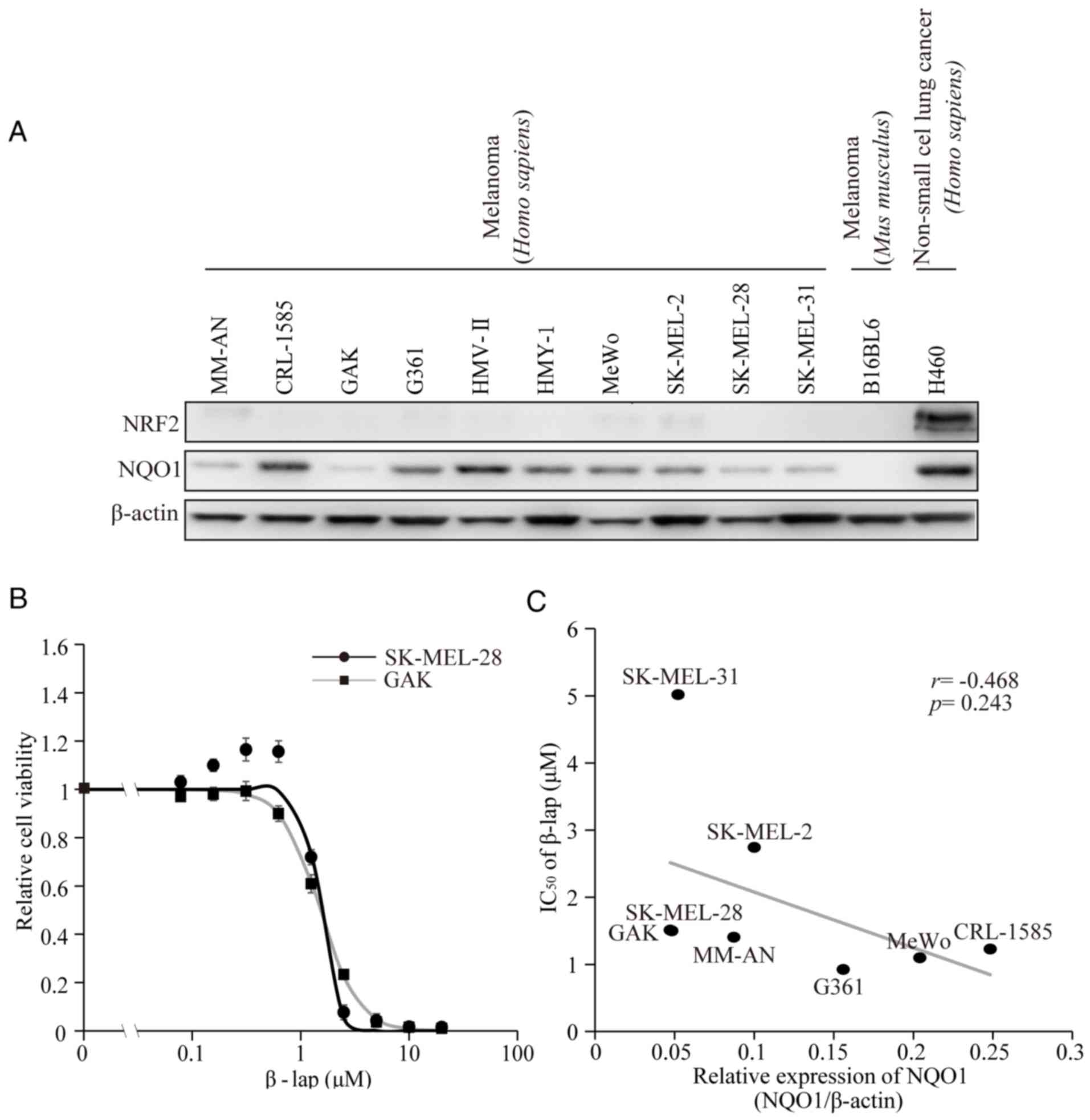
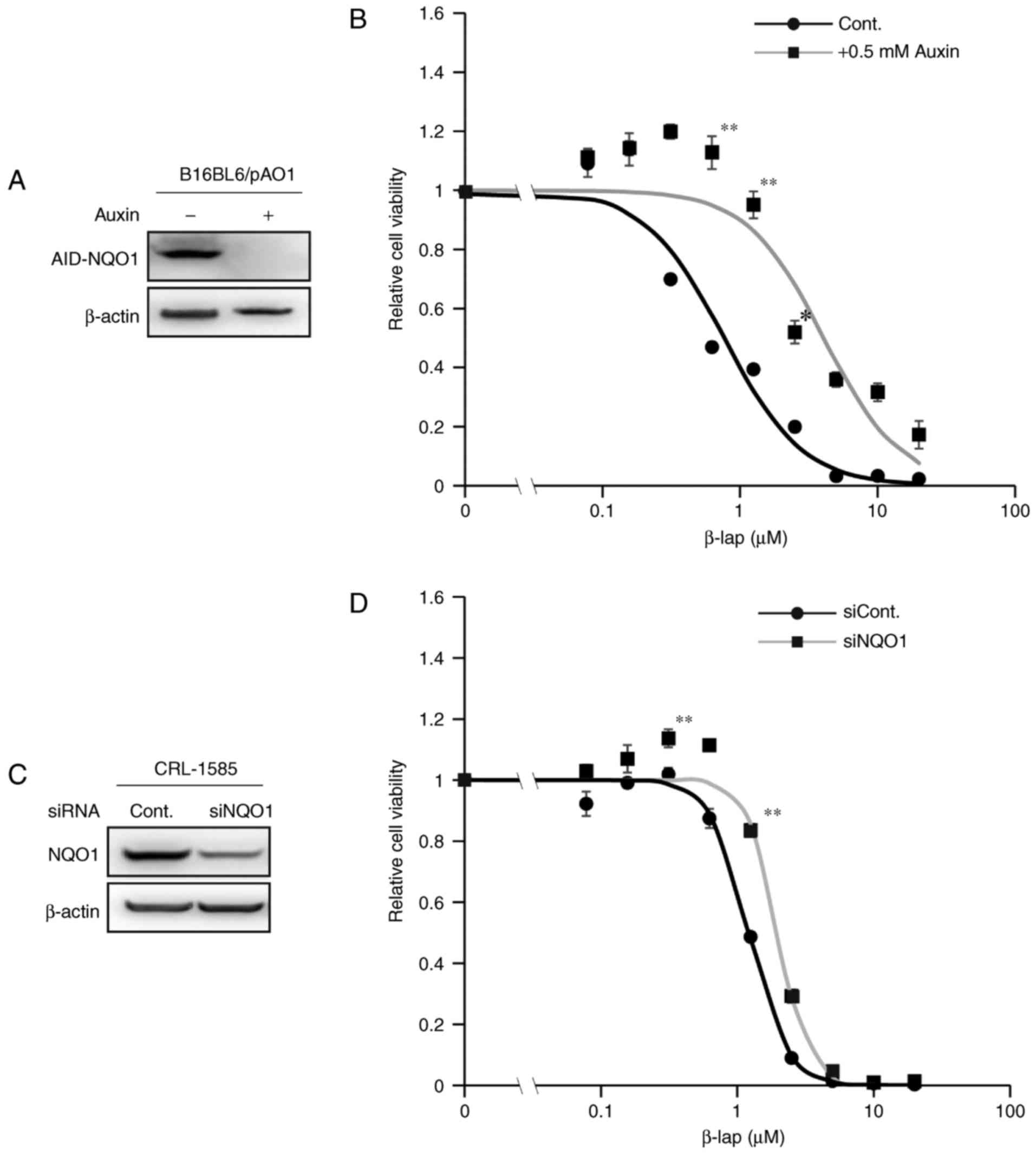
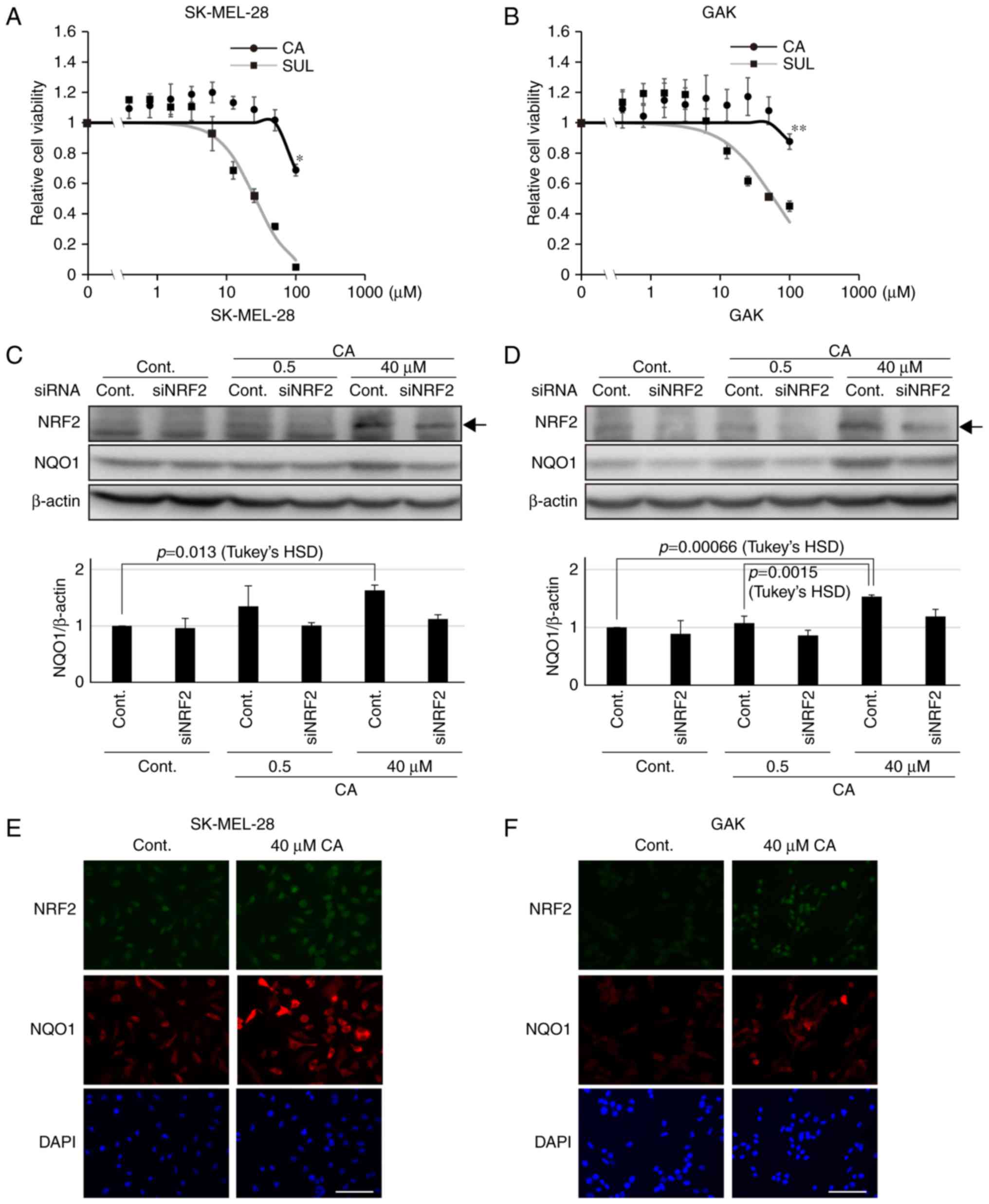
|
1
|
Scolyer RA, Judge MJ, Evans A, Frishberg
DP, Prieto VG, Thompson JF, Trotter MJ, Walsh MY, Walsh NM and
Ellis DW: International Collaboration on Cancer Reporting: Data set
for pathology reporting of cutaneous invasive melanoma:
Recommendations from the international collaboration on cancer
reporting (ICCR). Am J Surg Pathol. 37:1797–1814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tokuzumi A, Fukushima S, Miyashita A,
Nakahara S, Kubo Y, Yamashita J, Harada M, Nakamura K, Kajihara I,
Jinnin M and Ihn H: Cell division cycle-associated protein 1 as a
new melanoma-associated antigen. J Dermatol. 43:1399–1405. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J,
Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, et al:
Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in
BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature. 467:596–599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H,
Mamo S, Bremer R, Gillette S, Kong J, Haass NK, et al: Discovery of
a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent
antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3041–3046. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P,
Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W,
et al: Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature.
