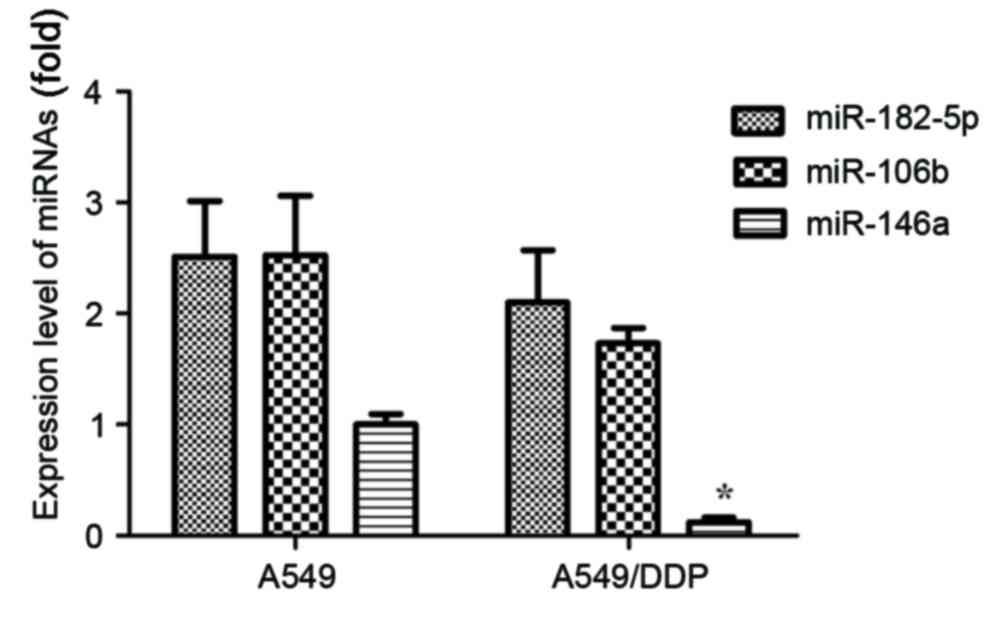
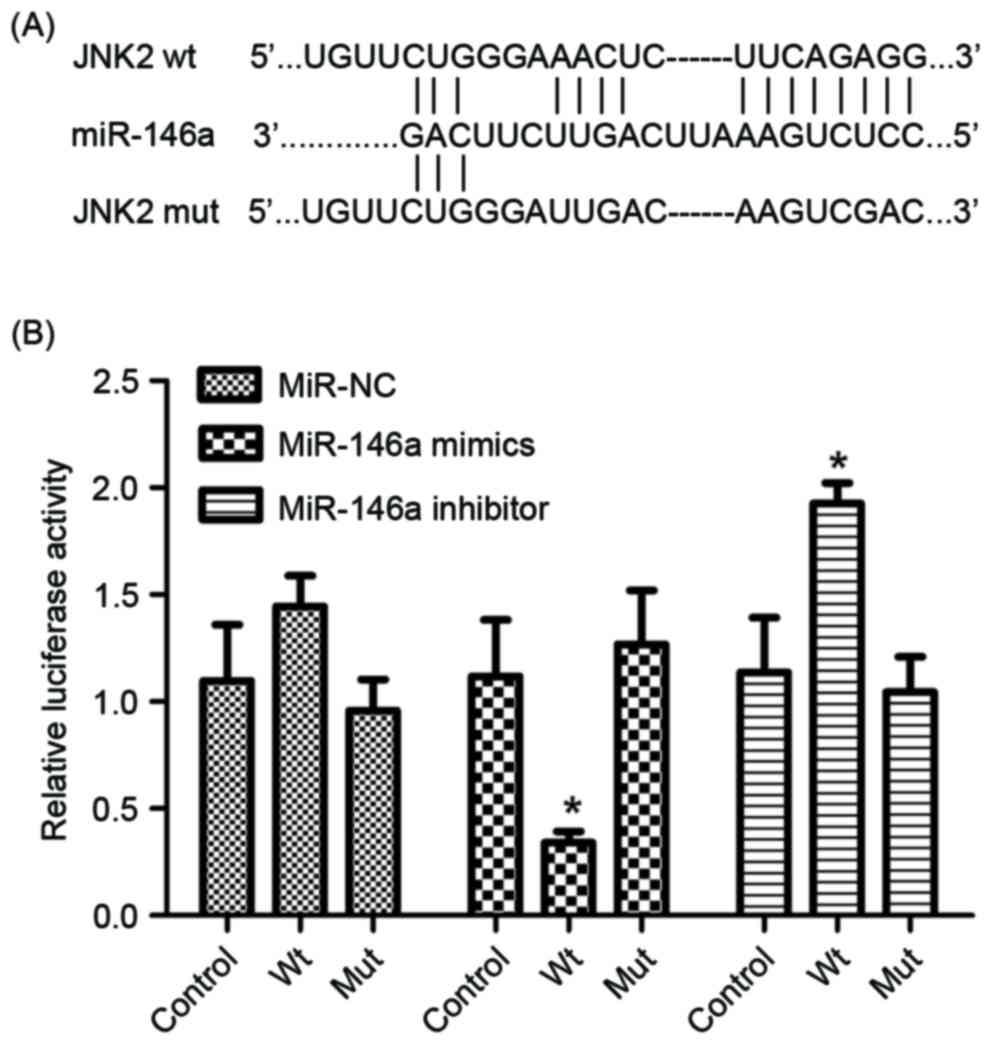
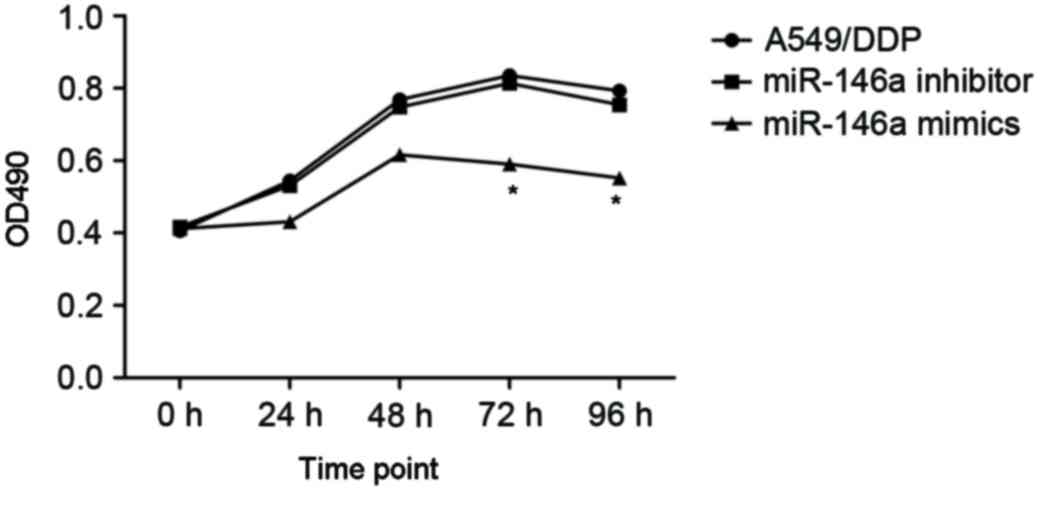
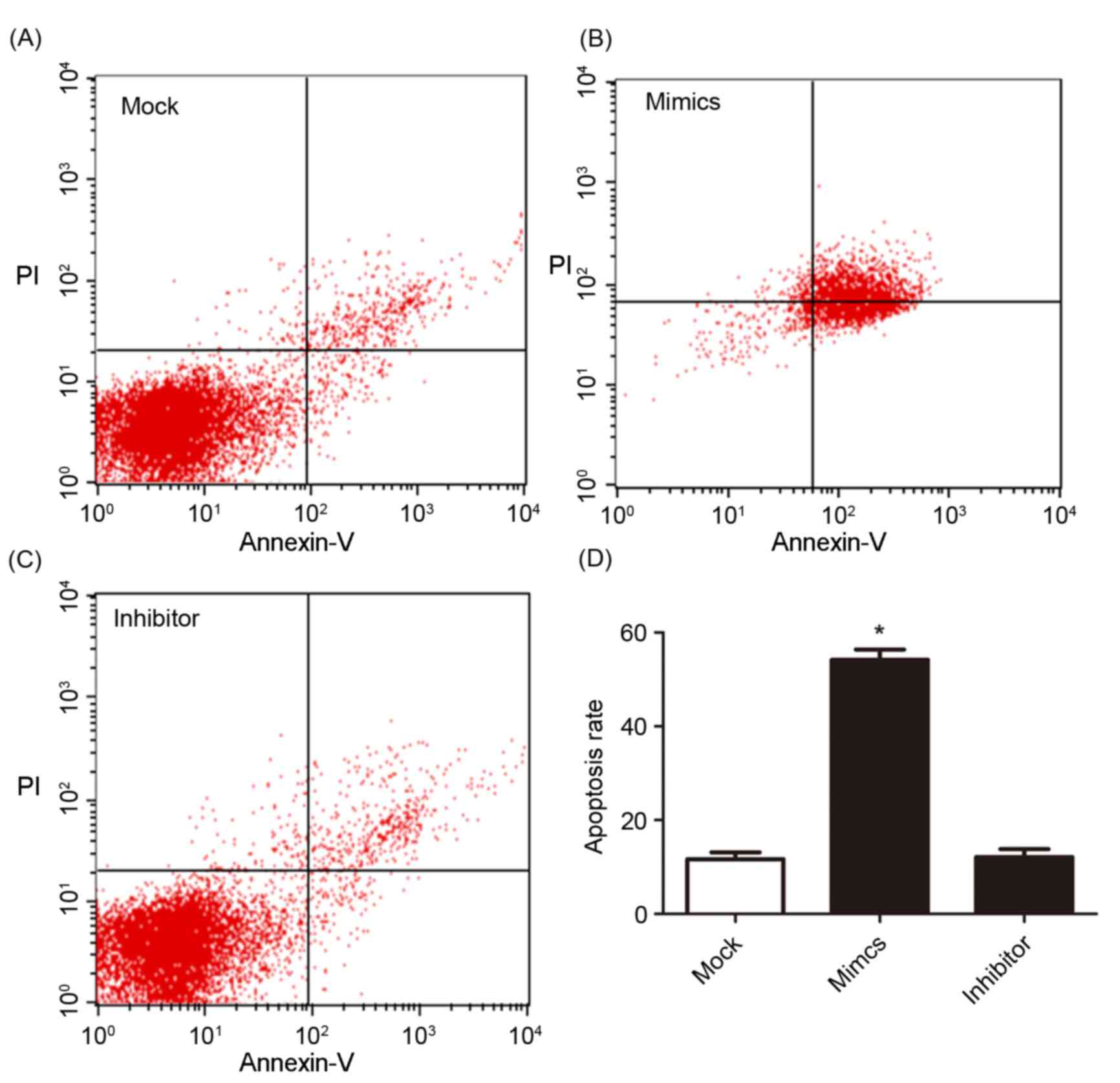
|
1
|
Eaton KD and Martins RG: Maintenance
chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
8:815–821. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Socinski MA, Crowell R, Hensing TE, Langer
CJ, Lilenbaum R, Sandler AB and Morris D: American College of Chest
Physicians: Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, Stage IV: ACCP
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines (2nd edition). Chest.
132 3 Suppl:277S–289S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Korita PV, Wakai T, Shirai Y, Matsuda Y,
Sakata J, Takamura M, Yano M, Sanpei A, Aoyagi Y, Hatakeyama K and
Ajioka Y: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 determines the
efficacy of cisplatin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 23:965–972. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rose MC, Kostyanovskaya E and Huang RS:
