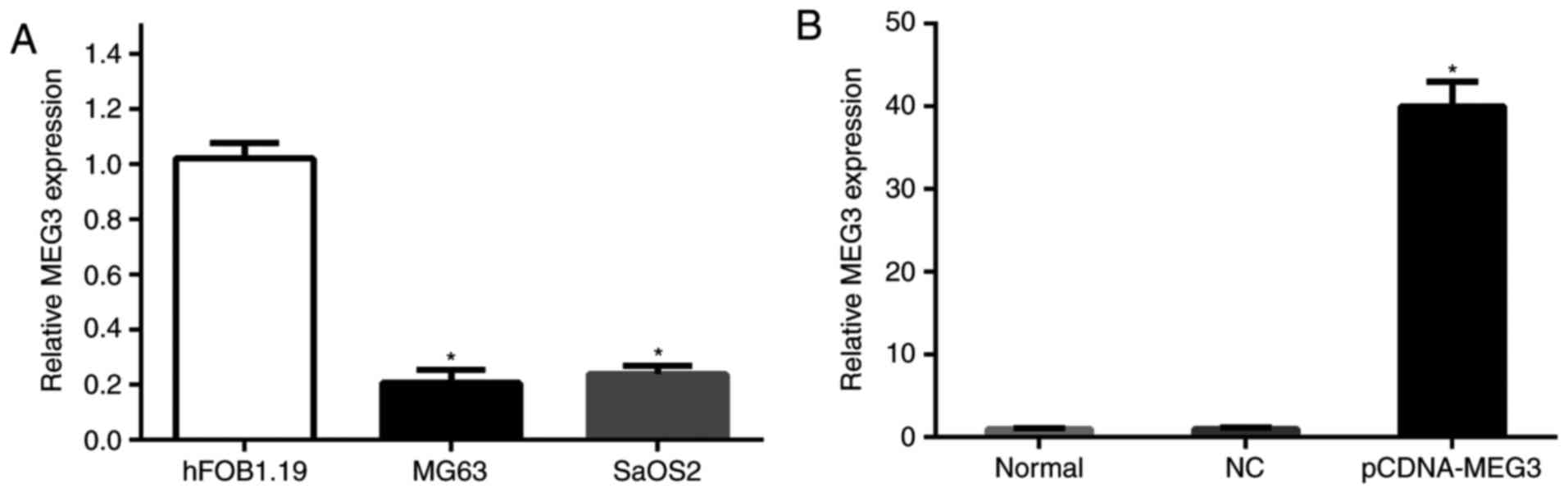
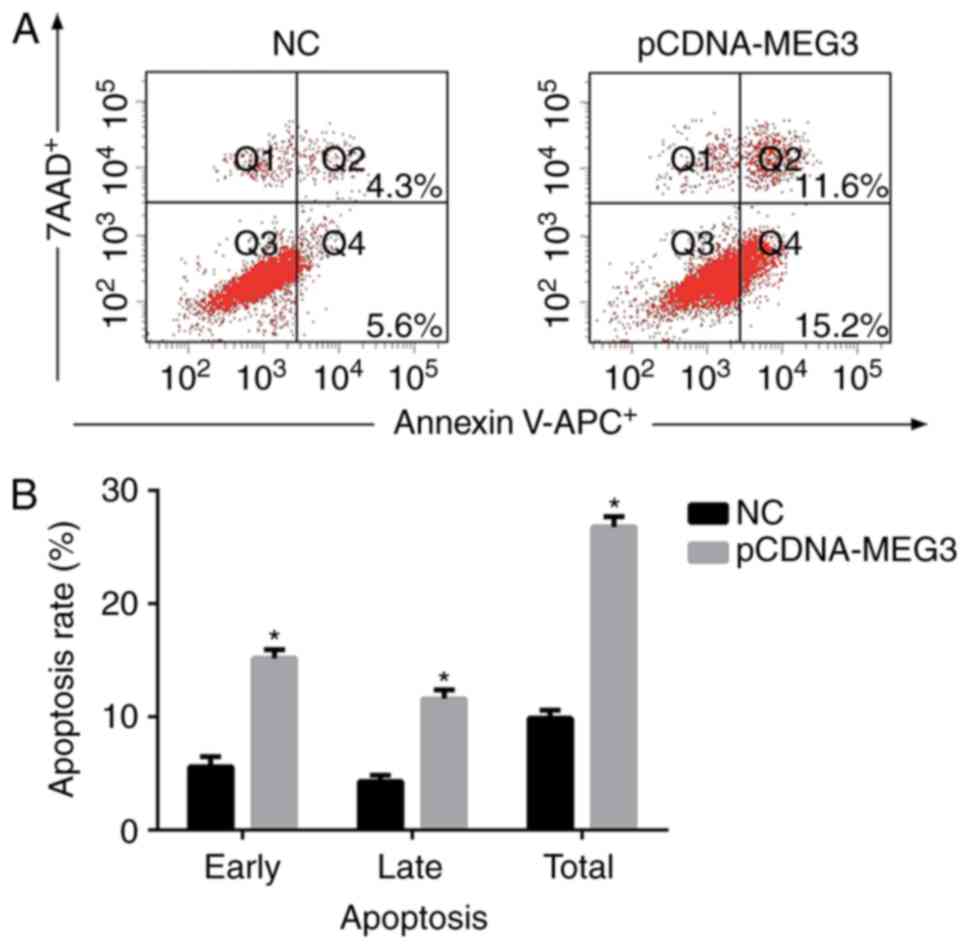
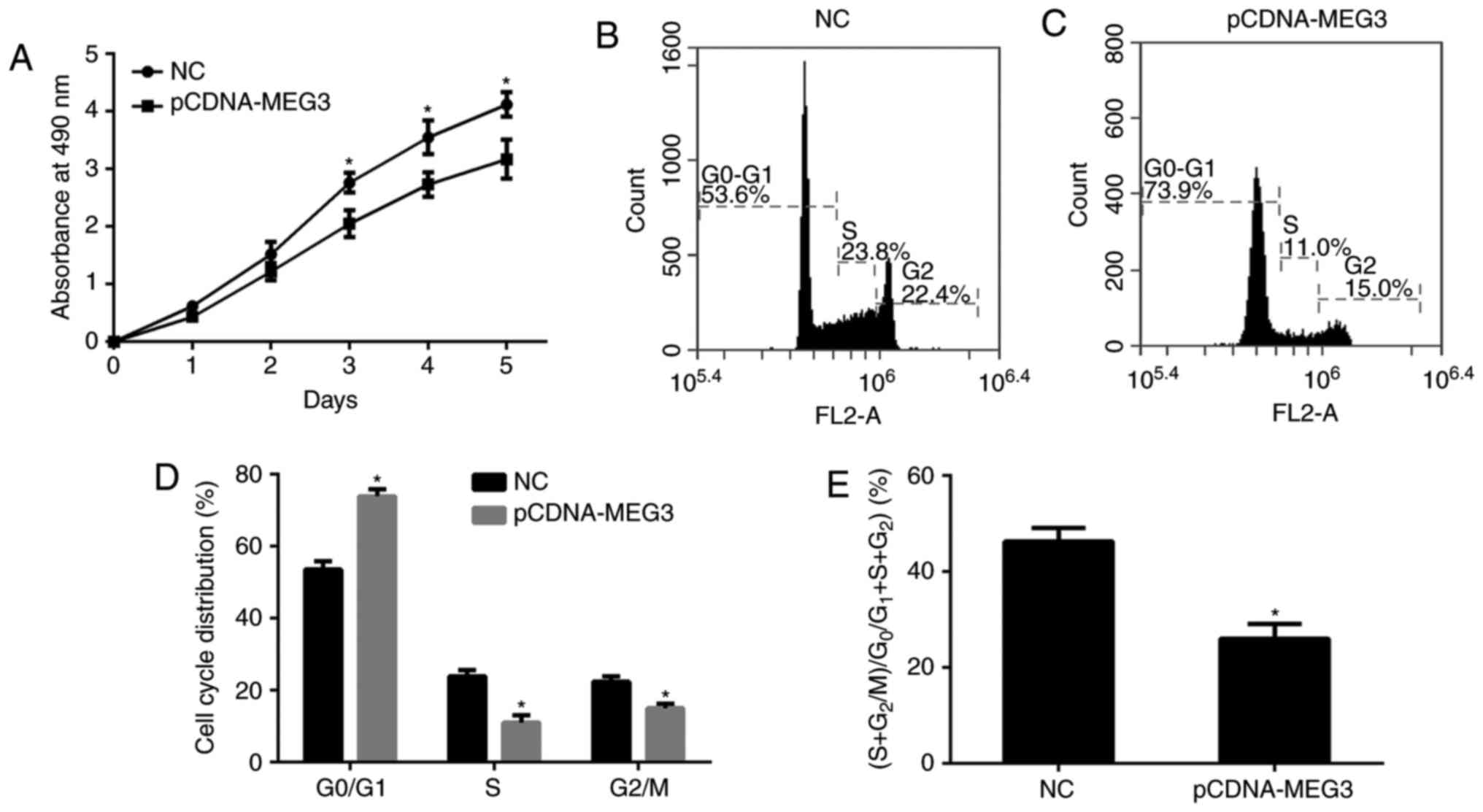
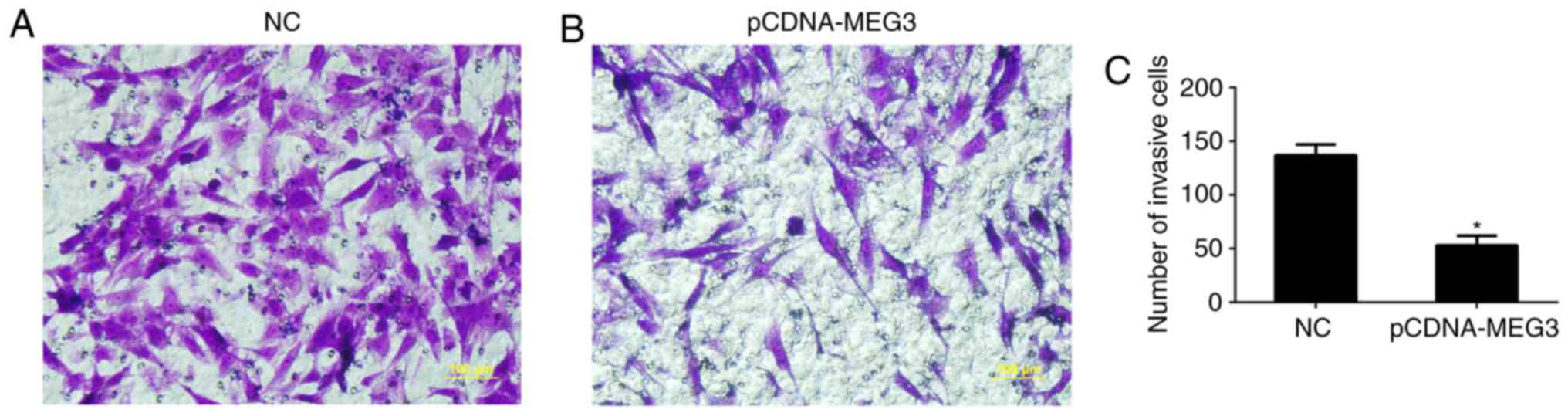
|
1
|
Endo-Munoz L, Cumming A, Sommerville S,
Dickinson I and Saunders NA: Osteosarcoma is characterised by
reduced expression of markers of osteoclastogenesis and antigen
presentation compared with normal bone. Br J Cancer. 103:73–81.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bielack SS, Marina N, Ferrari S, Helman
LJ, Smeland S, Whelan JS and Reaman GH: Osteosarcoma: The same old
drugs or more? J Clin Oncol. 26:3102–3103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gill J, Ahluwalia MK, Geller D and Gorlick
R: New targets and approaches in osteosarcoma. Pharmacol Ther.
137:89–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Allison DC, Carney SC, Ahlmann ER,
Hendifar A, Chawla S, Fedenko A, Angeles C and Menendez LR: A
meta-analysis of osteosarcoma outcomes in the modern medical era.
Sarcoma. 2012:7048722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perkel JM: Visiting ‘noncodarnia’.
Biotechniques. 54:303–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gibb EA, Brown CJ and Lam WL: The
functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol
Cancer. 10:382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ying L, Huang Y, Chen H, Wang Y, Xia L,
Chen Y, Liu Y and Qiu F: Downregulated MEG3 activates autophagy and
increases cell proliferation in bladder cancer. Mol Biosyst.
