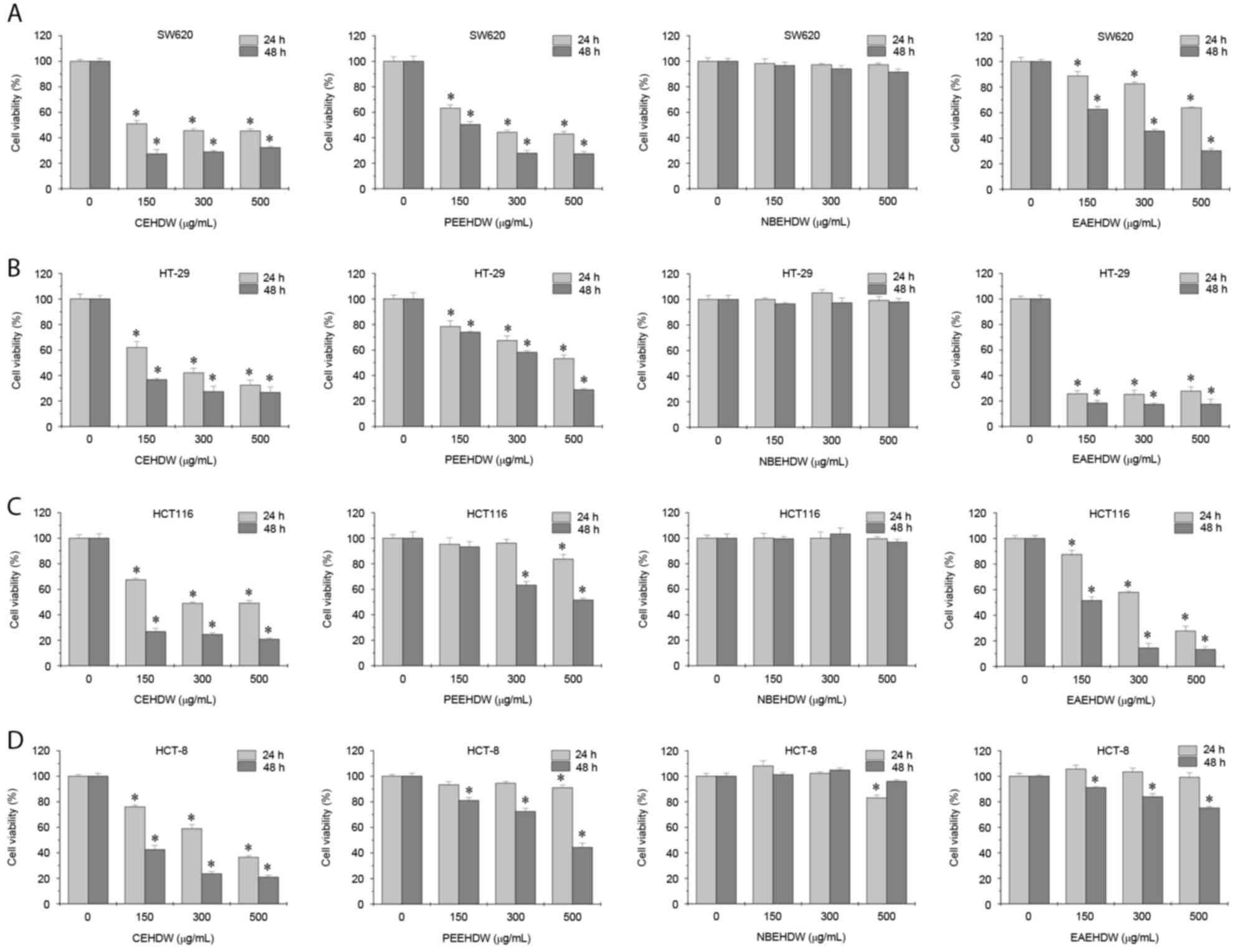
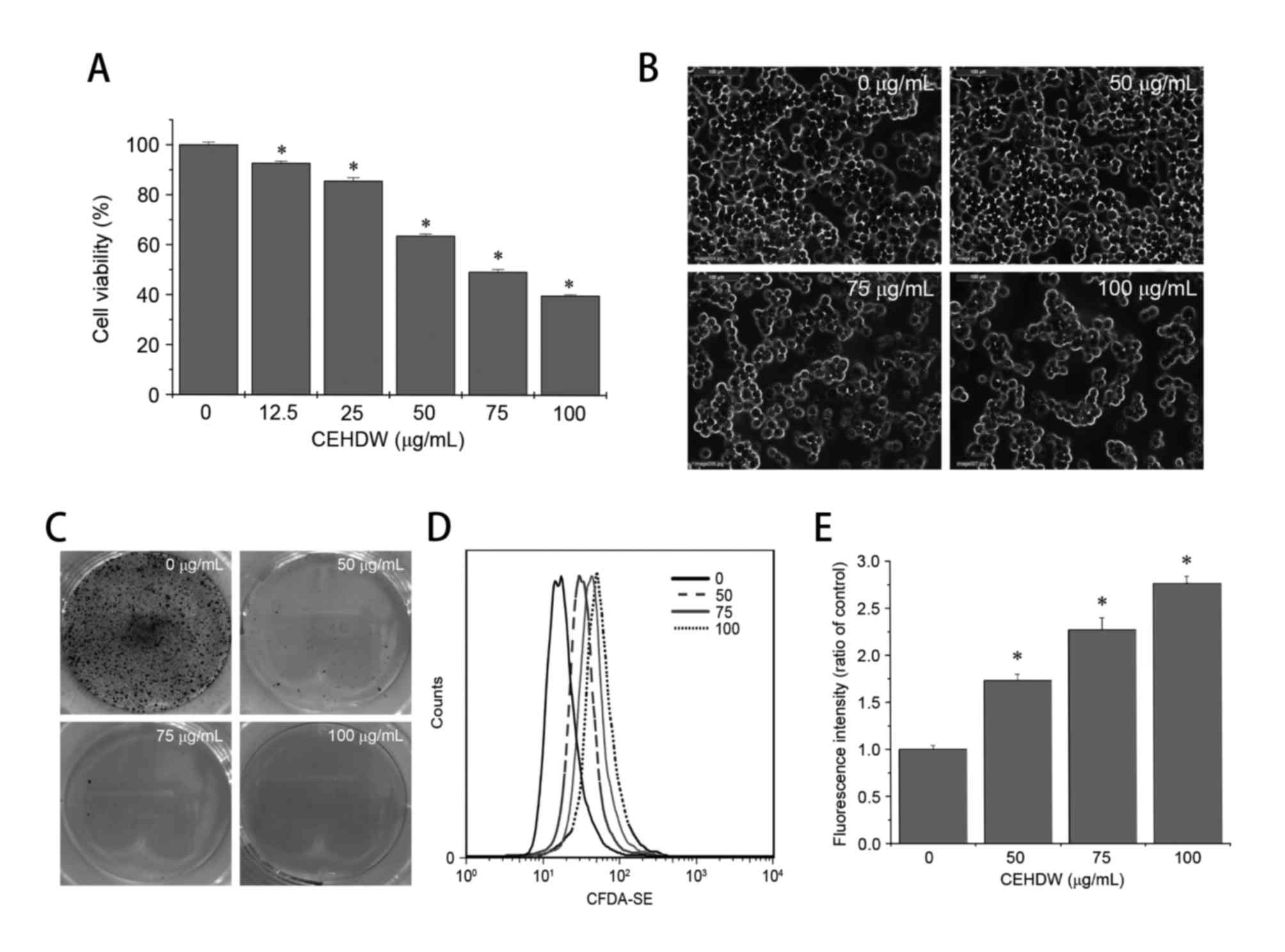
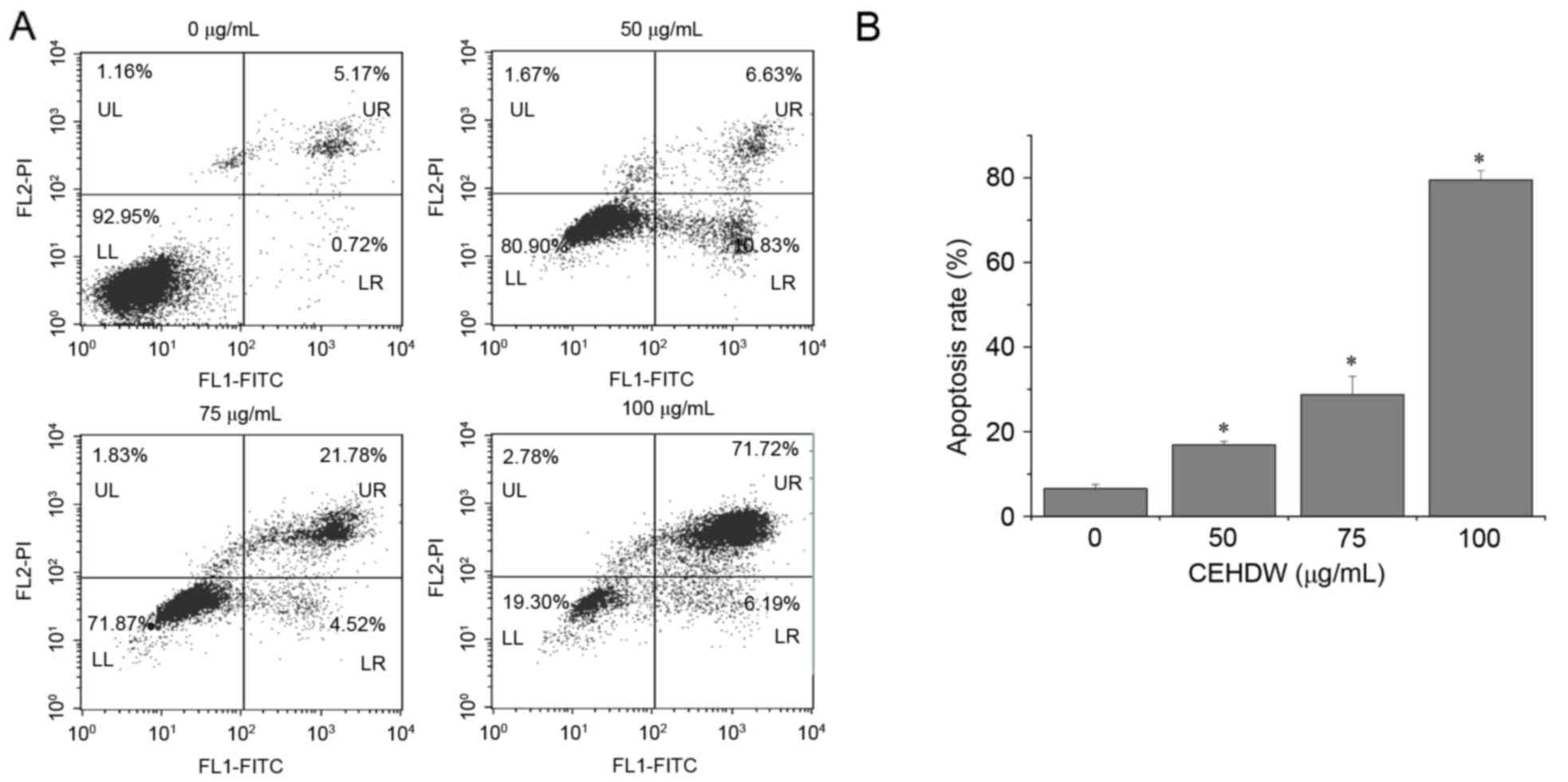
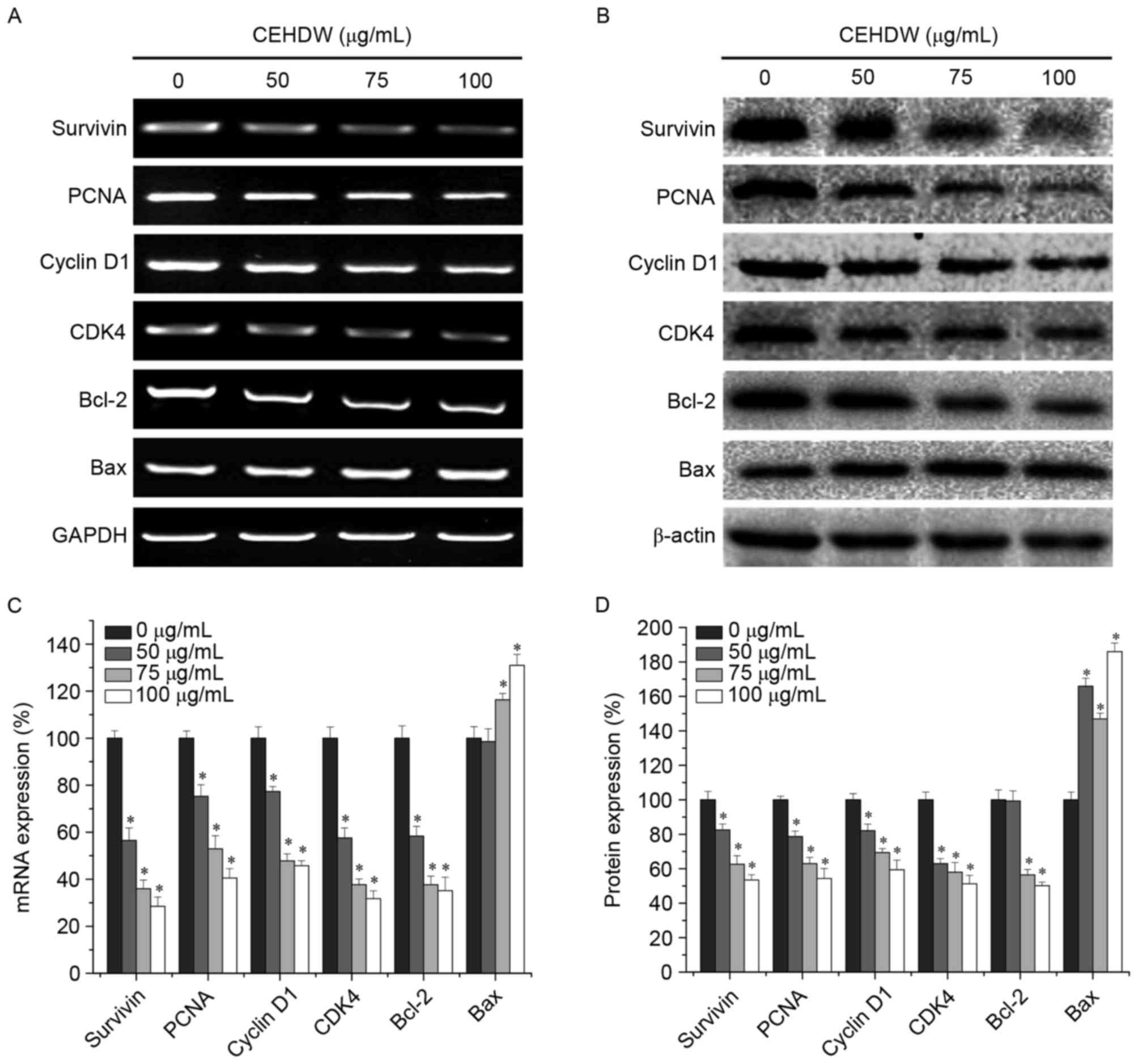
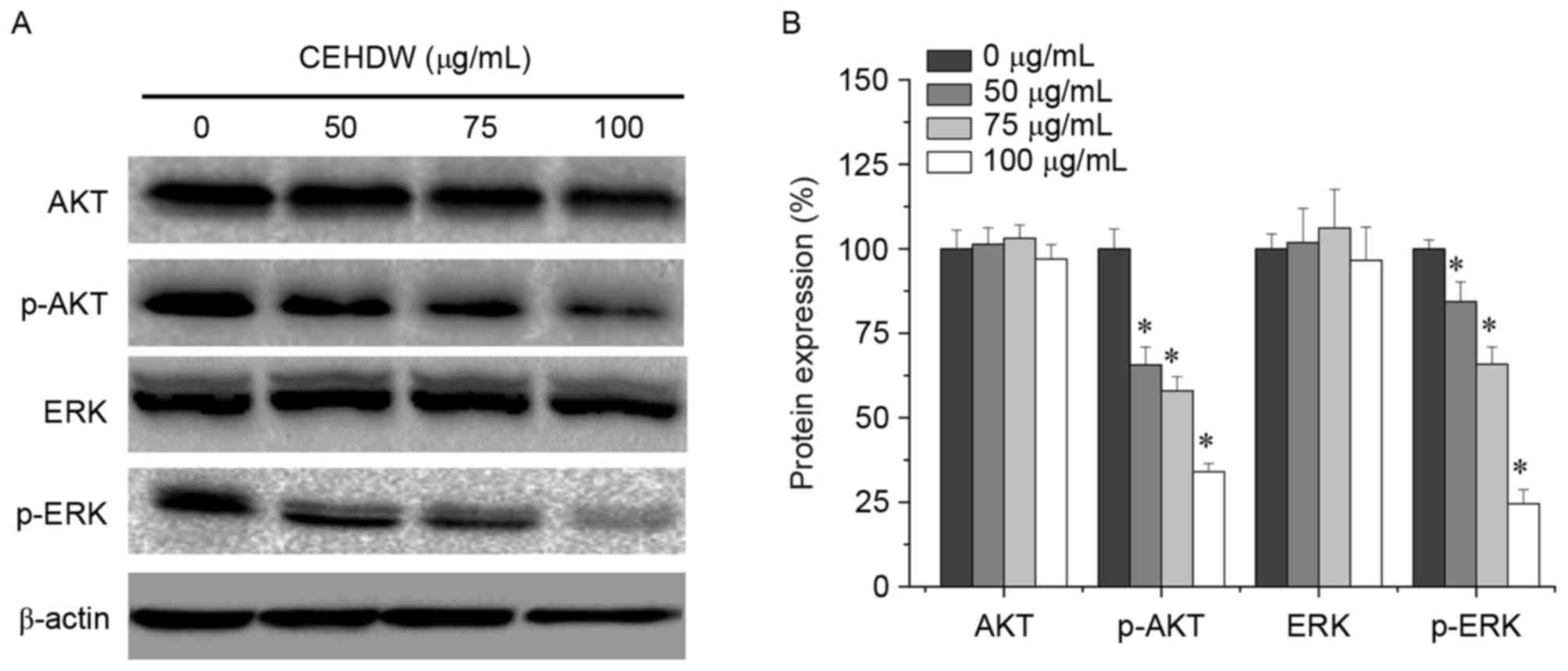
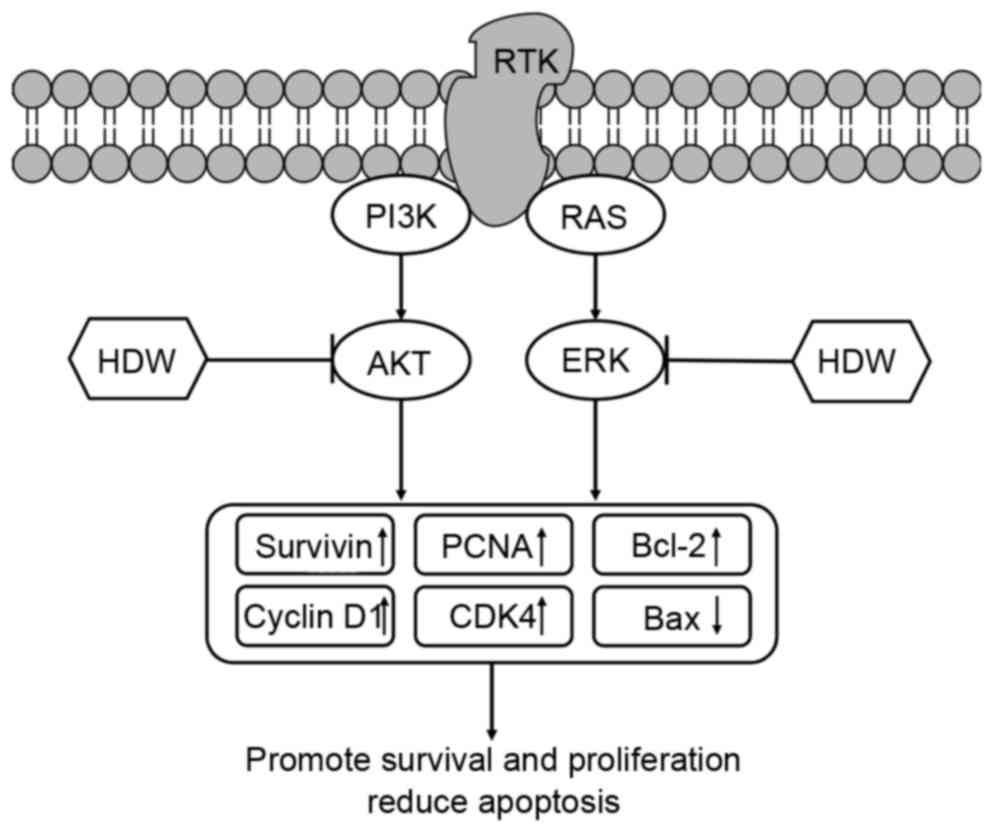
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McQuade RM, Bornstein JC and Nurgali K:
Anti-colorectal cancer chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea: Current
