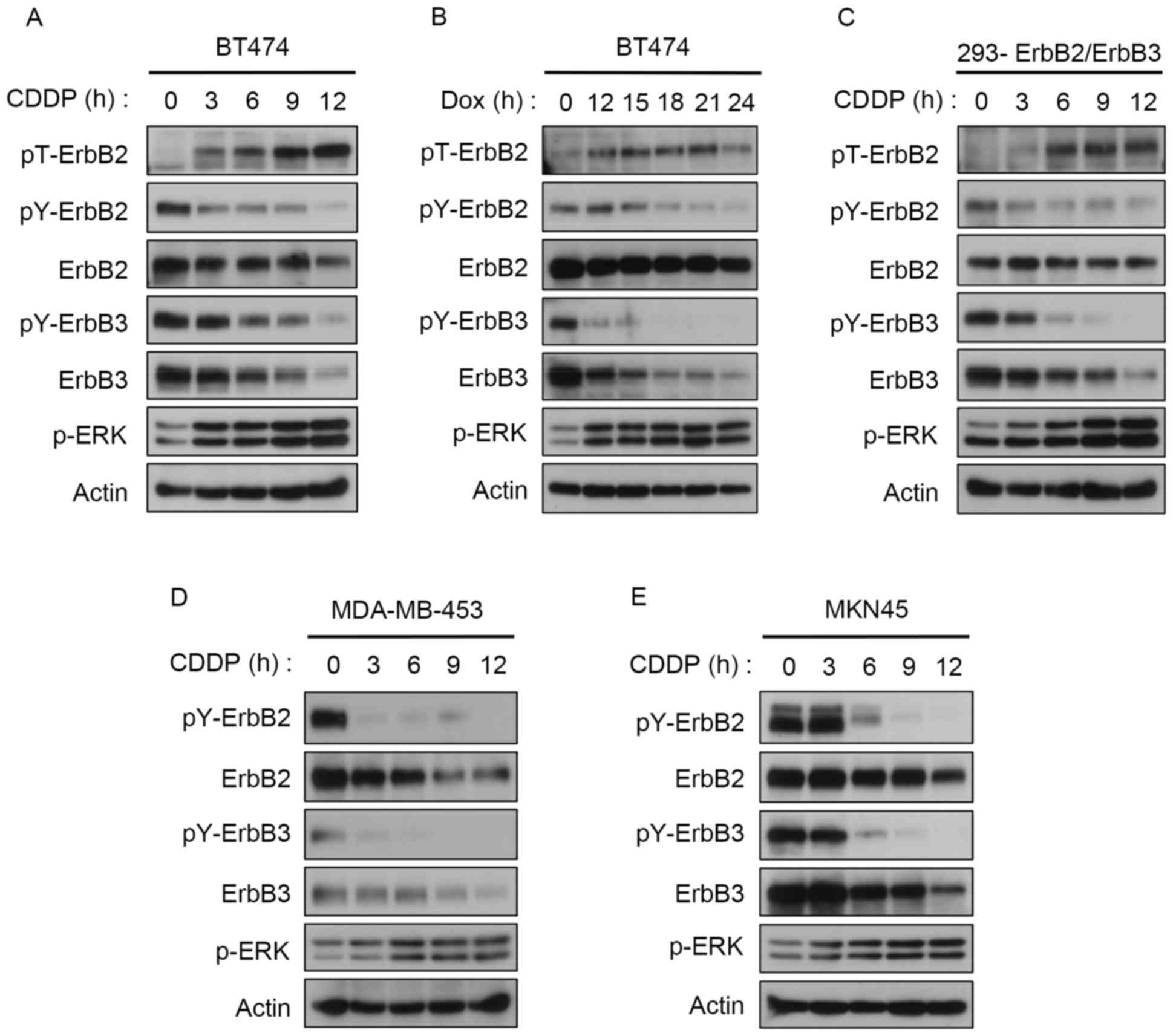
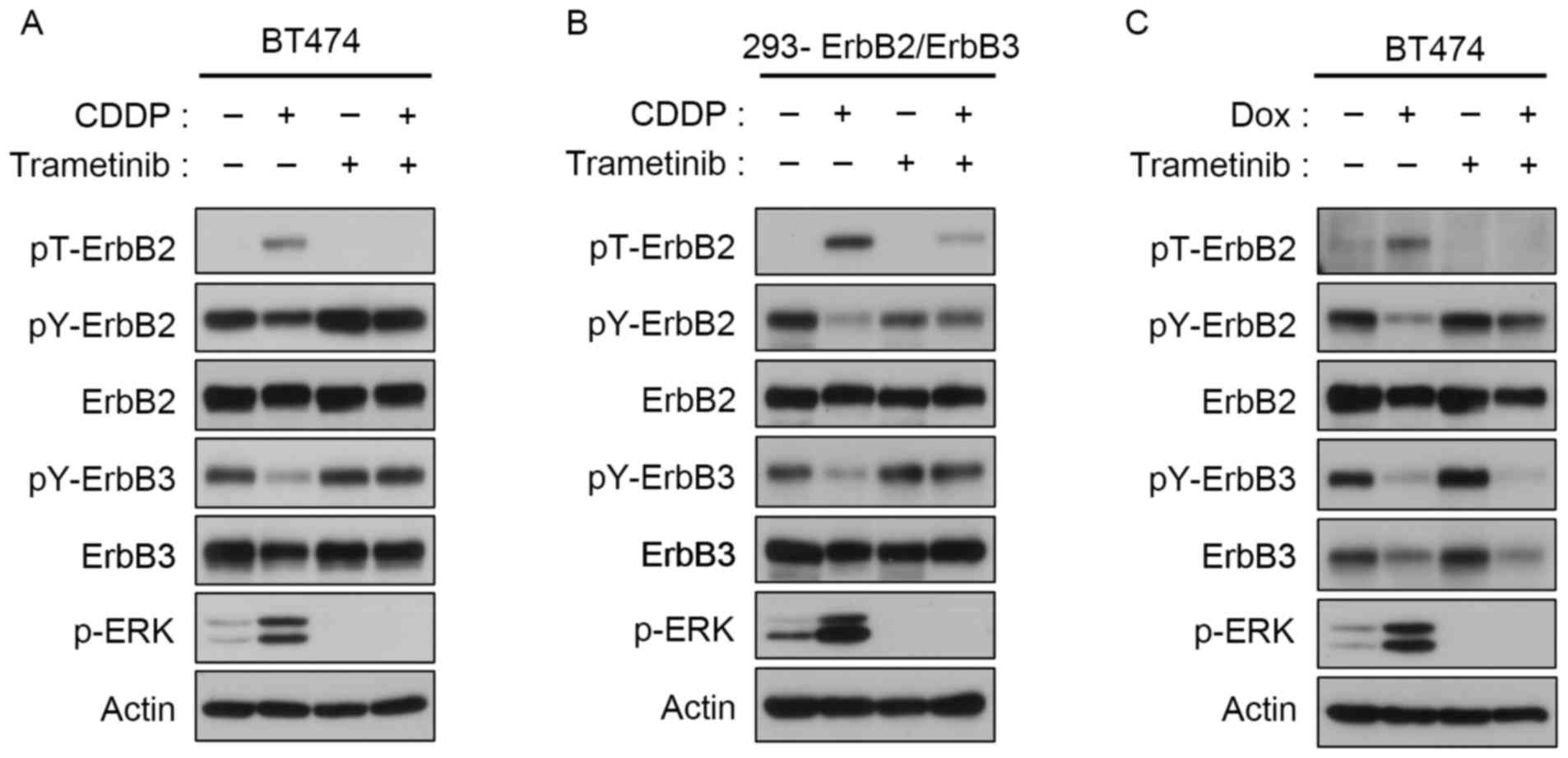
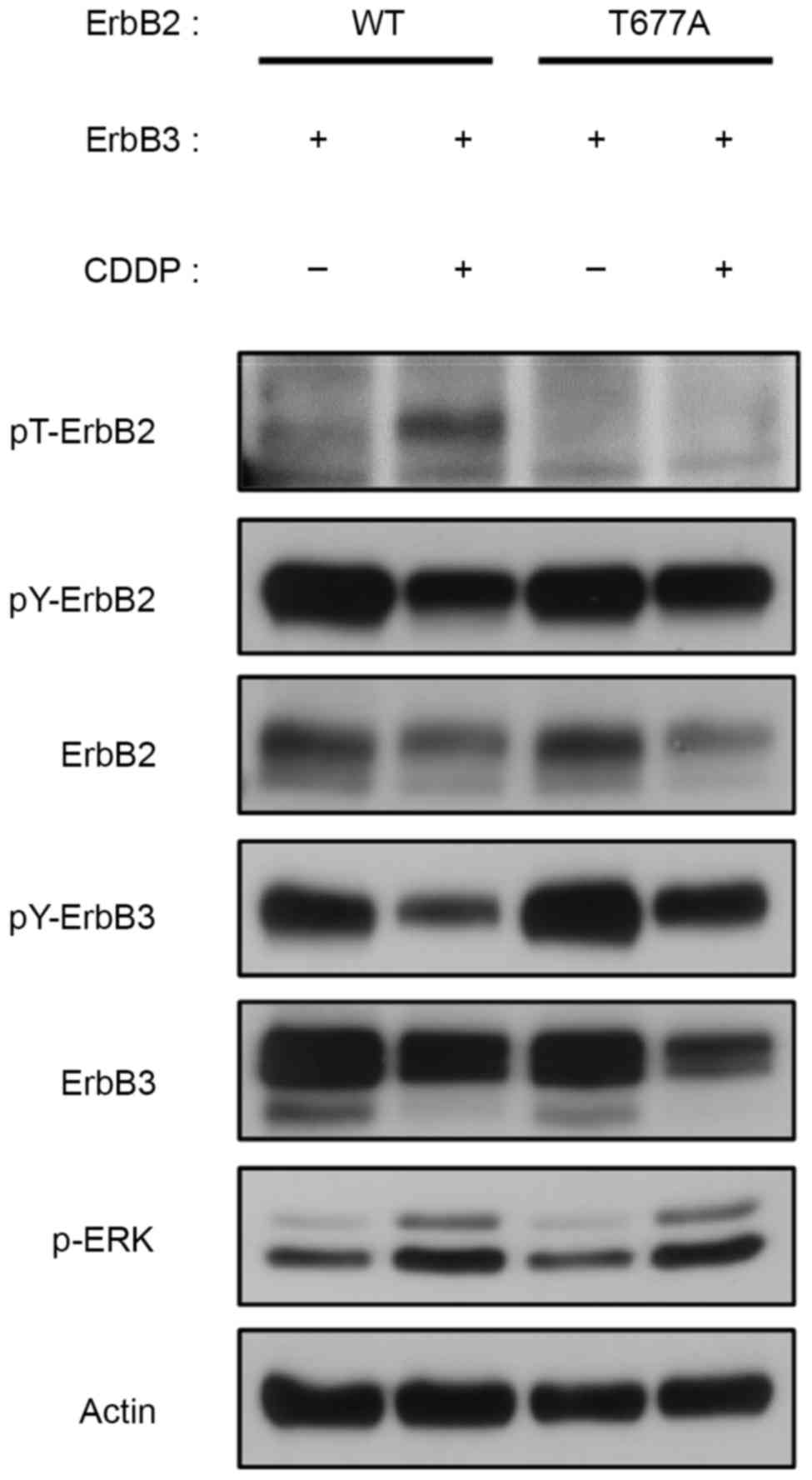
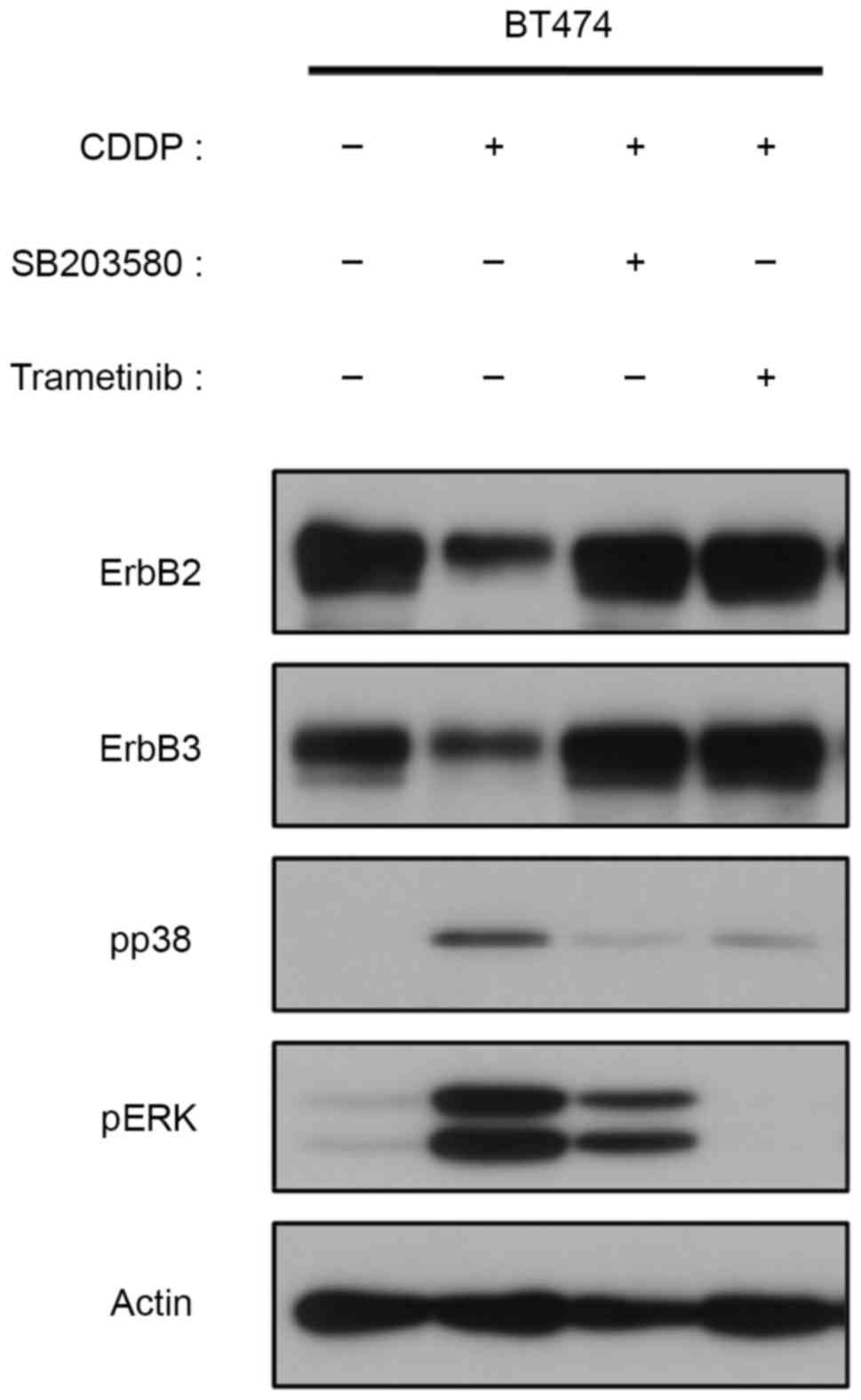
|
1
|
Roskoski R Jr: The ErbB/HER family of
protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol Res. 79:34–74. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sebastiana S, Settlemanb J, Reshkinc SJ,
Azzaritia A, Bellizzia A and Paradisoa A: The complexity of
targeting EGFR signalling in cancer: From expression to turnover.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:120–139. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schneider MR and Wolf E: The epidermal
growth factor receptor ligands at a glance. J Cell Physiol.
