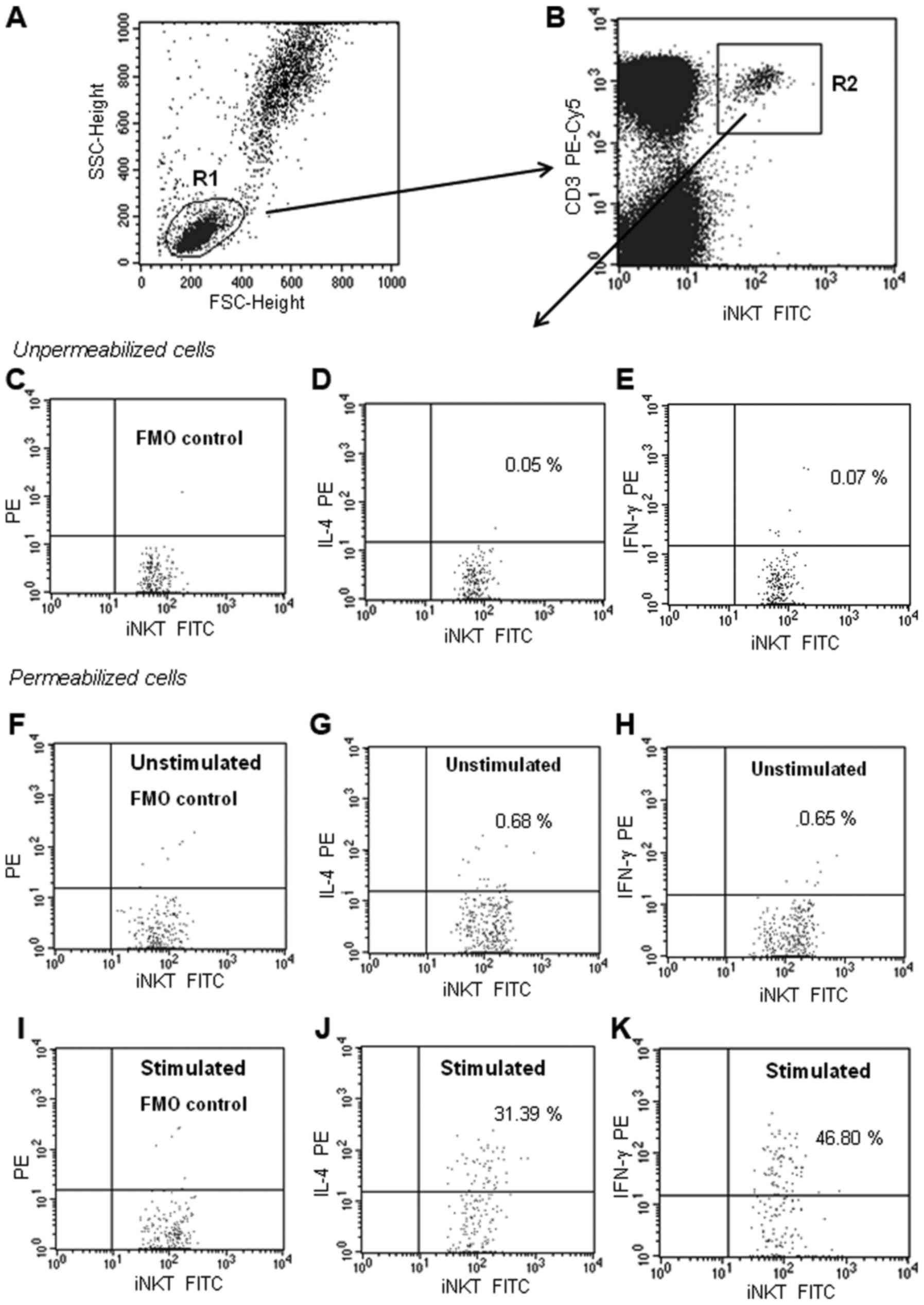
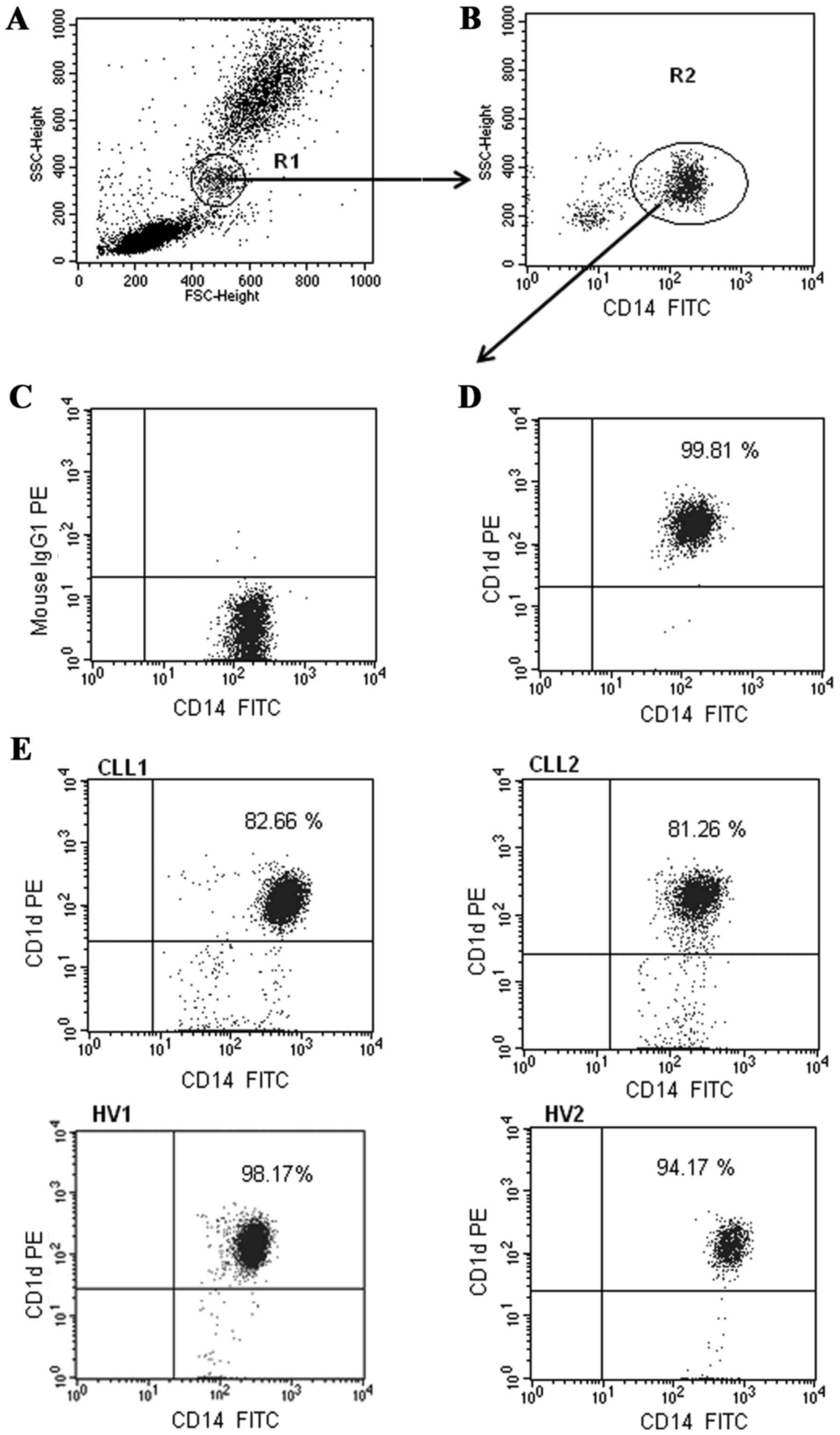
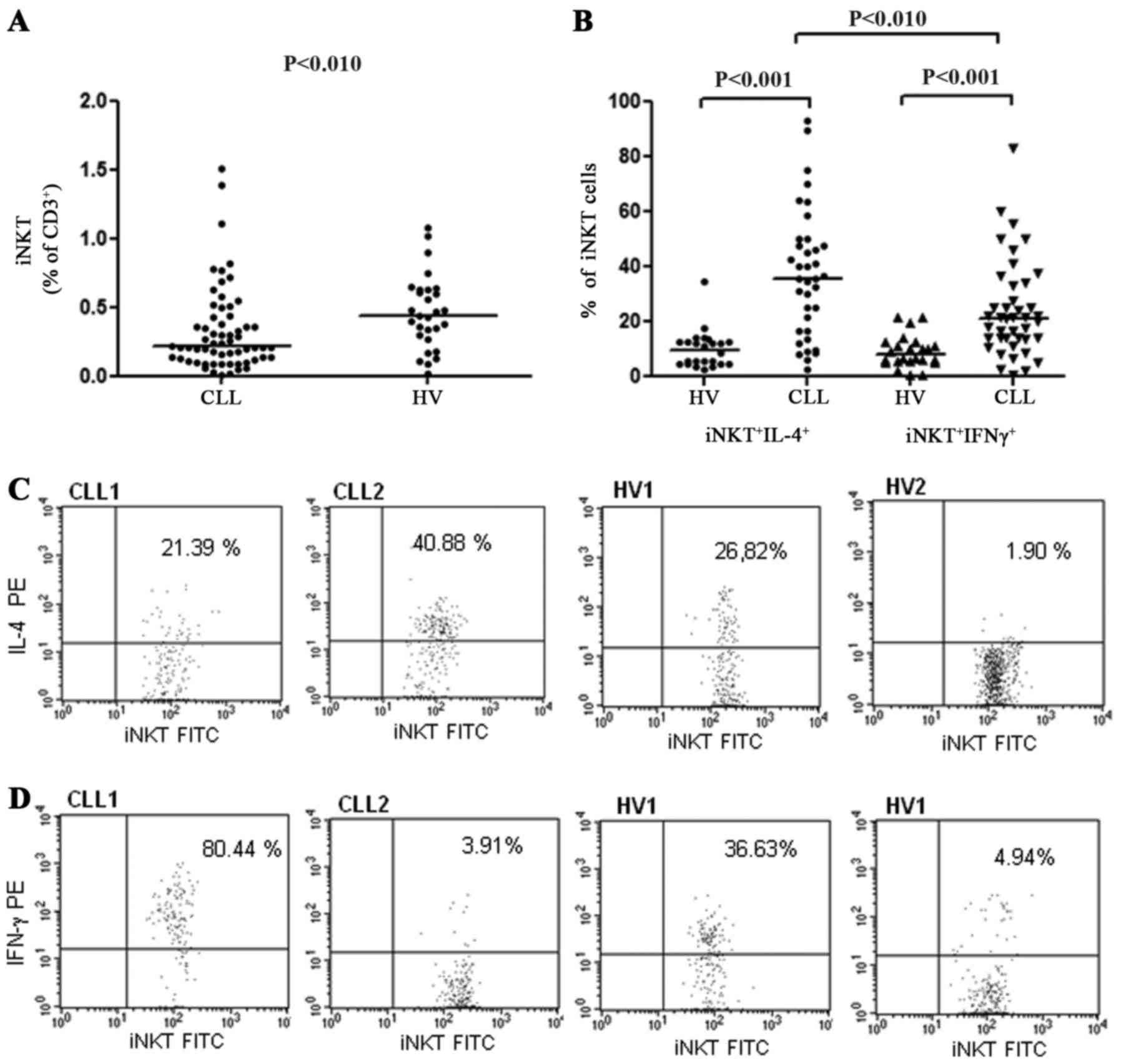
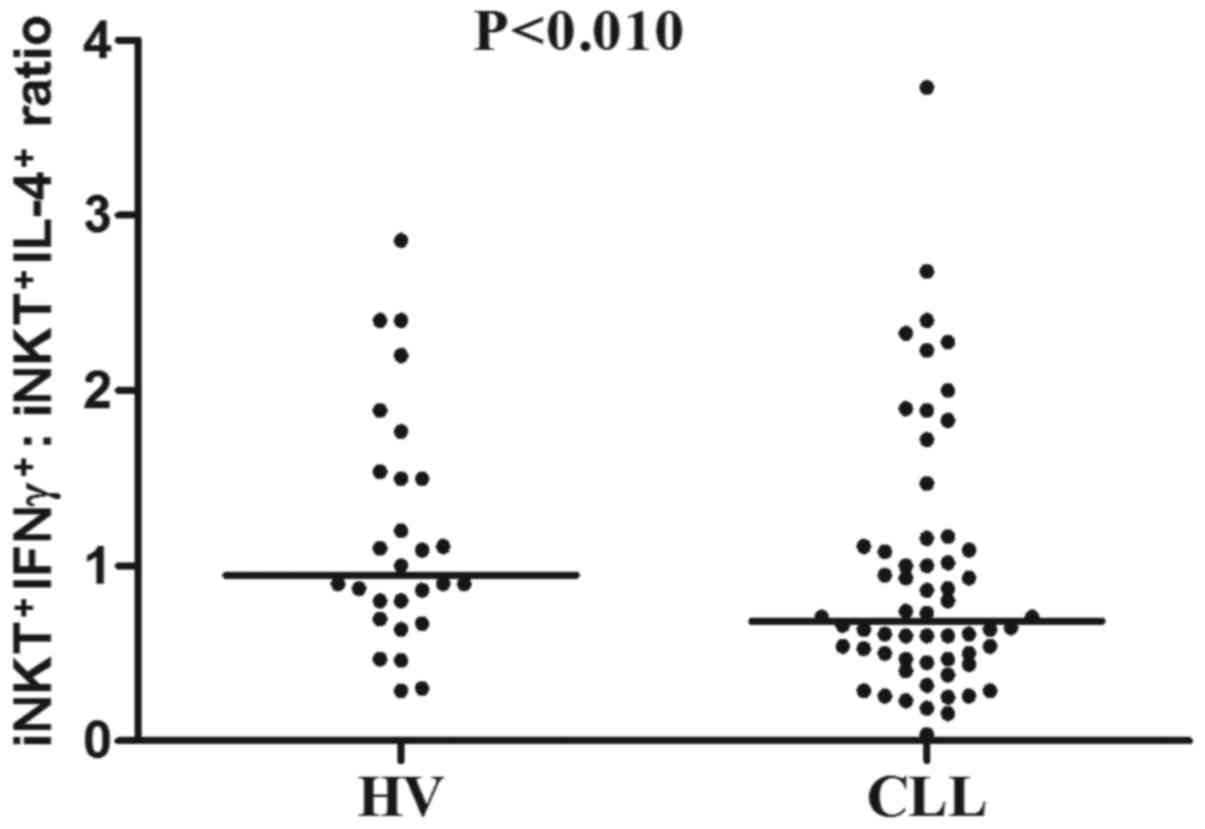
