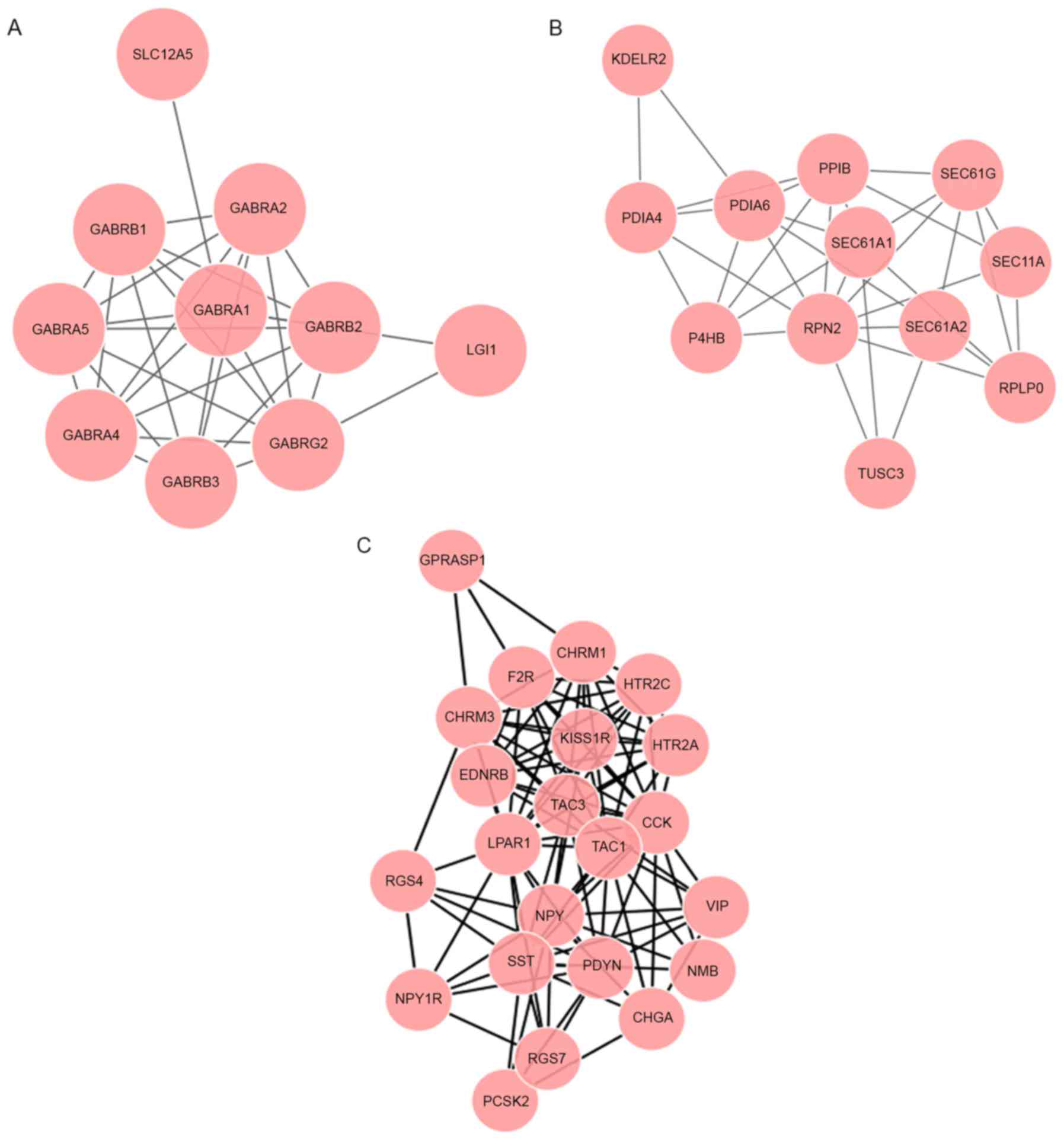
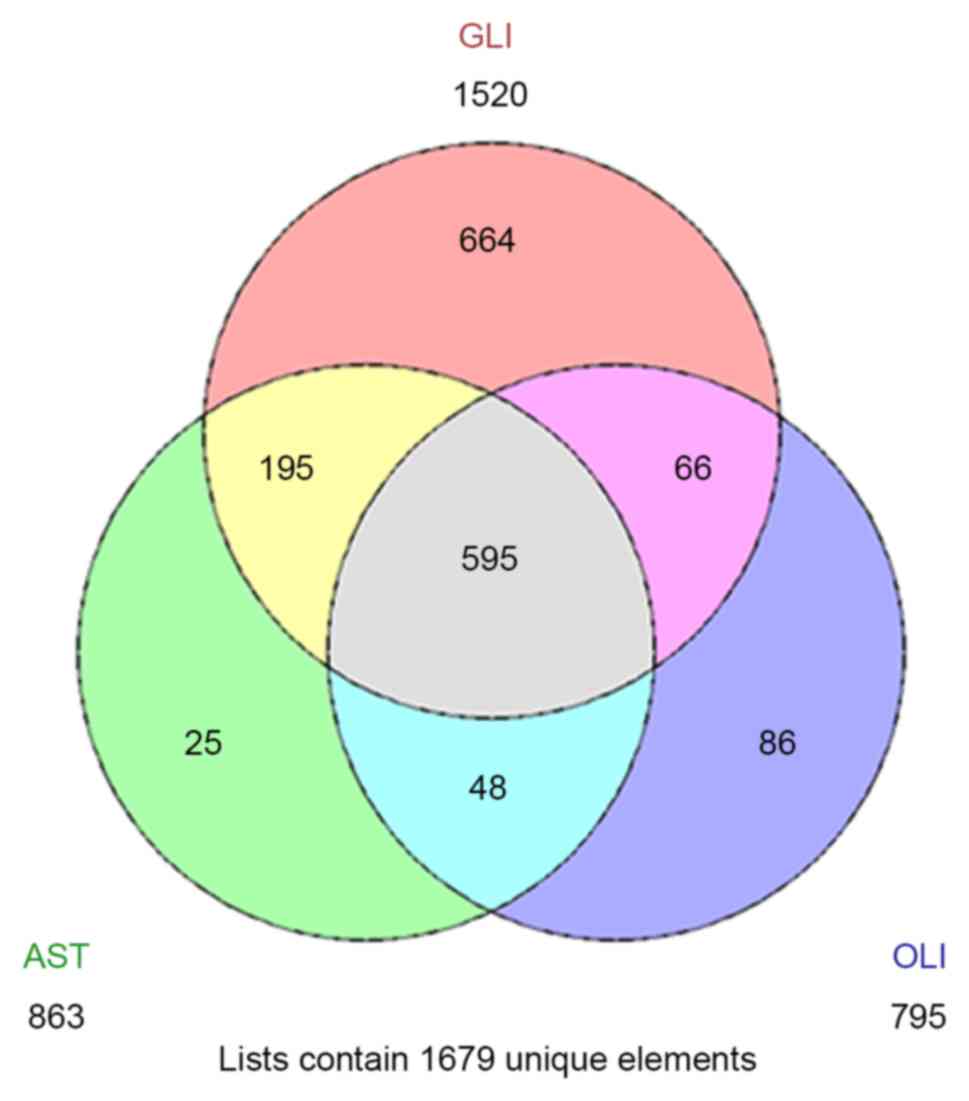
|
1
|
Hori M, Fukunaga I, Masutani Y, Taoka T,
Kamagata K, Suzuki Y and Aoki S: Visualizing non-Gaussian
diffusion: Clinical application of q-space imaging and diffusional
kurtosis imaging of the brain and spine. Magn Reson Med Sci.
11:221–233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chan AS, Leung SY, Wong MP, Yuen ST,
Cheung N, Fan YW and Chung LP: Expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor and its receptors in the anaplastic progression of
astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, and ependymoma. Am J Surg Pathol.
22:816–826. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pickuth D and Heywang-Köbrunner SH:
Neurosarcoidosis: Evaluation with MRI. J Neuroradiol. 27:185–188.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocaña A,
Peñuelas S, Arias A, Paris R, Tortosa A, Mora J, Baselga J and
Seoane J: High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in
glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the
methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell. 11:147–160. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wrensch M, Kelsey KT, Liu M, Miike R,
Moghadassi M, Sison JD, Aldape K, McMillan A, Wiemels J and Wiencke
JK: ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and adult glioma. Neuro Oncol.
