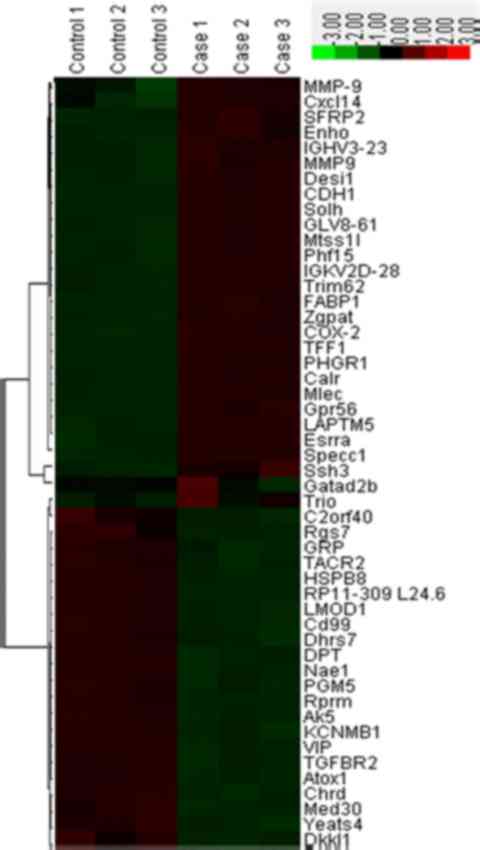
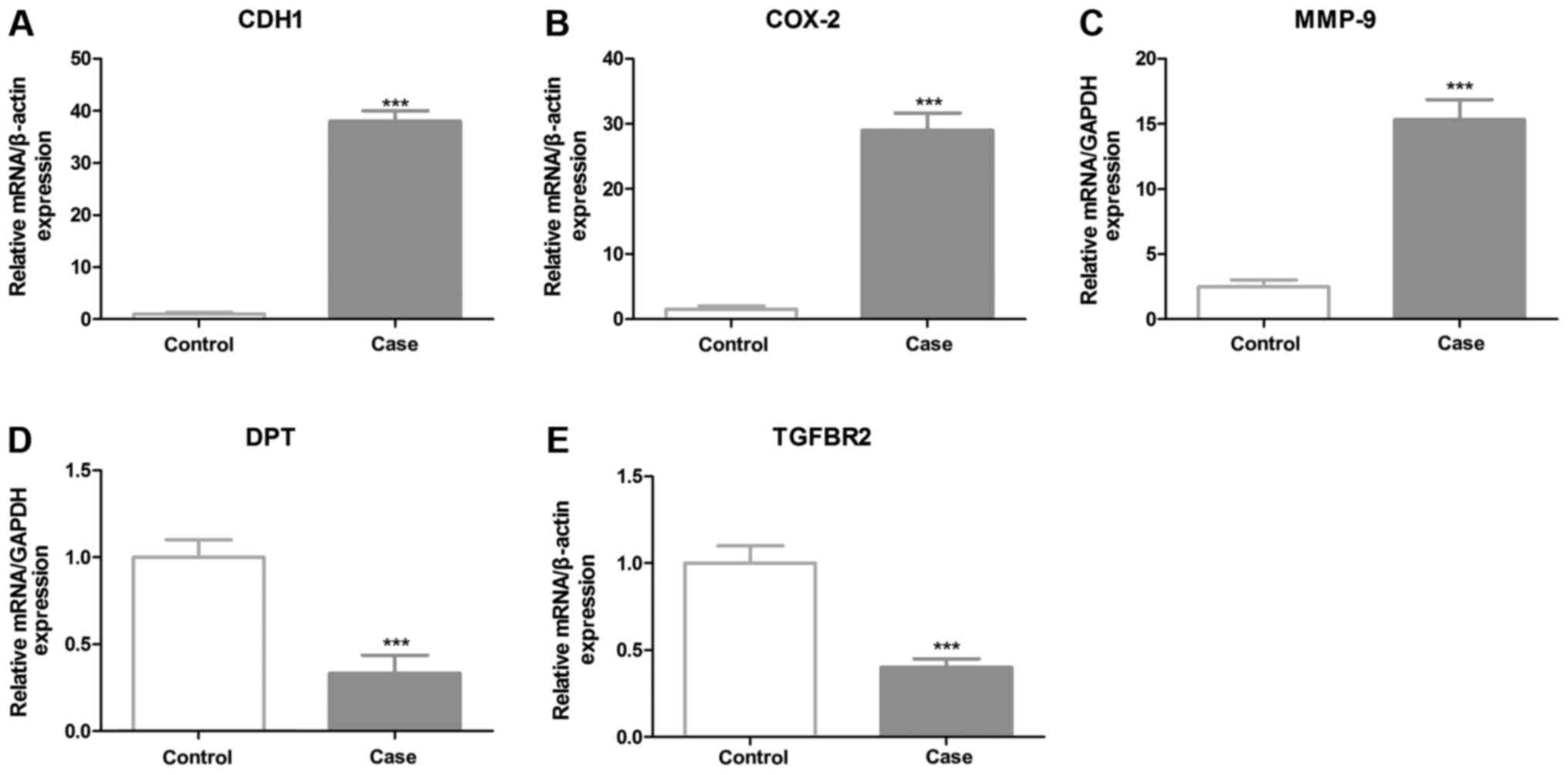
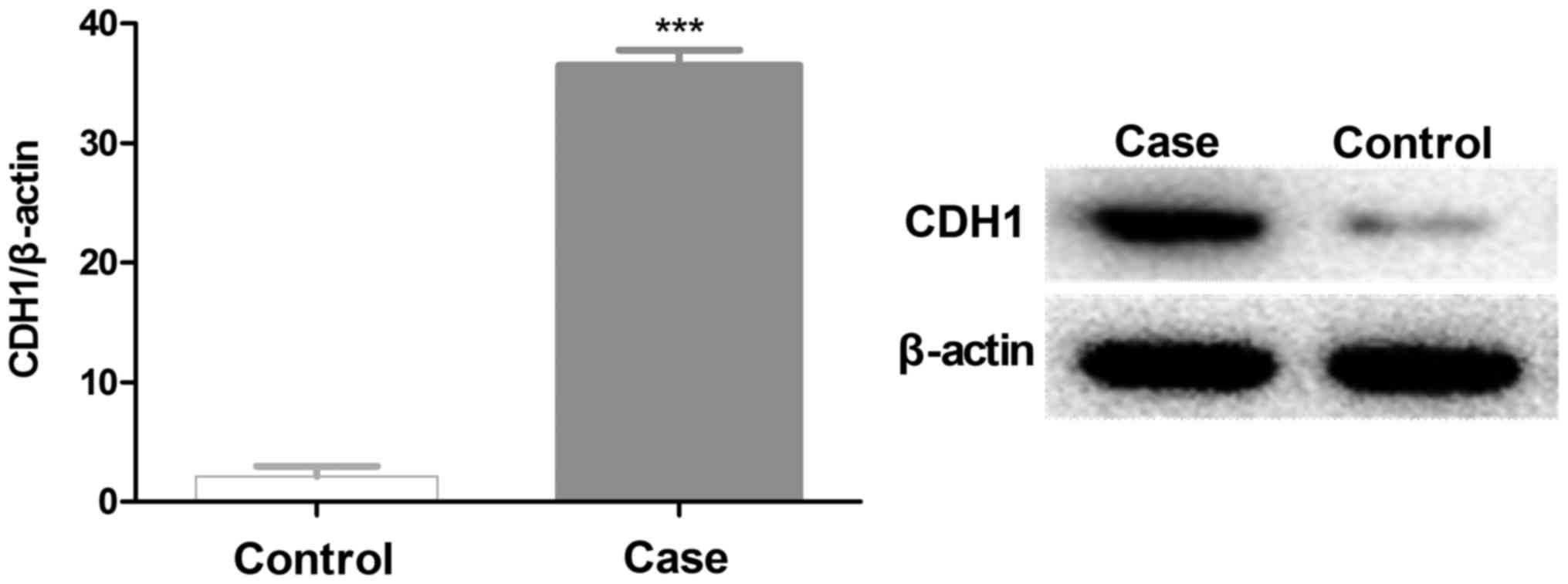
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patel SA: The inferior vena cava (IVC)
syndrome as the initial manifestation of newly diagnosed gastric
adenocarcinoma: A case report. J Med Case Rep. 9:2042015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Du T, Zhang B, Zhang S, Jiang X, Zheng P,
Li J, Yan M, Zhu Z and Liu B: Decreased expression of long
non-coding RNA WT1-AS promotes cell proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:12–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yao K, Nagahama T, Matsui T and Iwashita
A: Detection and characterization of early gastric cancer for
curative endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 25 Suppl
1:S44–S54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Amorim I, Smet A, Alves O, Teixeira S,
Saraiva AL, Taulescu M, Reis C, Haesebrouck F and Gärtner F:
Presence and significance of Helicobacter spp. in the gastric
mucosa of Portuguese dogs. Gut Pathog. 7:122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Delaunoit T: Latest developments and
emerging treatment options in the management of stomach cancer.
