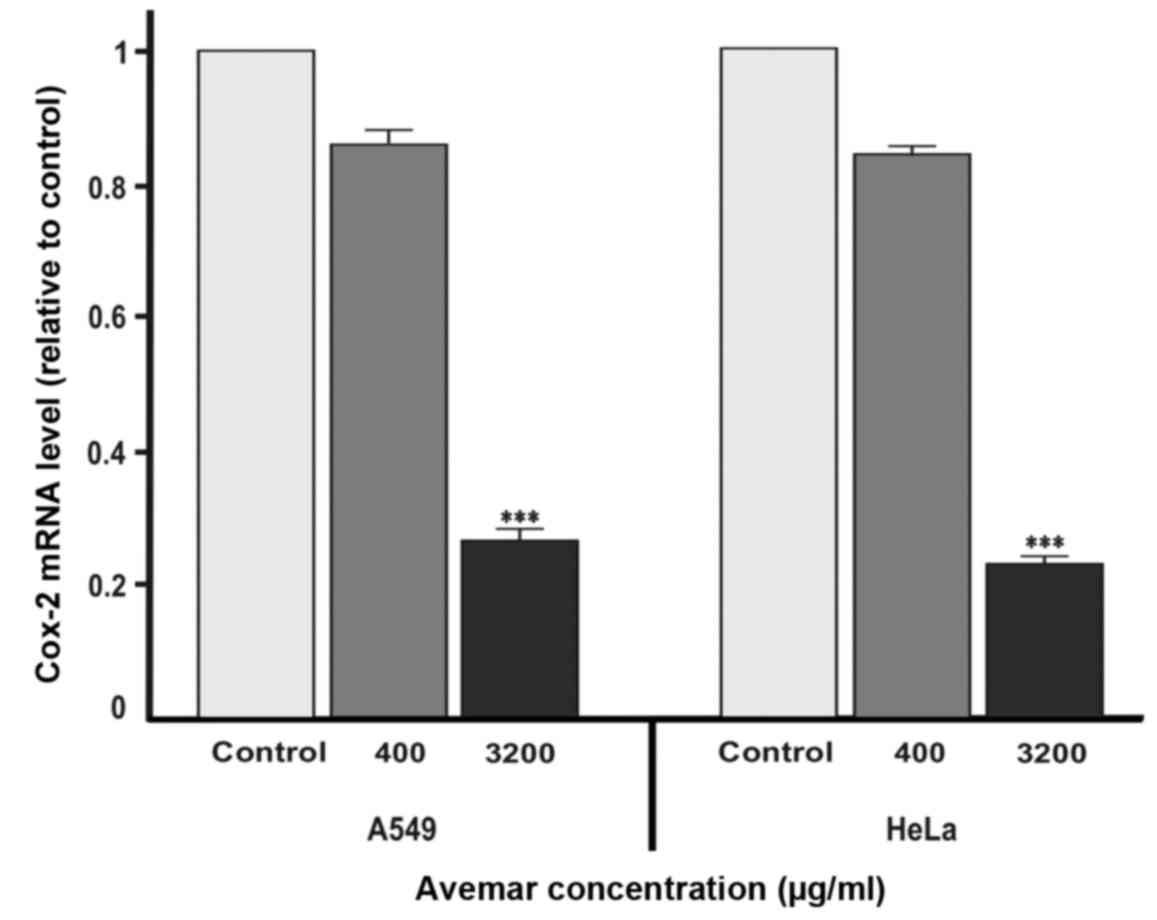
|
1
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adams RH and Alitalo K: Molecular
regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:464–478. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bar J and Onn A: Combined
anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic strategies for cancer.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 9:701–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao Y: Angiogenesis: What can it offer for
future medicine? Exp Cell Res. 316:1304–1308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mueller T and Voigt W: Fermented wheat
germ extract-nutrional supplement or anticancer drug? Nutrition.
10:892011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Saiko P, Ozsvar-Kozma M, Madlener S,
Bernhaus A, Lackner A, Grusch M, Horvath Z, Krupitza G, Jaeger W,
Ammer K, et al: Avemar, a nontoxic fermented wheat germ extract,
induces apoptosis and inhibits ribonucleotide reductase in human
HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 250:323–328. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hidvégi M, Ráso E, Tömösközi-Farkas R,
Paku S, Lapis K and Szende B: Effect of Avemar and Avemar C vitamin
C on tumor growth and metastasis in experimental animals.