7:495–507. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gurung RL, Lim SN, Khaw AK, Soon JF,
Shenoy K, Mohamed Ali S, Jayapal M, Sethu S, Baskar R and Hande MP:
Thymoquinone induces telomere shortening, DNA damage and apoptosis
in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 5:e121242010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Zhang J, Hoadley K, Kushwaha D,
Ramakrishnan V, Li S, Kang C, You Y, Jiang C, Song SW, et al:
miR-181d: A predictive glioblastoma biomarker that downregulates
MGMT expression. Neuro Oncol. 14:712–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun L, Hui AM, Su Q, Vortmeyer A,
Kotliarov Y, Pastorino S, Passaniti A, Menon J, Walling J, Bailey
R, et al: Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces
angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell. 9:287–300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei B, Wang L, Du C, Hu G, Wang L, Jin Y
and Kong D: Identification of differentially expressed genes
regulated by transcription factors in glioblastomas by
bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep. 11:2548–2554. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bohonak AJ and van der Linde K: RMA:
Software for reduced major axis regression, Java version.
2004.http://www.kimvdlinde.com/professional/rma.html
|
|
12
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(Database issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pirooznia M, Nagarajan V and Deng Y:
GeneVenn-A web application for comparing gene lists using Venn
diagrams. Bioinformation. 1:420–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng H, Ying H, Yan H, Kimmelman AC,
Hiller DJ, Chen AJ, Perry SR, Tonon G, Chu GC, Ding Z, et al: p53
and Pten control neural and glioma stem/progenitor cell renewal and
differentiation. Nature. 455:1129–1133. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishii N, Maier D, Merlo A, Tada M,
Sawamura Y, Diserens AC and Van Meir EG: Frequent co-alterations of
TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in
human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol. 9:469–479. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Shou J and Chen X: Dickkopf-1, an
inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway, is induced by p53.
Oncogene. 19:1843–1848. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ichimura K, Bolin MB, Goike HM, Schmidt
EE, Moshref A and Collins VP: Deregulation of the
p14ARF/MDM2/p53 pathway is a prerequisite for human
astrocytic gliomas with G1-S transition control gene abnormalities.
Cancer Res. 60:417–424. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan Q, Yu HL and Li JT: Study on the
expression of BDNF in human gliomas. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue
Ban. 40:415–417. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiong J, Zhou L, Lim Y, Yang M, Zhu YH, Li
ZW, Zhou FH, Xiao ZC and Zhou XF: Mature BDNF promotes the growth
of glioma cells in vitro. Oncol Rep. 30:2719–2724. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen H, Huang Q, Zhai DZ, Dong J, Wang AD
and Lan Q: CDK1 expression and effects of CDK1 silencing on the
malignant phenotype of glioma cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
29:484–488. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu WT, Chen C, Lu IC, Kuo SC, Lee KH,
Chen TL, Song TS, Lu YL, Gean PW and Hour MJ: MJ-66 induces
malignant glioma cells G2/M phase arrest and mitotic catastrophe
through regulation of cyclin B1/Cdk1 complex. Neuropharmacology.
86:219–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL and Burgering
BM: AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle
regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature.
404:782–787. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Holland EC, Celestino J, Dai C, Schaefer
L, Sawaya RE and Fuller GN: Combined activation of Ras and Akt in
neural progenitors induces glioblastoma formation in mice. Nat
Genet. 25:55–57. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rajaraman P, Brenner AV, Butler MA, Wang
SS, Pfeiffer RM, Ruder AM, Linet MS, Yeager M, Wang Z, Orr N, et
al: Common variation in genes related to innate immunity and risk
of adult glioma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1651–1658.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Enam SA, Rosenblum ML and Edvardsen K:
Role of extracellular matrix in tumor invasion: Migration of glioma
cells along fibronectin-positive mesenchymal cell processes.
Neurosurgery. 42:599–608. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|