417:949–954. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maldonado JL, Fridlyand J, Patel H, Jain
AN, Busam K, Kageshita T, Ono T, Albertson DG, Pinkel D and Bastian
BC: Determinants of BRAF mutations in primary melanomas. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 95:1878–1890. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pollock PM, Harper UL, Hansen KS, Yudt LM,
Stark M, Robbins CM, Moses TY, Hostetter G, Wagner U, Kakareka J,
et al: High frequency of BRAF mutations in nevi. Nat Genet.
33:19–20. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uribe P, Wistuba II and González S: BRAF
mutation: A frequent event in benign, atypical and malignant
melanocytic lesions of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 25:365–370.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML and
Tucker MA: Acral lentiginous melanoma: Incidence and survival
patterns in the United States, 1986–2005. Arch Dermatol.
145:427–434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kogushi-Nishi H, Kawasaki J, Kageshita T,
Ishihara T and Ihn H: The prevalence of melanocytic nevi on the
soles in the Japanese population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 60:767–771.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Planchon SM, Wuerzberger S, Frydman B,
Witiak DT, Hutson P, Church DR, Wilding G and Boothman DA:
Beta-lapachone-mediated apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia
(HL-60) and human prostate cancer cells: A p53-independent
response. Cancer Res. 55:3706–3711. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Docampo R, Cruz FS, Boveris A, Muniz RP
and Esquivel DM: beta-Lapachone enhancement of lipid peroxidation
and superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide formation by sarcoma 180
ascites tumor cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 28:723–728. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Siegel D, Yan C and Ross D: NAD(P)H:
Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) in the sensitivity and resistance
to antitumor quinones. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1033–1040. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bentle MS, Reinicke KE, Bey EA, Spitz DR
and Boothman DA: Calcium-dependent modulation of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 alters cellular metabolism and DNA repair. J Biol
Chem. 281:33684–33696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Davalli P, Mitic T, Caporali A, Lauriola A
and D'Arca D: ROS, cell senescence and novel molecular mechanisms
in aging and age-related diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:35651272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raj L, Ide T, Gurkar AU, Foley M, Schenone
M, Li X, Tolliday NJ, Golub TR, Carr SA, Shamji AF, et al:
Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the
stress response to ROS. Nature. 475:231–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, et
al: An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase
II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 236:313–322. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taguchi K, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M:
Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response
and cancer evolution. Genes Cells. 16:123–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kasai S, Arakawa N, Okubo A, Shigeeda W,
Yasuhira S, Masuda T, Akasaka T, Shibazaki M and Maesawa C:
NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase-1 expression sensitizes malignant
melanoma cells to the HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG. PLoS One.
11:e01531812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miura S, Shibazaki M, Kasai S, Yasuhira S,
Watanabe A, Inoue T, Kageshita Y, Tsunoda K, Takahashi K, Akasaka
T, et al: A somatic mutation of the KEAP1 gene in malignant
melanoma is involved in aberrant NRF2 activation and an increase in
intrinsic drug resistance. J Invest Dermatol. 134:553–556. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Satoh T, Kosaka K, Itoh K, Kobayashi A,
Yamamoto M, Shimojo Y, Kitajima C, Cui J, Kamins J, Okamoto S, et
al: Carnosic acid, a catechol-type electrophilic compound, protects
neurons both in vitro and in vivo through activation of the
Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via S-alkylation of targeted cysteines on Keap1.
J Neurochem. 104:1116–1131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E,
Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S,
Schmid B, et al: Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image
analysis. Nat Methods. 9:676–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okubo A, Yasuhira S, Shibazaki M,
Takahashi K, Akasaka T, Masuda T and Maesawa C: NAD(P)H
dehydrogenase, quinone 1 (NQO1), protects melanin-producing cells
from cytotoxicity of rhododendrol. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
29:309–316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bang W, Jeon YJ, Cho JH, Lee RH, Park SM,
Shin JC, Choi NJ, Choi YH, Cho JJ, Seo JM, et al: β-lapachone
suppresses the proliferation of human malignant melanoma cells by
targeting specificity protein 1. Oncol Rep. 35:1109–1116. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishimura K, Fukagawa T, Takisawa H,
Kakimoto T and Kanemaki M: An auxin-based degron system for the
rapid depletion of proteins in nonplant cells. Nat Methods.
