|
1
|
King TD, Suto MJ and Li Y: The
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: A potential therapeutic target in
the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. J Cell Biochem.
113:13–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Burkadze G and
Kolar Z: Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and
carcinogenesis. Pathobiology. 73:213–223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geyer FC, Lacroix-Triki M, Savage K,
Arnedos M, Lambros MB, MacKay A, Natrajan R and Reis-Filho JS:
β-Catenin pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with
triple-negative phenotype but not with CTNNB1 mutation. Mod Pathol.
24:209–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khramtsov AI, Khramtsova GF, Tretiakova M,
Huo D, Olopade OI and Goss KH: Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation
is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome.
Am J Pathol. 176:2911–2920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin SY, Xia W, Wang JC, Kwong KY, Spohn B,
Wen Y, Pestell RG and Hung MC: Beta-catenin, a novel prognostic
marker for breast cancer: Its roles in cyclin D1 expression and
cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:pp. 4262–4266. 2000;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howe LR and Brown AM: Wnt signaling and
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:36–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fisher DA, Kivimäe S, Hoshino J, Suriben
R, Martin PM, Baxter N and Cheyette BN: Three Dact gene family
members are expressed during embryonic development and in the adult
brains of mice. Dev Dyn. 235:2620–2630. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheyette BN, Waxman JS, Miller JR,
Takemaru K, Sheldahl LC, Khlebtsova N, Fox EP, Earnest T and Moon
RT: Dapper, a Dishevelled-associated antagonist of beta-catenin and
JNK signaling, is required for notochord formation. Dev Cell.
2:449–461. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teran E, Branscomb AD and Seeling JM: Dpr
acts as a molecular switch, inhibiting Wnt signaling when
unphosphorylated, but promoting Wnt signaling when phosphorylated
by casein kinase Idelta/epsilon. PLoS One. 4:e55222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu Y, Yan W, Liu X, Jia Y, Cao B, Yu Y, Lv
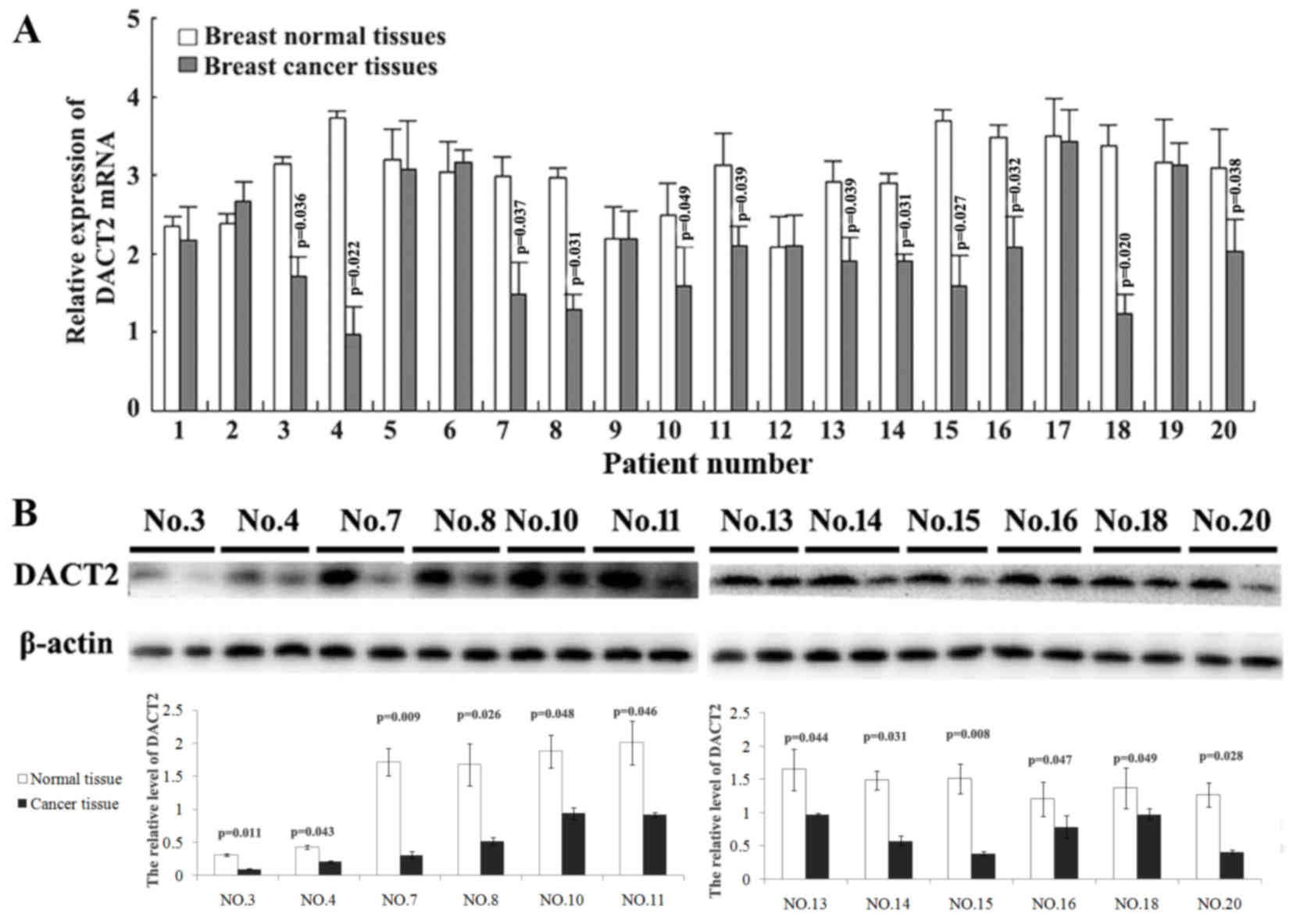
