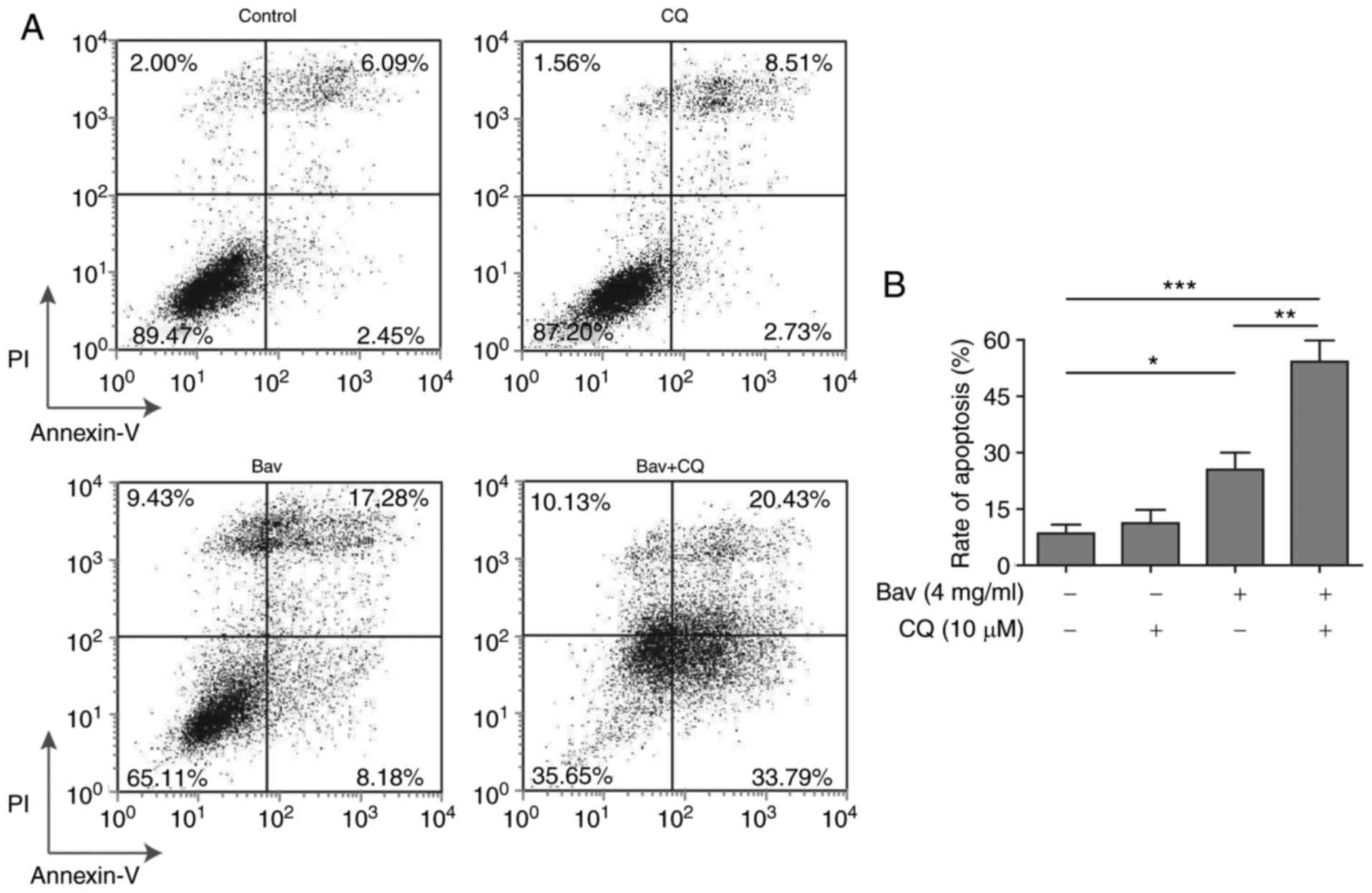
|
1
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Madany M, Thomas TM, Edwards L and Yu JS:
Immunobiology and immunotherapeutic targeting of glioma stem cells.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 853:139–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanu OO, Hughes B, Di C, Lin N, Fu J,
Bigner DD, Yan H and Adamson C: Glioblastoma multiforme
oncogenomics and signaling pathways. Clin Med Oncol. 3:39–52.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka S, Louis DN, Curry WT, Batchelor TT
and Dietrich J: Diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for
glioblastoma: No longer a dead end? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:14–26.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF, Laughton CA,
Madhusudan S and Bradshaw TD: Acquired resistance to temozolomide
in glioma cell lines: Molecular mechanisms and potential
translational applications. Oncology. 78:103–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cahill DP, Levine KK, Betensky RA, Codd
PJ, Romany CA, Reavie LB, Batchelor TT, Futreal PA, Stratton MR,
Curry WT, et al: Loss of the mismatch repair protein MSH6 in human
glioblastomas is associated with tumor progression during
temozolomide treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2038–2045. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramirez YP, Weatherbee JL, Wheelhouse RT
and Ross AH: Glioblastoma multiforme therapy and mechanisms of
resistance. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 6:1475–1506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chi AS, Sorensen AG, Jain RK and Batchelor
TT: Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in malignant gliomas.
Oncologist. 14:621–636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Das S and Marsden PA: Angiogenesis in
Glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 369:1561–1563. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wick W, Chinot OL, Bendszus M, Mason W,
Henriksson R, Saran F, Nishikawa R, Revil C, Kerloeguen Y and
Cloughesy T: Evaluation of pseudoprogression rates and tumor
progression patterns in a phase III trial of bevacizumab plus
radiotherapy/temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro
