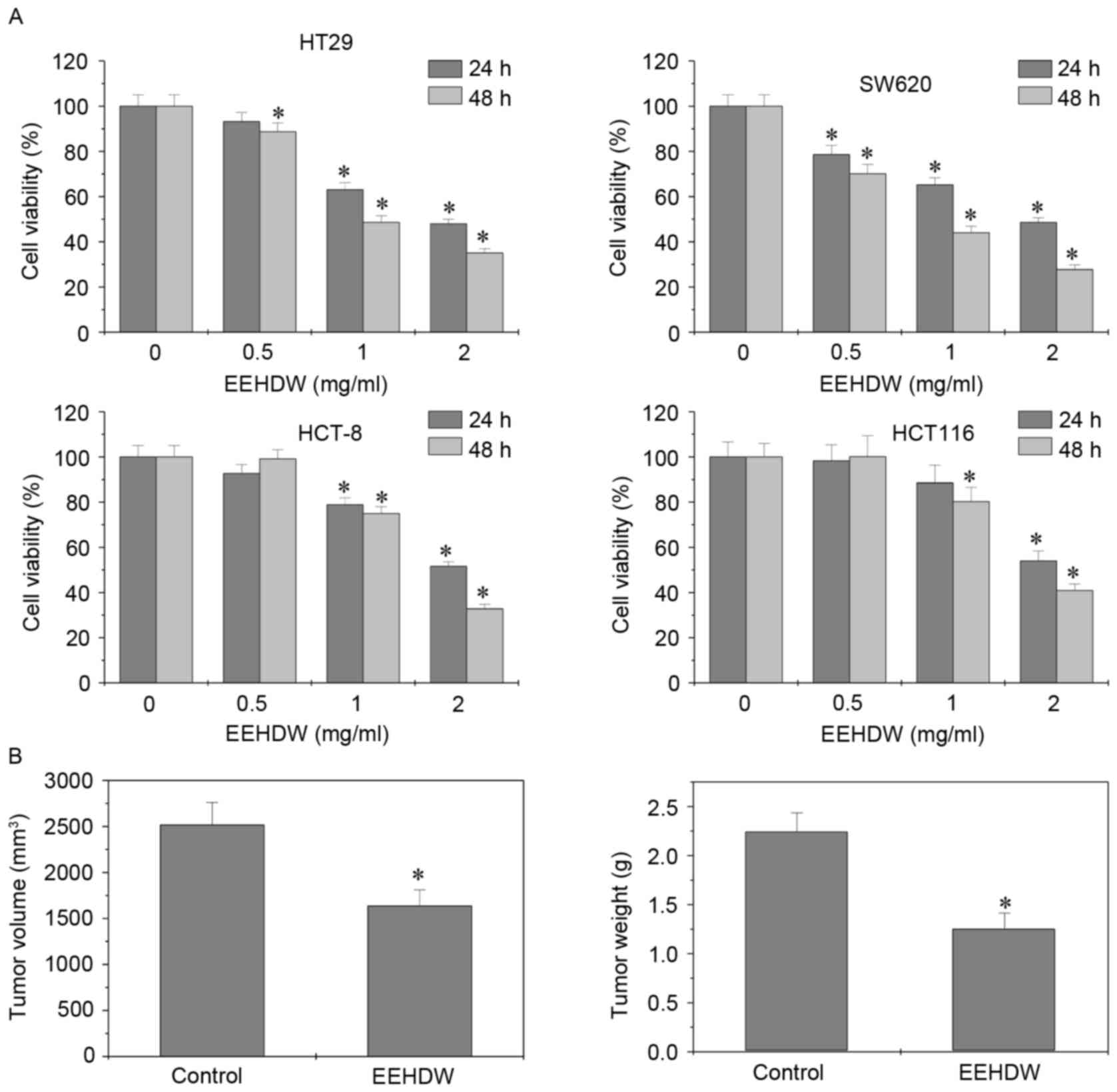
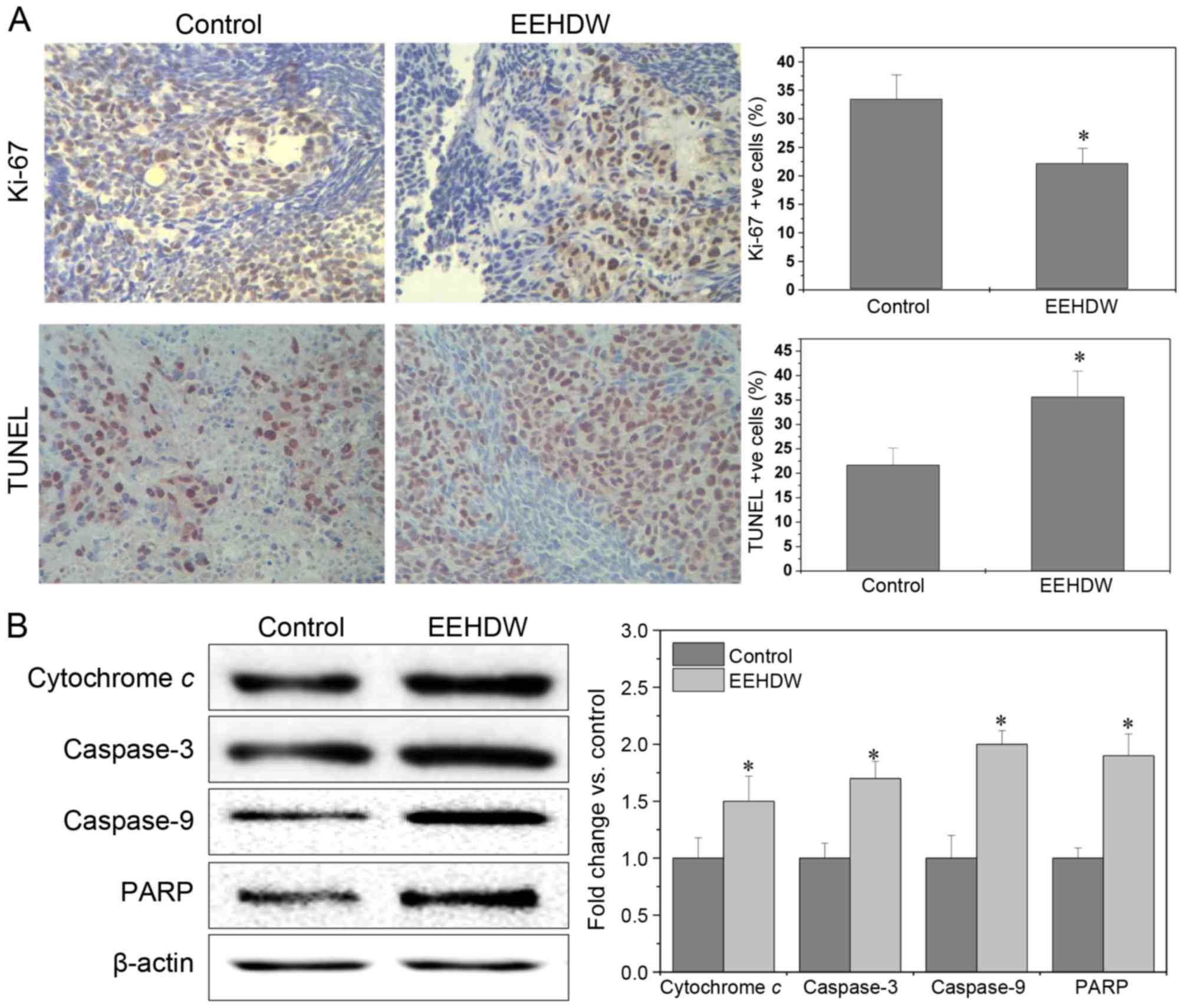
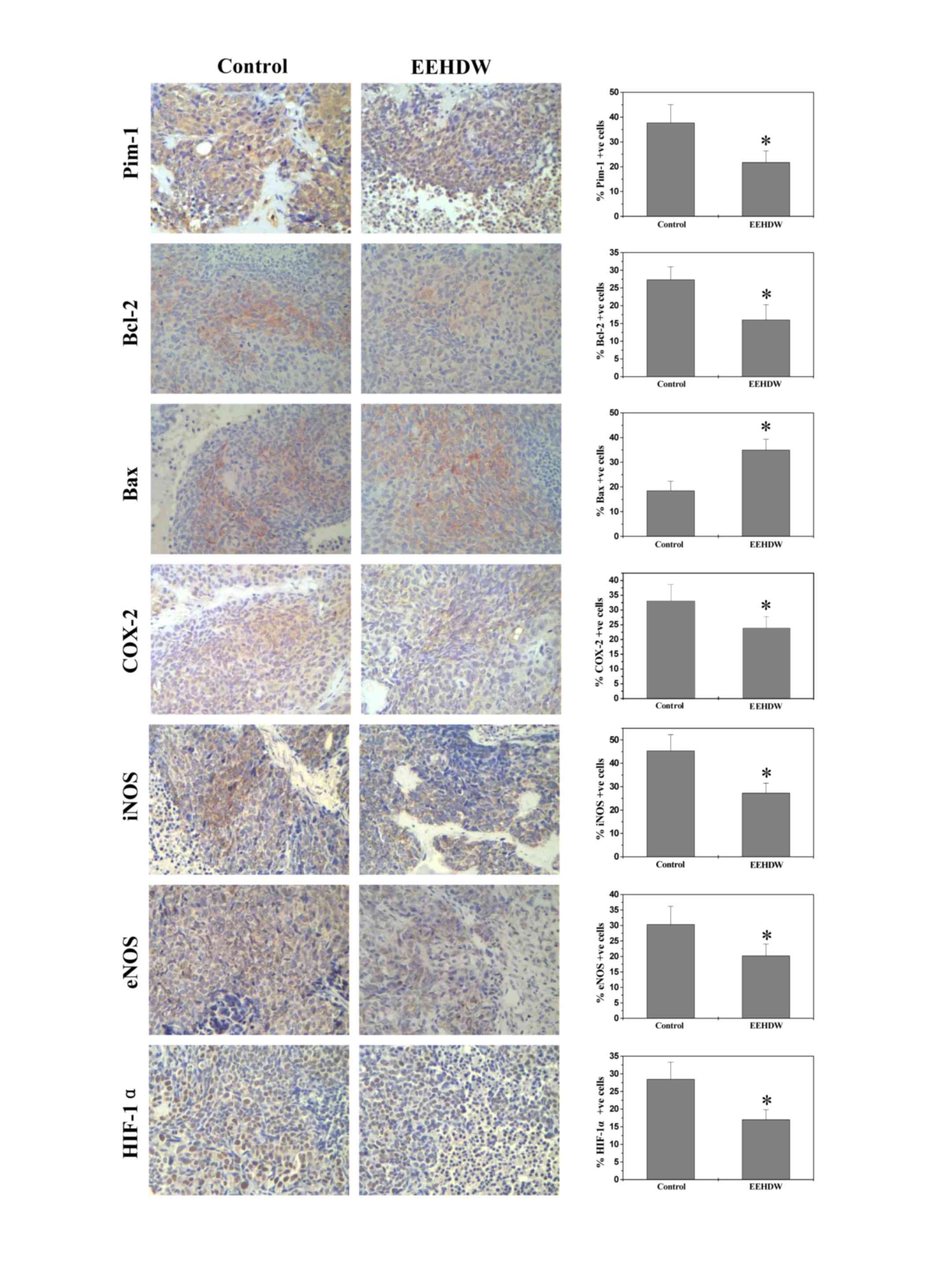
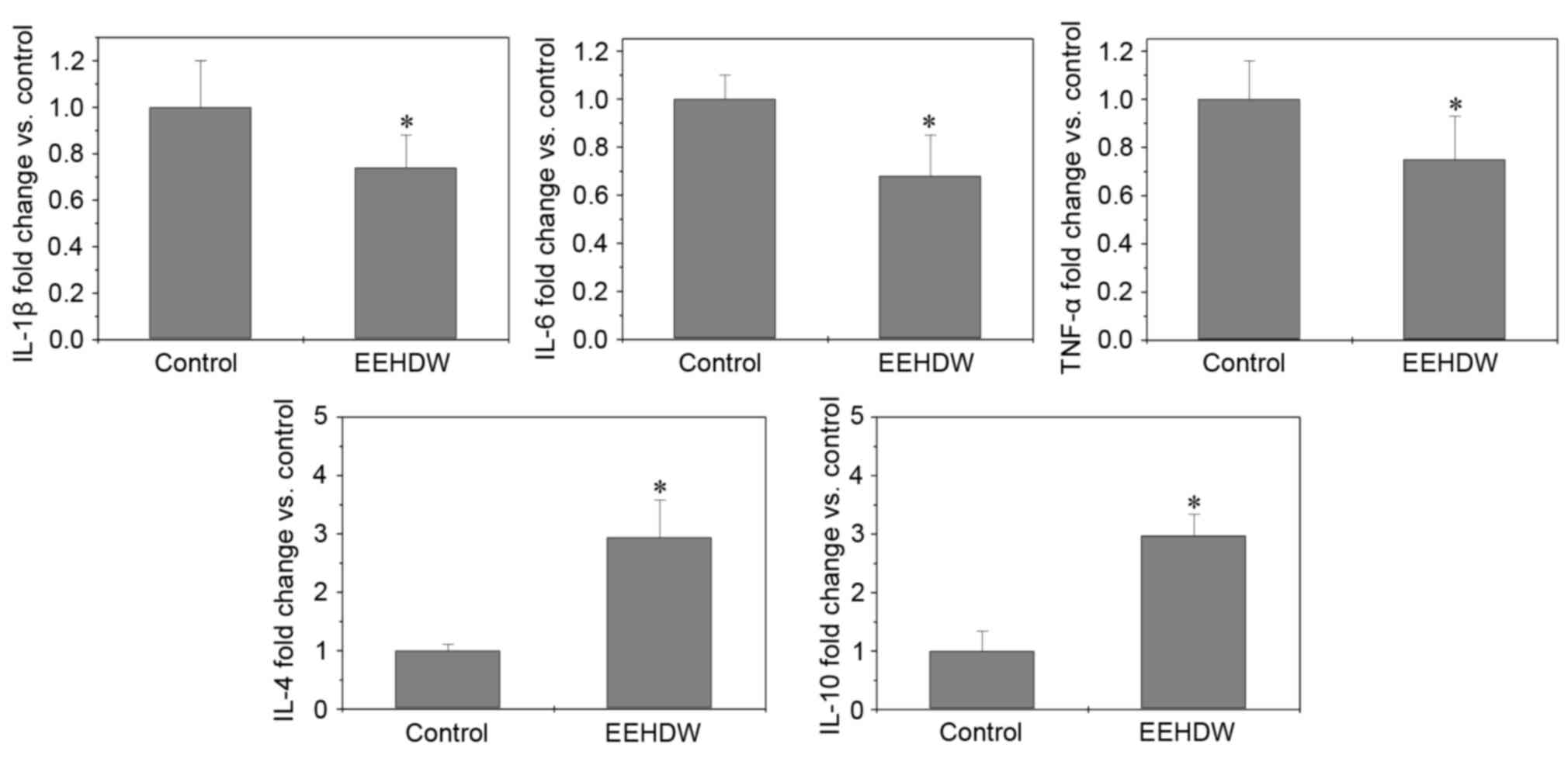
|
1
|
Siegel R, Miller K and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
World wide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Mao W, Wang X, Yu C and Du L:
Incidence and mortality of cancer in Zhejiang province in 2009.
Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 47:592–596. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT,
Minsky B, Nordlinger B and Starling N: Colorectal cancer. Lancet.
375:1030–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang WQ, Fu FF, Li YX, Wang WB, Wang HH,
Jiang HP and Teng LS: Molecular biomarkers of colorectal cancer:
Prognostic and predictive tools for clinical practice. J Zhejiang
Univ Sci B. 13:663–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aakif M, Balfe P, Elfaedy O, Awan FN,
Pretorius F, Silvio L, Castinera C and Mustafa H: Study on
colorectal cancer presentation, treatment and follow-up. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 31:1361–1363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du B and Shim JS: Targeting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to overcome drug resistance
in cancer. Molecules. 21:E9652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Van Cutsem E, Nordlinger B and Cervantes
A: Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines
for treatment. Ann Oncol. 21:93–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gustin DM and Brenner DE: Chemoprevention
of colon cancer: Current status and future prospects. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 21:323–348. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gorlick R and Bertino JR: Drug resistance
in colon cancer. Semin Oncol. 26:606–611. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Longley DB, Allen WL and Johnston PG: Drug
resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:184–196. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boose G and Stopper H: Genotoxicity of
several clinically used topoisomerase II inhibitors. Toxicol Lett.
