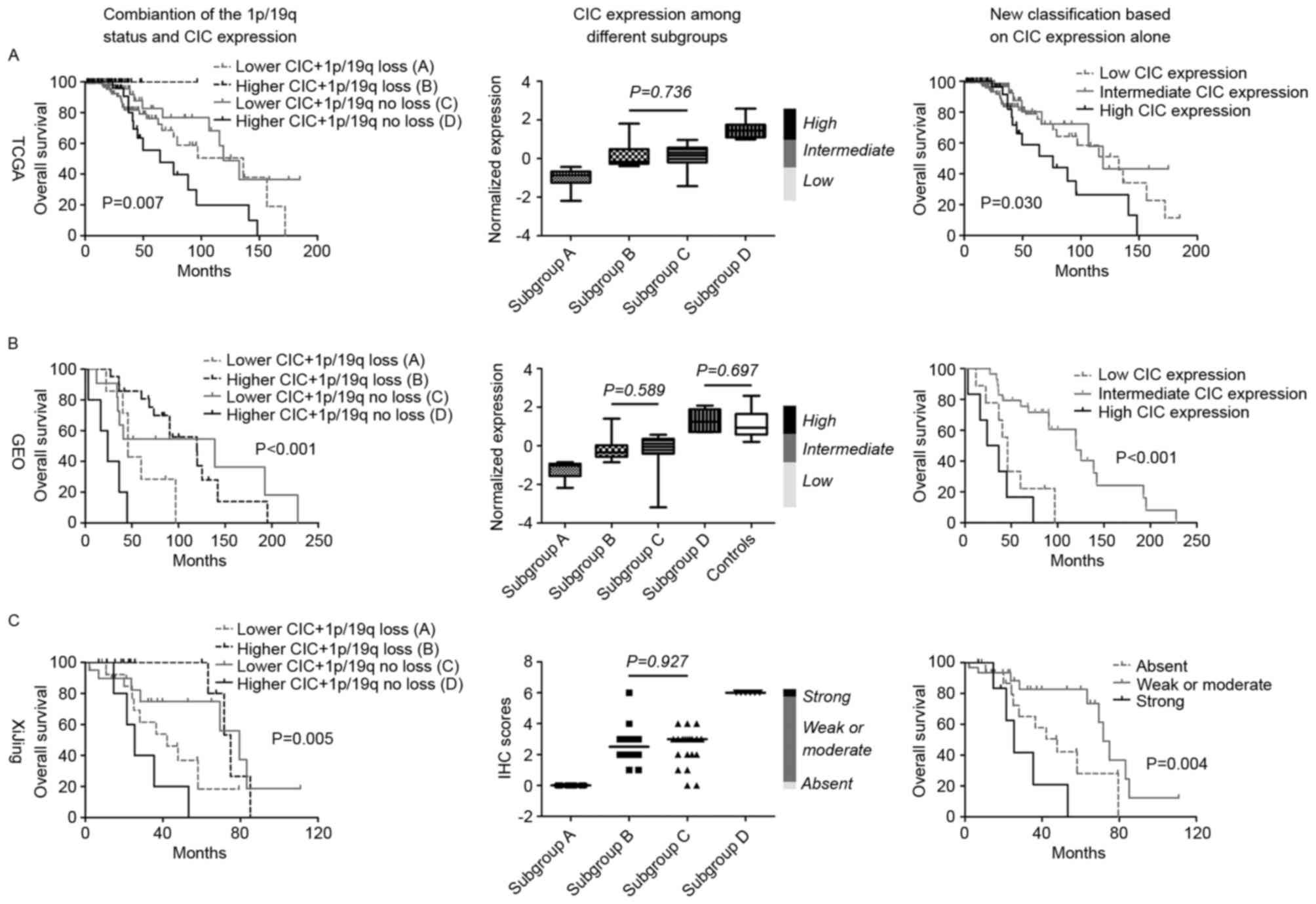
|
1
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, ;
Brat DJ, Verhaak RG, Aldape KD, Yung WK, Salama SR, Cooper LA,
Rheinbay E, Miller CR, Vitucci M, et al: Comprehensive, integrative
genomic analysis of diffuse lower-grade gliomas. N Engl J Med.
372:2481–2498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wesseling P, van den Bent M and Perry A:
Oligodendroglioma: Pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers.
Acta Neuropathol. 129:809–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sahm F, Koelsche C, Meyer J, Pusch S,
Lindenberg K, Mueller W, Herold-Mende C, von Deimling A and
Hartmann C: CIC and FUBP1 mutations in oligodendrogliomas,
oligoastrocytomas and astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 123:853–860.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gleize V, Alentorn A, Connen de Kérillis
L, Labussière M, Nadaradjane AA, Mundwiller E, Ottolenghi C,
Mangesius S, Rahimian A, Ducray F, et al: CIC inactivating
mutations identify aggressive subset of 1p19q codeleted gliomas.