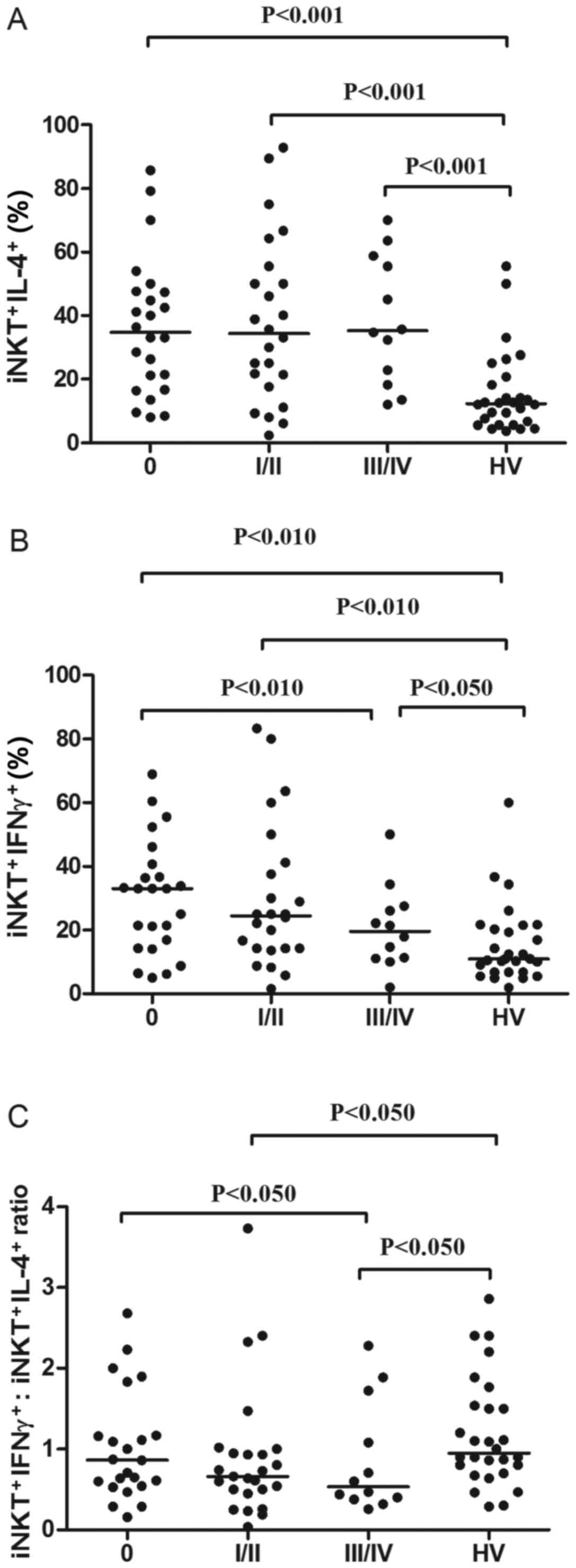
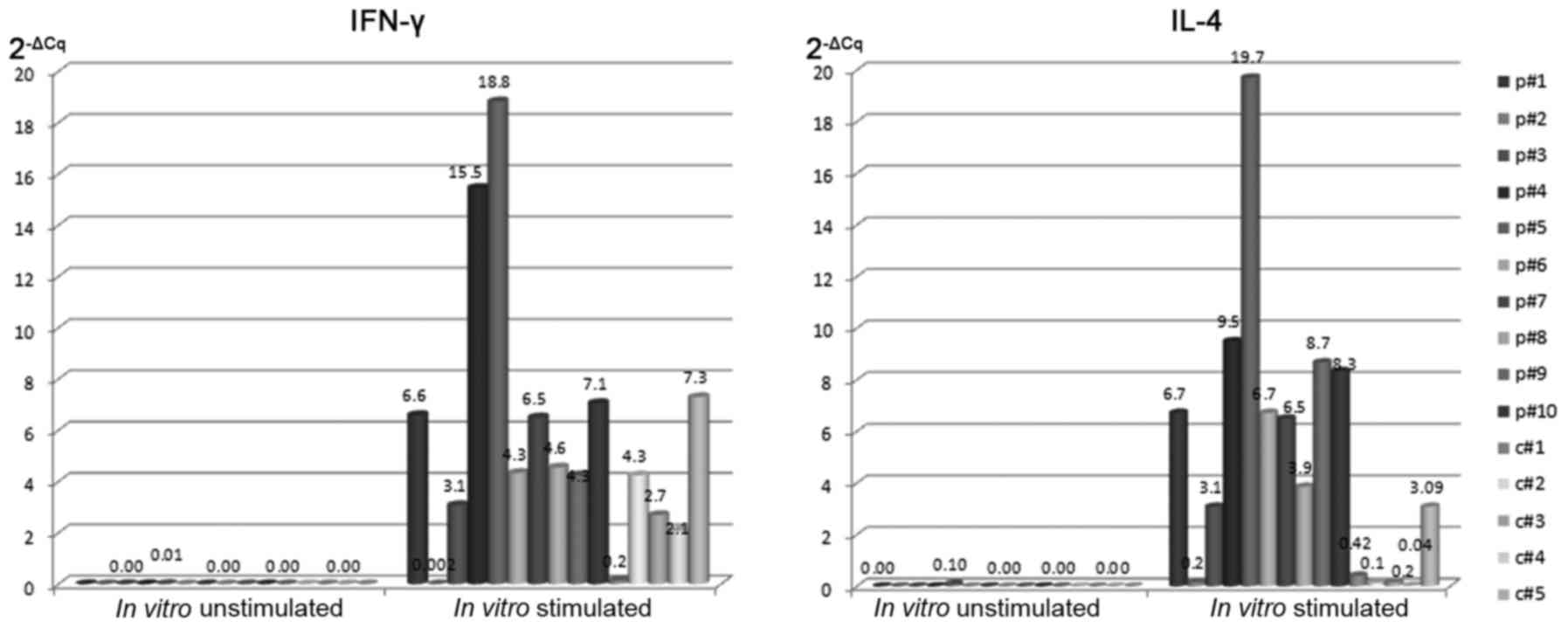
|
1
|
Joyce JA: Therapeutic targeting of the
tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 7:513–520. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Burger JA and Gribben JG: The
microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and other B
cell malignancies: Insight into disease biology and new targeted
therapies. Semin Cancer Biol. 24:71–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tinhofer I, Rubenzer G, Holler C,
Hofstaetter E, Stoecher M, Egle A, Steurer M and Greil R:
Expression levels of CD38 in T cells predict course of disease in
male patients with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood.