Oncol. 18:1434–1441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R,
Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea
D, et al: Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly
diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:709–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jahangiri A, De Lay M, Miller LM,
Carbonell WS, Hu YL, Lu K, Tom MW, Paquette J, Tokuyasu TA, Tsao S,
et al: Gene expression profile identifies tyrosine kinase c-Met as
a targetable mediator of antiangiogenic therapy resistance. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1773–1783. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piao Y, Liang J, Holmes L, Zurita AJ,
Henry V, Heymach JV and de Groot JF: Glioblastoma resistance to
anti-VEGF therapy is associated with myeloid cell infiltration,
stem cell accumulation, and a mesenchymal phenotype. Neuro Oncol.
14:1379–1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mesange P, Poindessous V, Sabbah M,
Escargueil AE, de Gramont A and Larsen AK: Intrinsic bevacizumab
resistance is associated with prolonged activation of autocrine
VEGF signaling and hypoxia tolerance in colorectal cancer cells and
can be overcome by nintedanib, a small molecule angiokinase
inhibitor. Oncotarget. 5:4709–4721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wileman T: Aggresomes and autophagy
generate sites for virus replication. Science. 312:875–878. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Münz C: Autophagy and antigen
presentation. Cell Microbiol. 8:891–898. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:651–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murrow L and Debnath J: Autophagy as a
stress-response and quality-control mechanism: Implications for
cell injury and human disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 8:105–137. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: p62 at the
crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell.
137:1001–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gugnoni M, Sancisi V, Manzotti G, Gandolfi
G and Ciarrocchi A: Autophagy and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition: An intricate interplay in cancer. Cell Death Dis.
