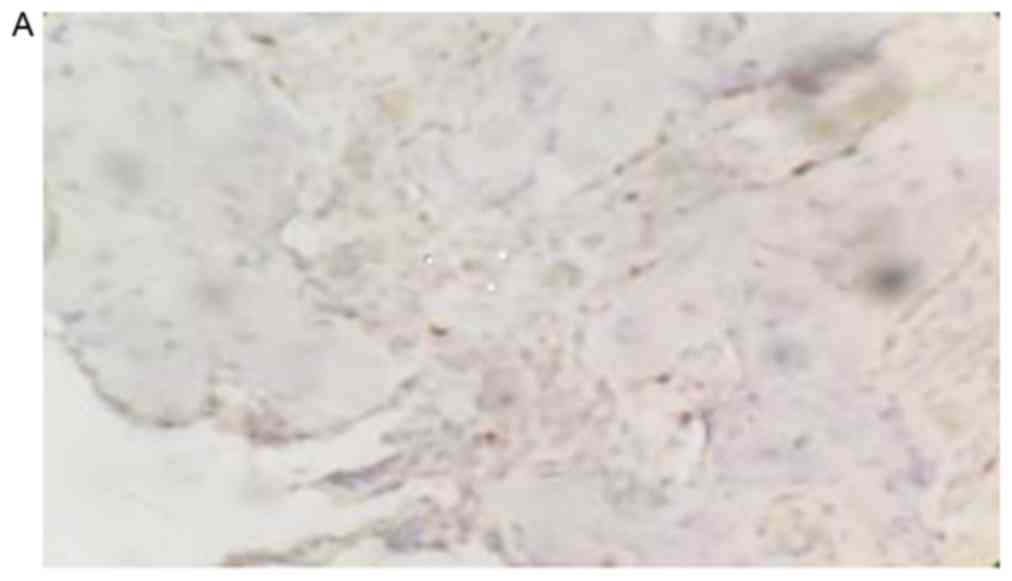
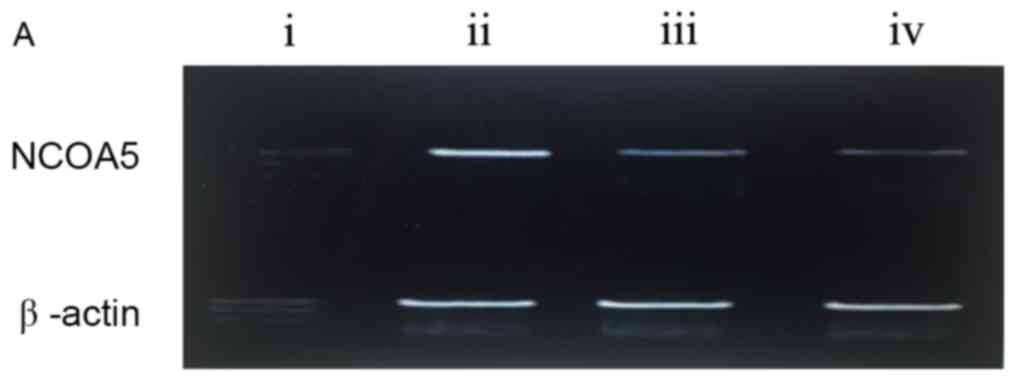
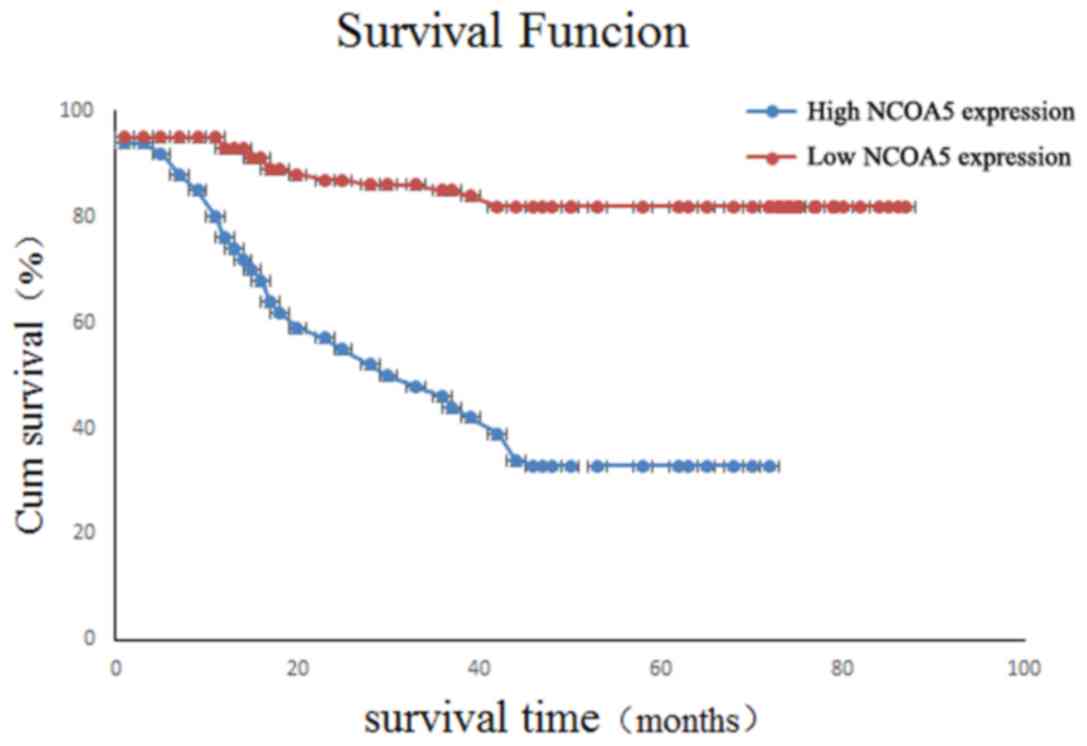
|
1
|
Huang J, Liu K, Song D, Ding M, Wang J,
Jin Q and Ni J: Krüppel-like factor 4 promotes high-mobility group
box 1-induced chemotherapy resistance in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer
Sci. 107:242–249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li YS, Deng ZH, Zeng C and Lei GH: JNK
pathway in osteosarcoma: Pathogenesis and therapeutics. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 36:465–470. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lamplot JD, Denduluri S, Qin J, Li R, Liu
X, Zhang H, Chen X, Wang N, Pratt A, Shui W, et al: The current and
future therapies for human osteosarcoma. Curr Cancer Ther Rev.
9:55–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chakravarthi PS, Kattimani VS, Prasad LK
and Satish PR: Juxtacortical osteosarcoma of the mandible:
Challenges in diagnosis and management. Natl J Maxillofac Surg.
6:127–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Commandeur AE, Styer AK and Teixeira JM:
Epidemiological and genetic clues for molecular mechanisms involved
in uterine leiomyoma development and growth. Hum Reprod Update.
21:593–615. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou W, Zhu Y, Chen S, Xu R and Wang K:
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promotes MG63 cell
proliferation and is associated with increased expression of