Cancer Manag Res. 3:257–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yegin EG, Kani T, Banzragch M, Kalayci C,
Bicakci E and Duman DG: Survival in patients with hypoechoic
muscularis propria lesions suggestive of gastrointestinal stromal
tumors in gastric wall. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 78:12–17.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Printz C: High-throughput sequencing
detects signs of cancer recurrence. Cancer. 118:40972012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Conley A, Minciacchi VR, Lee DH, Knudsen
BS, Karlan BY, Citrigno L, Viglietto G, Tewari M, Freeman MR,
Demichelis F and Di Vizio D: High-throughput sequencing of two
populations of extracellular vesicles provides an mRNA signature
that can be detected in the circulation of breast cancer patients.
RNA Biol. 14:305–316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dallol A, Buhmeida A, Al-Ahwal MS,
Al-Maghrabi J, Bajouh O, Al-Khayyat S, Alam R, Abusanad A, Turki R,
Elaimi A, et al: Clinical significance of frequent somatic
mutations detected by high-throughput targeted sequencing in
archived colorectal cancer samples. J Transl Med. 14:1182016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shaheen MF and Barrette P: Successful
endoscopic management of gastric perforation caused by ingesting a
sharp chicken bone. Int J Surg Case Rep. 9:12–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bonfrate L, Grattagliano I, Palasciano G
and Portincasa P: Dynamic carbon 13 breath tests for the study of
liver function and gastric emptying. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf).
3:12–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo YH, Liang L, He RQ, Wen DY, Deng GF,
Yang H, He Y, Ma W, Cai XY, Chen JQ and Chen G: RNA-sequencing
investigation identifies an effective risk score generated by three
novel lncRNAs for the survival of papillary thyroid cancer
patients. Oncotarget. 8:74139–74158. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tichá V, Jansa P and Tichý M:
Retrospective study of gastric cancer on the basis of Lauren's
classification criteria. Acta Univ Palacki Olomuc Fac Med.
