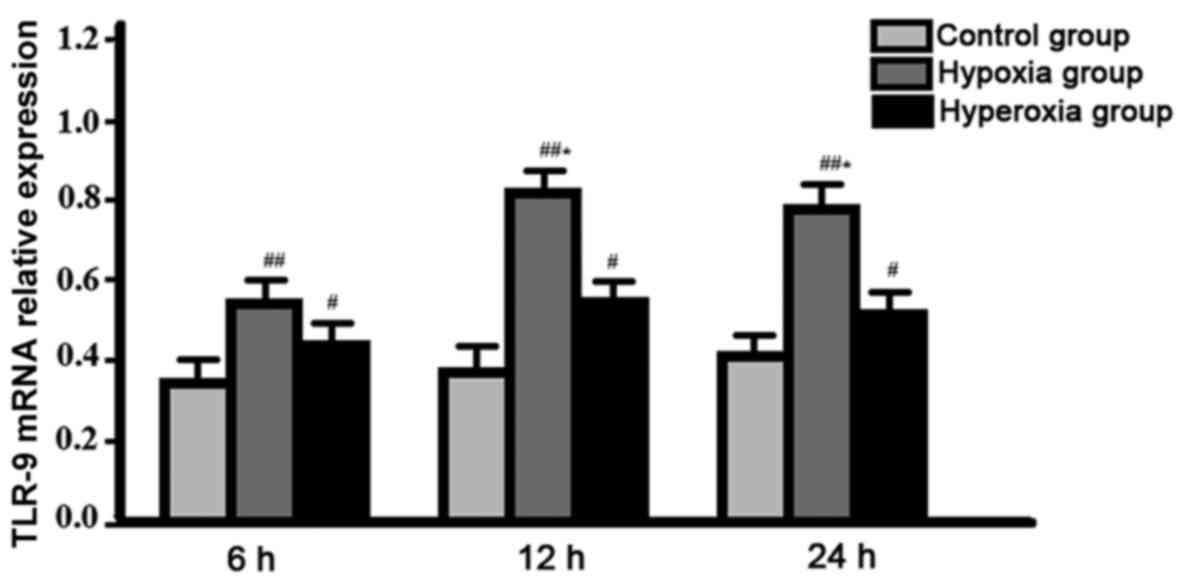
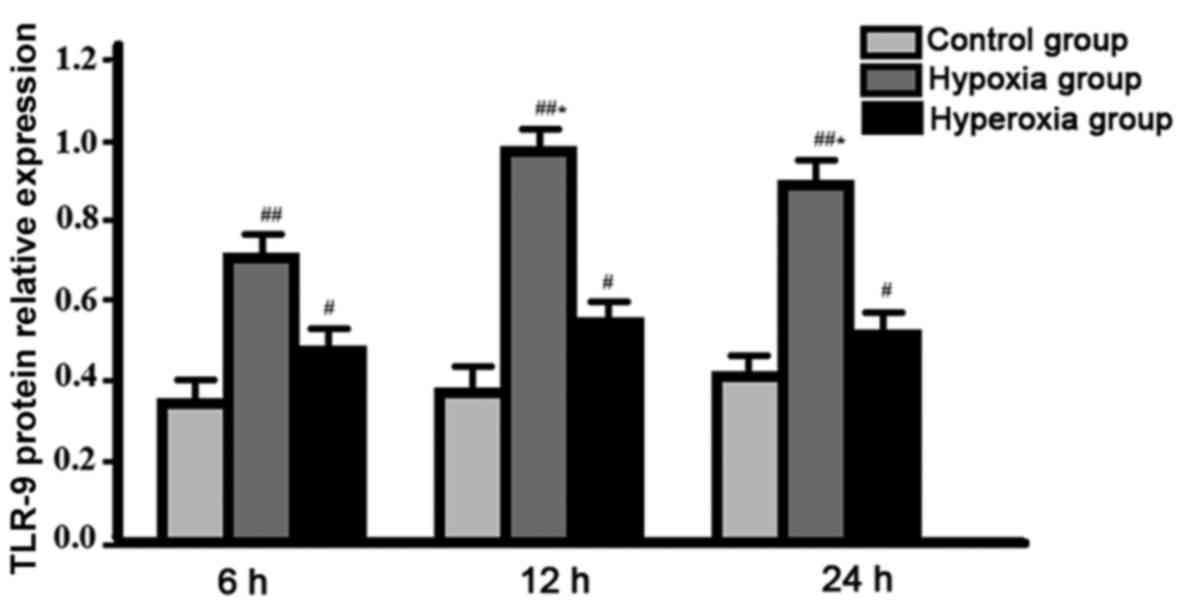
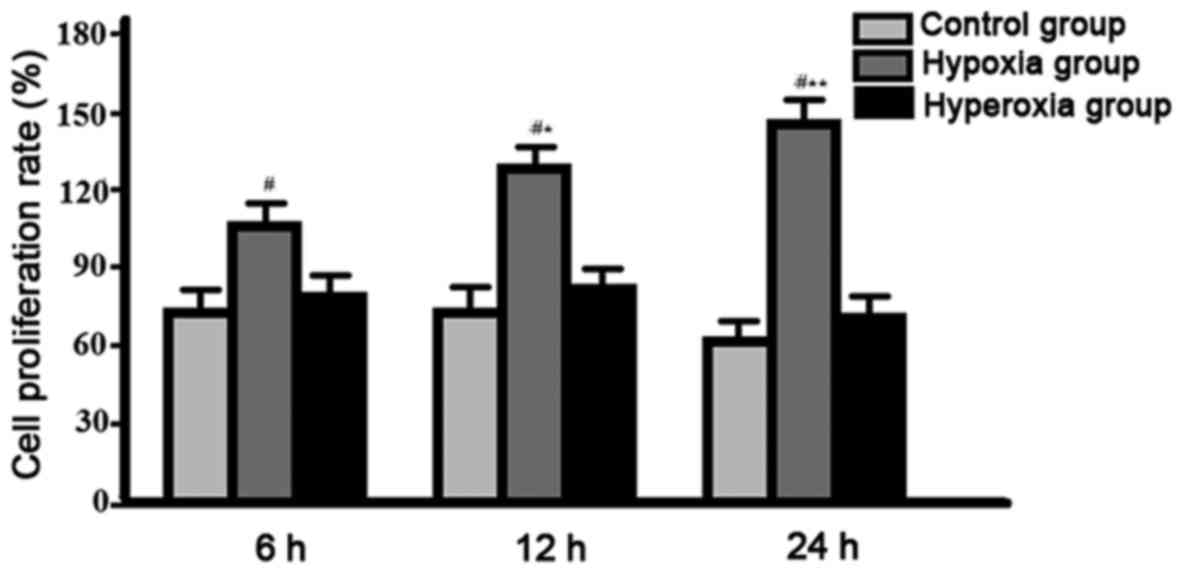
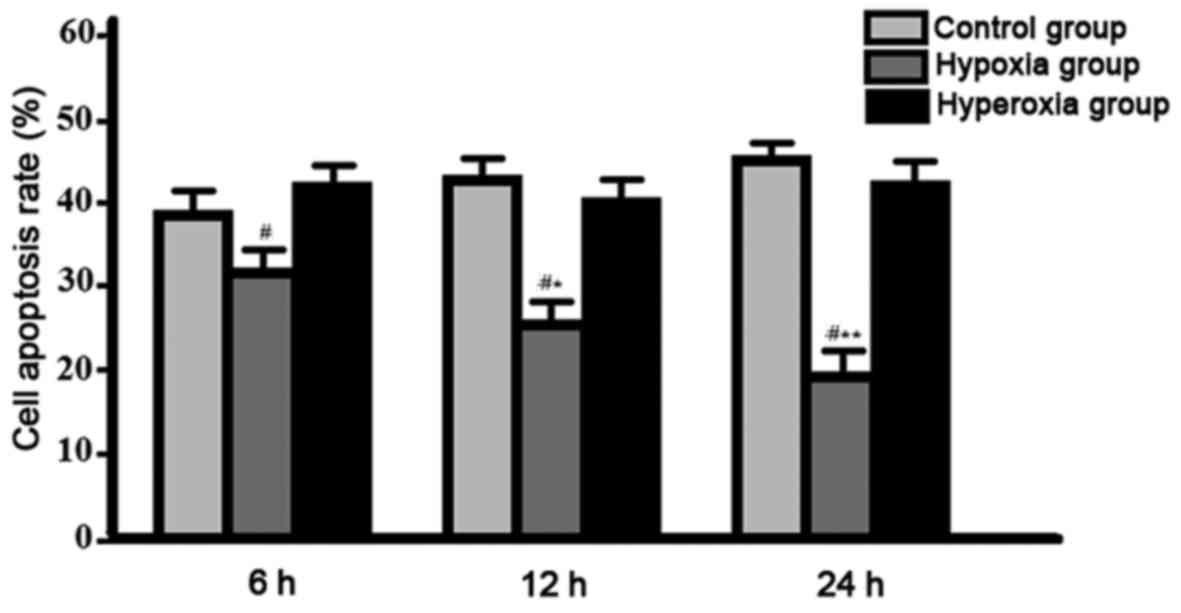
|
1
|
Yip C, Cook GJ, Wee J, Fong KW, Tan T and
Goh V: Clinical significance of hypoxia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
with a focus on existing and novel hypoxia molecular imaging. Chin
Clin Oncol. 5:242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu T and Xiao D: Oleuropein enhances
radiation sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by downregulating
PDRG1 through HIF1α-repressed microRNA-519d. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:32017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Zhang H, Xiong W, Ma J, Zhou
M, Lu J, Zeng Z, Bo X, Chen P, et al: SPLUNC1 reduces the
inflammatory response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells infected
with the EB virus by inhibiting the TLR9/NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep.