218:460–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh AB and Harris RC: Autocrine,
paracrine and juxtacrine signaling by EGFR ligands. Cell Signal.
17:1183–1193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sorkin A and Goh LK: Endocytosis and
intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp Cell Res. 314:3093–3106.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Avraham R and Yarden Y: Feedback
regulation of EGFR signalling: Decision making by early and delayed
loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:104–117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pines G, Köstler WJ and Yarden Y:
Oncogenic mutant forms of EGFR: Lessons in signal transduction and
targets for cancer therapy. FEBS Lett. 584:2699–2706. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park JW, Neve RM, Szollosi J and Benz CC:
Unraveling the biologic and clinical complexities of HER2. Clin
Breast Cancer. 8:392–401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ménard S, Tagliabue E, Campiglio M and
Pupa SM: Role of HER2 gene overexpression in breast carcinoma. J
Cell Physiol. 182:150–162. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sato K, Shin MS, Sakimura A, Zhou Y,
Tanaka T, Kawanishi M, Kawasaki Y, Yokoyama S, Koizumi K, Saiki I
and Sakurai H: Inverse correlation between Thr-669 and constitutive
tyrosine phosphorylation in the asymmetric epidermal growth factor
receptor dimer conformation. Cancer Sci. 104:1315–1322. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawasaki Y, Sakimura A, Park CM, Tomaru R,
Tanaka T, Ozawa T, Zhou Y, Narita K, Kishi H, Muraguchi A and
Sakurai H: Feedback control of ErbB2 via ERK-mediated
phosphorylation of a conserved threonine in the juxtamembrane
domain. Sci Rep. 6:315022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ,
Ullrich A and McGuire WL: Human breast cancer: Correlation of
relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene.
Science. 235:177–182. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Holbro T, Beerli RR, Maurer F, Koziczak M,
Barbas CF III and Hynes NE: The ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimer functions
as an oncogenic unit: ErbB2 requires ErbB3 to drive breast tumor
cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:pp. 8933–8938.
