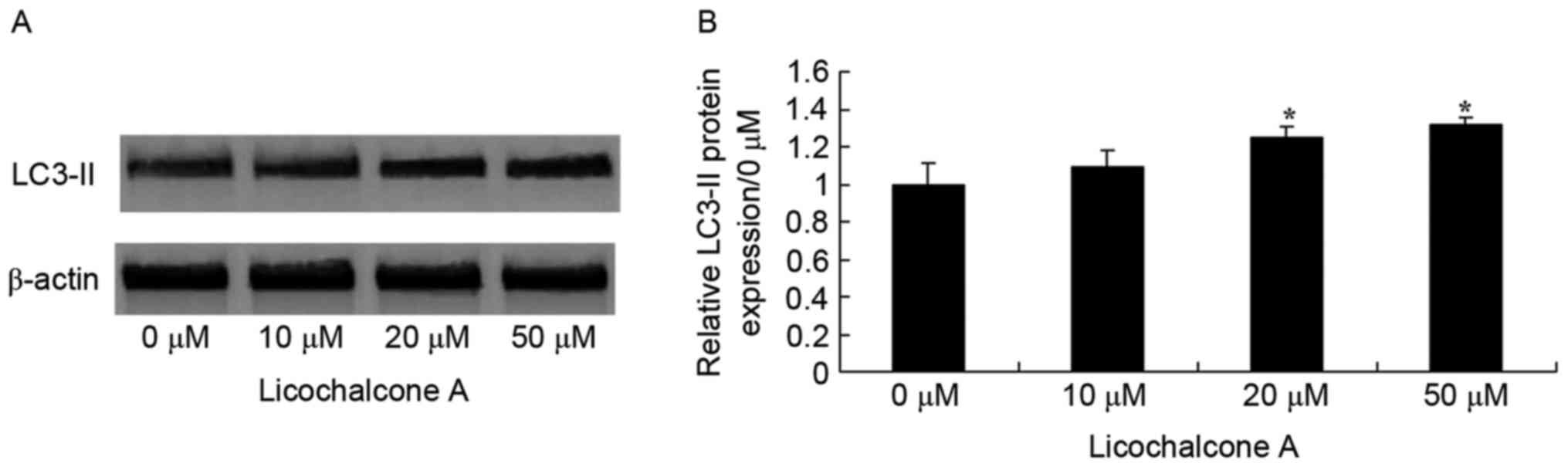
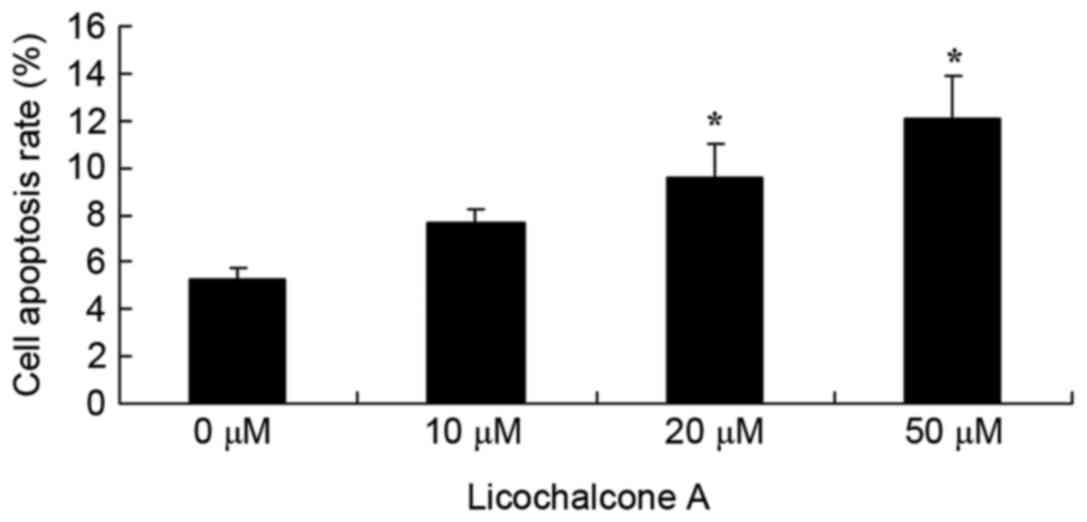
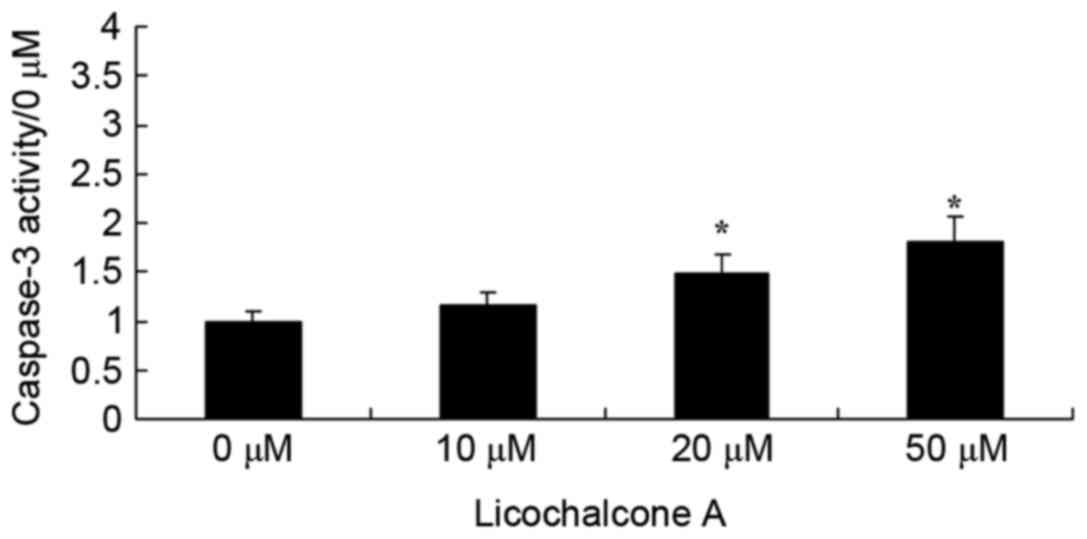
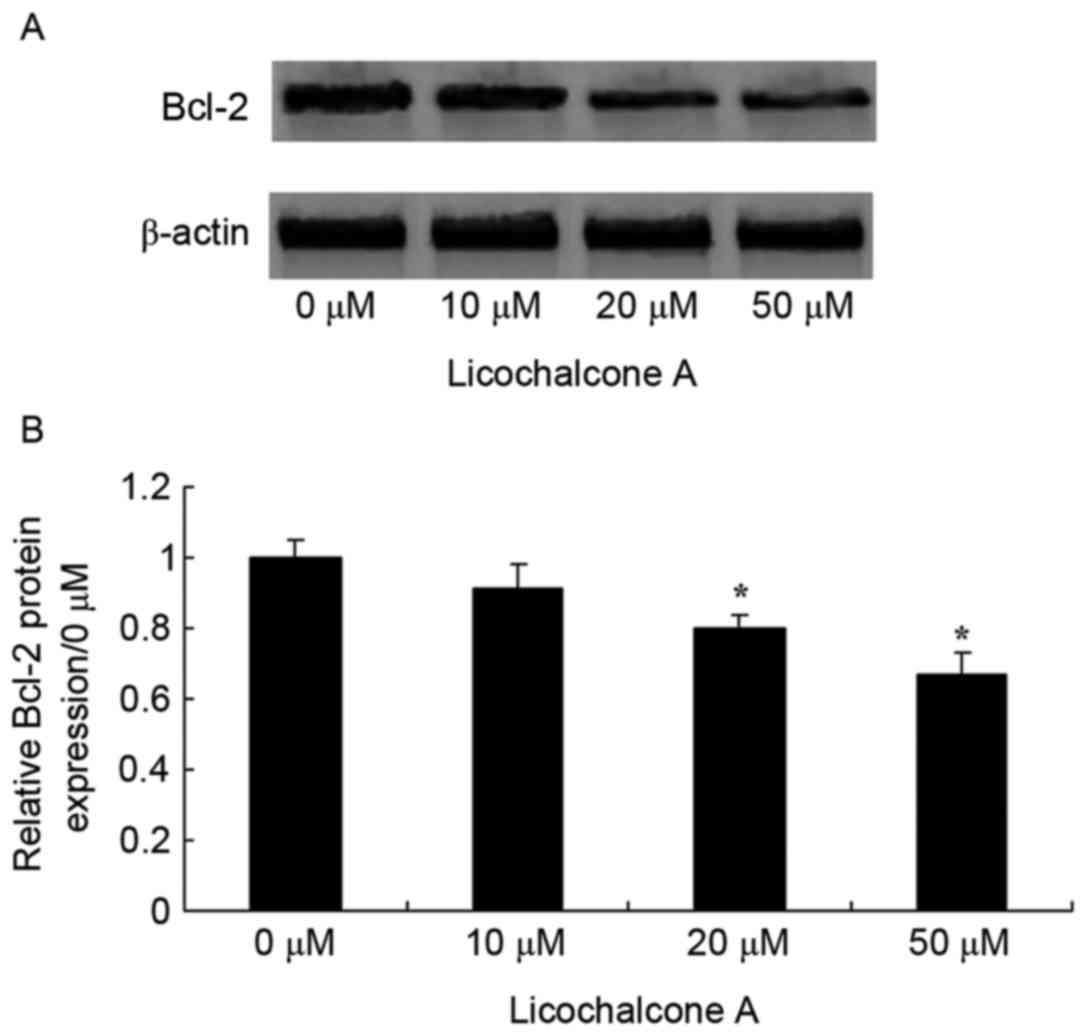
|
1
|
Bouvet V, Jans HS, Wuest M, Soueidan OM,
Grant T, Mercer J, McEwan AJ, West FG, Cheeseman CI and Wuest F:
Erratum: Automated synthesis and dosimetry of
6-deoxy-6-[F]fluoro-D-fructose (6-[F]FDF): A radiotracer for
imaging of GLUT5 in breast cancer. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
5:952014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zarzynska JM: The importance of autophagy
regulation in breast cancer development and treatment. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:7103452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pu Z, Zhang X, Chen Q, Yuan X and Xie H:
Establishment of an expression platform of OATP1B1 388GG and 521CC
genetic polymorphism and the therapeutic effect of tamoxifen in
