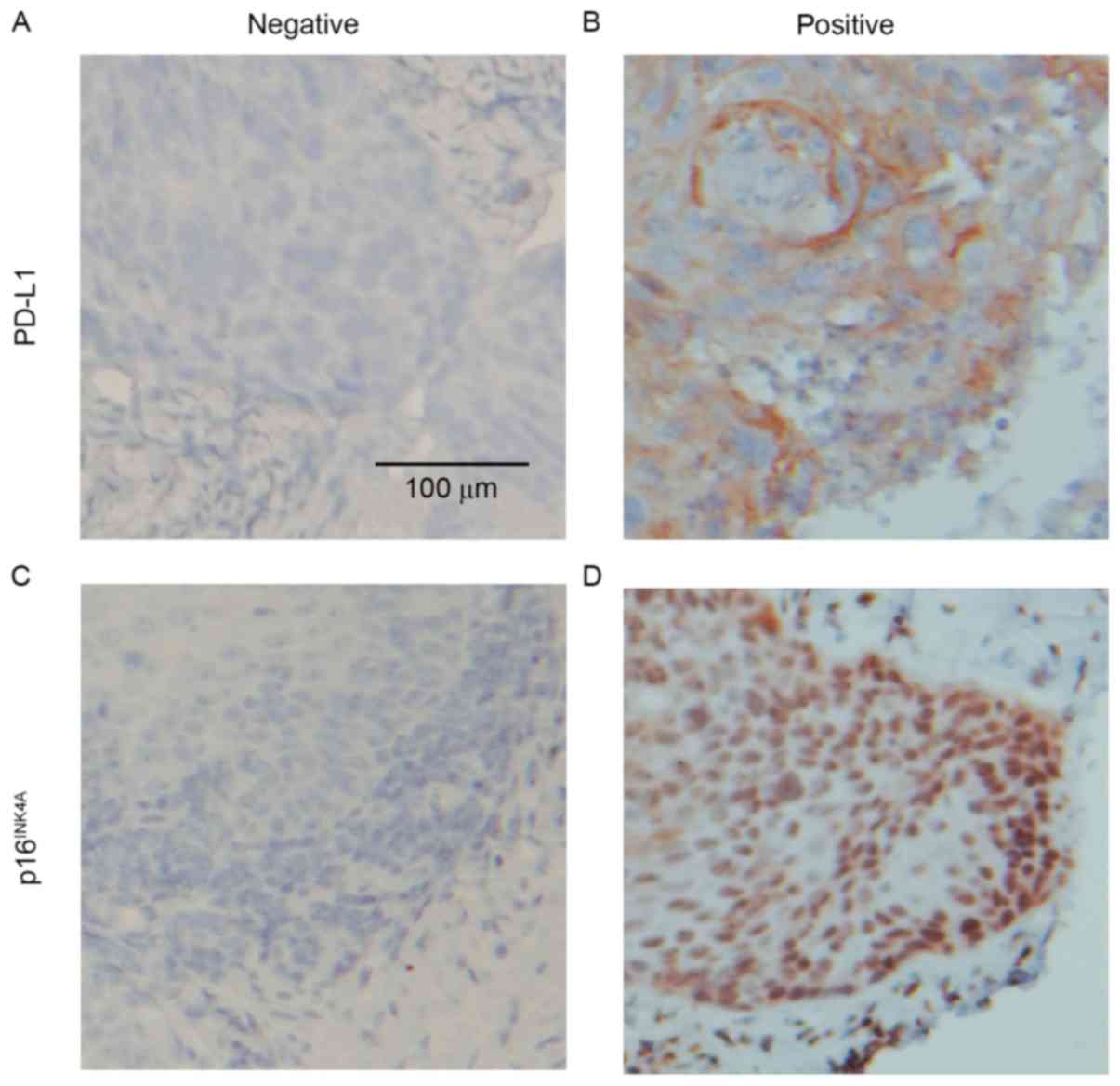
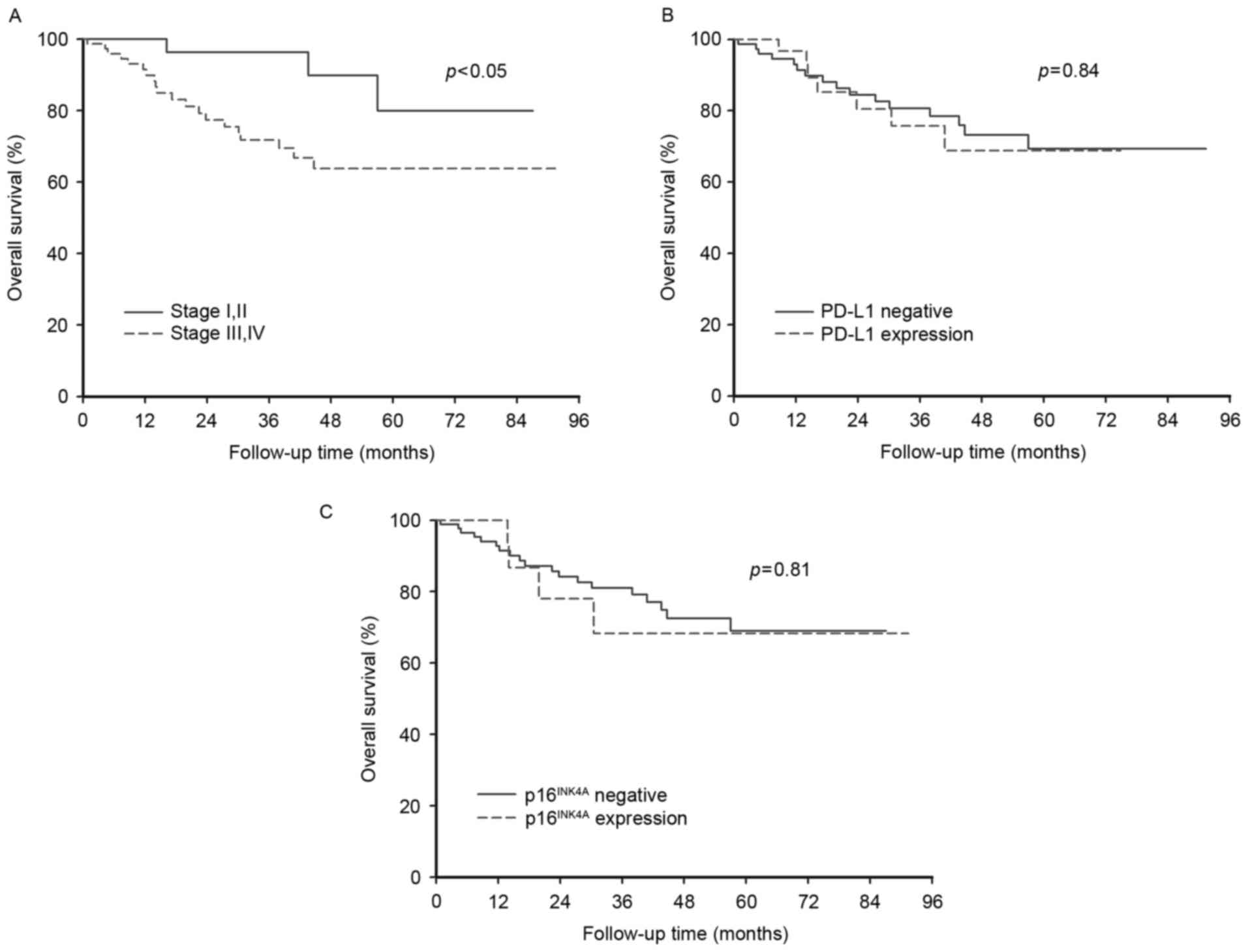
|
1
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kreimer AR, Clifford GM, Boyle P and
Franceschi S: Human papillomavirus types in head and neck squamous
cell carcinomas worldwide: A systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 14:467–475. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R,
Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tân PF, Westra WH, Chung CH, Jordan RC, Lu C,
et al: Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with
oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:24–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rischin D, Young RJ, Fisher R, Fox SB, Le
QT, Peters LJ, Solomon B, Choi J, O'Sullivan B, Kenny LM and
McArthur GA: Prognostic significance of p16INK4A and human
papillomavirus in patients with oropharyngeal cancer treated on
TROG 02.02 phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 28:4142–4148. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hashibe M, Brennan P, Benhamou S,
Castellsague X, Chen C, Curado MP, Dal Maso L, Daudt AW, Fabianova
E, Fernandez L, et al: Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco,
cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck
cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer
epidemiology consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:777–489. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith EM, Wang D, Kim Y, Rubenstein LM,
Lee JH, Haugen TH and Turek LP: P16INK4a expression, human
papillomavirus, and survival in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol.