2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Valabrega G, Montemurro F and Aglietta M:
Trastuzumab: Mechanism of action, resistance and future
perspectives in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
18:977–984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bailey TA, Luan H, Clubb RJ, Naramura M,
Band V, Raja SM and Band H: Mechanisms of Trastuzumab resistance in
ErbB2-driven breast cancer and newer opportunities to overcome
therapy resistance. J Carcinog. 10:282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bezlera M, Hengstlerb JG and Ullricha A:
Inhibition of doxorubicin-induced HER3-PI3K-AKT signalling enhances
apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 6:516–529. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin A, Ozawa T, Tajiri K, Obata T, Kondo
S, Kinoshita K, Kadowaki S, Takahashi K, Sugiyama T, Kishi H and
Muraguchi A: A rapid and efficient single-cell manipulation method
for screening antigen-specific antibody-secreting cells from human
peripheral blood. Nat Med. 15:1088–1092. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ozawa T, Piao X, Kobayashi E, Zhou Y,
Sakurai H, Andoh T, Jin A, Kishi H and Muraguchi A: A novel rabbit
immunospot array assay on a chip allows for the rapid generation of
rabbit monoclonal antibodies with high affinity. PLoS One.
7:e523832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sakurai H, Miyoshi H, Toriumi W and Sugita
T: Functional interactions of transforming growth factor
beta-activated kinase 1 with IkappaB kinases to stimulate NF-kappaB
activation. J Biol Chem. 274:10641–10648. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sakurai H, Suzuki S, Kawasaki N, Nakano H,
Okazaki T, Chino A, Doi T and Saiki I: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced IKK phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 on serine
536 is mediated through the TRAF2, TRAF5, and TAK1 signaling
pathway. J Biol Chem. 278:36916–36923. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Refaat A, Aminullah, Zhou Y, Kawanishi M,
Tomaru R, Abdelhamed S, Shin MS, Koizumi K, Yokoyama S, Saiki I and
Sakurai H: Role of tyrosine kinase-independent phosphorylation of
EGFR with activating mutation in cisplatin-treated lung cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:856–861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al: Perioperative chemotherapy versus
surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med.
355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishimura M, Shin MS, Singhirunnusorn P,
Suzuki S, Kawanishi M, Koizumi K, Saiki I and Sakurai H:
TAK1-mediated serine/threonine phosphorylation of epidermal growth
factor receptor via p38/extracellular signal-regulated kinase:
NF-{kappa}B-independent survival pathways in tumor necrosis factor
alpha signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5529–5539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim KK, Han A, Yano N, Ribeiro JR, Lokich
E, Singh RK and Moore RG: Tetrathiomolybdate mediates
cisplatin-induced p38 signaling and EGFR degradation and enhances
response to cisplatin therapy in gynecologic cancers. Sci Rep.
5:159112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Frey MR, Dise RS, Edelblum KL and Polk DB:
p38 kinase regulates epidermal growth factor receptor
downregulation and cellular migration. EMBO J. 25:5683–5692. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hornbeck PV, Kornhauser JM, Tkachev S,
Zhang B, Skrzypek E, Murray B, Latham V and Sullivan M:
PhosphoSitePlus: A comprehensive resource for investigating the
structure and function of experimentally determined
post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40(Database Issue): D261–D270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahsan A, Hiniker SM, Ramanand SG, Nyati S,
Hegde A, Helman A, Menawat R, Bhojani MS, Lawrence TS and Nyati MK:
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor degradation in
cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res.
70:2862–2869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Benhar M, Engelberg D and Levitzki A:
Cisplatin-induced activation of the EGF receptor. Oncogene.
21:8723–8731. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Winograd-Katz SE and Levitzki A: Cisplatin
induces PKB/Akt activation and p38(MAPK) phosphorylation of the EGF
receptor. Oncogene. 25:7381–7390. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boone JJ, Bhosle J, Tilby MJ, Hartley JA
and Hochhauser D: Involvement of the HER2 pathway in repair of DNA
damage produced by chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:3015–3023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Campiglio M, Somenzi G, Olgiati C, Beretta
G, Balsari A, Zaffaroni N, Valagussa P and Ménard S: Role of
proliferation in HER2 status predicted response to doxorubicin. Int
J Cancer. 105:568–573. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Lu Y, Liang K, Liu B and Fan Z:
Differential responses to doxorubicin-induced phosphorylation and
activation of Akt in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res.
7:R589–R597. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De U, Chun P, Choi WS, Lee BM, Kim ND,
Moon HR, Jung JH and Kim HS: A novel anthracene derivative, MHY412,
induces apoptosis in doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7/Adr human breast
cancer cells through cell cycle arrest and downregulation of
P-glycoprotein expression. Int J Oncol. 44:167–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|