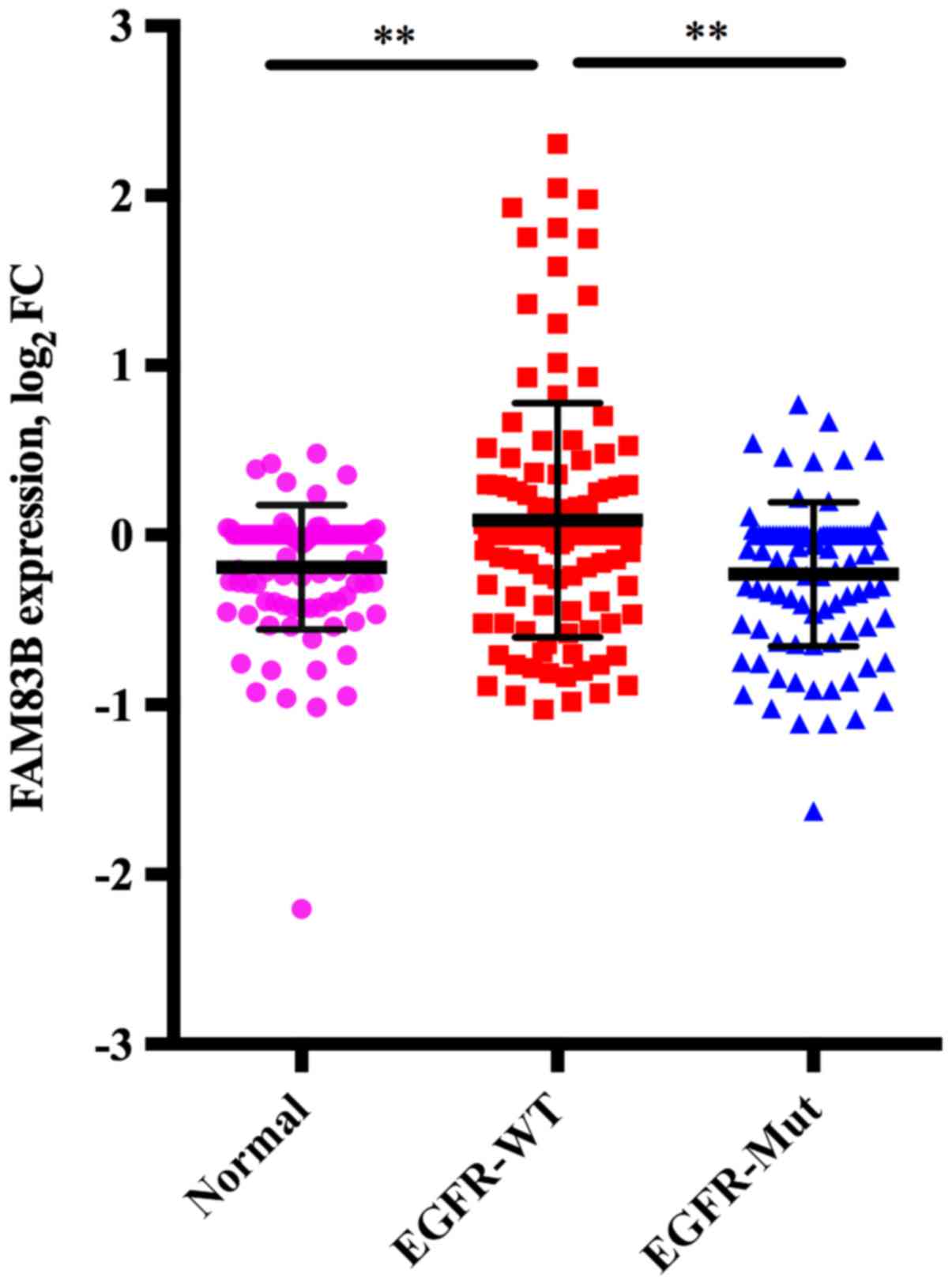
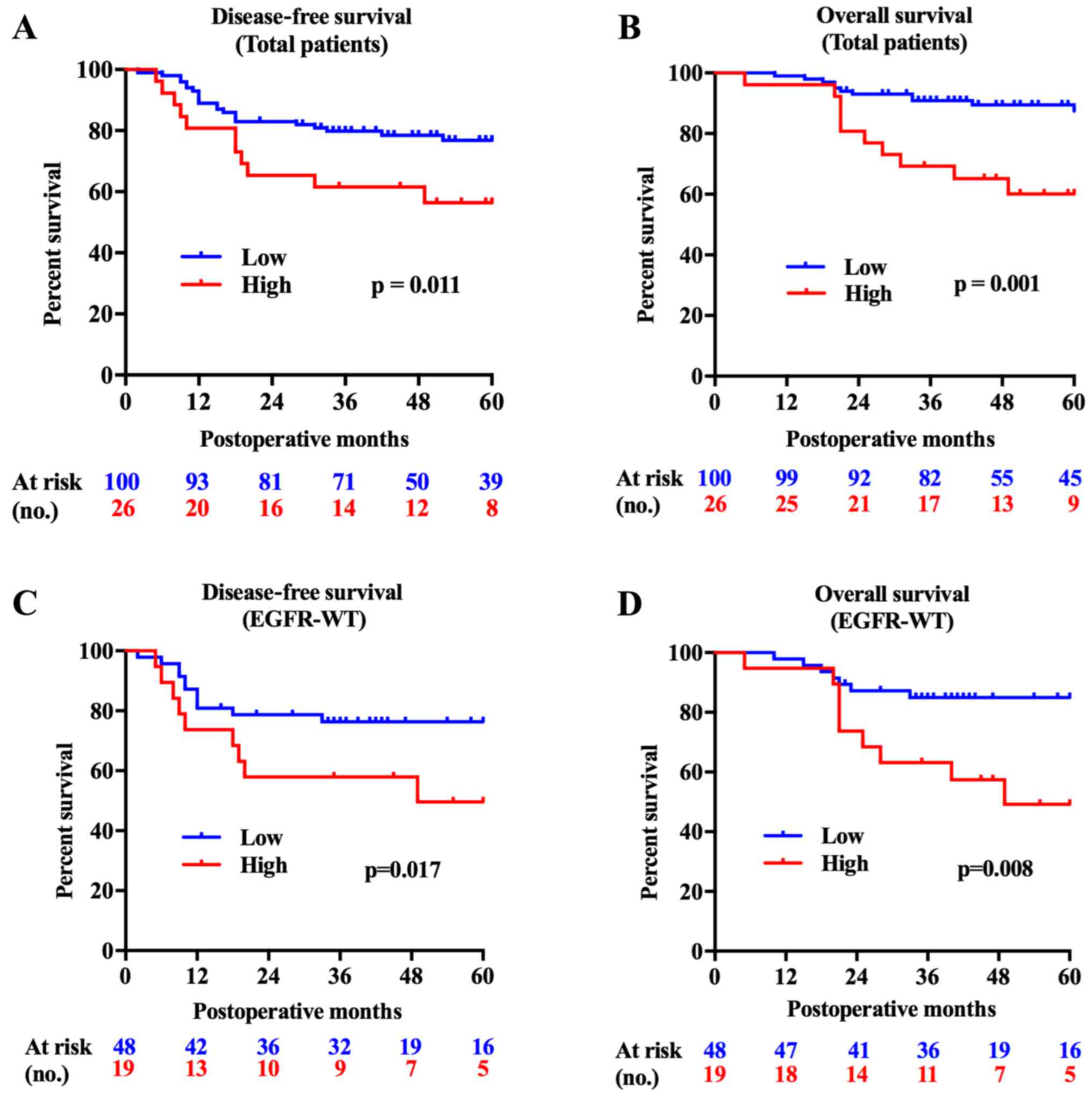
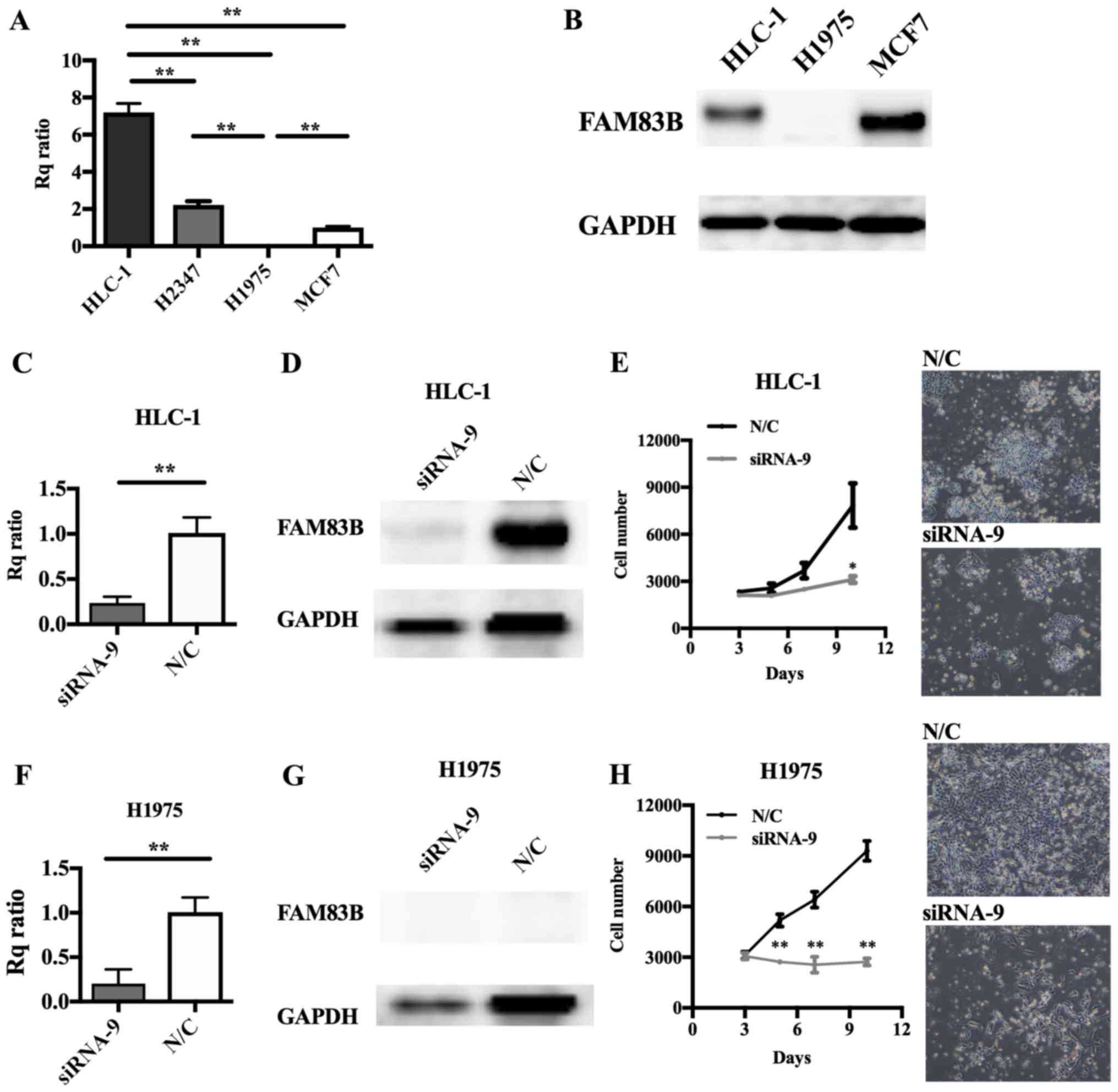
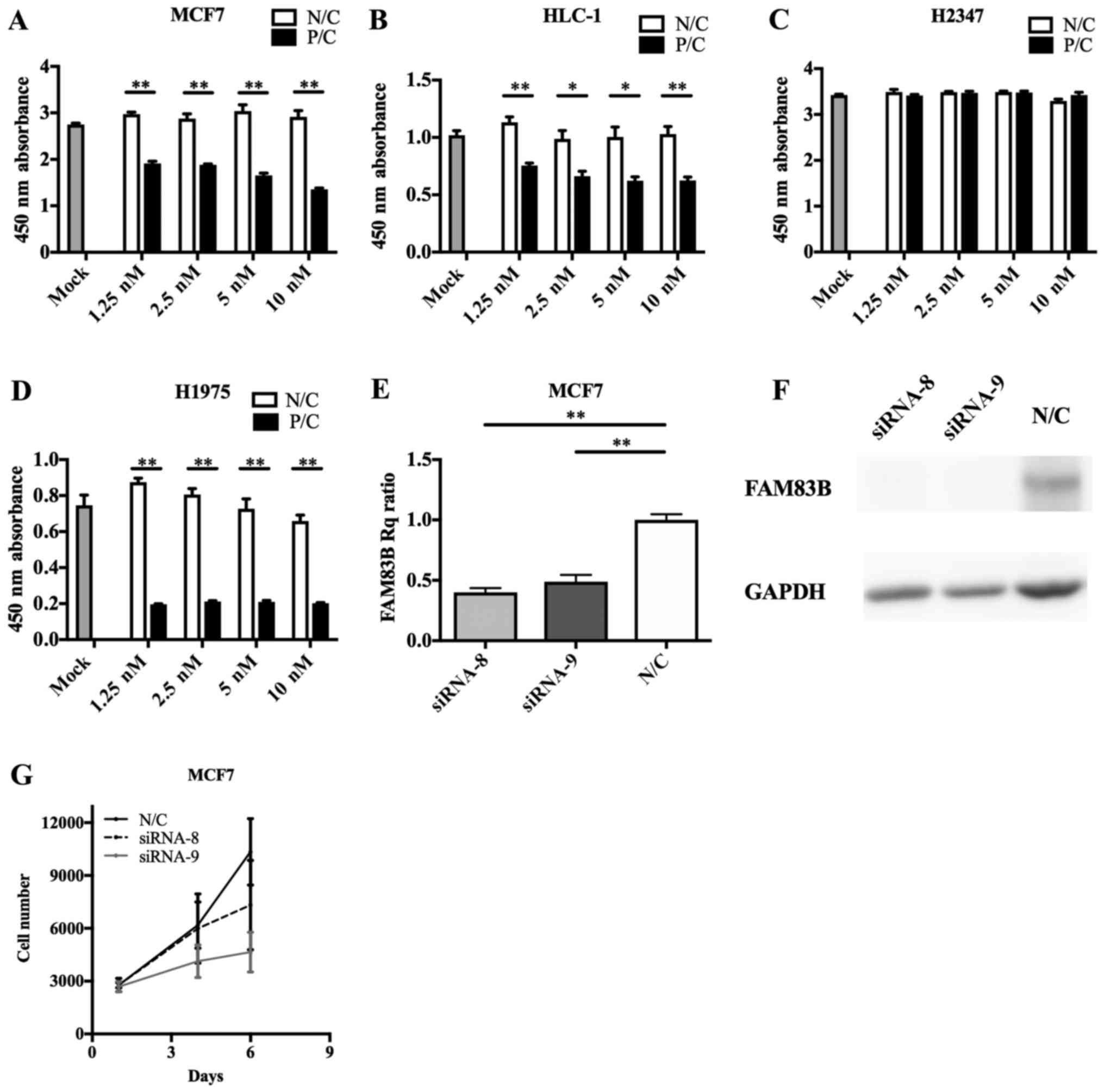
|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: World Cancer
Report 2014. IARC Press; Lyon: 2014, http://publications.iarc.fr/Non-Series-Publications/World-Cancer-Reports/World-Cancer-Report-2014
|
|
2
|
National Cancer Institute, . https://seer.cancer.govOctober 17–2003
|
|
3
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network, .
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.aspApril
17–2003
|
|
4
|
Kohno T, Tsuta K, Tsuchihara K, Nakaoku T,
Yoh K and Goto K: RET fusion gene: Translation to personalized lung
cancer therapy. Cancer Sci. 104:1396–1400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosell R, Ichinose Y, Taron M, Sarries C,
Queralt C, Mendez P, Sanchez JM, Nishiyama K, Moran T, Cirauqui B,
et al: Mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the EGFR gene
associated with gefitinib response in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer. 50:25–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shaw AT and Solomon B: Targeting
anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
17:2081–2086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ishinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa
K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, et al:
First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 371:2167–2177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Patel JD, Socinski MA, Garon EB, Reynolds
CH, Spigel DR, Olsen MR, Hermann RC, Jotte RM, Beck T, Richards DA,
et al: PointBreak: A randomized phase III study of pemetrexed plus
carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance pemetrexed and
bevacizumab versus paclitaxel plus carboplatin and bevacizumab
followed by maintenance bevacizumab in patients with stage IIIB or
IV nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
31:4349–4357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park K, Tan EH, O'Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer
M, Mok T, Hirsh V, Yang JC, Lee KH, Lu S, et al: Afatinib versus
gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase
2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol.