44:133–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salazar CR, Anayannis N, Smith RV, Wang Y,
Haigentz M Jr, Garg M, Schiff BA, Kawachi N, Elman J, Belbin TJ, et
al: Combined P16 and human papillomavirus testing predicts head and
neck cancer survival. Int J Cancer. 135:2404–2412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen SF, Yu FS, Chang YC, Fu E, Nieh S and
Lin YS: Role of human papillomavirus infection in carcinogenesis of
oral squamous cell carcinoma with evidences of prognostic
association. J Oral Pathol Med. 41:9–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ochi A, Graffeo CS, Zambirinis CP, Rehman
A, Hackman M, Fallon N, Barilla RM, Henning JR, Jamal M, Rao R, et
al: Toll-like receptor 7 regulates pancreatic carcinogenesis in
mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 122:4118–4129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Través PG, Luque A and Hortelano S:
Macrophages, inflammation, and tumor suppressors: ARF, a new player
in the game. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:5687832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong YK, Chang KW, Cheng CY and Liu CJ:
Association of CTLA-4 gene polymorphism with oral squamous cell
carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 35:51–54. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu CJ, Wong YK, Chang KW, Chang HC, Liu
HF and Lee YJ: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism is
associated with susceptibility to oral squamous cell carcinoma. J
Oral Pathol Med. 34:608–612. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen J, Feng Y, Lu L, Wang H, Dai L, Li Y
and Zhang P: Interferon-γ-induced PD-L1 surface expression on human
oral squamous carcinoma via PKD2 signal pathway. Immunobiology.
217:385–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Badoual C, Hans S, Merillon N, Van Ryswick
C, Ravel P, Benhamouda N, Levionnois E, Nizard M, Si-Mohamed A,
Besnier N, et al: PD-1-expressing tumor-infiltrating T cells are a
favorable prognostic biomarker in HPV-associated head and neck
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:128–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lyford-Pike S, Peng S, Young GD, Taube JM,
Westra WH, Akpeng B, Bruno TC, Richmon JD, Wang H, Bishop JA, et
al: Evidence for a role of the PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in immune
resistance of HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 73:1733–1741. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ukpo OC, Thorstad WL and Lewis JS Jr:
B7-H1 expression model for immune evasion in human
papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head
Neck Pathol. 7:113–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zandberg DP and Strome SE: The role of the
PD-L1:PD-1 pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Oral Oncol. 50:627–632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen YW, Kao SY and Yang MH: Analysis of
p16(INK4A) expression of oral squamous cell carcinomas in Taiwan:
Prognostic correlation without relevance to betel quid consumption.
J Surg Oncol. 106:149–154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen YW, Kao SY, Wang HJ and Yang MH:
Histone modification patterns correlate with patient outcome in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 119:4259–4267. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T,
Honjo T and Minato N: Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the
escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1
blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:pp. 12293–12297. 2002;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strome SE, Dong H, Tamura H, Voss SG,
Flies DB, Tamada K, Salomao D, Cheville J, Hirano F, Lin W, et al:
B7-H1 blockade augments adoptive T-cell immunotherapy for squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:6501–6505. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho YA, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, Hong SP and Hong
SD: Relationship between the expressions of PD-L1 and
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Oncol. 47:1148–4253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Braumüller H, Wieder T, Brenner E, Aßmann
S, Hahn M, Alkhaled M, Schilbach K, Essmann F, Kneilling M,
Griessinger C, et al: T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into
senescence. Nature. 494:361–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parry D, Bates S, Mann DJ and Peters G:
Lack of cyclin D-Cdk complexes in Rb-negative cells correlates with
high levels of p16INK4/MTS1 tumour suppressor gene product. Embo J.
14:503–511. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abiko K, Matsumura N, Hamanishi J,
Horikawa N, Murakami R, Yamaguchi K, Yoshioka Y, Baba T, Konishi I
and Mandai M: IFN-γ from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and
promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1501–1509.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Velcheti V, Schalper KA, Carvajal DE,
Anagnostou VK, Syrigos KN, Sznol M, Herbst RS, Gettinger SN, Chen L
and Rimm DL: Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell
lung cancer. Lab Invest. 94:107–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H and Nishimura M: B7-H1 expression on non-small
cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5094–5100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu J, Chen L, Zou L, Yang P, Wu R, Mao Y,
Zhou H, Li R, Wang K, Wang W, et al: MiR-20b, −21, and −130b
inhibit PTEN expression resulting in B7-H1 over-expression in
advanced colorectal cancer. Hum Immunol. 75:348–353. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sage J, Miller AL, Pérez-Mancera PA,
Wysocki JM and Jacks T: Acute mutation of retinoblastoma gene
function is sufficient for cell cycle re-entry. Nature.
424:223–228. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|