9:407–411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun M, Xia R, Jin F, Xu T, Liu Z, De W and
Liu X: Downregulated long noncoding RNA MEG3 is associated with
poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:1065–1073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu KH, Li W, Liu XH, Sun M, Zhang ML, Wu
WQ, Xie WP and Hou YY: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC
cells proliferation and induces apoptosis by affecting p53
expression. BMC Cancer. 13:4612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anwar SL, Krech T, Hasemeier B, Schipper
E, Schweitzer N, Vogel A, Kreipe H and Lehmann U: Loss of
imprinting and allelic switching at the DLK1-MEG3 locus in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e494622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ribarska T, Goering W, Droop J, Bastian
KM, Ingenwerth M and Schulz WA: Deregulation of an imprinted gene
network in prostate cancer. Epigenetics. 9:704–717. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Greife A, Knievel J, Ribarska T, Niegisch
G and Schulz WA: Concomitant downregulation of the imprinted genes
DLK1 and MEG3 at 14q32.2 by epigenetic mechanisms in urothelial
carcinoma. Clin Epigenetics. 6:292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo G, Wang M, Wu X, Tao D, Xiao X, Wang
L, Min F, Zeng F and Jiang G: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits
cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:2209–2220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng W, Si S, Zhang Q, Li C, Zhao F, Wang
F, Yu J and Ma R: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing
endogenous RNA to regulate gastric cancer progression. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 34:792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Mehta KR, Danila DC,
Scolavino S, Johnson SR and Klibanski A: A pituitary-derived MEG3
isoform functions as a growth suppressor in tumor cells. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:5119–5126. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Zhong Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Batista
DL, Gejman R, Ansell PJ, Zhao J, Weng C and Klibanski A: Activation
of p53 by MEG3 non-coding RNA. J Biol Chem. 282:24731–24742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu KH, Li W, Liu XH, Sun M, Zhang ML, Wu
WQ, Xie WP and Hou YY: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC
cells proliferation and induces apoptosis by affecting p53
expression. BMC Cancer. 13:4612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu J, Liu S, Ye F, Shen Y, Tie Y, Zhu J,
Wei L, Jin Y, Fu H, Wu Y and Zheng X: Long noncoding RNA MEG3
interacts with p53 protein and regulates partial p53 target genes
in hepatoma cells. PloS One. 10:e01397902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sherr CJ and Weber JD: The ARF/p53
pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 10:94–99. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ouchi T, Monteiro AN, August A, Aaronson
SA and Hanafusa H: BRCA1 regulates p53-dependent gene expression.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:2302–2306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu LX, Deng W, Zhou XT, Chen RP, Xiang
MQ, Guo YT, Pu ZJ, Li R, Wang GF and Wu LF: The mechanism of
adenosine-mediated activation of lncRNA MEG3 and its antitumor
effects in human hepatoma cells. Int J Oncol. 48:421–429. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lv D, Sun R, Yu Q and Zhang X: The long
non-coding RNA maternally expressed gene 3 activates p53 and is
downregulated in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Tumour Biol.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Wan L, Lu K, Sun M, Pan X, Zhang P,
Lu B, Liu G and Wang Z: The long noncoding RNA MEG3 contributes to
cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma. PloS One.
10:e01145862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ernst C and Morton CC: Identification and
function of long non-coding RNA. Front Cell Neurosci. 7:1682013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Honda R and Yasuda H: Activity of MDM2, a
ubiquitin ligase, toward p53 or itself is dependent on the RING
finger domain of the ligase. Oncogene. 19:1473–1476. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH:
Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature. 387:299–303. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marchetti P, Castedo M, Susin SA, Zamzami
N, Hirsch T, Macho A, Haeffner A, Hirsch F, Geuskens M and Kroemer
G: Mitochondrial permeability transition is a central coordinating
event of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 184:1155–1160. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee HJ, Lee EK, Seo YE, Shin YH, Kim HS,
Chun YH, Yoon JS, Kim HH, Han MY, Kim CK, et al: Roles of Bcl-2 and
caspase-9 and −3 in CD30-induced human eosinophil apoptosis. J
Microbiol Immunol Infect. 50:145–152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Swarnakar S, Paul S, Singh LP and Reiter
RJ: Matrix metalloproteinases in health and disease: Regulation by
melatonin. J Pineal Res. 50:8–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen X, Qiu J, Yang D, Lu J, Yan C, Zha X
and Yin Y: MDM2 promotes invasion and metastasis in invasive ductal
breast carcinoma by inducing matrix metalloproteinase-9. PloS One.
8:e787942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|