Pharmacogenomics of cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung
cancer. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 12:198–209. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang Y, Li H, Hou S, Hu B, Liu J and Wang
J: The noncoding RNA expression profile and the effect of lncRNA
AK126698 on cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer
cell. PLoS One. 8:e653092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin Y, Wang Z, Liu L and Chen L: Akt is
the downstream target of GRP78 in mediating cisplatin resistance in
ER stress-tolerant human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer.
71:291–297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Edwards JK, Pasqualini R, Arap W and Calin
GA: MicroRNAs and ultraconserved genes as diagnostic markers and
therapeutic targets in cancer and cardiovascular diseases. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:271–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fabbri M: miRNAs as molecular biomarkers
of cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 10:435–444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jackson A and Linsley PS: The therapeutic
potential of microRNA modulation. Discov Med. 9:311–318.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma J, Dong C and Ji C: MicroRNA and drug
resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:523–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu ZW, Zhong LP, Ji T, Zhang P, Chen WT
and Zhang CP: MicroRNAs contribute to the chemoresistance of
cisplatin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma lines. Oral Oncol.
46:317–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson GL and Nakamura K: The c-jun
kinase/stress-activated pathway: Regulation, function and role in
human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:1341–1348. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Johnson GL: MAPKs:
Function, regulation, role in cancer and therapeutic targeting.