33:2779–2788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karki K, Pande D, Negi R, Khanna S, Khanna
RS and Khanna HD: Correlation of serum toll like receptor 9 and
trace elements with lipid peroxidation in the patients of breast
diseases. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 30:11–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng Y, Qin Z, Ye Q, Chen P, Wang Z, Yan
Q, Luo Z, Liu X, Zhou Y, Xiong W, et al: Lactoferrin suppresses the
Epstein-Barr virus-induced inflammatory response by interfering
with pattern recognition of TLR2 and TLR9. Lab Invest.
94:1188–1199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammadi A, Billard C, Faussat AM and Kolb
JP: Stimulation of iNOS expression and apoptosis resistance in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells through
engagement of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR-7) and NF-kappaB
activation. Nitric Oxide. 19:138–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruan M, Zhang Z, Li S, Yan M, Liu S, Yang
W, Wang L and Zhang C: Activation of Toll-like receptor-9 promotes
cellular migration via up-regulating MMP-2 expression in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e927482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu SL, Li YJ, Liao K, Shi L, Zhang N, Liu
S, Hu YY, Li SL and Wang Y: 2-Methoxyestradiol inhibits the
proliferation and migration and reduces the radioresistance of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2 stem cells via NF-κB/HIF-1 signaling
pathway inactivation and EMT reversal. Oncol Rep. 37:793–802. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sung WW, Chu YC, Chen PR, Liao MH and Lee
JW: Positive regulation of HIF-1A expression by EBV oncoprotein
LMP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 382:21–31.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Xie G, Li L, Jiang Z, Yue Z and Pan
Z: The effect of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway on
proliferation and apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5–8F
cells induced by LPS. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 29:1012–1015. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dai Q, Li XP, Chai L, Long HA and Yang ZH:
Polymorphisms of Toll-like receptor 9 are associated with
nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility. Tumour Biol. 35:3247–3253.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bottoni U, Paolino G, Didona D, Corsetti
P, Clerico R, Cantisani C, Richetta AG, Arcidiacono V, Scali E,
Pranteda G, et al: Improvement of survival in patients with
melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers compared to patients without
double cutaneous malignancies. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:1640–1644. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hold GL, Rabkin CS, Gammon MD, Berry SH,
Smith MG, Lissowska J, Risch HA, Chow WH, Mowat NA, Vaughan TL, et
al: CD14-159C/T and TLR9-1237T/C polymorphisms are not associated
with gastric cancer risk in Caucasian populations. Eur J Cancer
Prev. 18:117–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grimmig T, Moench R, Kreckel J, Haack S,
Rueckert F, Rehder R, Tripathi S, Ribas C, Chandraker A, Germer CT,
et al: Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 signaling promotes
autoregulative tumor cell growth and VEGF/PDGF expression in human
pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E20602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ruan M, Thorn K, Liu S, Li S, Yang W and
Zhang C and Zhang C: The secretion of IL-6 by CpG-ODN-treated
cancer cells promotes T-cell immune responses partly through the
TLR-9/AP-1 pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
44:2103–2110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang ZH, Dai Q, Gu YJ, Guo QX and Gong L:
Cytokine and chemokine modification by Toll-like receptor
polymorphisms is associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer
Sci. 103:653–658. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han S, Xu W, Wang Z, Qi X, Wang Y, Ni Y,
Shen H, Hu Q and Han W: Crosstalk between the HIF-1 and Toll-like
receptor/nuclear factor-κB pathways in the oral squamous cell
carcinoma microenvironment. Oncotarget. 7:37773–37789. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|