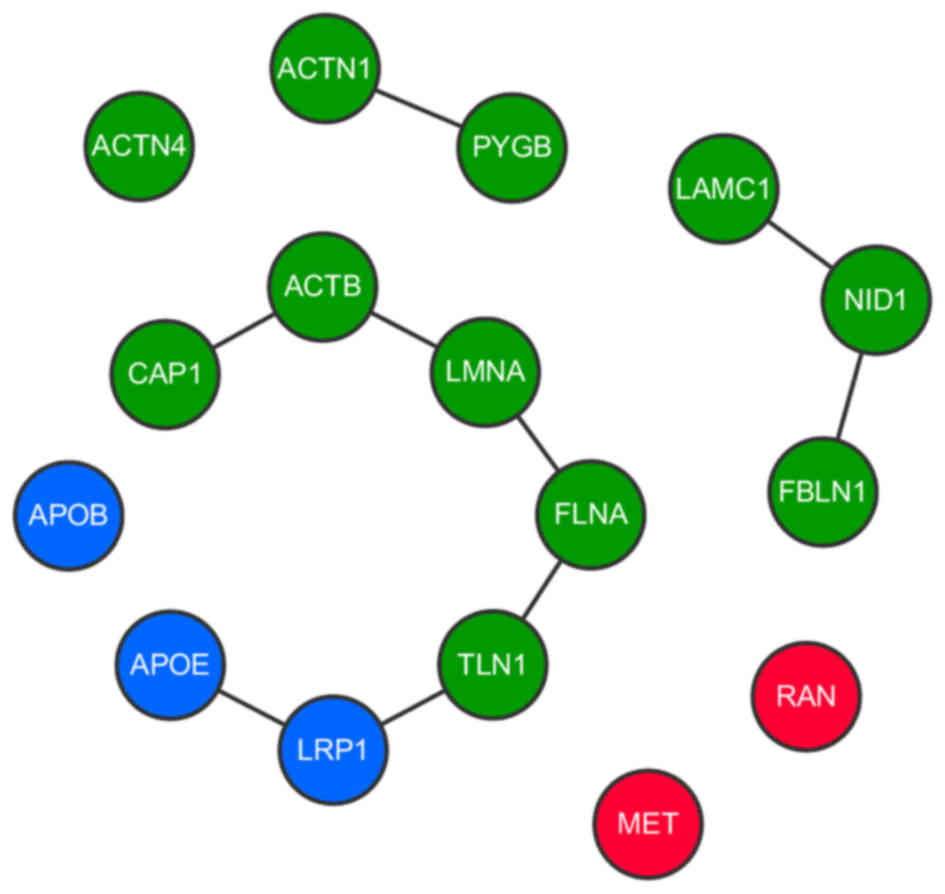
|
1
|
Thery C, Zitvogel L and Amigorena S:
Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol.
2:569–579. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stoorvogel W, Kleijmeer MJ, Geuze HJ and
Raposo G: The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic.
3:321–330. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valenti R, Huber V, Iero M, Filipazzi P,
Parmiani G and Rivoltini L: Tumor-released microvesicles as
vehicles of immunosuppression. Cancer Res. 67:2912–2915. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Atay S, Banskota S, Crow J, Sethi G, Rink
L and Godwin AK: Oncogenic KIT-containing exosomes increase
gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:pp. 711–716. 2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM,
Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, Buchanan M, Hosein AN, Basik M and
Wrana JL: Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine
Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell.
151:1542–1556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dimitroulis D, Damaskos C, Valsami S,
Davakis S, Garmpis N, Spartalis E, Athanasiou A, Moris D,
Sakellariou S, Kykalos S, et al: From diagnosis to treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An epidemic problem for both developed
and developing world. World J Gastroenterol. 23:5282–5294. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye
QH, Wang L, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Li Y, et al: A decade's studies on
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
130:187–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Tang ZY and Hou JX: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Insight from animal models. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 9:32–43. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He M, Qin H, Poon TC, Sze SC, Ding X, Co
NN, Ngai SM, Chan TF and Wong N: Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived
exosomes promote motility of immortalized hepatocyte through
transfer of oncogenic proteins and RNAs. Carcinogenesis.