treatments and side-effects. Int J Clin Med. 05:393–406. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Colorectal cancer facts and figures
2014–2016American Cancer Society. Atlanta: 2014
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Zhao H, Guo Y, Lin F, Tang L, Yao Y
and Abba ML: Clinical study of combining chemotherapy of
oxaliplatin or 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin with Hydroxycamptothecine
for advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Oncol Cancer Res. 6:117–123.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu J, Wang S, Zhang Y, Fan HT and Lin HS:
Traditional Chinese medicine and cancer: History, present
situation, and development. Thorac Cancer. 6:561–569. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhuang Q, Hong F, Shen A, Zheng L, Zeng J,
Lin W, Chen Y, Sferra TJ, Hong Z and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang
inhibits tumor cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via
suppressing the STAT3 pathway in a colorectal cancer mouse model.
Int J Oncol. 40:1569–1574. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Y, Lin Y, Li Y and Li C: Total
flavonoids of Hedyotis diffusa Willd inhibit inflammatory responses
in LPS-activated macrophages via suppression of the NF-kappaB and
MAPK signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:1116–1122. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao X, Li C, Tang YL, Zhang H and Chan SW:
Effect of Hedyotis diffusa water extract on protecting human
hepatocyte cells (LO2) from H2O2-induced cytotoxicity. Pharm Biol.
54:1148–1155. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuo YJ, Lin JP, Hsiao YT, Chou GL, Tsai
YH, Chiang SY, Lin JG and Chung JG: Ethanol extract of hedyotis
diffusa Willd affects immune responses in normal Balb/c mice in
vivo. In Vivo. 29:453–460. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yeh YC, Chen HY, Yang SH, Lin YH, Chiu JH,
Lin YH and Chen JL: Hedyotis diffusa combined with scutellaria
barbata are the core treatment of Chinese herbal medicine used for
breast cancer patients: A population-based study. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014:2023782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chao TH, Fu PK, Chang CH, Chang SN, Mao
Chiahung F and Lin CH: Evidence-based Chinese medicine research
group: Prescription patterns of Chinese herbal products for
post-surgery colon cancer patients in Taiwan. J Ethnopharmacol.