108:2950–2956. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mainou-Fowler T and Prentice AG:
Modulation of apoptosis with cytokines in B-cell chronic
lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 21:369–377. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Terabe M, Swann J, Ambrosino E, Sinha P,
Takaku S, Hayakawa Y, Godfrey DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Smyth MJ and
Berzofsky JA: A nonclassical non-Valpha14Jalpha18 CD1d-restricted
(type II) NKT cell is sufficient for down-regulation of tumor
immunosurveillance. J Exp Med. 202:1627–1633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gapin L: Development of invariant natural
killer T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 39:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dellabona P, Abrignani S and Casorati G:
iNKT-cell help to B cells: A cooperative job between innate and
adaptive immune responses. Eur J Immunol. 44:2230–2237. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Exley M, Porcelli S, Furman M, Garcia J
and Balk S: CD161 (NKR-P1A) costimulation of CD1d-dependent
activation of human T cells expressing invariant V alpha 24 J alpha
Q T cell receptor alpha chains. J Exp Med. 188:867–876. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Seino K and Taniguchi M: Functionally
distinct NKT cell subsets and subtypes. J Exp Med. 202:1623–1626.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M,
Smyth MJ and Van Kaer L: NKT cells: What's in a name? Nat Rev
Immunol. 4:231–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawano T, Cui J, Koezuka Y, Toura I,
Kaneko Y, Motoki K, Ueno H, Nakagawa R, Sato H, Kondo E, et al:
CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells
by glycosylceramides. Science. 278:1626–1629. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Spada FM, Koezuka Y and Porcelli SA:
CD1d-restricted recognition of synthetic glycolipid antigens by
human natural killer T cells. J Exp Med. 188:1529–1534. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayakawa Y, Godfrey DI and Smyth MJ:
Alpha-galactosylceramide: Potential immunomodulatory activity and
future application. Curr Med Chem. 11:241–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsuda JL, Naidenko OV, Gapin L, Nakayama
T, Taniguchi M, Wang CR, Koezuka Y and Kronenberg M: Tracking the
response of natural killer T cells to a glycolipid antigen using
CD1d tetramers. J Exp Med. 192:741–754. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsuda JL, Mallevaey T, Scott-Browne J
and Gapin L: CD1d-restricted iNKT cells, the ‘Swiss-Army knife’ of
the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 20:358–368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gumperz JE, Miyake S, Yamamura T and
Brenner MB: Functionally distinct subsets of CD1d-restricted
natural killer T cells revealed by CD1d tetramer staining. J Exp
Med. 195:625–636. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brennan PJ, Brigl M and Brenner MB:
Invariant natural killer T cells: An innate activation scheme
linked to diverse effector functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:101–117.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Godfrey DI and Kronenberg M: Going both
ways: Immune regulation via CD1d-dependent NKT cells. J Clin Inves.
114:1379–1388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fujii S, Shimizu K, Smith C, Bonifaz L and
Steinman RM: Activation of natural killer T cells by
alpha-galactosylceramide rapidly induces the full maturation of
dendritic cells in vivo and thereby acts as an adjuvant for
combined CD4 and CD8 T cell immunity to a coadministered protein. J
Exp Med. 198:267–279. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smyth MJ and Godfrey DI: NKT cells and
tumor immunity-a double-edged sword. Nat Immunol. 1:459–460. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tahir SM, Cheng O, Shaulov A, Koezuka Y,
Bubley GJ, Wilson SB, Balk SP and Exley MA: Loss of IFN-gamma
production by invariant NK T cells in advanced cancer. J Immunol.
167:4046–4050. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D,
Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Döhner H, Hillmen P, Keating MJ,
Montserrat E, Rai KR, et al: Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A report from the
international workshop on chronic lymphocytic leukemia updating the
national cancer institute-working group 1996 guidelines. Blood.
