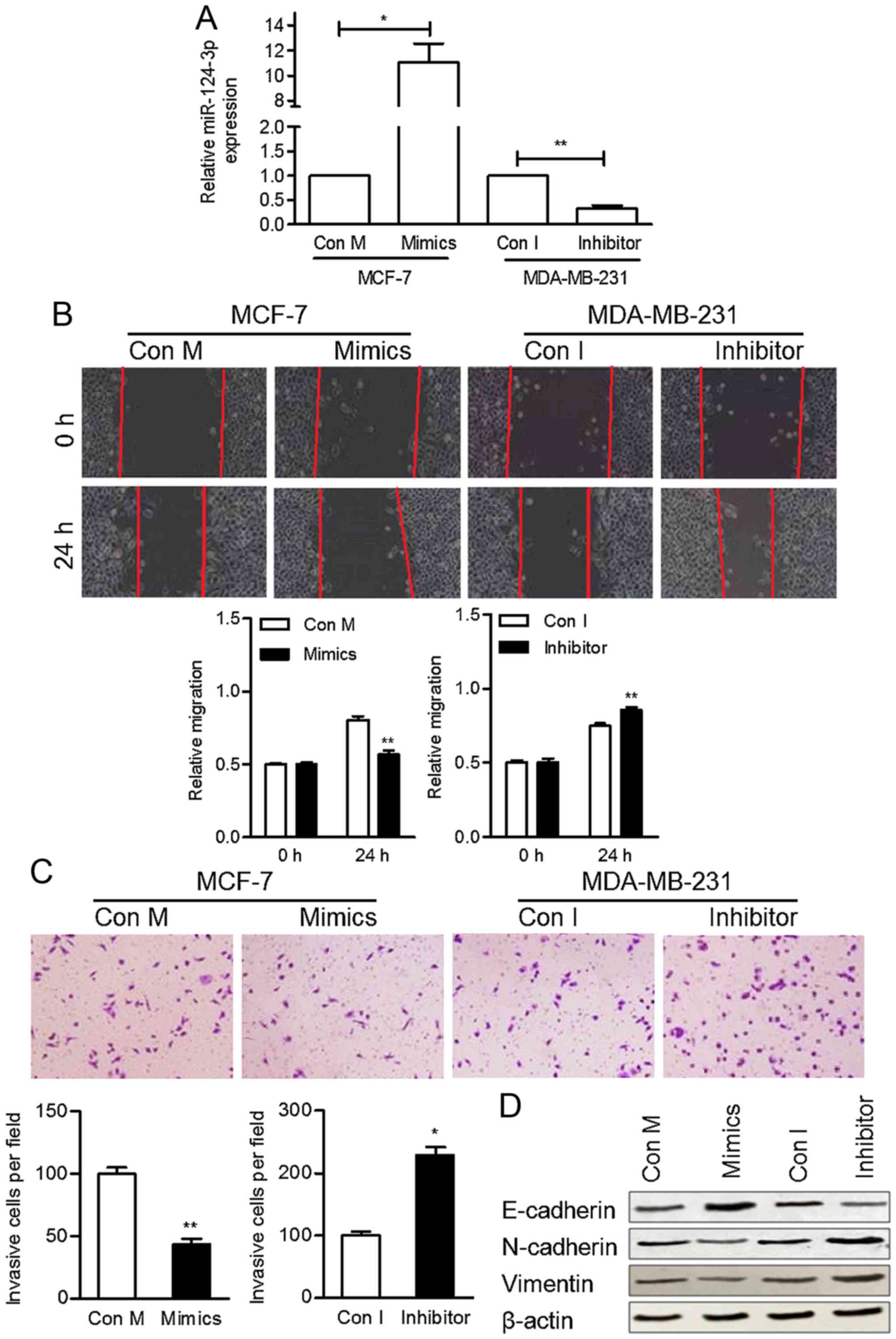
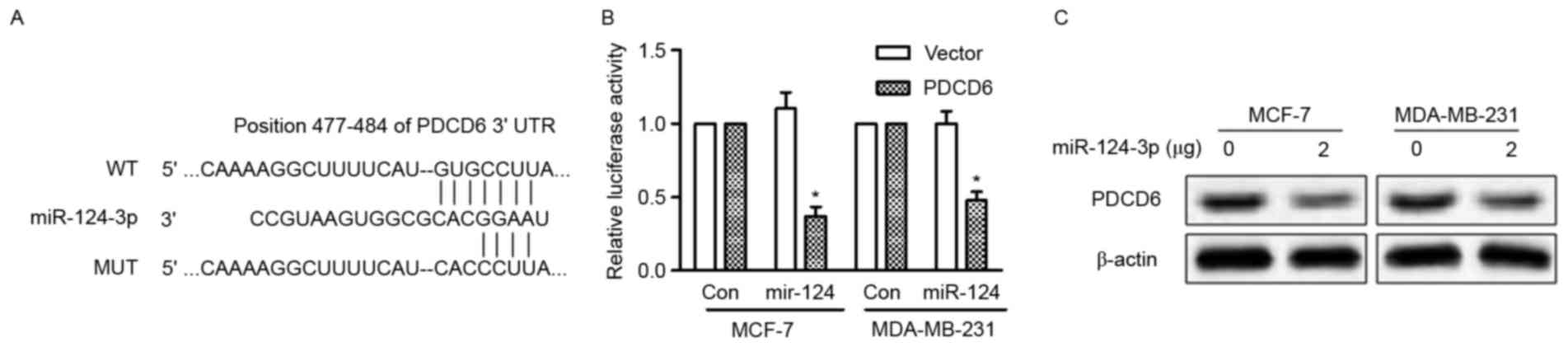
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ha R, Chow D and Wynn R: Global trend in
breast cancer imaging research 1992–2012: Bibliometric study. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 202:696–697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, Harewood
R, Spika D, Wang XS, Bannon F, Ahn JV, Johnson CJ, Bonaventure A,
et al: Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis
of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279
population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet.
