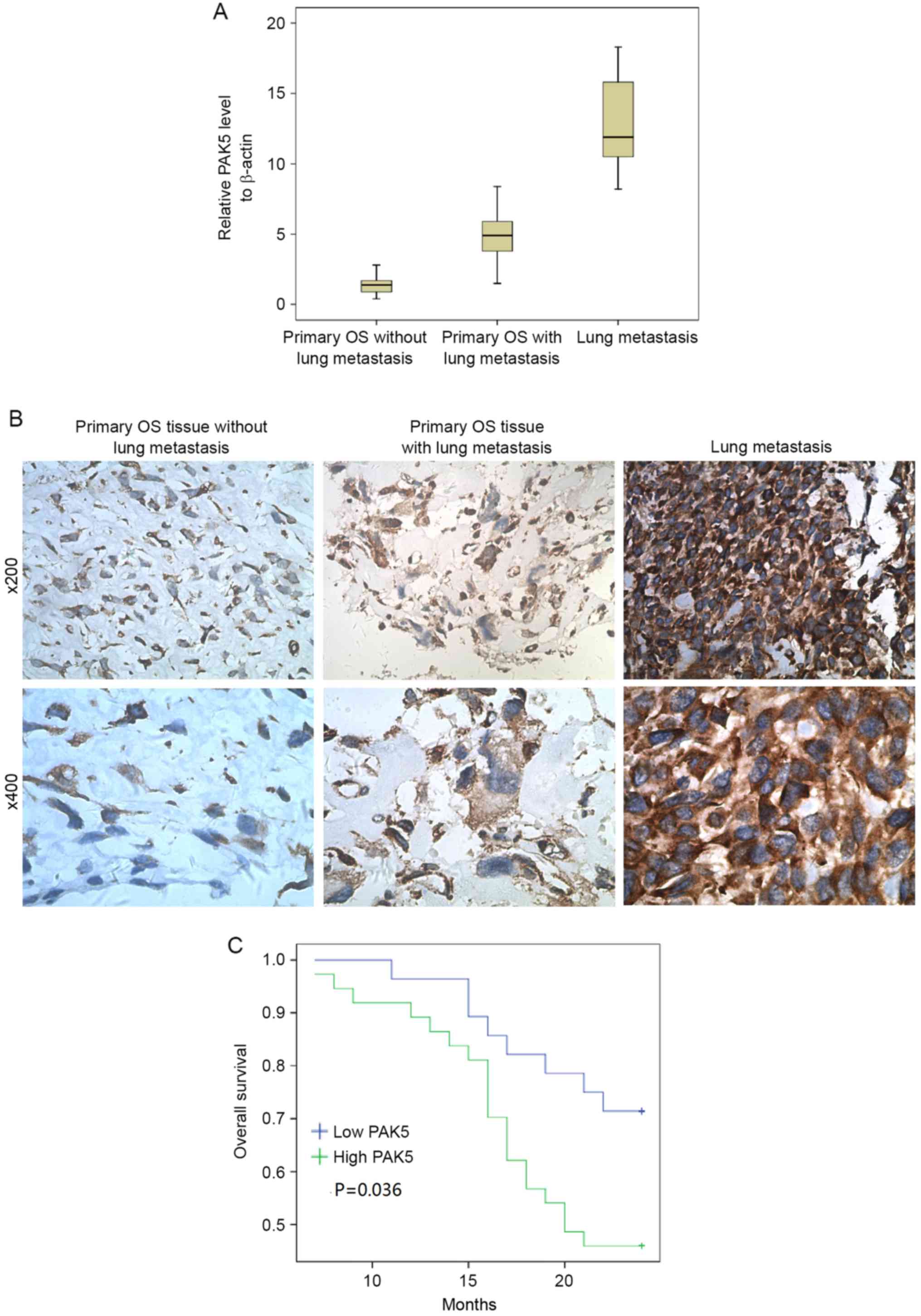
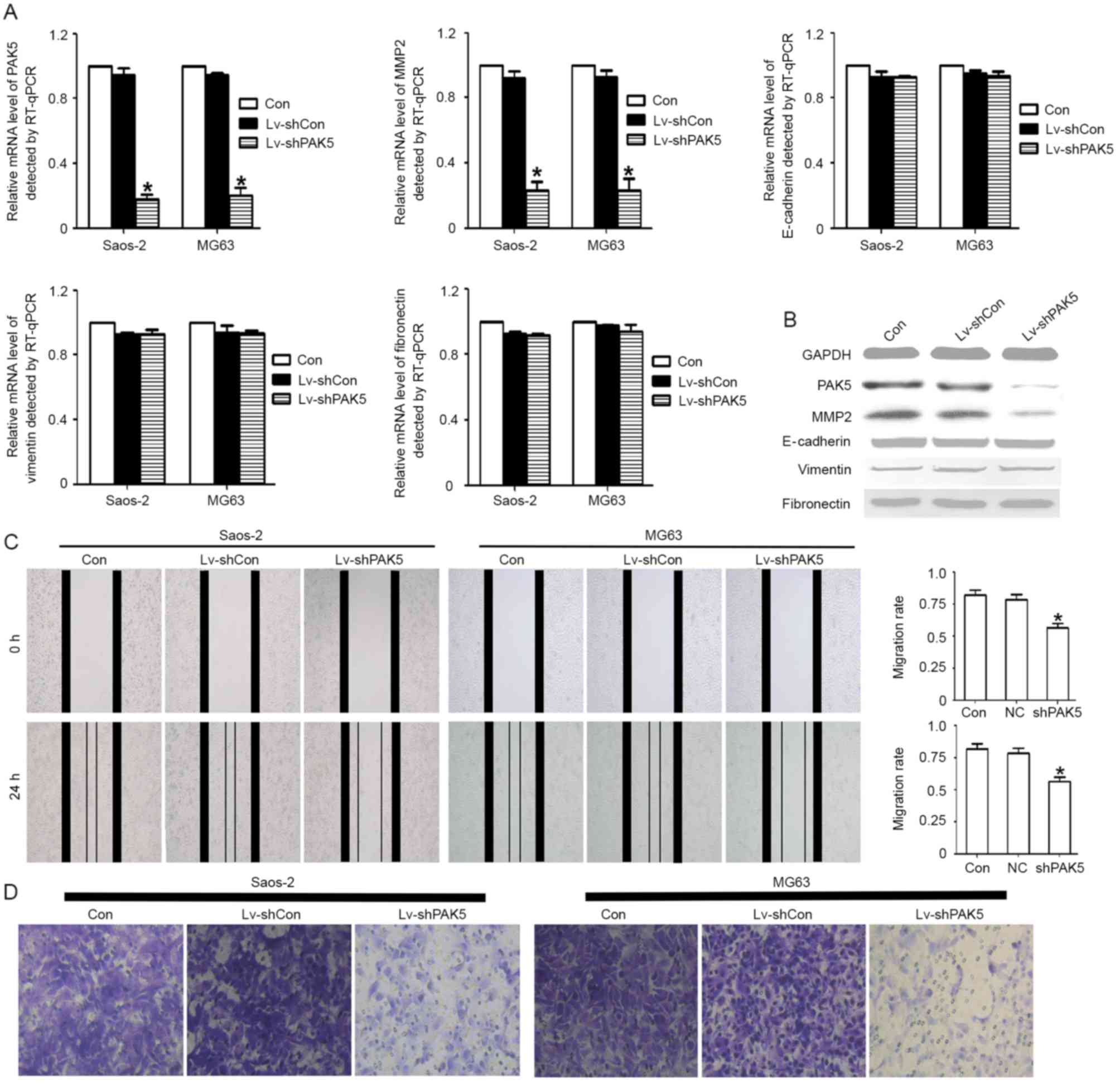
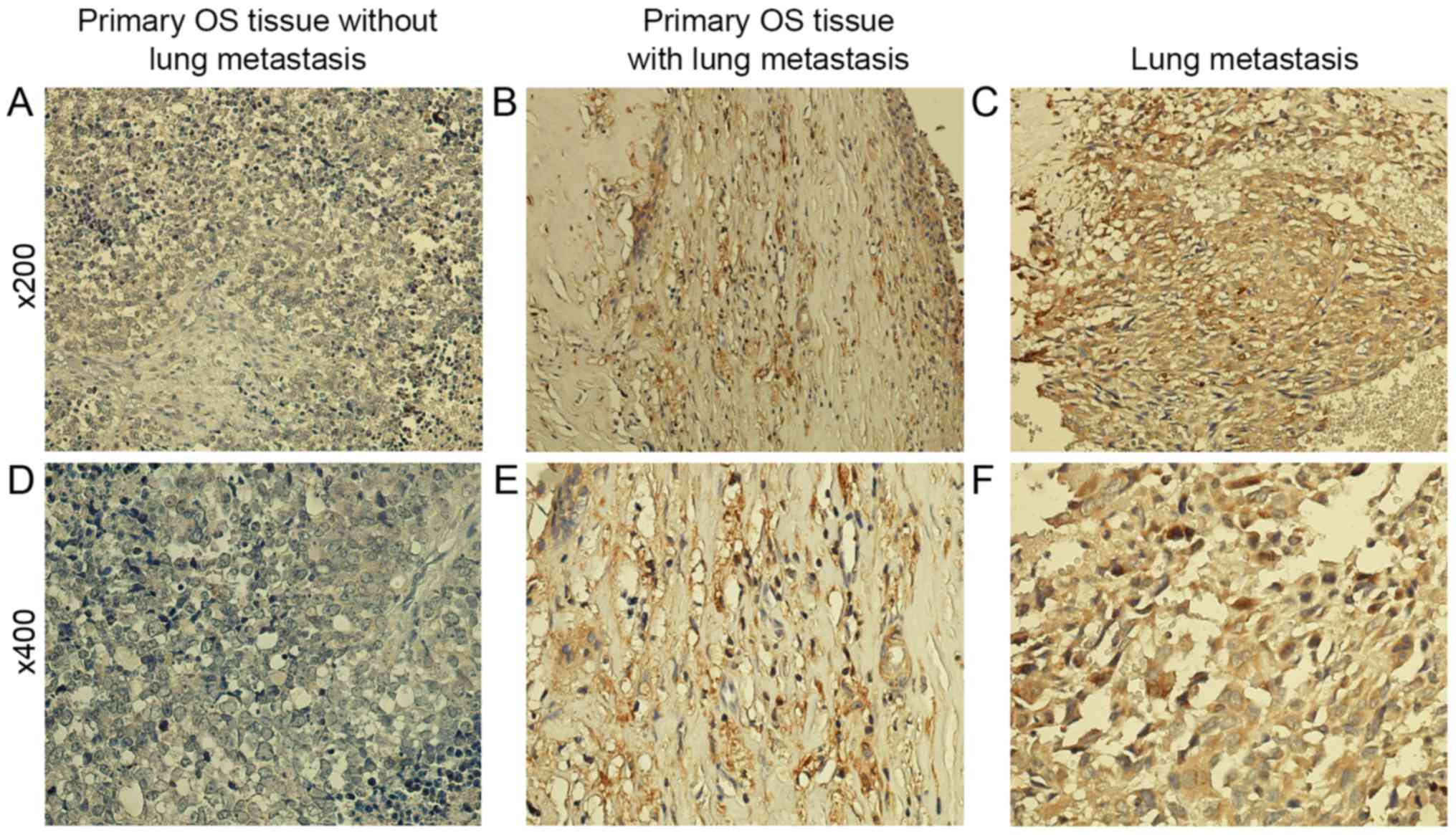
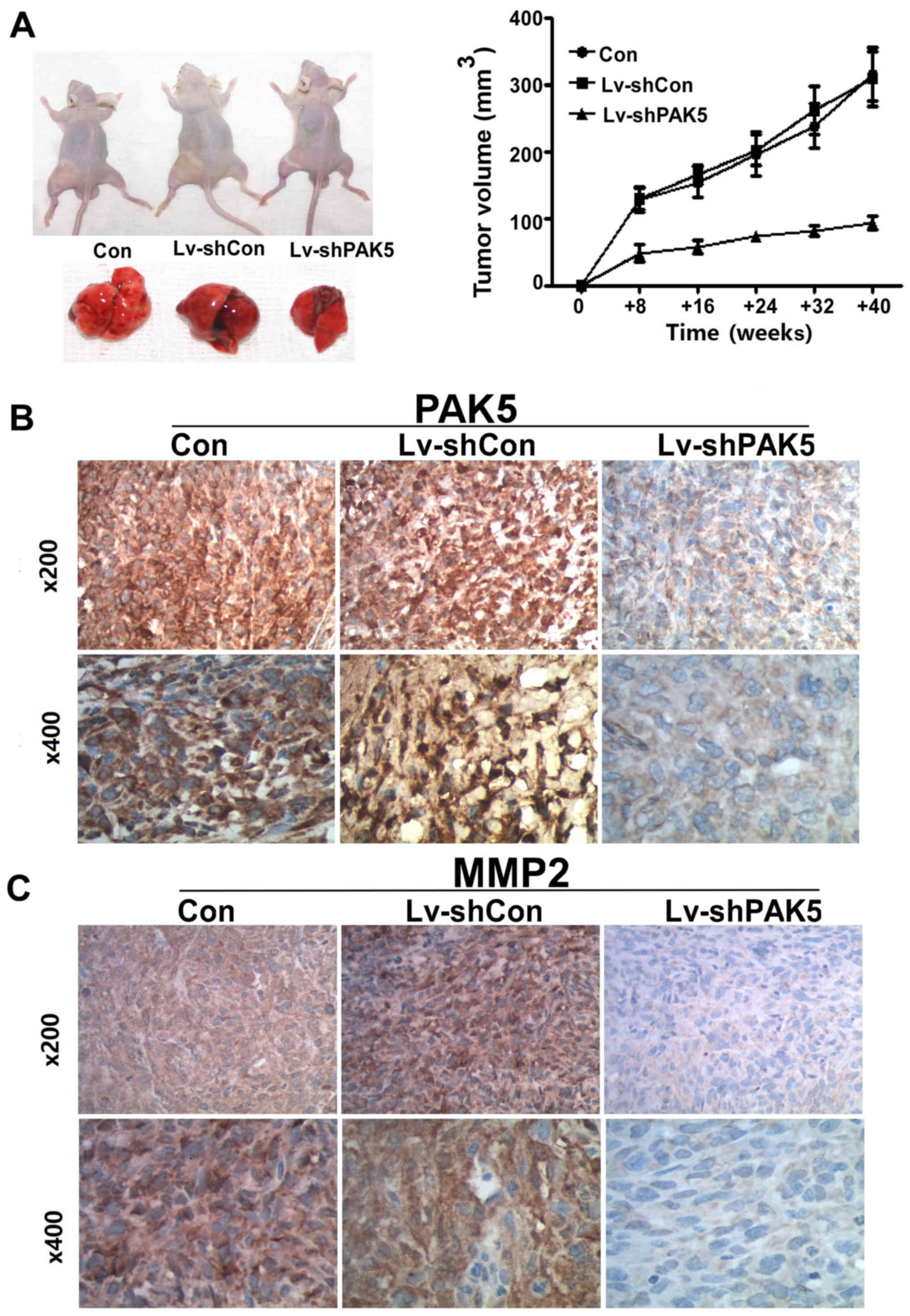
|
1
|
Chi S, Conklin L, Qin J, Meyers P, Huvos
AG, Healey JH and Gorlick R: The patterns of relapse in
osteosarcoma: The Memorial Sloan-Kettering experience. Pediatr
Blood Cancer. 42:46–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crompton BD, Goldsby RE, Weinberg VK,
Feren R, O'Donnell RJ and Ablin AR: Survival after recurrence of
osteosarcoma: A 20-year experience at a single institution. Pediatr
Blood Cancer. 47:255–259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gelderblom H, Jinks RC, Sydes M, Bramwell
VH, van Glabbeke M, Grimer RJ, Hogendoorn PC, McTiernan A, Lewis
IJ, Nooij MA, et al: Survival after recurrent osteosarcoma: Data