120:193–198. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen QH, Deng W, Li XW, Liu XF, Wang JM,
Wang LF, Xiao N, He Q, Wang YP and Fan YM: Novel CDH1 germline
mutations identified in Chinese gastric cancer patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:909–916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garziera M, Canzonieri V, Cannizzaro R,
Geremia S, Caggiari L, De Zorzi M, Maiero S, Orzes E, Perin T,
Zanussi S, et al: Identification and characterization of CDH1
germline variants in sporadic gastric cancer patients and in
individuals at risk of gastric cancer. PloS One. 8:e770352013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garziera M, De Re V, Geremia S, Seruca R,
Figueiredo J, Melo S, Simões-Correia J, Caggiari L, De Zorzi M,
Canzonieri V, et al: A novel CDH1 germline missense mutation in a
sporadic gastric cancer patient in north-east of Italy. Clin Exp
Med. 13:149–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hansford S, Kaurah P, Li-Chang H, Woo M,
Senz J, Pinheiro H, Schrader KA, Schaeffer DF, Shumansky K,
Zogopoulos G, et al: Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome:
CDH1 mutations and beyond. JAMA Oncol. 1:23–32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
de Campos EC, Ribeiro S, Higashi R,
Manfredini R, Kfouri D and Cavalcanti TC: Hereditary diffuse
gastric cancer: laparoscopic surgical approach associated to rare
mutattion of CDH1 gene. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 28:149–151. 2015.(In
English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van der Post RS, Vogelaar IP, Manders P,
van der Kolk LE, Cats A, van Hest LP, Sijmons R, Aalfs CM, Ausems
MG, Gómez García EB, et al: Accuracy of hereditary diffuse gastric
cancer testing criteria and outcomes in patients with a germline
mutation in CDH1. Gastroenterology. 149:897–906.e19. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Benusiglio PR, Colas C, Rouleau E,
Uhrhammer N, Romero P, Remenieras A, Moretta J, Wang Q, De Pauw A,
Buecher B, et al: Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome:
Improved performances of the 2015 testing criteria for the
identification of probands with a CDH1 germline mutation. J Med
Genet. 52:563–565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lajus TB and Sales RM: CDH1 germ-line
missense mutation identified by multigene sequencing in a family
with no history of diffuse gastric cancer. Gene. 568:215–219. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lynch HT and Lynch JF: Hereditary diffuse
gastric cancer: lifesaving total gastrectomy for CDH1 mutation
carriers. J Med Genet. 47:433–435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsukuma KE, Mullins FM, Dietz L, Zehnder
JL, Ford JM, Chun NM and Schrijver I: Hereditary diffuse gastric
cancer due to a previously undescribed CDH1 splice site mutation.
Hum Pathol. 41:1200–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pinheiro H, Bordeira-Carriço R, Seixas S,
Carvalho J, Senz J, Oliveira P, Inácio P, Gusmão L, Rocha J,
Huntsman D, et al: Allele-specific CDH1 downregulation and
hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 19:943–952. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen B, Zhou Y, Yang P, Liu L, Qin XP and
Wu XT: CDH1-160C>A gene polymorphism is an ethnicity-dependent
risk factor for gastric cancer. Cytokine. 55:266–273. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Kingham K, Ford JM, Rosing J, Van
Dam J, Jeffrey RB, Longacre TA, Chun N, Kurian A and Norton JA: A
prospective study of total gastrectomy for CDH1-positive hereditary
diffuse gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2594–2598. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang P, Luo HS, Li M and Tan SY:
Artesunate inhibits the growth and induces apoptosis of human
gastric cancer cells by downregulating COX-2. Onco Targets Ther.
8:845–854. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu F, Li K, Chen S, Liu Y and Li Y:
Pseudolaric acid B circumvents multidrug resistance phenotype in
human gastric cancer SGC7901/ADR cells by downregulating Cox-2 and
P-gp expression. Cell Biochem Biophys. 71:119–126. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bai YN, Zhang P, Li L, Wang SL, Yao NL,
Zhang RS, Liu Z, Yan D, Zhu YL, Ma JZ, et al: Effect of jianpi
tongluo jiedu recipe on expression levels of COX-2, NF-kappaBp65,
and Bcl-2 in gastric mucosa of patients with precancerous lesions
of gastric cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 35:167–173.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aziz F, Yang X, Wang X and Yan Q: Anti-LeY
antibody enhances therapeutic efficacy of celecoxib against gastric
cancer by downregulation of MAPKs/COX-2 signaling pathway:
Correlation with clinical study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:1221–1235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Chen JQ and Liu JL: COX-2
inhibitors and gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2014:1323202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schildberg C, Abbas M, Merkel S, Agaimy A,
Dimmler A, Schlabrakowski A, Croner R, Leupolt J, Hohenberger W and