cyclin-dependent kinase 1 in osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:713–719.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang J, Cheng D, Zhou S, Zhu B, Hu T and
Yang Q: Overexpression of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1 correlates
to poor prognosis and up-regulation of PI3K/mTOR in human
osteosarcoma. Int J Mol Sci. 16:28635–28646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu CY and Feng GS: NCOA5, a molecular
link between type 2 diabetes and liver cancer. Hepatobiliary Surg
Nutr. 3:106–108. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tetel MJ, Auger AP and Charlier TD: Who's
in charge? Nuclear receptor coactivator and corepressor function in
brain and behavior. Front Neuroendocrinol. 30:328–342. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao S, Li A, Liu F, Chen F, Williams M,
Zhang C, Kelley Z, Wu CL, Luo R and Xiao H: NCOA5
Haploinsufficiency results in glucose intolerance and subsequent
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 24:725–737. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lahusen T, Henke RT, Kagan BL, Wellstein A
and Riegel AT: The role and regulation of the nuclear receptor
co-activator AIB1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
116:225–237. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chauhan C, Zraly CB, Parilla M, Diaz MO
and Dingwall AK: Histone recognition and nuclear receptor
co-activator functions of Drosophila cara mitad, a homolog of the
N-terminal portion of mammalian MLL2 and MLL3. Development.
