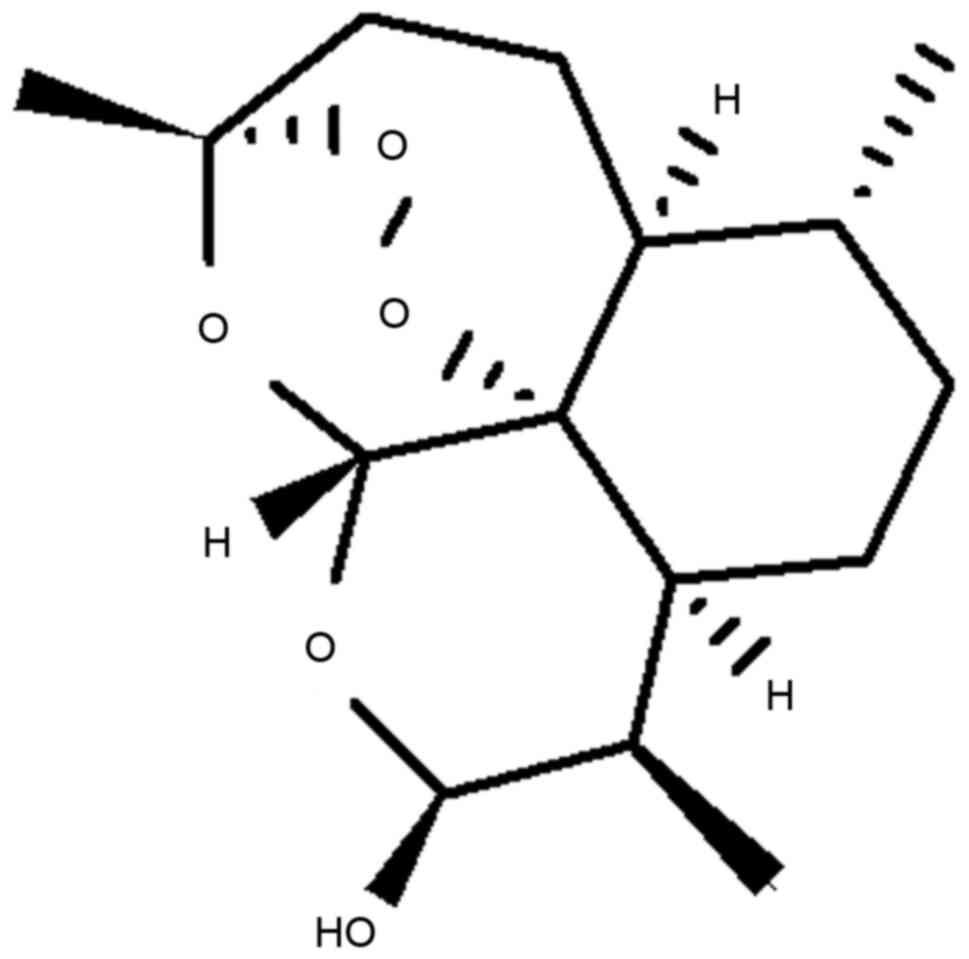
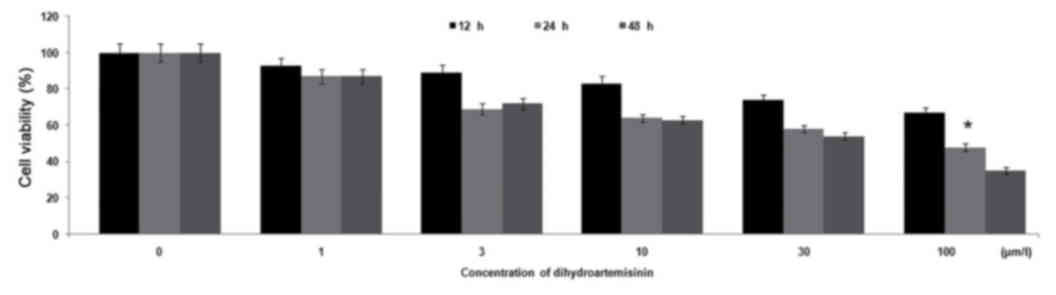
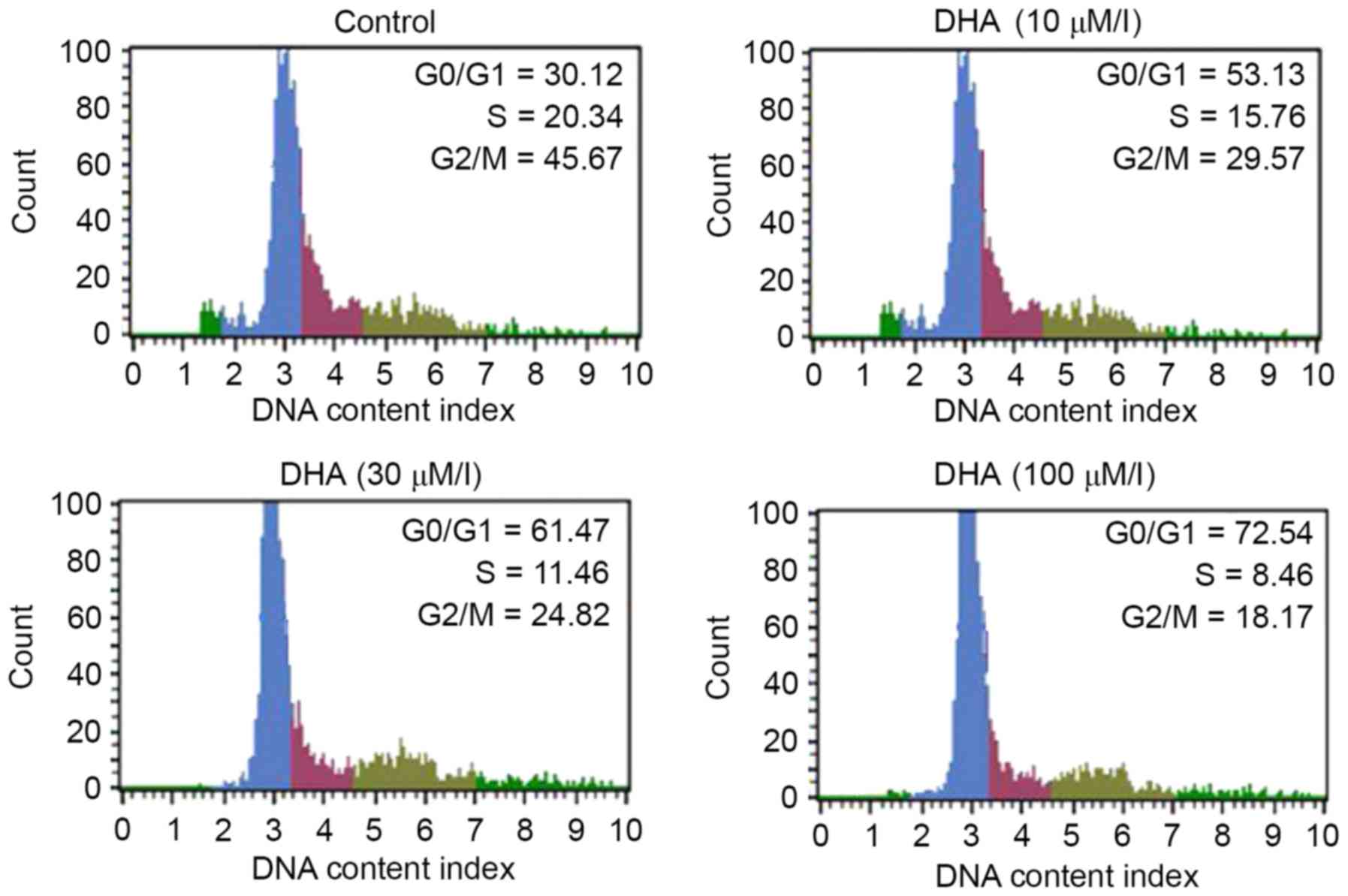