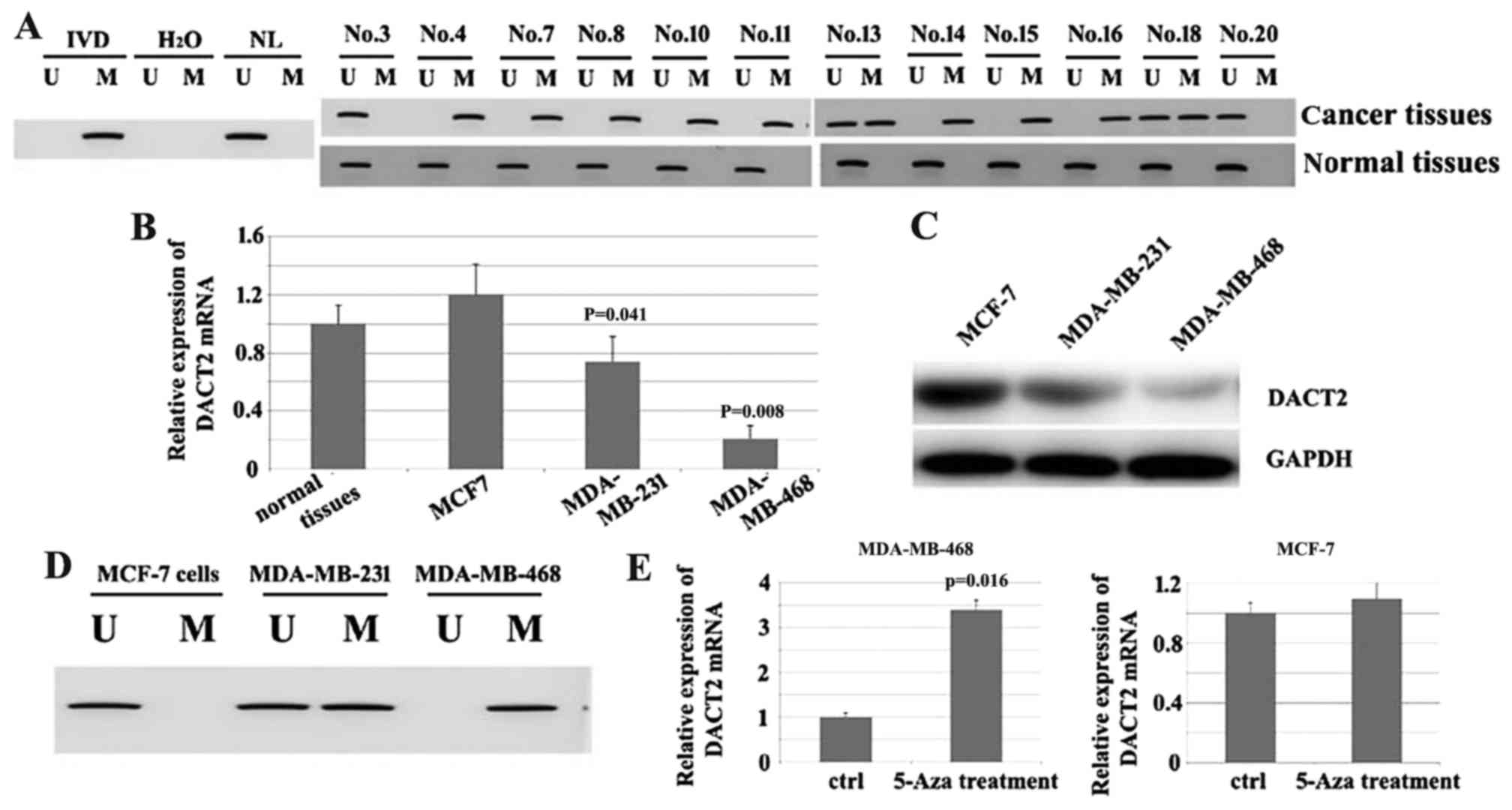
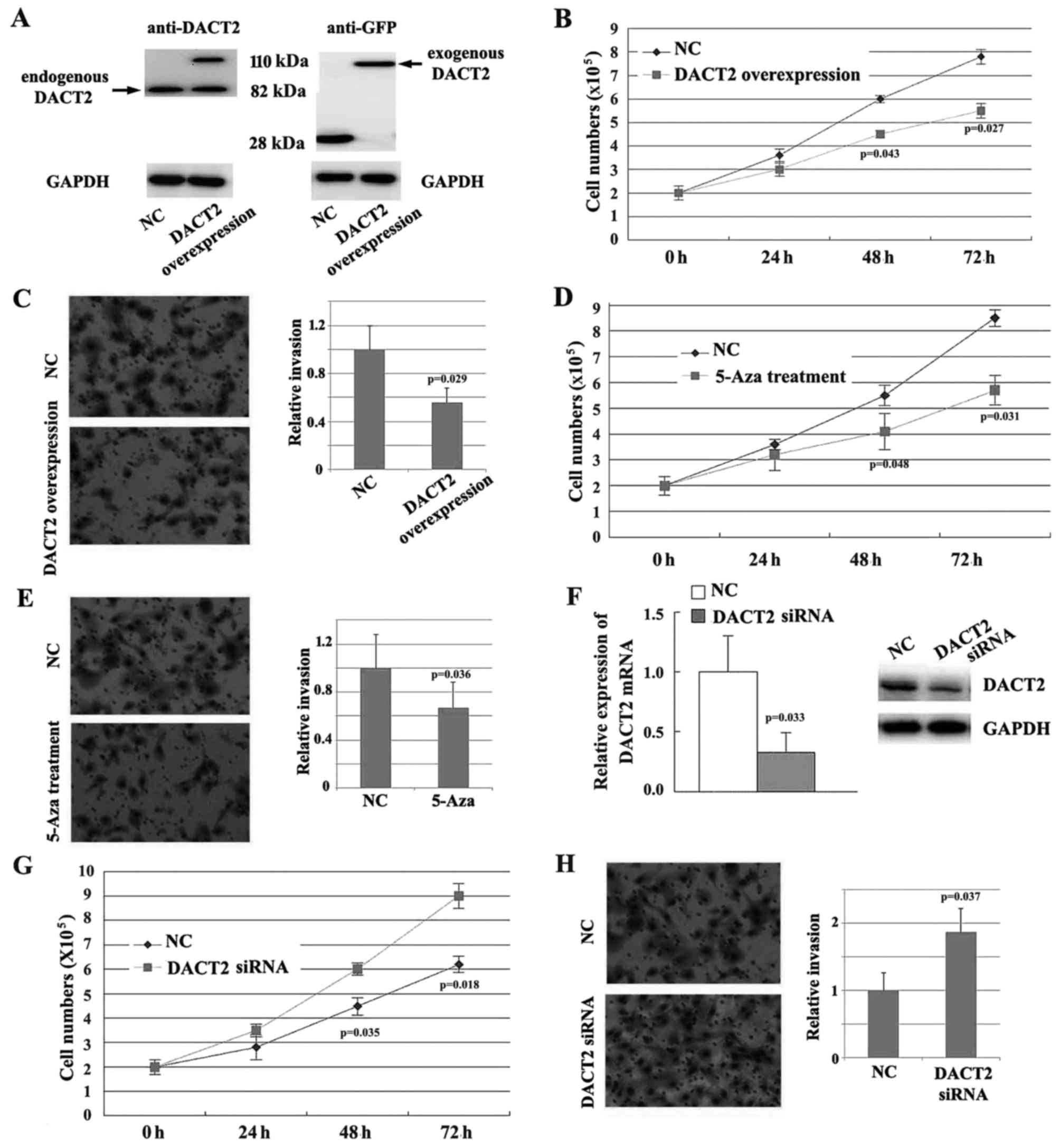
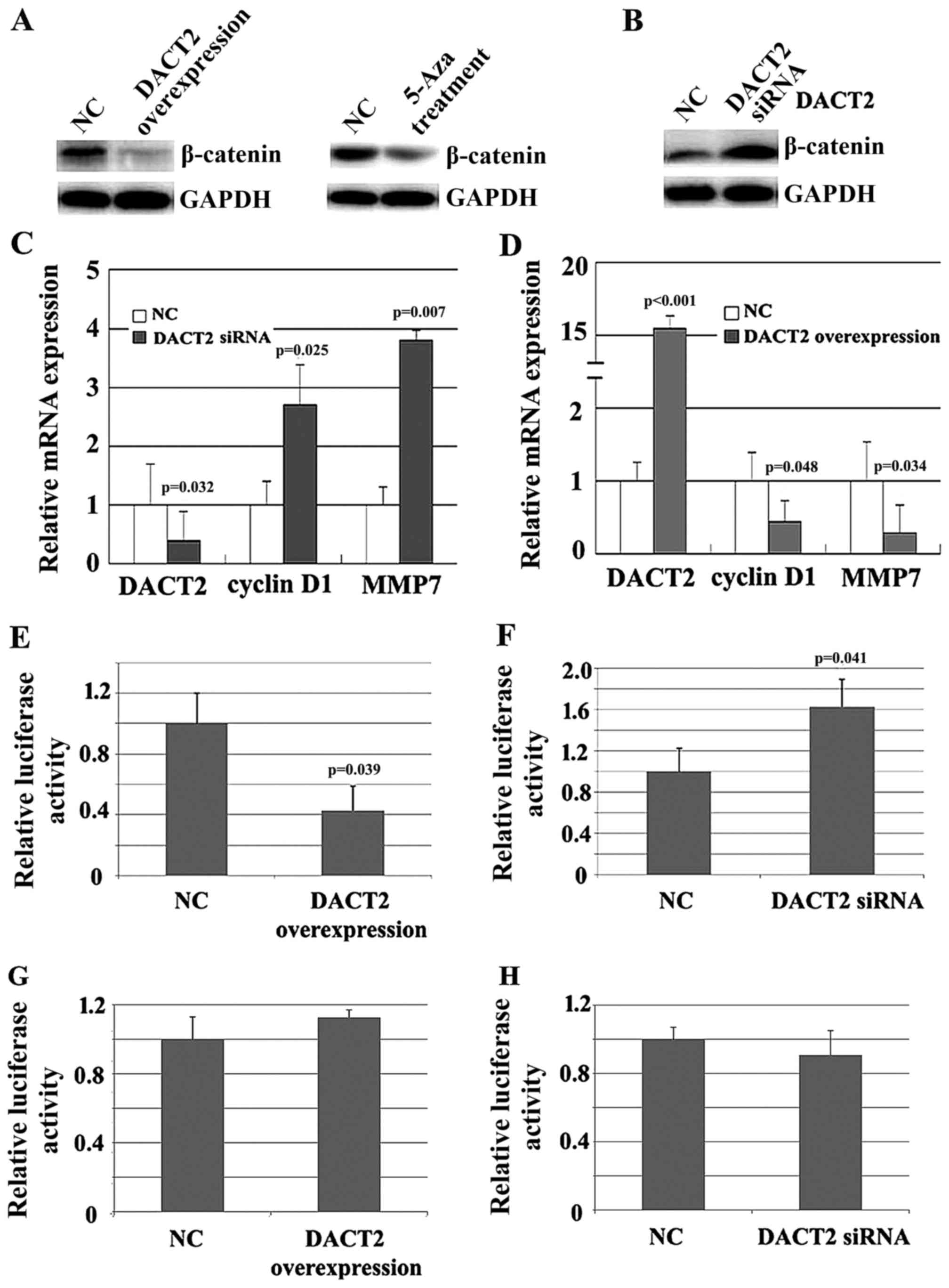
Y, Brock MV, Herman JG, Licchesi J, et al: DACT2 is frequently
methylated in human gastric cancer and methylation of DACT2
activated Wnt signaling. Am J Cancer Res. 4:710–724.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Zhang J, Gao L, McClellan S, Finan
MA, Butler TW, Owen LB, Piazza GA and Xi Y: MiR-181 mediates cell
differentiation by interrupting the Lin28 and let-7 feedback
circuit. Cell Death Differ. 19:378–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ha NC, Tonozuka T, Stamos JL, Choi HJ and
Weis WI: Mechanism of phosphorylation-dependent binding of APC to
beta-catenin and its role in beta-catenin degradation. Mol Cell.