Allgayer H: COX-2, TFF1, and Src define better prognosis in young
patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 108:409–413. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Z, Liu M, Liu X, Huang S, Li L, Song
B, Li H, Ren Q, Hu Z, Zhou Y and Qiao L: COX-2 regulates E-cadherin
expression through the NF-kappaB/Snail signaling pathway in gastric
cancer. Int J Mol Med. 32:93–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tseng YC, Tsai YH, Tseng MJ, Hsu KW, Yang
MC, Huang KH, Li AF, Chi CW, Hsieh RH, Ku HH and Yeh TS:
Notch2-induced COX-2 expression enhancing gastric cancer
progression. Mol Carcinog. 51:939–951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Targosz A, Brzozowski T, Pierzchalski P,
Szczyrk U, Ptak-Belowska A, Konturek SJ and Pawlik W: Helicobacter
pylori promotes apoptosis, activates cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and
inhibits heat shock protein HSP70 in gastric cancer epithelial
cells. Inflam Res. 61:955–966. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shin WG, Kim HJ, Cho SJ, Kim HS, Kim KH,
Jang MK, Lee JH and Kim HY: The COX-2-1195AA genotype is associated
with diffuse-type gastric cancer in Korea. Gut Liver. 6:321–327.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun WH, Yu Q, Shen H, Ou XL, Cao DZ, Yu T,
Qian C, Zhu F, Sun YL, Fu XL and Su H: Roles of Helicobacter pylori
infection and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric
carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2809–2813. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zucker S, Lysik RM, DiMassimo BI, Zarrabi
HM, Moll UM, Grimson R, Tickle SP and Docherty AJ: Plasma assay of
gelatinase B: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase complexes in
cancer. Cancer. 76:700–708. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B and
Szmitkowski M: The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and
their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li M, Yang G, Xie B, Babu K and Huang C:
Changes in matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels during progression of
atrial fibrillation. J Int Med Res. 42:224–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Avci N, Ture M, Deligonul A, Cubukcu E,
Olmez OF, Sahinturk S, Topak A, Kurt E, Evrensel T, Şahin AB and
Yakut T: Association and prognostic significance of the functional
−1562C/T polymorphism in the promoter region of MMP-9 in Turkish
patients with gastric cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 21:1243–1247. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xia Y, Lian S, Khoi PN, Yoon HJ, Joo YE,
Chay KO, Kim KK and Do Jung Y: Chrysin inhibits tumor
promoter-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking AP-1 via suppression
of ERK and JNK pathways in gastric cancer cells. PloS One.
10:e01240072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Akter H, Park M, Kwon OS, Song EJ, Park WS
and Kang MJ: Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by
neurotensin promotes cell invasion and migration through ERK
pathway in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:6053–6062. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shan YQ, Ying RC, Zhou CH, Zhu AK, Ye J,
Zhu W, Ju TF and Jin HC: MMP-9 is increased in the pathogenesis of
gastric cancer by the mediation of HER2. Cancer Gene Ther.
22:101–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shimura T, Dagher A, Sachdev M, Ebi M,
Yamada T, Yamada T, Joh T and Moses MA: Urinary ADAM12 and
MMP-9/NGAL complex detect the presence of gastric cancer. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 8:240–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamatoji M, Kasamatsu A, Kouzu Y, Koike H,
Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H and Uzawa K:
Dermatopontin: A potential predictor for metastasis of human oral
cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:2903–2911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Docea AO, Mitruţ P, Grigore D, Pirici D,
Călina DC and Gofiţă E: Immunohistochemical expression of TGF beta
(TGF-beta), TGF beta receptor 1 (TGFBR1), and Ki67 in intestinal
variant of gastric adenocarcinomas. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 53 Suppl
3:S683–S692. 2012.
|
|
51
|
Shinto O, Yashiro M, Kawajiri H, Shimizu
K, Shimizu T, Miwa A and Hirakawa K: Combination effect of a
TGF-beta receptor kinase inhibitor with 5-FU analog S1 on lymph
node metastasis of scirrhous gastric cancer in mice. Cancer Sci.
101:1846–1852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Park D II, Son HJ, Song SY, Choe WH, Lim
YJ, Park SJ, Kim JJ, Kim YH, Rhee PL, Paik SW, et al: Role of
TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta type II receptor in gastric cancer. The
Korean J Intern Med. 17:160–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Park SH, Kim YS, Park BK, Hougaard S and
Kim SJ: Sequence-specific enhancer binding protein is responsible
for the differential expression of ERT/ESX/ELF-3/ESE-1/jen gene in
human gastric cancer cell lines: Implication for the loss of
TGF-beta type II receptor expression. Oncogene. 20:1235–1245. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|