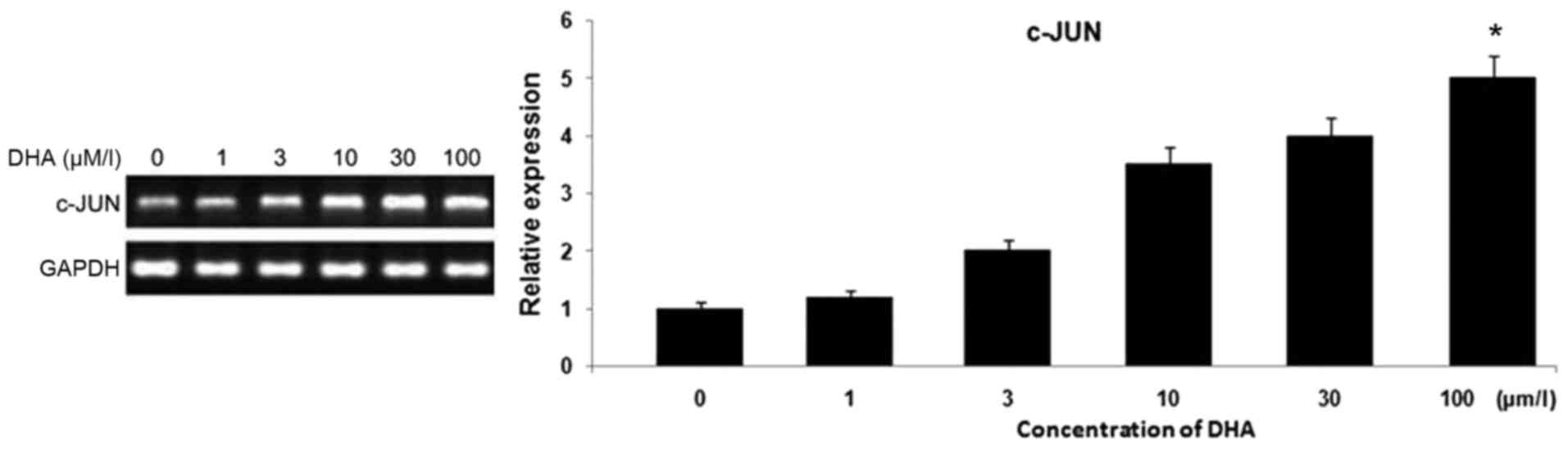
|
1
|
Wei ZL and Wang XH: The development of
NF-κB in the multiple myeloma. Med Res. 36:98–101. 2007.