155:702–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee HZ, Bau DT, Kuo CL, Tsai RY, Chen YC
and Chang YH: Clarification of the phenotypic characteristics and
anti-tumor activity of Hedyotis diffusa. Am J Chin Med. 39:201–213.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Chen X, Xu W, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Hedyotis Diffusa Willd extract induces
apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrion-dependent pathway in
human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1331–1338.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin J, Li Q, Chen H, Lin H, Lai Z and Peng
J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd. extract suppresses proliferation and
induces apoptosis via IL-6-inducible STAT3 pathway inactivation in
human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 9:1962–1970.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin J, Wei L, Shen A, Cai Q, Xu W, Li H,
Zhan Y, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract
suppresses Sonic hedgehog signaling leading to the inhibition of
colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 42:651–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin J, Wei L, Xu W, Hong Z, Liu X and Peng
J: Effect of hedyotis diffusa Willd extract on tumor angiogenesis.
Mol Med Rep. 4:1283–1288. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin M, Lin J, Wei L, Xu W, Hong Z, Cai Q,
Peng J and Zhu D: Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract inhibits HT-29
cell proliferation via cell cycle arrest. Exp Ther Med. 4:307–310.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Cai Q, Lin J, Fang Y, Zhan Y,
Shen A, Wei L, Wang L and Peng J: Chloroform fraction of
Scutellaria barbata D. Don promotes apoptosis and suppresses
proliferation in human colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:701–706.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong ZF, Tan W, Wang SP, Qiang WA and
Wang YT: Anti-proliferative activity and cell cycle arrest induced
by evodiamine on paclitaxel-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian
cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:164152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furtado RA, Rodrigues EP, Araujo FR,
Oliveira WL, Furtado MA, Castro MB, Cunha WR and Tavares DC:
Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid suppress preneoplastic lesions
induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in rat colon. Toxicol Pathol.
36:576–580. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Guo WJ and Yang QY: Effects of
ursolic acid and oleanolic acid on human colon carcinoma cell line
HCT15. World J Gastroenterol. 8:493–495. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Shen A, Sferra TJ,
Hong Z and Peng J: Ursolic acid promotes colorectal cancer cell
apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation via modulation of
multiple signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 43:1235–1243. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Reuter S,
Kannappan R, Deorukhkar A, Diagaradjane P, Wei C,
Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, et al: Ursolic acid inhibits
growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer in an orthotopic
nude mouse model by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways:
Chemosensitization with capecitabine. Clin Cancer Res.
18:4942–4953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kassi E, Papoutsi Z, Pratsinis H,
Aligiannis N, Manoussakis M and Moutsatsou P: Ursolic acid, a
naturally occurring triterpenoid, demonstrates anticancer activity
on human prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
133:493–500. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Chen D, Lin J and Peng J: Analysis
the difference chemical constituents among the different solvent
extracts from Hedyotis Diffusa Willd. Fujian Analysis &
Testing. 8–12. 2015.(in Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Feng Y, Wang N, Cheung F, Tan HY,
Zhong S, Li C and Kobayashi S: Chinese medicines induce cell death:
The molecular and cellular mechanisms for cancer therapy. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:5303422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li-Weber M: Targeting apoptosis pathways
in cancer by Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett. 332:304–312. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Casati C, Dalerba P, Rivoltini L, Gallino
G, Deho P, Rini F, Belli F, Mezzanzanica D, Costa A, Andreola S, et
al: The apoptosis inhibitor protein survivin induces tumor-specific
CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res.
63:4507–4515. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guzinska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A,
Kemona A and Czyzewska J: Correlation between proliferation
markers: PCNA, Ki-67, MCM-2 and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 in
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 29:3049–3052. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Muntean AG, Pang L, Poncz M, Dowdy SF,
Blobel GA and Crispino JD: Cyclin D-Cdk4 is regulated by GATA-1 and
required for megakaryocyte growth and polyploidization. Blood.
109:5199–5207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ye Q, Cai W, Zheng Y, Evers BM and She QB:
ERK and AKT signaling cooperate to translationally regulate
survivin expression for metastatic progression of colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 33:1828–1839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng M, Li J, Wang J, Ma C, Jiao Y, Wang
Y, Zhang J, Sun Q, Ju Y, Gao L, et al: High glucose increases
LPS-induced DC apoptosis through modulation of ERK1/2, AKT and
Bax/Bcl-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 14:982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|