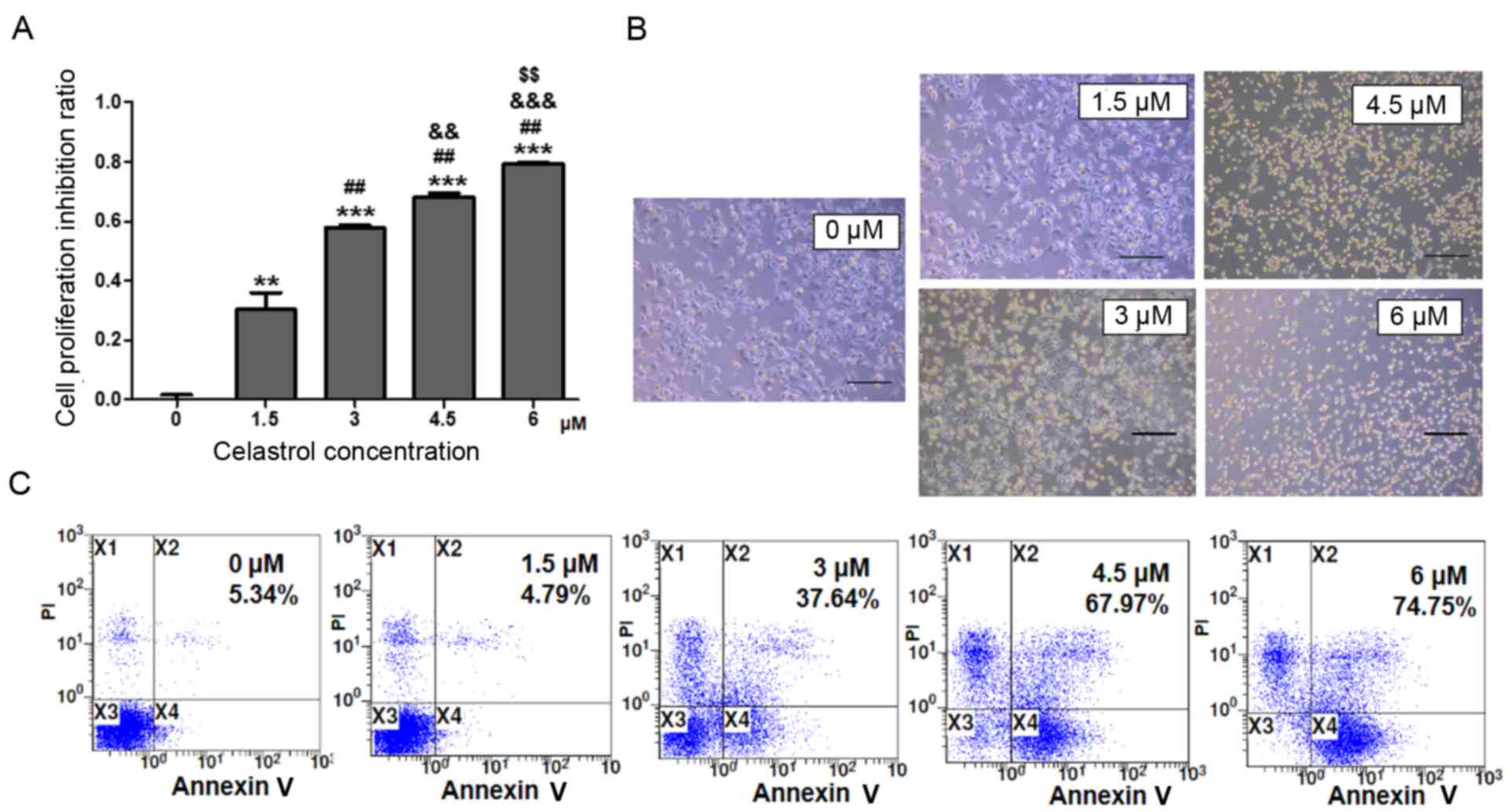
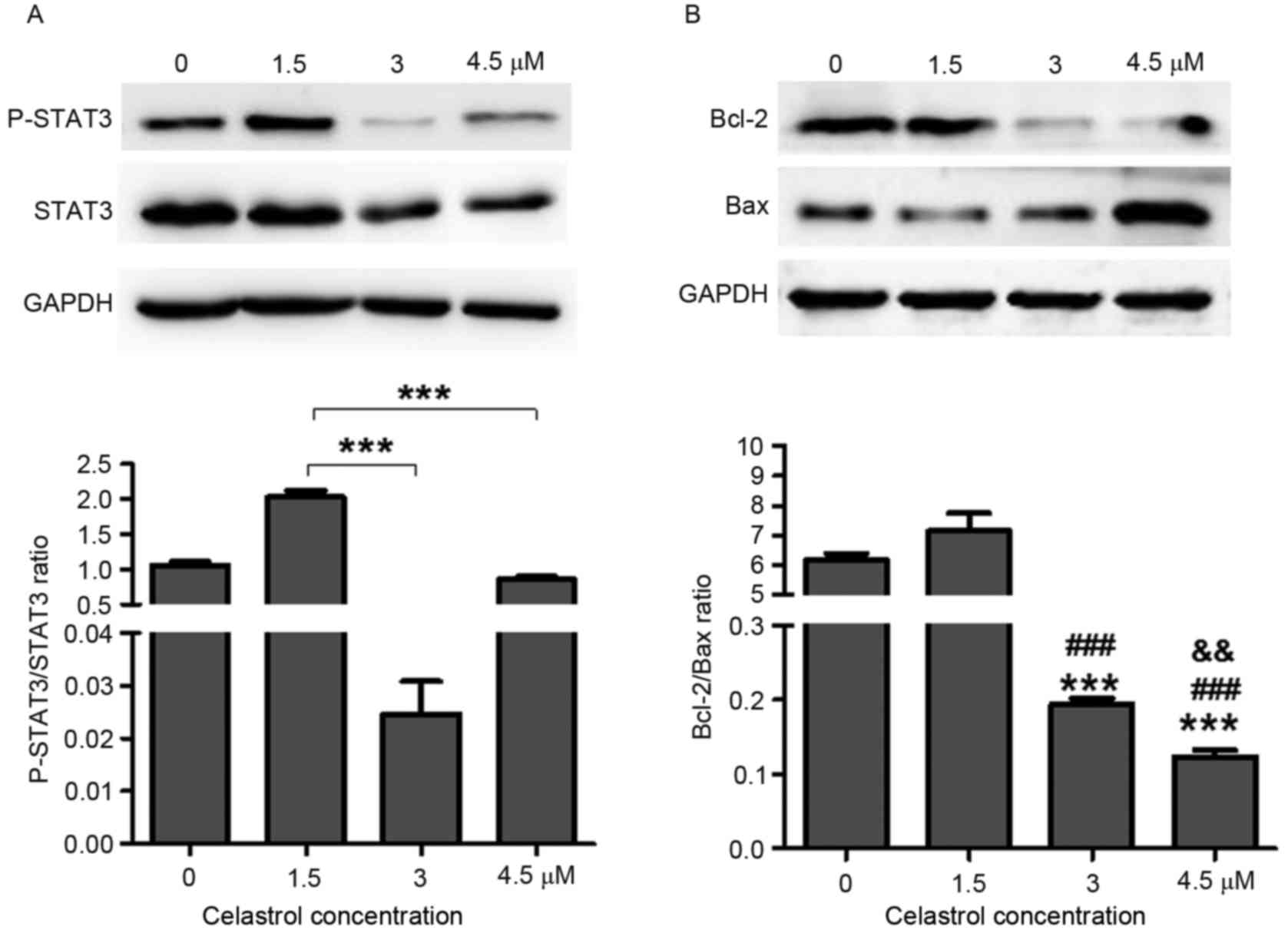
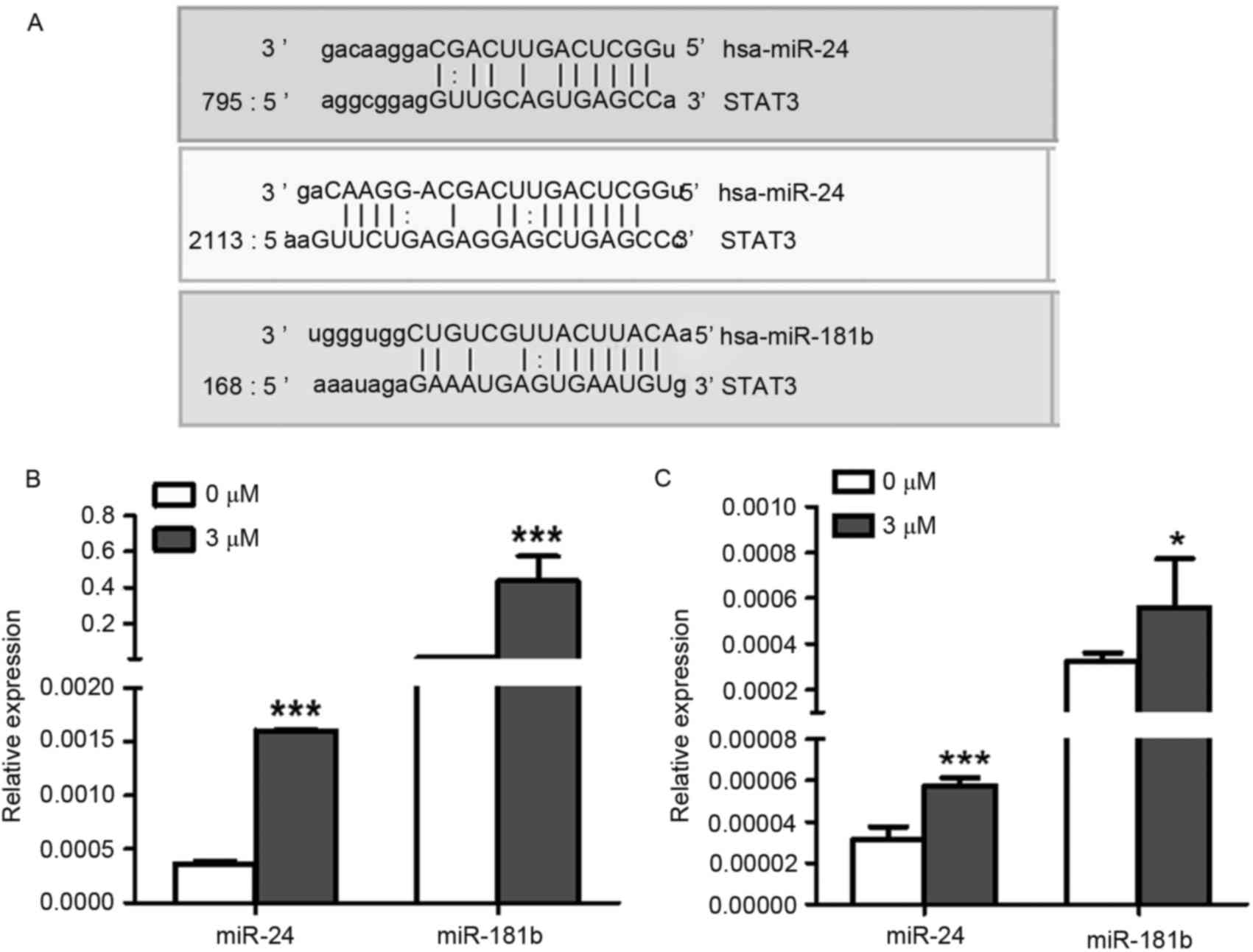
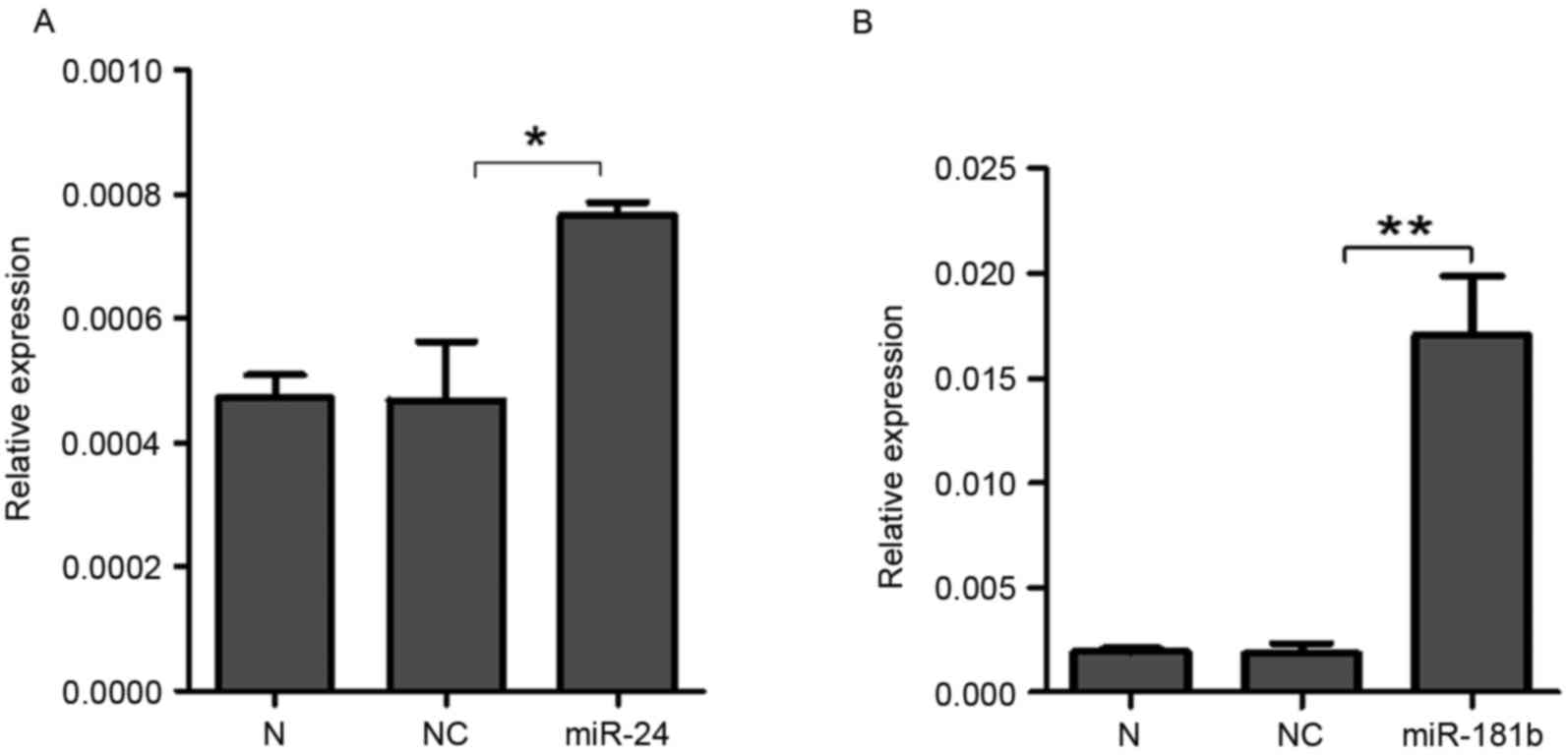
|
1
|
Salminen A, Lehtonen M, Paimela T and
Kaarniranta K: Celastrol: Molecular targets of thunder god vine.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:439–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li-Weber M: Targeting apoptosis pathways
in cancer by Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett. 332:304–312. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Corson TW and Crews CM: Molecular
understanding and modern application of traditional medicines:
Triumphs and trials. Cell. 130:769–774. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Patwardhan B and Mashelkar RA: Traditional
medicine-inspired approaches to drug discovery: Can Ayurveda show
the way forward? Drug Discov Today. 14:804–811. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koehn FE: High impact technologies for
natural products screening. Prog Drug Res. 65:175, 177–210.