|
|
2
|
Spisek R, Charalambous A, Mazumder A,
Vesole DH, Jagannath S and Dhodapkar MV: Bortezomib enhances
dendritic cell (DC)-mediated induction of immunity to human myeloma
via exposure of cell surface heat shock protein 90 on dying tumor
cells: Therapeutic implications. Blood. 109:4839–4845. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carocho M and Ferreira IC: A review on
antioxidants, prooxidants and related controversy: Natural and
synthetic compounds, screening and analysis methodologies and
future perspectives. Food Chem Toxicol. 51:15–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mecocci P and Polidori MC: Antioxidant
clinical trials in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:631–638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hawkes CA, Ng V and McLaurin JA: Small
molecule inhibitors of Aβ-aggregation and neurotoxicity. Drug Dev
Res. 70:111–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Joynera PM and Cichewicz RH: Bringing
natural products into the fold-exploring the therapeutic lead
potential of secondary metabolites for the treatment of
protein-misfolding related neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Prod
Rep. 28:26–47. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meshnick SR: Artemisinin: Mechanisms of
action, resistance and toxicity. Int J Parasitol. 32:1655–1660.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O'Neill PM: Medicinal chemistry: A worthy
adversary for malaria. Nature. 430:838–839. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang XJ, Ma ZQ, Zhang WP, Lu YB and Wei
EQ: Dihydroartemisinin exerts cytotoxic effects and inhibits
hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha activation in C6 glioma cells. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 59:849–856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nam W, Tak J, Ryu JK, Jung M, Yook JI, Kim
HJ and Cha IH: Effects of artemisinin and its derivatives on growth
inhibition and apoptosis of oral cancer cells. Head Neck.
29:335–340. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Singh NP and Lai H: Selective toxicity of
dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin toward human breast cancer
cells. Life Sci. 70:49–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen T, Li M, Zhang R and Wang H:
Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis and sensitizes human ovarian
cancer cells to carboplatin therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1358–1370.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang XM and Yang KD: Caspase, JNK/SAPK,
P38 MAPK and apoptosis. Foreign Med Sci (Section Hygiene). 35:5–10.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Du L, Wang FY, Zhang L and Liu T: Advance
in the research of JNK dependent apoptosis. China Trop Med.
18:841–844. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Xiao Y, Yang FQ, Li SP, Gao JL, Hu G, Lao
SC, Conceição EL, Fung KP, Wangl YT and Lee SM: Furanodiene induces
G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through MAPK signaling and
mitochondria-caspase pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:1044–1050. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Papa S, Zazzeroni F, Pham CG, Bubici C and
Franzoso G: Linking JNK signaling to NF-kappaB: A key to survival.
J Cell Sci. 117:5197–5208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murakami Y, Aizu-Yokota E, Sonoda Y, Ohta
S and Kasahara T: Suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress
induced caspase activation and cell death by the over expression of
Bcl-xl or Bcl-2. J Biochem. 141:401–410. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng J, Mao XO, Stevenson FF, Hsu M and
Andersen JK: The herbicide paraquat induces dopaminergic nigral
apoptosis through sustained activation of the JNK pathway. J Biol
Chem. 279:32626–32632. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Largo C, Alvarez S, Saez B, Blesa D,
Martin-Subero JI, González-García I, Brieva JA, Dopazo J, Siebert
R, Calasanz MJ and Cigudosa JC: Identification of overexpressed
genes in frequently gained/amplified chromosome regions in multiple
myeloma. Hematologica. 91:184–191. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Lin HH, Chen JH, Kuo WH and Wang CJ:
Chemopreventive properties of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. on human
gastric carcinoma cells through apoptosis induction and JNK/p38
MAPK signaling activation. Chem Biol Interac. 165:59–75. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Junttila MR, Li SP and Westermarck J:
Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in
the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 22:954–965. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|