139:1997–2008. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen VW, Ruiz BA, Hsieh MC, Wu XC, Ries LA
and Lewis DR: Analysis of stage and clinical/prognostic factors for
lung cancer from SEER registries: AJCC staging and collaborative
stage data collection system. Cancer. 120 Suppl 23:S3781–S3792.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chinenov Y, Gupte R and Rogatsky I:
Nuclear receptors in inflammation control: Repression by GR and
beyond. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 380:55–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pavlin MR, Brunzelle JS and Fernandez EJ:
Agonist ligands mediate the transcriptional response of nuclear
receptor heterodimers through distinct stoichiometric assemblies
with coactivators. J Biol Chem. 289:24771–24778. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gyamfi MA and Wan YJ: Pathogenesis of
alcoholic liver disease: The role of nuclear receptors. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 235:547–560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C and Wheeler DL: The
nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its
role in cancer. Discov Med. 12:419–432. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poos K, Smida J, Maugg D, Eckstein G,
Baumhoer D, Nathrath M and Korsching E: Genomic heterogeneity of
osteosarcoma-shift from single candidates to functional modules.
PLoS One. 10:e01230822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Basu-Roy U, Basilico C and Mansukhani A:
Perspectives on cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett.
338:158–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao R, Ni D, Tian Y, Ni B and Wang A:
Aberrant ADAM10 expression correlates with osteosarcoma
progression. Eur J Med Res. 19:92014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Talmadge JE and Gabrilovich DI: History of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:739–752. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dhar D, Seki E and Karin M: NCOA5, IL-6,
Type-2 diabetes and HCC: The deadly quartet. Cell Metab. 19:6–7.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cumsille P, Coronel A, Conca C, Quiñinao C
and Escudero C: Proposal of a hybrid approach for tumor progression
and tumor-induced angiogenesis. Theor Biol Med Model. 12:132015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arvelo F, Sojo F and Cotte C: Tumour
progression and metastasis. Ecancermedicalscience. 10:6172016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gillespie MA, Gold ES, Ramsey SA, Podolsky
I, Aderem A and Ranish JA: An LXR-NCOA5 gene regulatory complex
directs inflammatory crosstalk-dependent repression of macrophage
cholesterol efflux. EMBO J. 34:1244–1258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee E, Pandey NB and Popel AS: Crosstalk
between cancer cells and blood endothelial and lymphatic
endothelial cells in tumour and organ microenvironment. Expert Rev
Mol Med. 17:e32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marcu LG and Harriss-Phillips WM: In
Silico modelling of treatment-induced tumour cell kill:
Developments and advances. Comput Math Methods Med.
2012:9602562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang M, Yuan J, Peng C and Li Y: Collagen
as a double-edged sword in tumor progression. Tumour Biol.
35:2871–2882. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin G, Sun XJ, Han QB, Wang Z, Xu YP, Gu
JL, Wu W, Zhang GU, Hu JL, Sun WY and Mao WM: Epidermal growth
factor receptor protein overexpression and gene amplification are
associated with aggressive biological behaviors of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 10:901–906. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shiomi H, Eguchi Y, Tani T, Kodama M and
Hattori T: Cellular distribution and clinical value of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its receptor, and plasminogen
activator inhibitor-2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J
Pathol. 156:567–575. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|