36:1008–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Andreola G, Rivoltini L, Castelli C, Huber
V, Perego P, Deho P, Squarcina P, Accornero P, Lozupone F, Lugini
L, et al: Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion
of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J Exp Med. 195:1303–1316. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Pilla L,
Sovena G, Villa A, Corbelli A, Fais S, Parmiani G and Rivoltini L:
Human tumor-released microvesicles promote the differentiation of
myeloid cells with transforming growth factor-beta-mediated
suppressive activity on T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 66:9290–9298.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JW, Wieckowski E, Taylor DD, Reichert
TE, Watkins S and Whiteside TL: Fas ligand-positive membranous
vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce
apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1010–1020. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Yu S, Zinn K, Wang J, Zhang L, Jia
Y, Kappes JC, Barnes S, Kimberly RP, Grizzle WE and Zhang HG:
Murine mammary carcinoma exosomes promote tumor growth by
suppression of NK cell function. J Immunol. 176:1375–1385. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Linnane
S, Mason MD and Tabi Z: Human tumor-derived exosomes down-modulate
NKG2D expression. J Immunol. 180:7249–7258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu SD, Ma YS, Fang Y, Liu LL, Fu D and
Shen XZ: Role of the microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
development and progression. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:218–225. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vidal-Vanaclocha F: The liver
prometastatic reaction of cancer patients: Implications for
microenvironment-dependent colon cancer gene regulation. Cancer
Microenviron. 4:163–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hong C, Funk S and Whiteside T: Isolation
of biologically active exosomes from plasma of patients with
cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 1633:257–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keshava Prasad TS, Goel R, Kandasamy K,
Keerthikumar S, Kumar S, Mathivanan S, Telikicherla D, Raju R,
Shafreen B, Venugopal A, et al: Human Protein Reference Database −
2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D767–D77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khurana E, Fu Y, Chen J and Gerstein M:
Interpretation of genomic variants using a unified biological
network approach. PLoS Comput Biol. 9:e10028862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Razick S, Magklaras G and Donaldson IM:
iRefIndex: A consolidated protein interaction database with
provenance. BMC Bioinformatics. 9:4052008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W,
Liejendekker R, Harding CV, Melief CJ and Geuze HJ: B lymphocytes
secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 183:1161–1172.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caby MP, Lankar D, Vincendeau-Scherrer C,
Raposo G and Bonnerot C: Exosomal-like vesicles are present in
human blood plasma. Int Immunol. 17:879–887. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding SJ, Li Y, Shao XX, Zhou H, Zeng R,
Tang ZY and Xia QC: Proteome analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma
cell strains, MHCC97-H and MHCC97-L, with different metastasis
potentials. Proteomics. 4:982–994. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsuo H, Chevallier J, Mayran N, Le Blanc
I, Ferguson C, Fauré J, Blanc NS, Matile S, Dubochet J, Sadoul R,
et al: Role of LBPA and Alix in multivesicular liposome formation
and endosome organization. Science. 303:531–534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leiserson MD, Vandin F, Wu HT, Dobson JR,
Eldridge JV, Thomas JL, Papoutsaki A, Kim Y, Niu B, McLellan M, et
al: Pan-cancer network analysis identifies combinations of rare
somatic mutations across pathways and protein complexes. Nat Genet.
47:106–114. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Buschow SI, van Balkom BW, Aalberts M,
Heck AJ, Wauben M and Stoorvogel W: MHC class II-associated
proteins in B-cell exosomes and potential functional implications
for exosome biogenesis. Immunol Cell Biol. 88:851–856. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Santhana Kumar K, Tripolitsioti D, Ma M,
Grählert J, Egli KB, Fiaschetti G, Shalaby T, Grotzer MA and
Baumgartner M: The Ser/Thr kinase MAP4K4 drives c-Met-induced
motility and invasiveness in a cell-based model of SHH
medulloblastoma. Springerplus. 4:192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang F, Yang Z, Cao M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen
X, Gao Z, Xin J, Zhou S, Zhou Z, et al: MiR-203 suppresses tumor
growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through
repressing Ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett. 342:121–129.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakamura K, Sawada K, Kinose Y, Yoshimura
A, Toda A, Nakatsuka E, Hashimoto K, Mabuchi S, Morishige KI,
Kurachi H, et al: Exosomes promote ovarian cancer cell invasion
through transfer of CD44 to peritoneal mesothelial cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 15:78–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lemoinne S, Thabut D, Housset C, Moreau R,
Valla D, Boulanger CM and Rautou PE: The emerging roles of
microvesicles in liver diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
11:350–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi D, Lee T, Spinelli C,
Chennakrishnaiah S, D'Asti E and Rak J: Extracellular vesicle
communication pathways as regulatory targets of oncogenic
transformation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 67:11–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Théry C, Ostrowski M and Segura E:
Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev
Immunol. 9:581–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Cui X, Hu B, Lu C, Huang X, Cai J,
He S, Lv L, Cong X, Liu G, et al: Upregulated expression of CAP1 is
associated with tumor migration and metastasis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 210:169–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baum B, Li W and Perrimon N: A
cyclase-associated protein regulates actin and cell polarity during
Drosophila oogenesis and in yeast. Curr Biol. 10:964–973. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamazaki K, Takamura M, Masugi Y, Mori T,
Du W, Hibi T, Hiraoka N, Ohta T, Ohki M, Hirohashi S and Sakamoto
M: Adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 overexpressed in
pancreatic cancers is involved in cancer cell motility. Lab Invest.
89:425–432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mincheva-Nilsson L and Baranov V: Cancer
exosomes and NKG2D receptor-ligand interactions: Impairing
NKG2D-mediated cytotoxicity and anti-tumour immune surveillance.