116:7–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin J, Chuang CC and Zuo L: Potential
roles of microRNAs and ROS in colorectal cancer: Diagnostic
biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Oncotarget. 8:17328–17346.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma X and Wang Z: Anticancer drug discovery
in the future: An evolutionary perspective. Drug Discov Today.
14:1136–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang JJ, Hsu HY, Ho YH and Lin CC:
Comparative study on the immunocompetent activity of three
different kinds of Peh-Hue-Juwa-Chi-Cao, Hedyotis diffusa, H.
corymbosa and Mollugo pentaphylla after sublethal whole body
x-irradiation. Phytother Res. 11:428–432. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Song L: Zhonghuabencao. 61. Shanghai
Science and Technology Press; Shanghai: pp. 4331999, (In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Li R, Zhao H and Lin Y: Anti-tumor effect
and protective effect on chemotherapeutic damage of water soluble
extracts from Hedyotis diffusa. J Chin Pharmaceu Sci. 11:54–58.
2002.
|
|
20
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Chen X, Xu W, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd extract induces
apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrion-dependent pathway in
human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1331–1338.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin J, Wei L, Xu W, Hong Z, Liu X and Peng
J: Effect of hedyotis diffusa willd extract on tumor angiogenesis.
Mol Med Rep. 4:1283–1288. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd
inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via inhibition of STAT3
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin M, Lin J, Wei L, Xu W, Hong Z, Cai Q,
Peng J and Zhu D: Hedyotis diffusa willd extract inhibits HT-29
cell proliferation via cell cycle arrest. Exp Ther Med. 4:307–310.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin J, Wei L, Shen A, Cai Q, Xu W, Li H,
Zhan Y, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd extract
suppresses sonic hedgehog signaling leading to the inhibition of
colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 42:651–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Q, Wang X, Shen A, Zhang Y, Chen Y,
Sferra TJ, Lin J and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd overcomes
5-fluorouracil resistance in human colorectal cancer HCT-8/5-FU
cells by downregulating the expression of P-glycoprotein and
ATP-binding casette subfamily G member 2. Exp Ther Med.
10:1845–1850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cartana ET, Gheonea DI, Cherciu IF,
Streaţa I, Uscatu CD, Nicoli ER, Ioana M, Pirici D, Georgescu CV,
Alexandru DO, et al: Assessing tumor angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer by quantitative contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound and
molecular and immunohistochemical analysis. Endosc Ultrasound.
6:7–17. 2017.
|
|
27
|
Mimatsu K, Fukino N, Ogasawara Y, Saino Y
and Oida T: Utility of inflammatory marker- and nutritional
status-based prognostic factors for predicting the prognosis of
stage iv gastric cancer patients undergoing non-curative surgery.
Anticancer Res. 37:4215–4222.. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shima H, Pende M, Chen Y, Fumagalli S,
Thomas G and Kozma SC: Disruption of the p70(s6k)/p85(s6k) gene
reveals a small mouse phenotype and a new functional S6 kinase.
EMBO J. 17:6649–6659. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sebolt-Leopold JS: Development of
anticancer drugs targeting the MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene.
19:6594–6599. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taupin D and Podolski DK:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation regulates intestinal
epithelial differentiation. Gastroenterology. 116:1072–1080. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang X, Wang Q, Hu W and Evers BM:
Regulation of phorbol ester-mediated TRAF1 induction in human colon
cancer cells through a PKC/RAF/ERK/NF-kappaB-dependent pathway.
Oncogene. 23:1885–1895. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schwartsmann G, Di Leone LP, Dal Pizzol F
and Roesler R: MAPK pathway activation in colorectal cancer: A
therapeutic opportunity for GRP receptor antagonists. Lancet Oncol.