6:917–922. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Venugopal R and Jaiswal AK: Nrf1 and Nrf2
positively and c-Fos and Fra1 negatively regulate the human
antioxidant response element-mediated expression of NAD(P)H:
Quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:14960–14965. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh A, Misra V, Thimmulappa RK, Lee H,
Ames S, Hoque MO, Herman JG, Baylin SB, Sidransky D, Gabrielson E,
et al: Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung
cancer. PLoS Med. 3:e4202006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marks R: Epidemiology of melanoma. Clin
Exp Dermatol. 25:459–463. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jackson JK, Higo T, Hunter WL and Burt HM:
Topoisomerase inhibitors as anti-arthritic agents. Inflamm Res.
57:126–134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li CJ, Averboukh L and Pardee AB:
Beta-Lapachone, a novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor with a mode
of action different from camptothecin. J Biol Chem.
268:22463–22468. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li CJ, Li YZ, Pinto AV and Pardee AB:
Potent inhibition of tumor survival in vivo by beta-lapachone plus
taxol: Combining drugs imposes different artificial checkpoints.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:13369–13374. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ough M, Lewis A, Bey EA, Gao J, Ritchie
JM, Bornmann W, Boothman DA, Oberley LW and Cullen JJ: Efficacy of
beta-lapachone in pancreatic cancer treatment: Exploiting the
novel, therapeutic target NQO1. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:95–102. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chakrabarti G, Silvers MA, Ilcheva M, Liu
Y, Moore ZR, Luo X, Gao J, Anderson G, Liu L, Sarode V, et al:
Tumor-selective use of DNA base excision repair inhibition in
pancreatic cancer using the NQO1 bioactivatable drug, β-lapachone.
Sci Rep. 5:170662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamaguchi Y, Hearing VJ, Maeda A and
Morita A: NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase-1 as a new regulatory enzyme
that increases melanin synthesis. J Invest Dermatol. 130:645–647.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kosaka K and Yokoi T: Carnosic acid, a
component of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.), promotes
synthesis of nerve growth factor in T98G human glioblastoma cells.
Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1620–1622. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martin D, Rojo AI, Salinas M, Diaz R,
Gallardo G, Alam J, De Galarreta CM and Cuadrado A: Regulation of
heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf2 transcription factor in response
to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J Biol Chem.
279:8919–8929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rau O, Wurglics M, Paulke A, Zitzkowski J,
Meindl N, Bock A, Dingermann T, Abdel-Tawab M and
Schubert-Zsilavecz M: Carnosic acid and carnosol, phenolic
diterpene compounds of the labiate herbs rosemary and sage, are
activators of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma. Planta Med. 72:881–887. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Visanji JM, Thompson DG and Padfield PJ:
Induction of G2/M phase cell cycle arrest by carnosol and carnosic
acid is associated with alteration of cyclin A and cyclin B1
levels. Cancer Lett. 237:130–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Aeschbach R and
Loligers J: Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of active
rosemary constituents: Carnosol and carnosic acid. Xenobiotica.
22:257–268. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park SY, Song H, Sung MK, Kang YH, Lee KW
and Park JH: Carnosic acid inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in B16F10 melanoma cells: A possible mechanism for the
inhibition of cell migration. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12698–12713. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Barni MV, Carlini MJ, Cafferata EG,
Puricelli L and Moreno S: Carnosic acid inhibits the proliferation
and migration capacity of human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
27:1041–1048. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang X, Motea EA, Moore ZR, Yao J, Dong
Y, Chakrabarti G, Kilgore JA, Silvers MA, Patidar PL, Cholka A, et
al: Leveraging an NQO1 bioactivatable drug for tumor-selective use
of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Cancer Cell.
30:940–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, .
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker
RE, Kang HM, Marth GT and McVean GA: An integrated map of genetic
variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 491:56–65. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fagerholm R, Hofstetter B, Tommiska J,
Aaltonen K, Vrtel R, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi A, Kilpivaara O,
Mannermaa A, Kosma VM, et al: NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1
NQO1*2 genotype (P187S) is a strong prognostic and predictive
factor in breast cancer. Nat Genet. 40:844–853. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jamieson D, Cresti N, Bray J, Sludden J,
Griffin MJ, Hawsawi NM, Famie E, Mould EV, Verrill MW, May FE and
Boddy AV: Two minor NQO1 and NQO2 alleles predict poor response of
breast cancer patients to adjuvant doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide
therapy. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 21:808–819. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|