MCF-7 cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2420–2428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang LW, Qu AP, Yuan JP, Chen C, Sun SR,
Hu MB, Liu J and Li Y: Computer-based image studies on tumor nests
mathematical features of breast cancer and their clinical
prognostic value. PLoS One. 8:e823142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chukkapalli S, Amessou M, Dilly AK, Dekhil
H, Zhao J, Liu Q, Bejna A, Thomas RD, Bandyopadhyay S, Bismar TA,
et al: Role of the EphB2 receptor in autophagy, apoptosis and
invasion in human breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 320:233–246.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang WB, Yao M, Jokar I, Alhakamy N,
Berkland C, Chen J, Brantley-Sieders D and Cheng N: The CCL2
chemokine is a negative regulator of autophagy and necrosis in
luminal B breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
150:309–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lamparska-Przybysz M, Gajkowska B and
Motyl T: BID-deficient breast cancer MCF-7 cells as a model for the
study of autophagy in cancer therapy. Autophagy. 2:47–48. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H, Guo M, Chen JH, Wang Z, Du XF,
Liu PX and Li WH: Osteopontin knockdown inhibits αv,β3
integrin-induced cell migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis
of breast cancer cells by inducing autophagy and inactivating the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:991–1002. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KH, Yoon G, Cho JJ, Cho JH, Cho YS,
Chae JI and Shim JH: Licochalcone A induces apoptosis in malignant
pleural mesothelioma through downregulation of Sp1 and subsequent
activation of mitochondria-related apoptotic pathway. Int J Oncol.
