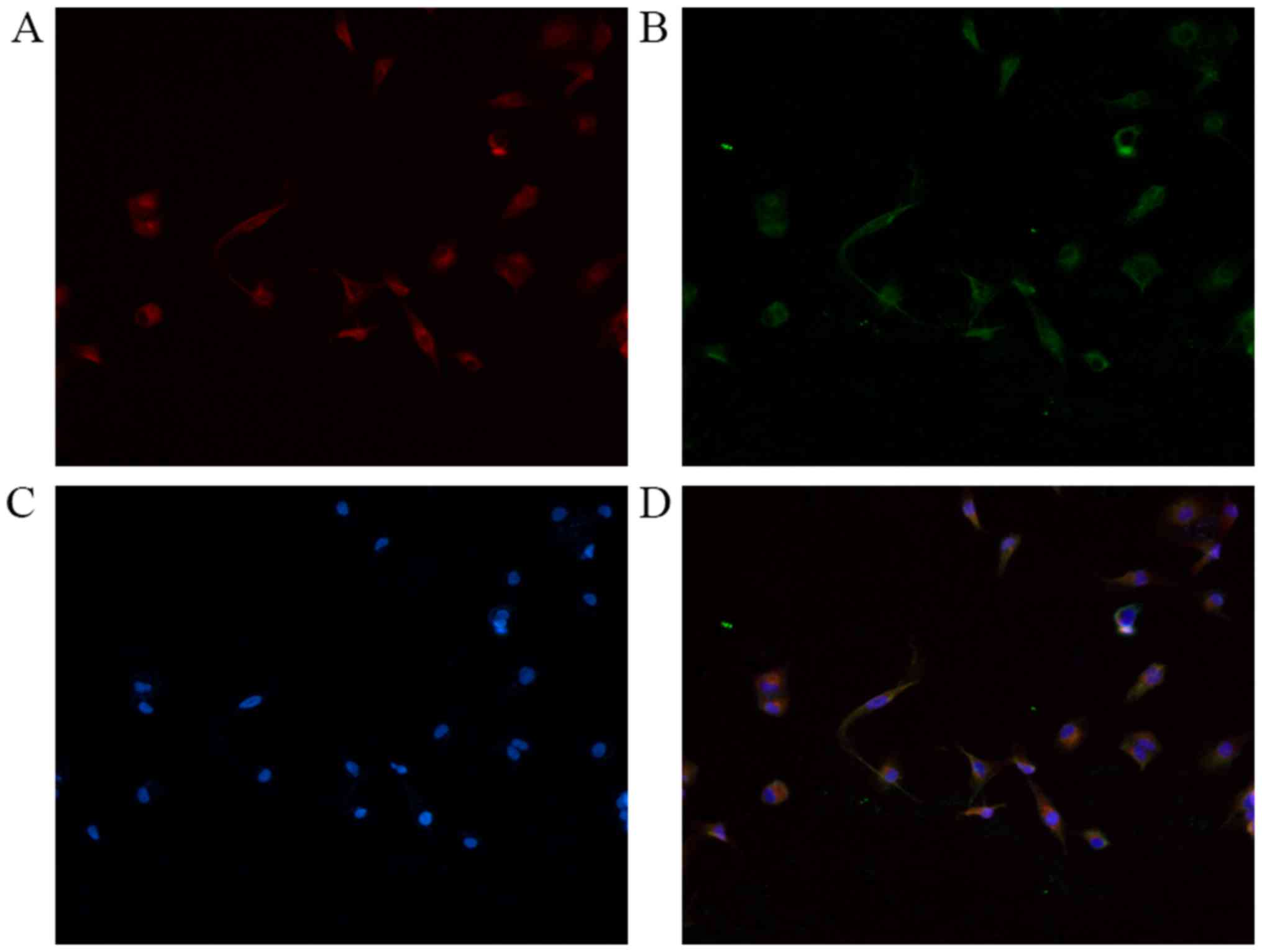
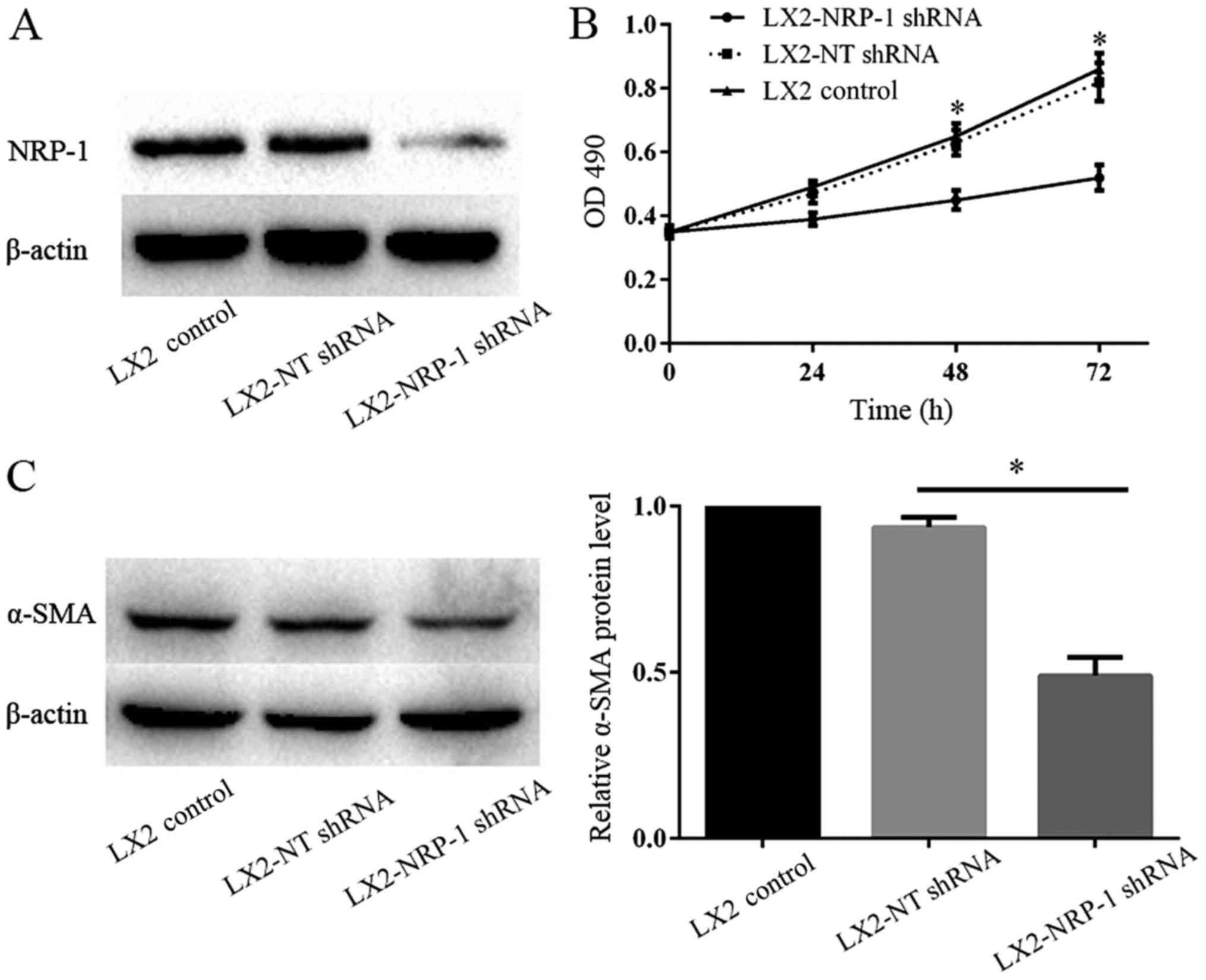
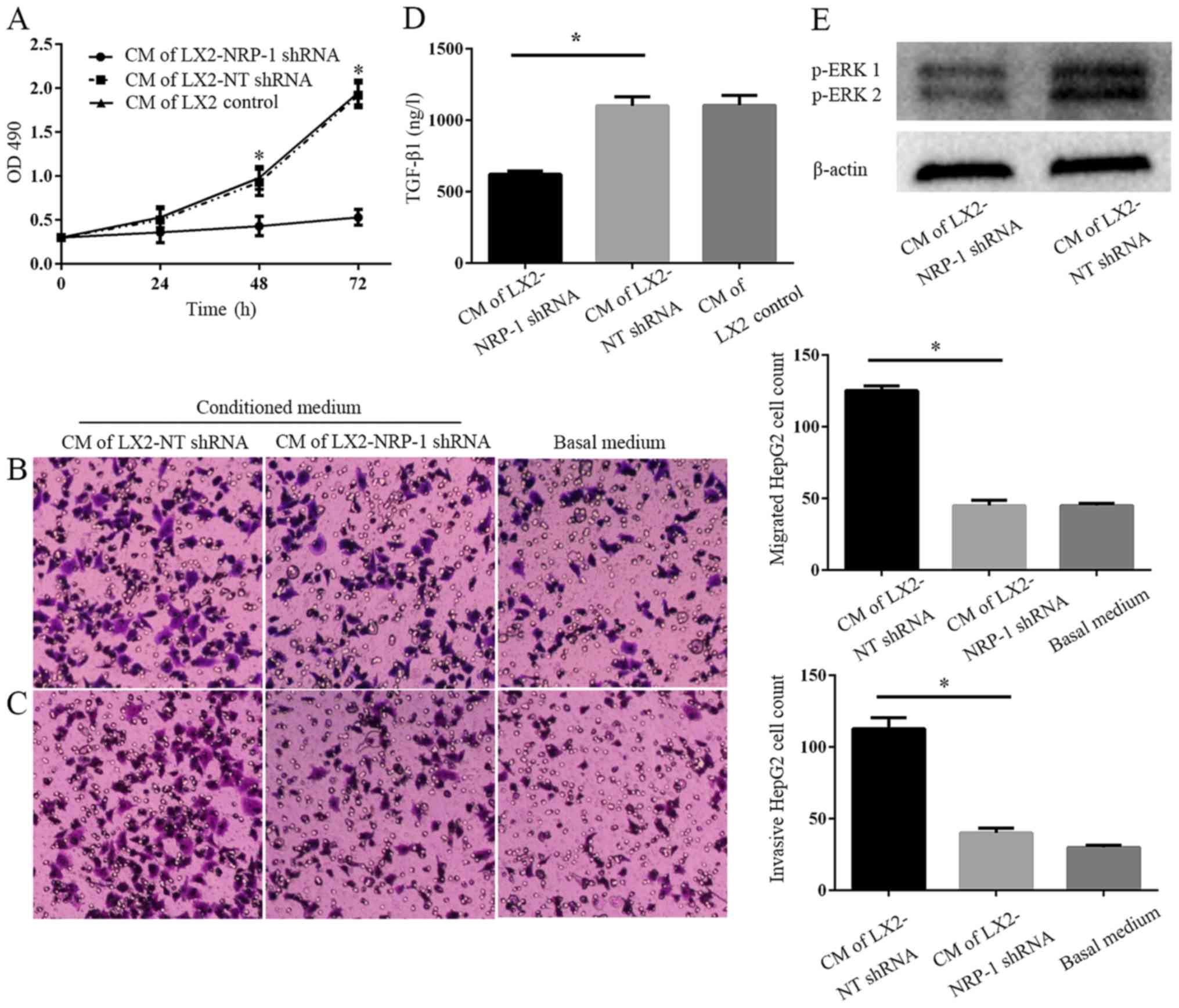
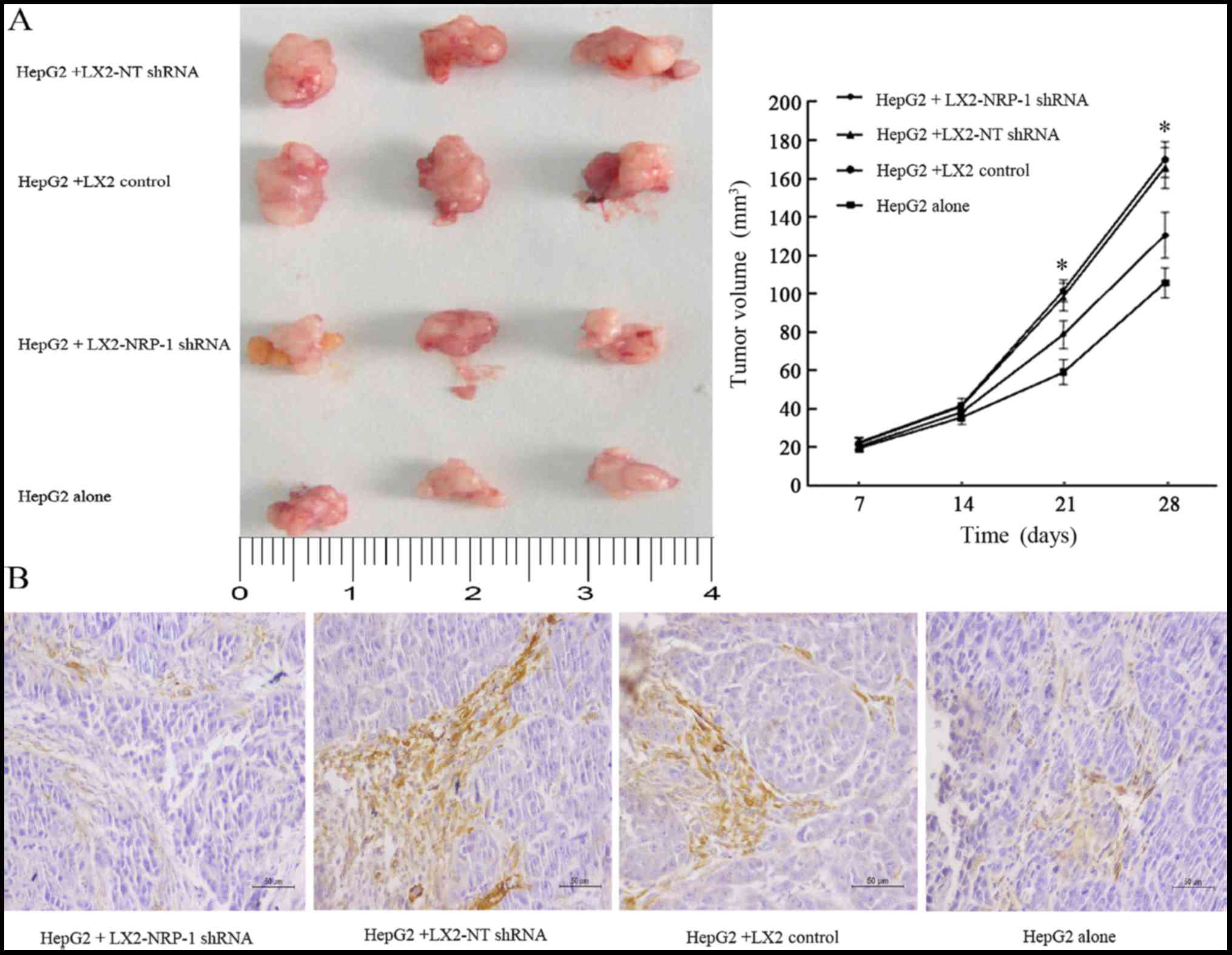
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer
J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Albini A and Sporn MB: The tumour
microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:139–147. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan XL, Fu CJ, Chen L, Qin JH, Zeng Q,
Yuan HF, Nan X, Chen HX, Zhou JN, Lin YL, et al: Mesenchymal stem
cells from primary breast cancer tissue promote cancer
proliferation and enhance mammosphere formation partially via
EGF/EGFR/Akt pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 132:153–164. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coulouarn C, Corlu A, Glaise D, Guénon I,
Thorgeirsson SS and Clément B: Hepatocyte-stellate cell cross-talk
in the liver engenders a permissive inflammatory microenvironment
that drives progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
72:2533–2542. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Zijl F, Mair M, Csiszar A, Schneller
D, Zulehner G, Huber H, Eferl R, Beug H, Dolznig H and Mikulits W:
Hepatic tumor-stroma crosstalk guides epithelial to mesenchymal
transition at the tumor edge. Oncogene. 28:4022–4033. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amann T, Bataille F, Spruss T, Mühlbauer
M, Gäbele E, Schölmerich J, Kiefer P, Bosserhoff AK and Hellerbrand
C: Activated hepatic stellate cells promote tumorigenicity of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:646–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai
YT, Giger RJ and Ginty DD: Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor.
