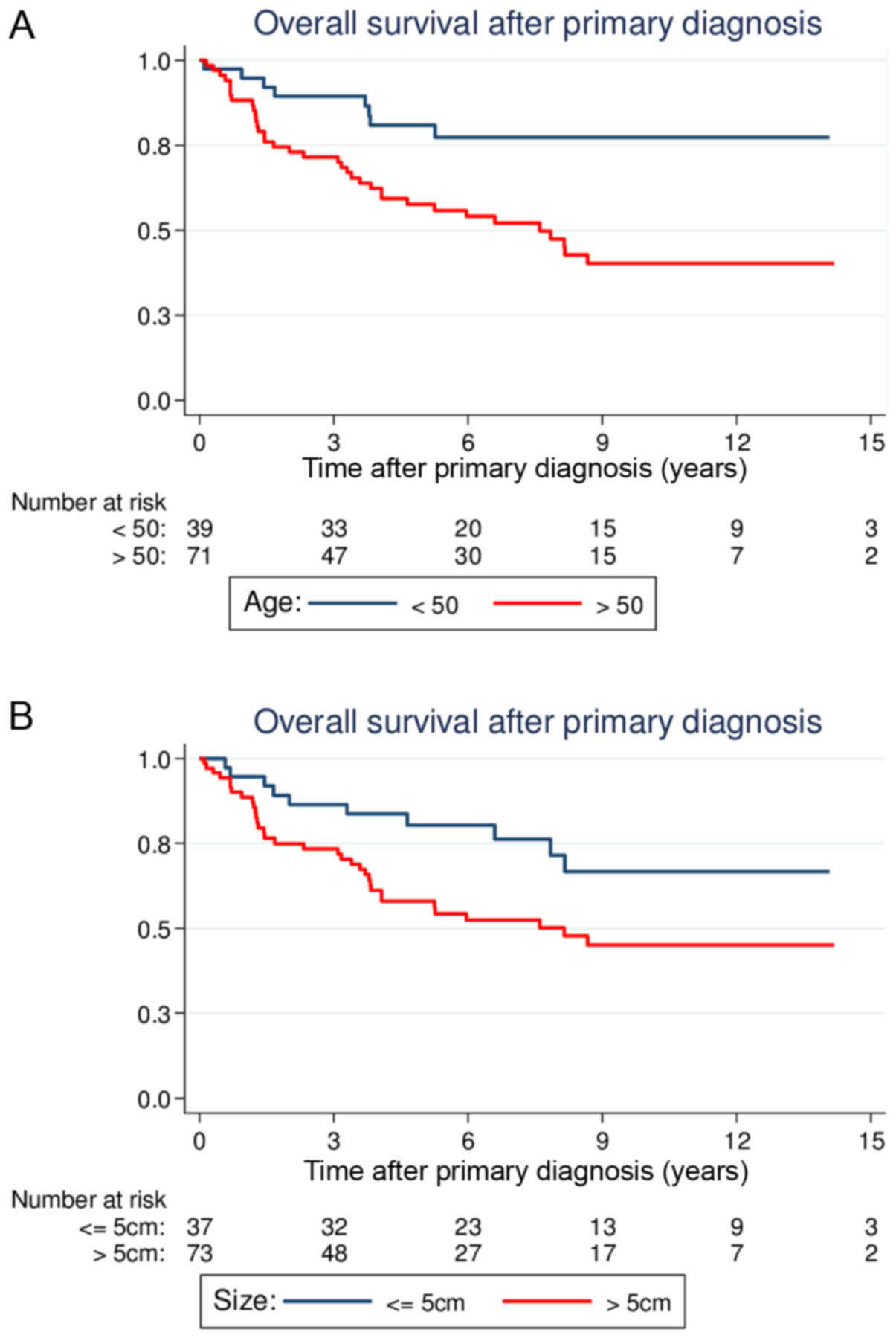
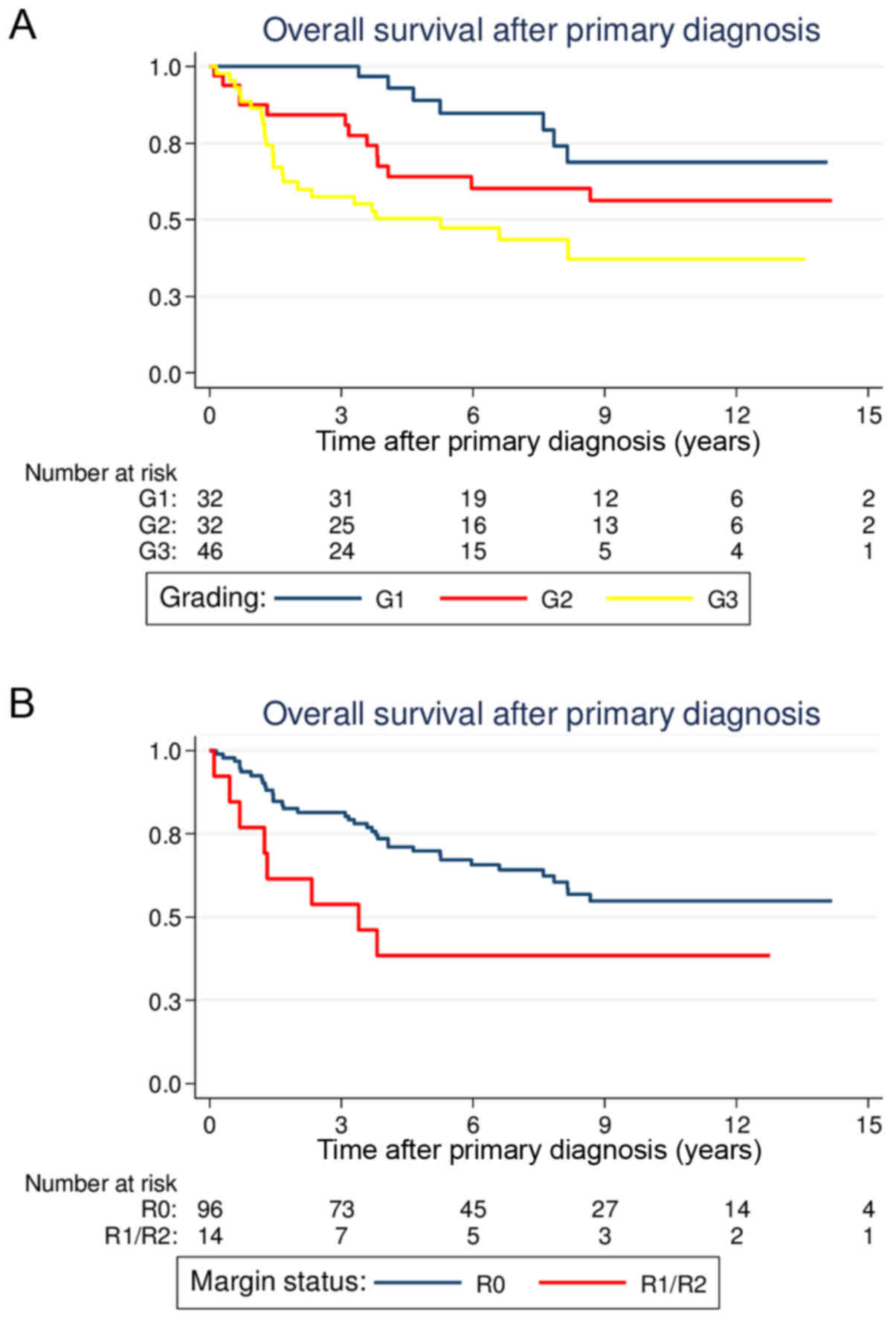
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J
and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:43–66.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kachroo P, Pak PS, Sandha HS, Lee C,
Elashoff D, Nelson SD, Chmielowski B, Selch MT, Cameron RB, Holmes
EC, et al: Single-institution, multidisciplinary experience with
surgical resection of primary chest wall sarcomas. J Thorac Oncol.
7:552–558. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gross JL, Younes RN, Haddad FJ,
Deheinzelin D, Pinto CA and Costa ML: Soft-tissue sarcomas of the
chest wall: Prognostic factors. Chest. 127:902–908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oksuz DC, Ozdemir S, Kaydihan N,
Dervisoglu S, Hiz M, Tuzun H, Mandel NM, Koca S and Dincbas FO:
Long-term treatment results in soft tissue sarcomas of the thoracic
wall treated with pre-or-postoperative radiotherapy-a single
institution experience. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9949–9953.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsukushi S, Nishida Y, Sugiura H,
Nakashima H and Ishiguro N: Soft tissue sarcomas of the chest wall.