from 3 European Osteosarcoma Intergroup (EOI) randomized controlled
trials. Eur J Cancer. 47:895–902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hattinger CM, Pasello M, Ferrari S, Picci
P and Serra M: Emerging drugs for high-grade osteosarcoma. Expert
Opin Emerg Drugs. 15:615–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ray-Coquard I and Le Cesne A: A role for
maintenance therapy in managing sarcoma. Cancer Treat Rev.
38:368–378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sells MA and Chernoff J: Emerging from the
Pak: The p21-activated protein kinase family. Trends Cell Biol.
7:162–167. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM and Gill
GN: Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase
signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.
1:253–259. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marlin JW, Eaton A, Montano GT, Chang YW
and Jakobi R: Elevated p21-activated kinase 2 activity results in
anchorage independent growth and resistance to anticancer
drug-induced cell death. Neoplasia. 11:286–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Somanath PR, Vijai J, Kichina JV, Byzova T
and Kandel ES: The role of PAK-1 in activation of MAP kinase
cascade and oncogenic transformation by Akt. Oncogene.
28:2365–2369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maroto B, Ye MB, von Lohneysen K,
Schnelzer A and Knaus UG: P21-activated kinase is required for
mitotic progression and regulates Plk1. Oncogene. 27:4900–4908.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaffer ZM and Chernoff J: p21-activated
kinases: Three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
34:713–717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dan C, Nath N, Liberto M and Minden A:
PAK5, a new brainspecific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in
N1E-115 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 22:567–577. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cotteret S, Jaffer ZM, Beeser A and
Chernoff J: p21-activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria
and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD. Mol Cell Biol.
23:5526–5539. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Giroux V, Dagorn JC and Iovanna JL: A
review of kinases implicated in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology.