Anticancer Res. 18:2353–2358. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Demidov LV, Manziuk LV, Kharkevitch GY,
Pirogova NA and Artamonova EV: Adjuvant fermented wheat germ
extract (Avemar) nutraceutical improves survival of high-risk skin
melanoma patients: A randomized, pilot, phase II clinical study
with a 7-year follow-up. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 23:477–482.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heimbach JT, Sebestyen G, Semjen G and
Kennepohl E: Safety studies regarding a standardized extract of
fermented wheat germ. Int J Toxicol. 26:253–259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Comin-Anduix B, Boros LG, Marin S, Boren
J, Callol-Masot C, Centelles JJ, Torres JL, Angell N, Bassilian S
and Cascante M: Fermented wheat germ extract inhibits
glycolysis/pentose cycle enzymes and induces apoptosis through
Poly(ADP-riboz) polymerase activation in Jurkat T-cell leukemia
tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 277:46408–46414. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mueller T, Jordan K and Voigt W: Promising
cytotoxic profile of fermented wheat germ extract
(Avemar®) in human cancer cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 30:422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garami M, Schuler D, Babosa M, Borgulya G,
Hauser P, Müller J, Paksy A, Szabó E, Hidvégi M and Fekete G:
Fermented wheat germ extract reduces chemotherapy-induced febrile
neutropenia in pediatric cancer patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
26:631–635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jakab F, Shoenfeld Y, Balogh A, Nichelatti
M, Hoffmann A, Kahán Z, Lapis K, Mayer A, Sápy P, Szentpétery F, et
al: A medical nutriment has supportive value in the treatment of
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 89:465–469. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang JY, Xiao X, Dong Y, Wu J, Yao F and
Zhou XH: Effect of fermented wheat germ extract with lactobacillus
plantarum dy-1 on HT-29 cell proliferation and apoptosis. J Agric
Food Chem. 63:2449–2457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koyama S, Sato E, Tsukadaira A, Haniuda M,
Numanami H, Kurai M, Nagai S and Izumi T: Vascular endothelial
growth factor mRNA and protein expression in airway epithelial cell
lines in vitro. Eur Respir J. 20:1449–1456. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Şimşek E, Aydemir EA, İmir N, Koçak O,
Kuruoğlu A and Fışkın K: Dimethyl sulfoxide-caused changes in pro-
and anti-angiogenic factor levels could contribute to an
anti-angiogenic response in HeLa cells. Neuropeptides. 53:37–43.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hidvégi M, Rásό E, Tömösközi-Farkas R,
Lapis K and Szende B: Effect of MSC on the immune response of mice.
Immunopharmacology. 41:183–186. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szende B, Rásό E, Hidvégi M, Tömösköziné
FR, Paku S, Prónai L, Bocsi J and Lapis K: A new
benzoquinone-containing antimetastatic product. Orv Hetil.
139:2893–2897. 1998.(In Hungarian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hidvégi M, Rásό E, Tömösközi-Farkas R,
Szende B, Paku S, Prónai L, Bocsi J and Lapis K: MSC, a new
benzoquinone-containing natural product with antimetastatic effect.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 14:277–289. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taleb H, Morris RK, Withycombe CE,
Maddocks SE and Kanekanian AD: Date syrup derived polyphenols
attenuate angiogenic responses and exhibits anti-inflammatory
activity mediated by VEGF and COX-2 expression in endothelial
cells. Nutr Res. 36:636–647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Costa C, Incio J and Soares R:
Angiogenesis and chronic inflammation: Cause or consequence?
Angiogenesis. 10:149–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scoditti E, Calabriso N, Massaro M,
Pellegrino M, Storelli C, Martines G, De Caterina R and Carluccio
MA: Mediterranean diet polyphenols reduce inflammatory angiogenesis
through MMP-9 and Cox-2 inhibition in human vascular endothelial
cells: A potentially protective mechanism in atherosclerotic
vascular disease and cancer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 527:81–89. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Corona G, Deiana M, Incani A, Vauzour D,
Dessí MA and Spencer JP: Inhibition of p38/CREB phosphorylation and
Cox-2 expression by olive oil polyphenols underlies their
anti-proliferative effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
362:606–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Medda R, Lyros O, Schmidt JL, Jovanovic N,
Nie L, Link BJ, Otterson MF, Stoner GD, Shaker R and Rafiee P:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic effect of black raspberry
extract on human esophageal and intestinal microvascular
endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 97:167–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsujii M, Kawano S and DuBois RN:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells increases
metastatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3336–3340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sawaoka H, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Gunawan ES,
Sasaki Y, Kawano S and Hori M: Cyclooxygenase inhibitors suppress
angiogenesis and reduce tumor growth in vivo. Lab Invest.
79:1469–1477. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Braunhut SJ and Moses MA: Retinoids
modulate endothelial cell production of matrix-degrading proteases
and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP). J Biol Chem.
269:13472–13479. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vacca A, Moretti S, Ribatti D, Pellegrino
A, Pimpinelli N, Bianchi B, Bonifazi E, Ria R, Serio G and Dammacco
F: Progression of mycosis fungoides is associated with changes in
angiogenesis and expression of the matrix metalloproteinases 2 and
9. Eur J Cancer. 33:1685–1692. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Yoshida H, Yoshioka T,
Nishimoto H and Itohara S: Reduced angiogenesis and tumor
progression in gelatinase A-deficient mice. Cancer Res.
58:1048–1051. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang MD, Chang WS, Tsaia CW, Wang MF, Chan
YC, Chan KC, Lu MC, Kao AW, Hsu CM and Bau DT: Inhibitory effects
of AVEMAR on proliferation and metastasis of oral cancer cells.
Nutr Cancer. 68:473–480. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|