6:444–445. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fang JY and Richardson BC: The MAPK
signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 6:322–327.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation and
cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann NY Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell J: Stat3: A
STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in
response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science.
264:95–98. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bromberg J and Wang TC: Inflammation and
cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell. 15:79–80.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata
Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, Nagayasu T and Sekine I: Activation of
STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep. 15:1445–1451. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin Q, Lai R, Chirieac LR, Li C, Thomazy
VA, Grammatikakis I, Rassidakis GZ, Zhang W, Fujio Y, Kunisada K,
et al: Constitutive activation of JAK3/STAT3 in colon carcinoma
tumors and cell lines: Inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am J
Pathol. 167:969–980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang
QC, Zhang YJ, Lu R, Chen YX and Fang JY: Inhibition of JAK1,
2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and reduces
tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia.
10:287–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
García-Caballero M, Paupert J, Blacher S,
Van de Velde M, Quesada AR, Medina MA and Noël A: Targeting
VEGFR-3/-2 signaling pathways with AD0157: A potential strategy
against tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic
metastases. J Hematol Oncol. 10:1222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Eaden JA, Abrams KR and Mayberry JF: The
risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis.
Gut. 48:526–535. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L and Karin M: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huber S, Gagliani N, Zenewicz LA, Huber
FJ, Bosurgi L, Hu B, Hedl M, Zhang W, O'Connor W Jr, Murphy AJ, et
al: IL-22BP is regulated by the inflammasome and modulates
tumorigenesis in the intestine. Nature. 491:259–263. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hyun YS, Han DS, Lee AR, Eun CS, Youn J
and Kim HY: Role of IL-17A in the development of colitis-associated
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:931–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jauch D, Martin M, Schiechl G, Kesselring
R, Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK and Fichtner-Feigl S: Interleukin 21
controls tumour growth and tumour immunosurveillance in
colitis-associatedtumorigenesis in mice. Gut. 60:1678–1686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kirchberger S, Royston DJ, Boulard O,
Thornton E, Franchini F, Szabady RL, Harrison O and Powrie F:
Innate lymphoid cells sustain colon cancer through production of
interleukin-22 in a mouse model. J Exp Med. 210:917–931. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, Kondo T,
Kagaya T, Kaneko S, Oshima M, Fujii C and Mukaida N: Blocking
TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with
chronic colitis. J Clin Invest. 118:560–570. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Stolfi C, Rizzo A, Franzè E, Rotondi A,
Fantini MC, Sarra M, Caruso R, Monteleone I, Sileri P,
Franceschilli L, et al: Involvement of interleukin-21 in the
regulation of colitis-associated colon cancer. J Exp Med.
208:2279–2290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lanca T and Silva-Santos B: The split
nature of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes: Implicationsfor cancer
surveillance and immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 1:717–725. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Monteleone G, Pallone F and Stolfi C: The
dual role of inflammation in colon carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
13:11071–11084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: The
influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep.
17:215–234. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Peng J, Chen Y, Lin J, Zhuang Q, Xu W,
Hong Z and Sferra TJ: Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract suppresses
proliferation and promotes apoptosis by inhibiting STAT3 pathway in
human multiple myeloma cells. Mol Med Rep. 4:313–318.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd
inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via inhibition of STAT3
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wei L, Chen Y, Lin J, Zhao Y, Chen X, Xu
W, Liu X, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Scutellaria barbata D. don induces
apoptosis of human colon carcinoma cell through activation of the
mitochondrion-dependent pathway. J Med Plants Res. 5:1962–1970.
2011.
|
|
61
|
Wei L, Lin J, Xu W, Hong Z, Liu X, Sferra
TJ and Peng J: Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by scutellaria
barbata D. don via suppressing proliferation, migration and tube
formation of endothelial cells and downregulation of the expression
of VEGF-A in cancer cells. J Med Plants Res. 5:3260–3268. 2011.
|
|
62
|
Zheng L, Chen Y, Lin W, Zhuang Q, Chen X,
Xu W, Liu X, Peng J and Sferra TJ: Spica Prunellae extract promotes
mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis in a human colon carcinoma cell
line. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 5:327–335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|