7:e25202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E and Karin M:
Autophagy, inflammation and immunity: A troika governing cancer and
its treatment. Cell. 166:288–298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dou Z, Xu C, Donahue G, Shimi T, Pan JA,
Zhu J, Ivanov A, Capell BC, Drake AM, Shah PP, et al: Autophagy
mediates degradation of nuclear lamina. Nature. 527:105–109. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perera RM, Stoykova S, Nicolay BN, Ross
KN, Fitamant J, Boukhali M, Lengrand J, Deshpande V, Selig MK,
Ferrone CR, et al: Transcriptional control of autophagy-lysosome
function drives pancreatic cancer metabolism. Nature. 524:361–365.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N,
Zhang M, Han W, Lou F, Yang J, Zhang Q, et al: Autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer
treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cufi S, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyàs E, López-Bonet E,
Martin-Castillo B, Joven J and Menendez JA: The anti-malarial
chloroquine overcomes primary resistance and restores sensitivity
to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Sci Rep. 3:24692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang MC, Wu MY, Hwang MH, Chang YT, Huang
HJ, Lin AM and Yang JC: Chloroquine enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity
in gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
10:e01191352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aveic S and Tonini GP: Resistance to
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in solid tumors: Can we improve
the cancer fighting strategy by blocking autophagy? Cancer Cell
Int. 16:622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Allen M, Bjerke M, Edlund H, Nelander S
and Westermark B: Origin of the U87MG glioma cell line: Good news
and bad news. Sci Transl Med. 8:354re32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dolgin E: Venerable brain-cancer cell line
faces identity crisis. Nature. 537:149–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han J, Jun Y, Kim SH, Hoang HH, Jung Y,
Kim S, Kim J, Austin RH, Lee S and Park S: Rapid emergence and
mechanisms of resistance by U87 glioblastoma cells to doxorubicin
in an in vitro tumor microfluidic ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:pp. 14283–14288. 2016; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ichimura Y, Kirisako T, Takao T, Satomi Y,
Shimonishi Y, Ishihara N, Mizushima N, Tanida I, Kominami E, Ohsumi
M, et al: A ubiquitin-like system mediates protein lipidation.
Nature. 408:488–492. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Larsen KB, Lamark T, Øvervatn A,
Harneshaug I, Johansen T and Bjørkøy G: A reporter cell system to
monitor autophagy based on p62/SQSTM1. Autophagy. 6:784–793. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Johansen T and Lamark T: Selective
autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy.
7:279–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter
M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M,
Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S, et al: Regulation of mammalian
autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
90:1383–1435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmelzle T and Hall MN: TOR, a central
controller of cell growth. Cell. 103:253–262. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao X, Lai D, Zhang L and Xu H: Induction
of autophagy and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/TOR pathways by
azadirachtin a in Spodoptera litura cells. Sci Rep. 6:354822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zha QB, Zhang XY, Lin QR, Xu LH, Zhao GX,
Pan H, Zhou D, Ouyang DY, Liu ZH and He XH: Cucurbitacin E induces
autophagy via downregulating mTORC1 signaling and upregulating AMPK
activity. PLoS One. 10:e01243552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guo XL, Li D, Sun K, Wang J, Liu Y, Song
JR, Zhao QD, Zhang SS, Deng WJ, Zhao X, et al: Inhibition of
autophagy enhances anticancer effects of bevacizumab in
hepatocarcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:473–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JG, Shin JH, Shim HS, Lee CY, Kim DJ,
Kim YS and Chung KY: Autophagy contributes to the chemo-resistance
of non-small cell lung cancer in hypoxic conditions. Respir Res.
16:1382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dragowska WH, Weppler SA, Wang JC, Wong
LY, Kapanen AI, Rawji JS, Warburton C, Qadir MA, Donohue E, Roberge
M, et al: Induction of autophagy is an early response to gefitinib
and a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. PLoS One.
8:e765032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang Z, Liu Y, Wei X, Zhou X, Gong C,
Zhang T, Jin P, Xu S, Ma D and Gao Q: Co-targeting EGFR and
autophagy impairs ovarian cancer cell survival during detachment
from the ECM. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 15:215–226. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nihira K, Miki Y, Iida S, Narumi S, Ono K,
Iwabuchi E, Ise K, Mori K, Saito M, Ebina M, et al: An activation
of LC3A-mediated autophagy contributes to de novo and acquired
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung
adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 234:277–288. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|