15:511–521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du W, Liu X, Fan G, Zhao X, Sun Y, Wang T,
Zhao R, Wang G, Zhao C, Zhu Y, et al: From cell membrane to the
nucleus: An emerging role of E-cadherin in gene transcriptional
regulation. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1712–1719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsukamoto AS, Grosschedl R, Guzman RC,
Parslow T and Varmus HE: Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic
mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and
adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 55:619–625. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang L, Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang K, Wu J, Yuan
YC, Deng X, Chen L, Kim CC, Lau S, et al: FZD7 has a critical role
in cell proliferation in triple negative breast cancer. Oncogene.
30:4437–4446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lindvall C, Zylstra CR, Evans N, West RA,
Dykema K, Furge KA and Williams BO: The Wnt co-receptor Lrp6 is
required for normal mouse mammary gland development. PLoS One.
4:e58132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Badders NM, Goel S, Clark RJ, Klos KS, Kim
S, Bafico A, Lindvall C, Williams BO and Alexander CM: The Wnt
receptor, Lrp5, is expressed by mouse mammary stem cells and is
required to maintain the basal lineage. PLoS One. 4:e65942009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lindvall C, Evans NC, Zylstra CR, Li Y,
Alexander CM and Williams BO: The Wnt signaling receptor Lrp5 is
required for mammary ductal stem cell activity and Wnt1-induced
tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem. 281:35081–35087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Willemsen RH, de Kort SW, van der Kaay DC
and Hokken-Koelega AC: Independent effects of prematurity on
metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors in short
small-for-gestational-age children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
93:452–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki H, Toyota M, Carraway H, Gabrielson
E, Ohmura T, Fujikane T, Nishikawa N, Sogabe Y, Nojima M, Sonoda T,
et al: Frequent epigenetic inactivation of Wnt antagonist genes in
breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:1147–1156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matsuda Y, Schlange T, Oakeley EJ, Boulay
A and Hynes NE: WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility
and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231
xenograft growth. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Identification and
characterization of human DAPPER1 and DAPPER2 genes in silico. Int
J Oncol. 22:907–913. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Girard L, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Virmani AK,
Gazdar AF and Minna JD: Genome-wide allelotyping of lung cancer
identifies new regions of allelic loss, differences between small
cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, and loci
clustering. Cancer Res. 60:4894–4906. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Steinemann D, Gesk S, Zhang Y, Harder L,
Pilarsky C, Hinzmann B, Martin-Subero JI, Calasanz MJ, Mungall A,
Rosenthal A, et al: Identification of candidate tumor-suppressor
genes in 6q27 by combined deletion mapping and electronic
expression profiling in lymphoid neoplasms. Genes, Chromosomes
Cancer. 37:421–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia Y, Yang Y, Brock MV, Zhan Q, Herman JG
and Guo M: Epigenetic regulation of DACT2, a key component of the
Wnt signalling pathway in human lung cancer. J Pathol. 230:194–204.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang X, Yang Y, Liu X, Herman JG, Brock
MV, Licchesi JD, Yue W, Pei X and Guo M: Epigenetic regulation of
the Wnt signaling inhibitor DACT2 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Epigenetics. 8:373–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu L,
Yang S, Li X, Dong H, Xu L, Su L, et al: DACT2 is a functional
tumor suppressor through inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway and
associated with poor survival in colon cancer. Oncogene.
34:2575–2585. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Z, Herman JG, Brock MV, Sheng J,
Zhang M, Liu B and Guo M: Methylation of DACT2 promotes papillary
thyroid cancer metastasis by activating Wnt signaling. PLoS One.
9:e1123362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li L, Zhang Y, Fan Y, Sun K, Su X, Du Z,
Tsao SW, Loh TK, Sun H, Chan AT, et al: Characterization of the
nasopharyngeal carcinoma methylome identifies aberrant disruption
of key signaling pathways and methylated tumor suppressor genes.
Epigenomics. 7:155–173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schussel JL, Kalinke LP, Sassi LM, de
Oliveira BV, Pedruzzi PA, Olandoski M, Alvares LE, Garlet GP and
Trevilatto PC: Expression and epigenetic regulation of DACT1 and
DACT2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 15:11–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kivimäe S, Yang XY and Cheyette BN: All
Dact (Dapper/Frodo) scaffold proteins dimerize and exhibit
conserved interactions with Vangl, Dvl, and serine/threonine
kinases. BMC Biochem. 12:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|