Semin Cancer Biol. 28:24–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi DS, Park JO, Jang SC, Yoon YJ, Jung
JW, Choi DY, Kim JW, Kang JS, Park J, Hwang D, et al: Proteomic
analysis of microvesicles derived from human colorectal cancer
ascites. Proteomics. 11:2745–2751. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meckes DG Jr, Gunawardena HP, Dekroon RM,
Heaton PR, Edwards RH, Ozgur S, Griffith JD, Damania B and
Raab-Traub N: Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma
herpesvirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. E2925–E2933.
2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Al Kaabi A, Traupe T, Stutz M, Buchs N and
Heller M: Cause or effect of arteriogenesis: Compositional
alterations of microparticles from CAD patients undergoing external
counterpulsation therapy. PLoS One. 7:e468222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H,
Mathivanan S, Scott AM and Simpson RJ: Comparison of
ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and
immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer
cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 56:293–304. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liang B, Peng P, Chen S, Li L, Zhang M,
Cao D, Yang J, Li H, Gui T, Li X and Shen K: Characterization and
proteomic analysis of ovarian cancer-derived exosomes. J
Proteomics. 80:171–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ramakrishnaiah V, Thumann C, Fofana I,
Habersetzer F, Pan Q, de Ruiter PE, Willemsen R, Demmers JA, Stalin
Raj V, Jenster G, et al: Exosome-mediated transmission of hepatitis
C virus between human hepatoma Huh7.5 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:pp. 13109–13113. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Setti M, Osti D, Richichi C, Ortensi B,
Del Bene M, Fornasari L, Beznoussenko G, Mironov A, Rappa G, Cuomo
A, et al: Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of CLIC1 protein
is a novel mechanism for the regulation of glioblastoma growth.
Oncotarget. 6:31413–31427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P,
Thuwajit C and Hermoso M: Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the
tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res. 2014:1491852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Park JE, Tan HS, Datta A, Lai RC, Zhang H,
Meng W, Lim SK and Sze SK: Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its
microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by
secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics.
9:1085–1099. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ahles T, Li Y, McDonald BC, Schwartz GN,
Kaufman PA, Tsongalis GJ, Moore JH and Saykin AJ: Longitudinal
assessment of cognitive changes associated with adjuvant treatment
for breast cancer: The impact of APOE and smoking. Psychooncology.
23:1382–1390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chandler P, Song Y, Lin J, Zhang S, Sesso
HD, Mora S, Giovannucci EL, Rexrode KE, Moorthy MV, Li C, et al:
Lipid biomarkers and long-term risk of cancer in the Women's Health
Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 103:1397–1407. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang K, Zhu T, Gao D, Zhang Y, Zhao Q,
Liu S, Su T, Bernier M and Zhao R: Filamin A expression correlates
with proliferation and invasive properties of human metastatic
melanoma tumors: Implications for survival in patients. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 140:1913–1926. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tian ZQ, Shi JW, Wang XR, Li Z and Wang
GY: New cancer suppressor gene for colorectal adenocarcinoma:
Filamin A. World J Gastroenterol. 21:2199–2205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wieczorek K and Niewiarowska J: Filamin A
as a mediator of alterations in cancer cells. Postepy Biochem.
60:77–83. 2014.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang JL, Qian YB, Zhu LX and Xiong QR:
Talin1, a valuable marker for diagnosis and prognostic assessment
of human hepatocelluar carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
12:3265–3269. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Youns MM, Abdel Wahab AH, Hassan ZA and
Attia MS: Serum talin-1 is a potential novel biomarker for
diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3819–3823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiao W, Wang J, Li H, Xia D, Yu G, Yao W,
Yang Y, Xiao H, Lang B, Ma X, et al: Fibulin-1 is epigenetically
down-regulated and related with bladder cancer recurrence. BMC
Cancer. 14:6772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hosseini-Beheshti E, Choi W, Weiswald LB,
Kharmate G, Ghaffari M, Roshan-Moniri M, Hassona MD, Chan L, Chin
MY, Tai IT, et al: Exosomes confer pro-survival signals to alter
the phenotype of prostate cells in their surrounding environment.
Oncotarget. 7:14639–14658. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yuen H, Chan K, Grills C, Murray JT,
Platt-Higgins A, Eldin OS, O'Byrne K, Janne P, Fennell DA, Johnston
PG, et al: Ran is a potential therapeutic target for cancer cells
with molecular changes associated with activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 and Ras/MEK/ERK pathways. Clin Cancer Res.
18:380–391. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Banyard J and Bielenberg D: The role of
EMT and MET in cancer dissemination. Connect Tissue Res.
56:403–413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Berbari NF, Sharma N, Malarkey EB,
Pieczynski JN, Boddu R, Gaertig J, Guay-Woodford L and Yoder BK:
Microtubule modifications and stability are altered by cilia
perturbation and in cystic kidney disease. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken).
70:24–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|