17:577–589. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chan BA and Hughes BG: Targeted therapy
for non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and the promise
of the future. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 4:36–54. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sholl LM, Aisner DL, Varella-Garcia M,
Berry LD, Dias-Santagata D, Wistuba II, Chen H, Fujimoto J, Kugler
K, Franklin WA, et al: Multi-institutional oncogenic driver
mutation analysis in lung adenocarcinoma: The lung cancer mutation
consortium experience. J Thorac Oncol. 10:768–777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okabe N, Ezaki J, Yamaura T, Muto S, Osugi
J, Tamura H, Imai J, Ito E, Yanagisawa Y, Honma R, et al: FAM83B is
a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 46:999–1006. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cipriano R, Graham J, Miskimen KL, Bryson
BL, Bruntz RC, Scott SA, Brown HA, Stark GR and Jackson MW: FAM83B
mediates EGFR- and RAS-driven oncogenic transformation. J Clin
Invest. 122:3197–3210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miura A, Honma R, Togashi T, Yanagisawa Y,
Ito E, Imai J, Goshima N, Watanabe S and Nomura N: Differential
responses of normal human coronary artery endothelial cells against
multiple cytokines comparatively assessed by gene expression
profiles. FEBS Lett. 580:6871–6879. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:pp. 4350–4354. 1979; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leslie HS, Mary KG and Christian W: TNM
classification of malignant tumours. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell; Oxford:
2009
|
|
21
|
Snijders AM, Lee SY, Hang B, Hao W,
Bissell MJ and Mao JH: FAM83 family oncogenes are broadly involved
in human cancers: An integrative multi-omics approach. Mol Oncol.
11:167–179. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bartel CA, Parameswaran N, Cipriano R and
Jackson MW: FAM83 proteins: Fostering new interactions to drive
oncogenic signaling and therapeutic resistance. Oncotarget.
7:52597–52612. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tzivion G, Luo Z and Avruch J: A dimeric
14-3-3 protein is an essential cofactor for Raf kinase activity.
Nature. 394:88–92. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cipriano R, Miskimen KL, Bryson BL, Foy
CR, Bartel CA and Jackson MW: Conserved oncogenic behavior of the
FAM83 family regulates MAPK signaling in human cancer. Mol Cancer
Res. 12:1156–1165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cipriano R, Miskimen KL, Bryson BL, Foy
CR, Bartel CA and Jackson MW: FAM83B-mediated activation of
PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling cooperates to promote epithelial cell
transformation and resistance to targeted therapies. Oncotarget.
4:729–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cipriano R, Bryson BL, Miskimen KL, Bartel
CA, Hernandez-Sanchez W, Bruntz RC, Scott SA, Lindsley CW, Brown HA
and Jackson MW: Hyperactivation of EGFR and downstream effector
phospholipase D1 by oncogenic FAM83B. Oncogene. 33:3298–3306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grant S: FAM83A and FAM83B: Candidate
oncogenes and TKI resistance mediators. J Clin Invest.
122:3048–3051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang SK, Hu Y, Yang J, Smith CE,
Richardson AS, Yamakoshi Y, Lee YL, Seymen F, Koruyucu M, Gencay K,
et al: Fam83 h null mice support a neomorphic mechanism for human
ADHCAI. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 4:46–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carithers LJ and Moore HM: The
genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Biopreserv Biobank.
13:307–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Melé M, Ferreira PG, Reverter F, DeLuca
DS, Monlong J, Sammeth M, Young TR, Goldmann JM, Pervouchine DD,
Sullivan TJ, et al: Human genomics. The human transcriptome across
tissues and individuals. Science. 348:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkami P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways and
networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles.
Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|