Ann Neurol. 78:355–374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van Den Bent MJ, Brandes AA, Taphoorn MJ,
Kros JM, Kouwenhoven MC, Delattre JY, Bernsen HJ, Frenay M, Tijssen
CC, Grisold W, et al: Adjuvant procarbazine, lomustine and
vincristine chemotherapy in newly diagnosed anaplastic
oligodendroglioma: Long-term follow-up of EORTC brain tumor group
study 26951. J Clin Oncol. 31:344–350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reuss DE, Sahm F, Schrimpf D, Wiestler B,
Capper D, Koelsche C, Schweizer L, Korshunov A, Jones DT, Hovestadt
V, et al: ATRX and IDH1-R132H immunohistochemistry with subsequent
copy number analysis and IDH sequencing as a basis for an
‘integrated’ diagnostic approach for adult astrocytoma,
oligodendroglioma and glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 129:133–146.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiao Y, Killela PJ, Reitman ZJ, Rasheed
AB, Heaphy CM, de Wilde RF, Rodriguez FJ, Rosemberg S, Oba-Shinjo
SM, Nagahashi Marie SK, et al: Frequent ATRX, CIC, FUBP1 and IDH1
mutations refine the classification of malignant gliomas.
Oncotarget. 3:709–722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yip S, Butterfield YS, Morozova O,
Chittaranjan S, Blough MD, An J, Birol I, Chesnelong C, Chiu R,
Chuah E, et al: Concurrent CIC mutations, IDH mutations and 1p/19q
loss distinguish oligodendrogliomas from other cancers. J Pathol.
226:7–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan AK, Pang JC, Chung NY, Li KK, Poon
WS, Chan DT, Shi Z, Chen L, Zhou L and Ng HK: Loss of CIC and FUBP1
expressions are potential markers of shorter time to recurrence in
oligodendroglial tumors. Mod Pathol. 27:332–342. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bettegowda C, Agrawal N, Jiao Y, Sausen M,
Wood LD, Hruban RH, Rodriguez FJ, Cahill DP, McLendon R, Riggins G,
et al: Mutations in CIC and FUBP1 contribute to human
oligodendroglioma. Science. 333:1453–1455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jimenez G, Shvartsman SY and Paroush Z:
The Capicua repressor-a general sensor of RTK signaling in
development and disease. J Cell Sci. 125:1383–1391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fuller GN and Scheithauer BW: The 2007
revised World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumours
of the central nervous system: Newly codified entities. Brain
Pathol. 17:304–307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen X, Yun J, Fei F, Yi J, Tian R, Li S
and Gan X: Prognostic value of nuclear hepatoma-derived growth
factor (HDGF) localization in patients with breast cancer. Pathol
Res Pract. 208:437–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gravendeel LA, Kouwenhoven MC, Gevaert O,
de Rooi JJ, Stubbs AP, Duijm JE, Daemen A, Bleeker FE, Bralten LB,
Kloosterhof NK, et al: Intrinsic gene expression profiles of
gliomas are a better predictor of survival than histology. Cancer
Res. 69:9065–9072. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erdem-Eraslan L, Gravendeel LA, de Rooi J,
Eilers PH, Idbaih A, Spliet WG, den Dunnen WF, Teepen JL, Wesseling
P, Sillevis Smitt PA, et al: Intrinsic molecular subtypes of glioma
are prognostic and predict benefit from adjuvant procarbazine,
lomustine and vincristine chemotherapy in combination with other
prognostic factors in anaplastic oligodendroglial brain tumors: A
report from EORTC study 26951. J Clin Oncol. 31:328–336. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Woo HG, Park ES, Cheon JH, Kim JH, Lee JS,
Park BJ, Kim W, Park SC, Chung YJ, Kim BG, et al: Gene
expression-based recurrence prediction of hepatitis B virus-related
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2056–2064.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 15545–15550. 2005;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hothorn T and Zeileis A: Generalized
maximally selected statistics. Biometrics. 64:1263–1269. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chittaranjan S, Chan S, Yang C, Yang KC,
Chen V, Moradian A, Firme M, Song J, Go NE, Blough MD, et al:
Mutations in CIC and IDH1 cooperatively regulate 2-hydroxyglutarate
levels and cell clonogenicity. Oncotarget. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee CJ, Chan WI and Scotting PJ: CIC, a
gene involved in cerebellar development and ErbB signaling, is
significantly expressed in medulloblastomas. J Neurooncol.
73:101–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|