J Thorac Oncol. 4:834–837. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salas S, Bui B, Stoeckle E, Terrier P,
Ranchere-Vince D, Collin F, Leroux A, Guillou L, Michels JJ,
Trassard M, et al: Soft tissue sarcomas of the trunk wall (STS-TW):
A study of 343 patients from the French Sarcoma Group (FSG)
database. Ann Oncol. 20:1127–1135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maretty-Nielsen K, Aggerholm-Pedersen N,
Safwat A, Jørgensen PH, Hansen BH, Baerentzen S, Pedersen AB and
Keller J: Prognostic factors for local recurrence and mortality in
adult soft tissue sarcoma of the extremities and trunk wall: A
cohort study of 922 consecutive patients. Acta Orthop. 85:323–332.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stojadinovic A, Leung DH, Hoos A, Jaques
DP, Lewis JJ and Brennan MF: Analysis of the prognostic
significance of microscopic margins in 2,084 localized primary
adult soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 235:424–434. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Geel AN, Wouters MW, Lans TE, Schmitz
PI and Verhoef C: Chest wall resection for adult soft tissue
sarcomas and chondrosarcomas: Analysis of prognostic factors. World
J Surg. 35:63–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wouters MW, van Geel AN, Nieuwenhuis L,
van Tinteren H, Verhoef C, van Coevorden F and Klomp HM: Outcome
after surgical resections of recurrent chest wall sarcomas. J Clin
Oncol. 26:5113–5118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walsh GL, Davis BM, Swisher SG, Vaporciyan
AA, Smythe WR, Willis-Merriman K, Roth JA and Putnam JB Jr: A
single-institutional, multidisciplinary approach to primary
sarcomas involving the chest wall requiring full-thickness
resections. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 121:48–60. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith GM, Johnson GD, Grimer RJ and Wilson
S: Trends in presentation of bone and soft tissue sarcomas over 25
years: Little evidence of earlier diagnosis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl.
93:542–547. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gordon MS, Hajdu SI, Bains MS and Burt ME:
Soft tissue sarcomas of the chest wall. Results of surgical
resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 101:843–854. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Coindre JM: Grading of soft tissue
sarcomas: Review and update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 130:1448–1453.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fletcher CD: The evolving classification
of soft tissue tumours-an update based on the new 2013 WHO
classification. Histopathology. 64:2–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schemper M and Smith TL: A note on
quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin
Trials. 17:343–346. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Clark TG, Bradburn MJ, Love SB and Altman
DG: Survival analysis part I: Basic concepts and first analyses. Br
J Cancer. 89:232–238. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coindre JM, Terrier P, Guillou L, Le
Doussal V, Collin F, Ranchère D, Sastre X, Vilain MO, Bonichon F
and Bui N'Guyen B: Predictive value of grade for metastasis
development in the main histologic types of adult soft tissue
sarcomas: A study of 1240 patients from the French Federation of
cancer centers sarcoma group. Cancer. 91:1914–1926. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mery CM, George S, Bertagnolli MM and Raut
CP: Secondary sarcomas after radiotherapy for breast cancer:
Sustained risk and poor survival. Cancer. 115:4055–4063. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McMillan RR, Sima CS, Moraco NH, Rusch VW
and Huang J: Recurrence patterns after resection of soft tissue
sarcomas of the chest wall. Ann Thorac Surg. 96:1223–1228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marulli G, Duranti L, Cardillo G, Luzzi L,
Carbone L, Gotti G, Perissinotto E, Rea F and Pastorino U: Primary
chest wall chondrosarcomas: Results of surgical resection and
analysis of prognostic factors. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
45:e194–e201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Widhe B and Bauer HC: Scandinavian Sarcoma
Group: Surgical treatment is decisive for outcome in chondrosarcoma
of the chest wall: A population-based Scandinavian Sarcoma Group
study of 106 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 137:610–614. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|