Oncogene. 26:3097–3099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cuevas BD, Abell AN and Johnson GL: Role
of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases in signal
integration. Oncogene. 26:3159–3171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bode AM and Dong Z: The functional
contrariety of JNK. Mol Carcinog. 46:591–598. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bubici C and Papa S: JNK signalling in
cancer: In need of new, smarter therapeutic targets. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:24–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Panczyk M: Pharmacogenetics research on
chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer over the last 20
years. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9775–9827. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Subramanian S and Steer CJ: MicroRNAs as
gatekeepers of apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 223:289–298.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haenisch S and Cascorbi I: miRNAs as
mediators of drug resistance. Epigenomics. 4:369–381. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sui H, Cai GX, Pan SF, Deng WL, Wang YW,
Chen ZS, Cai SJ, Zhu HR and Li Q: miR200c attenuates P-gp-mediated
MDR and metastasis by targeting JNK2/c-Jun signaling pathway in
colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:3137–3151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Echevarría-Vargas IM, Valiyeva F and
Vivas-Mejía PE: Upregulation of miR-21 in cisplatin resistant
ovarian cancer via JNK-1/c-Jun pathway. PLoS One. 9:e970942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Grève J:
miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tomokuni A, Eguchi H, Tomimaru Y, Wada H,
Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Tanemura M, Nagano H, Mori M
and Doki Y: miR-146a suppresses the sensitivity to interferon-α in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
414:675–680. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hansen PR, Holm AM, Svendsen UG, Olsen PS
and Andersen CB: Apoptosis and formation of peroxynitrite in the
lungs of patients with obliterative bronchiolitis. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 19:160–166. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sui H, Zhou S, Wang Y, Liu X, Zhou L, Yin
P, Fan Z and Li Q: COX-2 contributes to P-glycoprotein-mediated
multidrug resistance via phosphorylation of c-Jun at Ser63/73 in
colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:667–675. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H,
Meng W, Lim SK and Sze SK: Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its
microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by
secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics.
9:1085–1099. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma A, Kumar M, Aich J, Hariharan M,
Brahmachari SK, Agrawal A and Ghosh B: Posttranscriptional
regulation of interleukin-10 expression by hsa-miR-106a. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 5761–5766. 2009, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kamiya T, Kobayashi Y, Kanaoka K,
Nakashima T, Kato Y, Mizuno A and Sakai H: Fluorescence microscopic
demonstration of cathepsin K activity as the major lysosomal
cysteine proteinase in osteoclasts. J Biochem. 123:752–759. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Vandenboom TG II, Wang Z, Kong D,
Ali S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH: miR-146a suppresses invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:1486–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Grève J:
miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stevenson M, Joyner J, Dildar K, et al:
The role of miR-146a and novel Rhenium compounds on prostate cancer
cell lines derived from African Americans and European American
patients. Cancer Res. 75:4840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Imanaka Y, Tsuchiya S, Sato F, Shimada Y,
Shimizu K and Tsujimoto G: MicroRNA-141 confers resistance to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis by targeting YAP1 in human esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 56:270–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pacifico F, Crescenzi E, Mellone S,
Iannetti A, Porrino N, Liguoro D, Moscato F, Grieco M, Formisano S
and Leonardi A: Nuclear factor-{kappa}B contributes to anaplastic
thyroid carcinomas through up-regulation of miR-146a. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 95:1421–1430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS,
Meyers C and Zheng ZM: Aberrant expression of oncogenic and
tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for
cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D and Ying SY:
Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer.
RNA. 14:417–424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:4277–4284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou Z, Xie L, Yu L, Qian X and Liu B:
MicroRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates
cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med Oncol. 29:886–892. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hayakawa J, Depatie C, Ohmichi M and
Mercola D: The activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) by
DNA-damaging agents serves to promote drug resistance via
activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2)-dependent enhanced DNA
repair. J Biol Chem. 278:20582–20592. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Buschmann T, Potapova O, Bar-Shira A,
Ivanov VN, Fuchs SY, Henderson S, Fried VA, Minamoto T,
Alarcon-Vargas D, Pincus MR, et al: Jun NH2-terminal kinase
phosphorylation of p53 on Thr-81 is important for p53 stabilization
and transcriptional activities in response to stress. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:2743–2754. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Noguchi K, Kitanaka C, Yamana H, Kokubu A,
Mochizuki T and Kuchino Y: Regulation of c-Myc through
phosphorylation at Ser-62 and Ser-71 by c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J
Biol Chem. 274:32580–32587. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park J, Kim I, Oh YJ, Lee K, Han PL and
Choi EJ: Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase antagonizes an
anti-apoptotic action of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 272:16725–16728. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee DH, Ha JH, Kim Y, Jang M, Park SJ,
Yoon HS, Kim EH, Bae KH, Park BC, Park SG, et al: A conserved
mechanism for binding of p53 DNA-binding domain and anti-apoptotic
Bcl-2 family proteins. Mol Cells. 37:264–269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|