111:5446–5456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana
AD, Levy RN and Pasternack BS: Clinical staging of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 46:219–234. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bojarska-Junak A, Hus I, Chocholska S,
Tomczak W, Woś J, Czubak P, Putowski L and Roliński J: CD1d
expression is higher in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with
unfavorable prognosis. Leuk Res. 38:435–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bojarska-Junak A, Hus I, Chocholska S,
Wasik-Szczepanek E, Sieklucka M, Dmoszyńska A and Roliński J: BAFF
and APRIL expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia:
Correlation with biological and clinical features. Leuk Res.
33:1319–1327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sieklucka M, Pozarowski P, Bojarska-Junak
A, Hus I, Dmoszynska A and Rolinski J: Apoptosis in B-CLL: The
relationship between higher ex vivo spontaneous apoptosis
before treatment in III–IV Rai stage patients and poor outcome.
Oncol Rep. 19:1611–1620. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bojarska-Junak A, Hus I, Olszewska-Bożek
K, Chocholska S, Wąsik-Szczepanek E, Tomczak W, Miłczak J,
Dmoszyńska A and Roliński J: Analysis of ex vivo apoptosis of B and
T cells from peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol Pol. 43:336–341. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Christopoulos P, Pfeifer D, Bartholomé K,
Follo M, Timmer J, Fisch P and Veelken H: Definition and
characterization of the systemic T-cell dysregulation in untreated
indolent B-cell lymphoma and very early CLL. Blood. 117:3836–3846.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rossmann ED, Lewin N, Jeddi-Tehrani M,
Osterborg A and Mellstedt H: Intracellular T cell cytokines in
patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL). Eur J
Haematol. 68:299–306. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weinkove R, Brooks CR, Carter JM, Hermans
IF and Ronchese F: Functional invariant natural killer T-cell and
CD1d axis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Implications for
immunotherapy. Haematologica. 98:376–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Borg NA, Wun KS, Kjer-Nielsen L, Wilce MC,
Pellicci DG, Koh R, Besra GS, Bharadwaj M, Godfrey DI, McCluskey J
and Rossjohn J: CD1d-lipid-antigen recognition by the
semi-invariant NKT T-cell receptor. Nature. 448:44–49. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fernandez CS, Cameron G, Godfrey DI and
Kent SJ: Ex-vivo α-galactosylceramide activation of NKT
cells in humans and macaques. J Immunol Methods. 382:150–159. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ai W, Li H, Song N, Li L and Chen H:
Optimal method to stimulate cytokine production and its use in
immunotoxicity assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
10:3834–3842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Z, Yuan X, Luo Y, He Y, Jiang Y, Chen
ZK and Sun E: Evaluating the effects of immunosuppressants on human
immunity using cytokine profiles of whole blood. Cytokine.
45:141–147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hill SJ, Peters SH, Ayliffe MJ, Merceica J
and Bansal AS: Reduced IL-4 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)
expression by CD4 T cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic
leukaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 117:8–117. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dhodapkar MV, Geller MD, Chang DH, Shimizu
K, Fujii S, Dhodapkar KM and Krasovsky J: A reversible defect in
natural killer T cell function characterizes the progression of
premalignant to malignantmultiple myeloma. J Exp Med.
197:1667–1676. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Singh N, Hong S, Scherer DC, Serizawa I,
Burdin N, Kronenberg M, Koezuka Y and Van Kaer L: Cutting edge:
Activation of NK T cells by CD1d and alpha-galactosylceramide
directs conventional T cells to the acquisition of a Th2 phenotype.
J Immunol. 163:2373–2377. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burdin N, Brossay L and Kronenberg M:
Immunization with alpha-galactosylceramide polarizes CD1-reactive
NK T cells towards Th2 cytokine synthesis. Eur J Immunol.