2008.
|
|
6
|
Lipsky PE and Tao XL: A potential new
treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: Thunder god vine. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 26:713–723. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Canter PH, Lee HS and Ernst E: A
systematic review of randomised clinical trials of Tripterygium
wilfordii for rheumatoid arthritis. Phytomedicine. 13:371–377.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Petronelli A, Pannitteri G and Testa U:
Triterpenoids as new promising anticancer drugs. Anticancer Drugs.
20:880–892. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK and Aggarwal
BB: Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced
apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting
NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB
activation. Blood. 109:2727–2735. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang H, Chen D, Cui QC, Yuan X and Dou QP:
Celastrol, a triterpene extracted from the Chinese ‘Thunder of God
Vine,’ is a potent proteasome inhibitor and suppresses human
prostate cancer growth in nude mice. Cancer Res. 66:4758–4765.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen M, Rose AE, Doudican N, Osman I and
Orlow SJ: Celastrol synergistically enhances temozolomide
cytotoxicity in melanoma cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1946–1953. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai Y, DeSano JT, Meng Y, Ji Q, Ljungman
M, Lawrence TS and Xu L: Celastrol potentiates radiotherapy by
impairment of DNA damage processing in human prostate cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 74:1217–1225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rajendran P, Li F, Shanmugam MK, Kannaiyan
R, Goh JN, Wong KF, Wang W, Khin E, Tergaonkar V, Kumar AP, et al:
Celastrol suppresses growth and induces apoptosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma through the modulation of STAT3/JAK2
signaling cascade in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
5:631–643. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Costantino L and Barlocco D: STAT 3 as a
target for cancer drug discovery. Curr Med Chem. 15:834–843. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sha M, Ye J, Zhang LX, Luan ZY, Chen YB
and Huang JX: Celastrol induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells
by miR-21 inhibiting PI3K/Akt-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Pharmacology. 93:39–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li H, Li Y, Liu D, Sun H and Liu J:
MiR-224 is critical for celastrol-induced inhibition of migration
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:448–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang PY, Sun YX, Zhang S, Pang M, Zhang
HH, Gao SY, Zhang C, Lv CJ and Xie SY: Let-7c inhibits A549 cell
proliferation through oncogenic TRIB2 related factors. FEBS Lett.
587:2675–26812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
You S, Li R, Park D, Xie M, Sica GL, Cao
Y, Xiao ZQ and Deng X: Disruption of STAT3 by niclosamide reverses
radioresistance of human lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:606–616.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Real PJ, Sierra A, De Juan A, Segovia JC,
Lopez-Vega JM and Fernandez-Luna JL: Resistance to chemotherapy via
Stat3-dependent overexpression of Bcl-2 in metastatic breast cancer
cells. Oncogene. 21:7611–7618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang C, Chi YL, Wang PY, Wang YQ, Zhang
YX, Deng J, Lv CJ and Xie SY: miR-511 and miR-1297 inhibit human
lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by targeting oncogene TRIB2.
PLoS One. 7:e460902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li YJ, Zhang YX, Wang PY, Chi YL, Zhang C,
Ma Y, Lv CJ and Xie SY: Regression of A549 lung cancer tumors by
anti-miR-150 vector. Oncol Rep. 27:129–134. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji N, Li J, Wei ZKong F, Jin H, Chen X, Li
Y and Deng Y: Effect of celastrol on growth inhibition of prostate
cancer cells through the regulation of hERG channel in vitro.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:3084752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
DiSanto JP: Cytokines: Shared receptors,
distinct functions. Curr Biol. 7:R424–R426. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dogan I, Cumaoglu A, Aricioglu A and
Ekmekci A: Inhibition of ErbB2 by herceptin reduces viability and
survival, induces apoptosis and oxidative stress in Calu-3 cell
line. Mol Cell Biochem. 347:41–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian SS, Lamb P, Seidel HM and RBRosen J
Stein: Rapid activation of the STAT3 transcription factor by
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 84:1760–1764.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao Q, Li YY, He WF, Zhang ZZ, Zhou Q, Liu
X, Shen Y and Huang TT: Interplay between microRNAs and the STAT3
signaling pathway in human cancers. Physiol Genomics. 45:1206–1214.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|