46:1385–1392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen M, Theander TG, Christensen SB, Hviid
L, Zhai L and Kharazmi A: Licochalcone A, a new antimalarial agent,
inhibits in vitro growth of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium
falciparum and protects mice from P. yoelii infection. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 38:1470–1475. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shibata S, Inoue H, Iwata S, Ma RD, Yu LJ,
Ueyama H, Takayasu J, Hasegawa T, Tokuda H, Nishino A, et al:
Inhibitory effects of licochalcone A isolated from Glycyrrhiza
inflata root on inflammatory ear edema and tumour promotion in
mice. Planta Med. 57:221–224. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rovito D, Giordano C, Plastina P, Barone
I, De Amicis F, Mauro L, Rizza P, Lanzino M, Catalano S, Bonofiglio
D and Andò S: Omega-3 DHA- and EPA-dopamine conjugates induce
PPARgamma-dependent breast cancer cell death through autophagy and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1850:2185–2195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jain K, Paranandi KS, Sridharan S and Basu
A: Autophagy in breast cancer and its implications for therapy. Am
J Cancer Res. 3:251–265. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang P, Tuo L, Wu Q and Cao X:
Licochalcone-A sensitizes human esophageal carcinoma cells to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by proteasomal degradation of XIAP.
Hepatogastroenterology. 61:1229–1234. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang HC, Tsai LL, Tsai JP, Hsieh SC, Yang
SF, Hsueh JT and Hsieh YH: Licochalcone A inhibits the migration
and invasion of human lung cancer cells via inactivation of the Akt
signaling pathway with downregulation of MMP-1/−3 expression.
Tumour Biol. 35:12139–12149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng G, Shen H, Yang Y, Cai X and Xun W:
Licochalcone A as a potent antitumor agent suppresses growth of
human oral cancer SCC-25 cells in vitro via caspase-3 dependent
pathways. Tumour Biol. 35:6549–6555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang L, Graham PH, Hao J, Ni J, Bucci J,
Cozzi PJ, Kearsley JH and Li Y: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors
enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells
through inducing apoptosis, reducing autophagy, suppressing NHEJ
and HR repair pathways. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsai JP, Lee CH, Ying TH, Lin CL, Lin CL,
Hsueh JT and Hsieh YH: Licochalcone A induces autophagy through
PI3K/Akt/mTOR inactivation and autophagy suppression enhances
Licochalcone A-induced apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 6:28851–28866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hao W, Yuan X, Yu L, Gao C, Sun X, Wang D
and Zheng Q: Licochalcone A-induced human gastric cancer BGC-823
cells apoptosis by regulating ROS-mediated MAPKs and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 5:103362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Xu P, Chen D, Fan X, Xu Y, Li M,
Yang X and Wang C: Roles of autophagy-related genes Beclin-1 and
LC3 in the development and progression of prostate cancer and
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Biomed Rep. 1:855–860.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan ST, Qin Y, Zhou ZW, He ZX, Zhang X,
Yang T, Yang YX, Wang D, Qiu JX and Zhou SF: Plumbagin induces G2/M
arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:1601–1626. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou M, Lu N, Hu C, Liu W, Sun Y, Wang X,
You Q, Gu C, Xi T and Guo Q: Beclin 1-mediated autophagy in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: implication in anticancer
efficiency of oroxylin A via inhibition of mTOR signaling. Cell
Signal. 24:1722–1732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li JP, Yang YX, Liu QL, Zhou ZW, Pan ST,
He ZX, Zhang X, Yang T, Pan SY, Duan W, et al: The pan-inhibitor of
Aurora kinases danusertib induces apoptosis and autophagy and
suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human breast
cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:1027–1062. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|