Cell. 90:753–762. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G
and Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor
cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial
growth factor. Cell. 92:735–745. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Jia H and
Zachary I: Neuropilins: Structure, function and role in disease.
Biochem J. 411:211–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zachary IC, Frankel P, Evans IM and
Pellet-Many C: The role of neuropilins in cell signalling. Biochem
Soc Trans. 37:1171–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao S, Yaqoob U, Das A, Shergill U,
Jagavelu K, Huebert RC, Routray C, Abdelmoneim S, Vasdev M, Leof E,
et al: Neuropilin-1 promotes cirrhosis of the rodent and human
liver by enhancing PDGF/TGF-beta signaling in hepatic stellate
cells. J Clin Invest. 120:2379–2394. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng JB, Geng ZM, Chen Q and Wang L:
Construction of recombinant lentiviral vector containing shRNA for
human neuropilin-1 gene. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
28:1200–1203. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tusnio A, Taciak M, Barszcz M,
Paradziej-Łukowicz J, Olędzka I, Wiczkowski W, Szumska M and
Skomiał J: Thermal sterilization affects the content of selected
compounds in diets for laboratory animals. J Anim Feed Sci.
23:351–360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Shen H, Tao J, Song H, Ma L, Wang
L and Geng Z: Effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on
proliferation and invasion of gallbladder carcinoma cells. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 35:1149–1154. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Billadeau DD, Abdelhakim H, Leof E,
Kaibuchi K, Bernabeu C, Bloom GS, Yang L, Boardman L, Shah VH and
Kang N: IQGAP1 suppresses TβRII-mediated myofibroblastic activation
and metastatic growth in liver. J Clin Invest. 123:1138–1156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ,
Lin SM, Yoshida H, Kudo M, Lee JM, Choi BI, Poon RT, et al: Asian
pacific association for the study of the liver consensus
recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int.
4:439–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Junttila MR and de Sauvage FJ: Influence
of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response.
Nature. 501:346–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hernandez-Gea V, Toffanin S, Friedman SL
and Llovet JM: Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
144:512–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carloni V, Luong TV and Rombouts K:
Hepatic stellate cells and extracellular matrix in hepatocellular
carcinoma: More complicated than ever. Liver Int. 34:834–843. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mikula M, Proell V, Fischer AN and
Mikulits W: Activated hepatic stellate cells induce tumor
progression of neoplastic hepatocytes in a TGF-beta dependent
fashion. J Cell Physiol. 209:560–567. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fischer AN, Fuchs E, Mikula M, Huber H,
Beug H and Mikulits W: PDGF essentially links TGF-beta signaling to
nuclear beta-catenin accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Oncogene. 26:3395–3405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta DK, Singh N and Sahu DK: TGF-β
mediated crosstalk between malignant hepatocyte and tumor
microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Growth
Metastasis. 7:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coulouarn C and Clément B: Stellate cells
and the development of liver cancer: Therapeutic potential of
targeting the stroma. J Hepatol. 60:1306–1309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu Y, Lin N, Chen Z and Xu R:
Hypoxia-induced secretion of platelet-derived growth factor-BB by
hepatocellular carcinoma cells increases activated hepatic stellate
cell proliferation, migration and expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor-A. Mol Med Rep. 11:691–697. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Min L, He B and Hui L: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Semin
Cancer Biol. 21:10–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takeishi K, Taketomi A, Shirabe K, Toshima
T, Motomura T, Ikegami T, Yoshizumi T, Sakane F and Maehara Y:
Diacylglycerol kinase alpha enhances hepatocellular carcinoma
progression by activation of Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. J Hepatol.
57:77–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chan LK, Chiu YT, Sze KM and Ng IO:
Tensin4 is up-regulated by EGF-induced ERK1/2 activity and promotes
cell proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:20964–20976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|