385:977–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ge L, Zheng B, Li M, Niu L and Li Z:
MicroRNA-497 suppresses osteosarcoma tumor growth in vitro and in
vivo. Oncol Lett. 11:2207–2212. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Z, Gersbach E, Zhang X, Xu X, Dong R,
Lee P, Liu J, Kong B, Shao C and Wei JJ: miR-106a represses the Rb
tumor suppressor p130 to regulate cellular proliferation and
differentiation in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Mol Cancer
Res. 11:1314–1325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He J, Zhang W, Zhou Q, Zhao T, Song Y,
Chai L and Li Y: Low-expression of microRNA-107 inhibits cell
apoptosis in glioma by upregulation of SALL4. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 45:1962–1973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen B, Zhang Y, Yu S, Yuan Y, Zhong Y, Lu
J and Feng J: MicroRNA-339, an epigenetic modulating target is
involved in human gastric carcinogenesis through targeting NOVA1.
FEBS Lett. 589:3205–3211. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Xu D, Bao C, Zhang Y, Chen D, Zhao
F, Ding J, Liang L, Wang Q, Liu L, et al: MicroRNA-135b, a HSF1
target, promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating RECK
and EVI5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2421–2433.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kan H, Guo W, Huang Y and Liu D:
MicroRNA-520g induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SMAD7.
FEBS Lett. 589:102–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Simbrich A, Wellmann I, Heidrich J,
Heidinger O and Hense HW: Trends in advanced breast cancer
incidence rates after implementation of a mammography screening
program in a German population. Cancer Epidemiol. 44:44–51. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su D, Xu H, Feng J, Gao Y, Gu L, Ying L,
Katsaros D, Yu H, Xu S and Qi M: PDCD6 is an independent predictor
of progression free survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Transl
Med. 10:312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Q, Wang Y, Lu X, Zhao Z, Zhu L, Chen
S, Wu Q, Chen C and Wang Z: MiR-125b regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting Sema4C in
paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:3268–3279.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sahlberg K Kleivi, Bottai G, Naume B,
Burwinkel B, Calin GA, Børresen-Dale AL and Santarpia L: A serum
microRNA signature predicts tumor relapse and survival in
triple-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
21:1207–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M,
Yu XT, Cao DX, Chen GQ, He JR and Zhao Q: MiR-124 targets Slug to
regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:713–722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong LL, Chen LM, Wang WM and Zhang LM:
Decreased expression of microRNA-124 is an independent unfavorable
prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer. Diagn Pathol.
10:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li L, Luo J, Wang B, Wang D, Xie X, Yuan
L, Guo J, Xi S, Gao J, Lin X, et al: Microrna-124 targets
flotillin-1 to regulate proliferation and migration in breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:1632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arabkheradmand A, Safari A, Seifoleslami
M, Yahaghi E and Gity M: Down-regulated microRNA-124 expression as
predictive biomarker and its prognostic significance with
clinicopathological features in breast cancer patients. Diagn
Pathol. 10:1782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li H, Xie S, Liu M, Chen Z, Liu X, Wang L,
Li D and Zhou Y: The clinical significance of downregulation of
mir-124-3p, mir-146a-5p, mir-155-5p and mir-335-5p in gastric
cancer tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol. 45:197–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Yu Z, Li Y, Liu S, Gao C, Hou X, Yao
R and Cui L: The tumor suppressor miR-124 inhibits cell
proliferation by targeting STAT3 and functions as a prognostic
marker for postoperative NSCLC patients. Int J Oncol. 46:798–808.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
An L, Liu Y, Wu A and Guan Y: microRNA-124
inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulating ROCK1 in glioma.
PLoS One. 8:e694782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Wang Q, Zhao Q and Di W: MiR-124
inhibits the migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells by
targeting SphK1. J Ovarian Res. 6:842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Peng XH, Huang HR, Lu J, Liu X, Zhao FP,
Zhang B, Lin SX, Wang L, Chen HH, Xu X, et al: MiR-124 suppresses
tumor growth and metastasis by targeting Foxq1 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W, Mao YQ, Wang H, Yin WJ, Zhu SX
and Wang WC: MiR-124 suppresses cell motility and adhesion by
targeting talin 1 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int.
15:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
la Cour JM, Høj BR, Mollerup J, Simon R,
Sauter G and Berchtold MW: The apoptosis linked gene ALG-2 is
dysregulated in tumors of various origin and contributes to cancer
cell viability. Mol Oncol. 1:431–439. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|