29:2014–2025. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dancescu M, Rubio-Trujillo M, Biron G,
Bron D, Delespesse G and Sarfati M: Interleukin 4 protects chronic
lymphocytic leukemic B cells from death by apoptosis and
upregulates Bcl-2 expression. J Exp Med. 176:1319–1326. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smyth MJ, Crowe NY, Pellicci DG,
Kyparissoudis K, Kelly JM, Takeda K, Yagita H and Godfrey DI:
Sequential production of interferon-gamma by NK1.1(+) T cells and
natural killer cells is essential for the antimetastatic effect of
alpha-galactosylceramide. Blood. 99:1259–1266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Palmer VL, Nganga VK, Rothermund ME, Perry
GA and Swanson PC: Cd1d regulates B cell development but not B cell
accumulation and IL10 production in mice with pathologic CD5(+) B
cell expansion. BMC Immunol. 16:662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Molling JW, Kölgen W, van der Vliet HJ,
Boomsma MF, Kruizenga H, Smorenburg CH, Molenkamp BG, Langendijk
JA, Leemans CR, von Blomberg BM, et al: Peripheral blood
IFN-gamma-secreting Valpha24+Vbeta11+ NKT cell numbers are
decreased in cancer patients independent of tumor type or tumor
load. Int J Cancer. 116:87–93. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Giaccone G, Punt CJ, Ando Y, Ruijter R,
Nishi N, Peters M, von Blomberg BM, Scheper RJ, van der Vliet HJ,
van den Eertwegh AJ, et al: A phase I study of the natural killer
T-cell ligand alpha-galactosylceramide (KRN7000) in patients with
solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3702–3709. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoneda K, Morii T, Nieda M, Tsukaguchi N,
Amano I, Tanaka H, Yagi H, Narita N and Kimura H: The peripheral
blood Valpha24+ NKT cell numbers decrease in patients with
haematopoietic malignancy. Leuk Res. 29:147–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hus I, Bojarska-Junak A, Gonet-Sebastianka
J, Glazer M, Drab E, Woś J and Roliński J: iNKT cell percentage is
decreased in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and
correlates inversely with the clinical stage and negative
prognostic factors. Centr Eur J Immunol. 36:79–84. 2011.
|
|
47
|
Singh AK, Shukla NK and Das SN: Altered
invariant natural killer T cell subsets and its functions in
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Scand J Immunol.
78:468–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fujii S, Shimizu K, Klimek V, Geller MD,
Nimer SD and Dhodapkar MV: Severe and selective deficiency of
interferon-gamma-producing invariant natural killer T cells in
patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol.
122:617–622. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fais F, Morabito F, Stelitano C, Callea V,
Zanardi S, Scudeletti M, Varese P, Ciccone E and Grossi CE: CD1d is
expressed on B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and mediates
alpha-galactosylceramide presentation to natural killer T
lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 109:402–411. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fujii S, Shimizu K, Okamoto Y, Kunii N,
Nakayama T, Motohashi S and Taniguchi M: NKT cells as an ideal
anti-tumor immunotherapeutic. Front Immunol. 4:4092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mendiratta SK, Martin WD, Hong S,
Boesteanu A, Joyce S and Van Kaer L: CD1d1 mutant mice are
deficient in natural T cells that promptly produce IL-4. Immunity.
6:469–477. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang X, Bishop KA, Hegde S, Rodenkirch LA,
Pike JW and Gumperz JE: Human invariant natural killer T cells
acquire transient innate responsiveness via histone H4 acetylation
induced by weak TCR stimulation. J Exp Med. 209:987–1000. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lanasa MC: Novel insights into the biology
of CLL. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010:70–76.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bojarska-Junak A, Hus I, Sieklucka M,
Wasik-Szczepanek E, Mazurkiewicz T, Polak P, Dmoszynska A and
Rolinski J: Natural killer-like T CD3+/CD16+CD56+ cells in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia: Intracellular cytokine expression and
relationship with clinical outcome. Oncol Rep. 24:803–810. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Robertson FC, Berzofsky JA and Terabe M:
NKT cell networks in the regulation of tumor immunity. Front
Immunol. 5:5432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Hu X, Guo C, Zhang Q, Peng J,
Zhang J, Li L, Zhang T and Xu C: Polarization of natural killer T
cells towards an NKT2 subpopulation occurs after stimulation with
alpha-galactosylceramide and rhG-CSF in aplastic anemia. Acta
Haematol. 119:178–186. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mattarollo SR and Smyth MJ: NKT cell
adjuvants in therapeutic vaccines against hematological cancers.
Oncoimmunology. 2:e226152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
McEwen-Smith RM, Salio M and Cerundolo V:
The regulatory role of invariant NKT cells in tumor immunity.
Cancer Immunol Res. 3:425–435. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
La Cava A, Van Kaer L and Fu-Dong-Shi:
CD4+CD25+ Tregs and NKT cells: Regulators regulating regulators.
Trends Immunol. 27:322–327. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|