9:738–754. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gong W, An Z, Wang Y, Pan X, Fang W, Jiang
B and Zhang H: P21-activated kinase 5 is overexpressed during
colorectal cancer progression and regulates colorectal carcinoma
cell adhesion and migration. Int J Cancer. 125:548–555. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu J, Li K, Li M, Wu X, Zhang L, Ding Q,
Wu W, Yang J, Mu J, Wen H, et al: A role for p21-activated kinase 7
in the development of gastric cancer. FEBS J. 280:46–55. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang XX, Cheng Q, Zhang SN, Qian HY, Wu
JX, Tian H, Pei DS and Zheng JN: PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling controls
the migration and invasion in breast cancer cell. Tumor Biol.
34:2721–2729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han ZX, Wang XX, Zhang SN, Wu JX, Qian HY,
Wen YY, Tian H, Pei DS and Zheng JN: Downregulation of PAK5
inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the
PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol. 31:234–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin F, Shen Z, Tang LN, Zheng SE, Sun YJ,
Min DL and Yao Y: KLF8 knockdown suppresses proliferation and
invasion in human osteosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:1613–1617.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Ke Q, Shao Y, Zhu G, Li Y, Geng N,
Jin F and Li F: GATA1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer cells through PAK5 oncogenic signaling. Oncotarget.
6:4345–4356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li D, Yao X and Zhang P: The
overexpression of P21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) promotes
paclitaxel-chemoresistance of epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cell
Biochem. 383:191–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhai J, Qu S, Li X, Zhong J, Chen X, Qu Z
and Wu D: miR-129 suppresses tumor cell growth and invasion by
targeting PAK5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:161–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pandey A, Dan I, Kristiansen TZ, Watanabe
NM, Voldby J, Kajikawa E, Khosravi-Far R, Blagoev B and Mann M:
Cloning and characterization of PAK5, a novel member of mammalian
p21-activated kinase-II subfamily that is predominantly expressed
in brain. Oncogene. 21:3939–3948. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Farfalli GL, Albergo JI, Lobos PA, Smith
DE, Streitenberger PD, Rodríguez MG Pallotta and Aponte-Tinao LA:
Osteosarcoma lung metastases. Survival after chemotherapy and
surgery. Medicina (B Aires). 75:87–90. 2015.(In Spanish).
|
|
28
|
Poletajew S, Fus L and Wasiutynski A:
Current concepts onpathogenesis and biology of metastatic
osteosarcoma tumors. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 13:537–545. 2011.(In
English, Polish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Endo-Munoz L, Evdokiou A and Saunders NA:
The role of osteoclasts and tumour-associated macrophages in
osteosarcoma metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826:434–442.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Friedrich P, Ortiz R, Strait K, Fuentes S,
Gamboa Y, Arambú I, Ah-Chu-Sanchez M, London W, Rodríguez-Galindo C
and Antillón-Klussmann F: Pediatric sarcoma in Central America:
Outcomes, challenges, and plans for improvement. Cancer.
119:871–879. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rainusso N, Wang LL and Yustein JT: The
adolescent and oung adult with cancer: State of the art-bone
tumors. Curr Oncol Rep. 15:296–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hiller C, Wegler JL and Forest CP:
Osteosarcoma: Accurately diagnosing this bone-chilling disease.
JAAPA. 29:29–35. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meyers PA: Muramyl tripeptide
(mifamurtide) for the treatment of osteosarcoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:1035–1049. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Seong BK, Lau J, Adderley T, Kee L,
Chaukos D, Pienkowska M, Malkin D, Thorner P and Irwin MS: SATB2
enhances migration and invasion in osteosarcoma by regulating genes
involved in cytoskeletal organization. Oncogene. 34:3582–3592.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lamora A, Talbot J, Bougras G, Amiaud J,
Leduc M, Chesneau J, Taurelle J, Stresing V, Le Deley MC, Heymann
MF, et al: Overexpression of smad7 blocks primary tumor growth and
lung metastasis development in osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5097–5112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luther GA, Lamplot J, Chen X, Rames R,
Wagner ER, Liu X, Parekh A, Huang E, Kim SH, Shen J, et al: IGFBP5
domains exert distinct inhibitory effects on the tumorigenicity and
metastasis of human osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 336:222–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wong LE, Reynolds AB, Dissanayaka NT and
Minden A: p120-catenin is a binding partner and substrate for Group
B Pak kinases. J Cell Biochem. 110:1244–1254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han ZX, Wang XX, Zhang SN, Wu JX, Qian HY,
Wen YY, Tian H, Pei DS and Zheng JN: Downregulation of PAK5
inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the
PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol. 31:234–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu J, Ping W, Zu Y and Sun W:
Correlations of lysyl oxidase with MMP2/MMP9 expression and its
prognostic value in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:6040–6047. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|