|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 (Internet). International Agency
for Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2013, http://globocan.iarc.frFebruary 28–2017
|
|
2
|
Lepage C, Rachet B, Jooste V, Faivre J and
Coleman MP: Continuing rapid increase in esophageal adenocarcinoma
in England and Wales. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:2694–2699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pohl H and Welch HG: The role of
overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of
esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:142–146. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eslick GD: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 3817–25. (vii)2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crane LM, Schaapveld M, Visser O, Louwman
MW, Plukker JT and van Dam GM: Oesophageal cancer in The
Netherlands: Increasing incidence and mortality but improving
survival. Eur J Cancer. 43:1445–1451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stavrou EP, McElroy HJ, Baker DF, Smith G
and Bishop JF: Adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus: Incidence and
survival rates in New South Wales, 1972–2005. Med J Aust.
191:310–314. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Bras GF, Farooq MH, Falk GW and Andl
CD: Esophageal cancer: The latest on chemoprevention and state of
the art therapies. Pharmacol Res. 113:236–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D,
Bishop K, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, et
al: SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2013. National Cancer
Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2016, http://seercancergov/csr/1975_2013/February
28–2017
|
|
10
|
Mariette C, Balon JM, Piessen G, Fabre S,
Van Seuningen I and Triboulet JP: Pattern of recurrence following
complete resection of esophageal carcinoma and factors predictive
of recurrent disease. Cancer. 97:1616–1623. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, Ohashi M,
Suzuki T and Hatakeyama K: Recurrence pattern of squamous cell
carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical
esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg.
198:205–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mehrotra S, Languino LR, Raskett CM,
Mercurio AM, Dohi T and Altieri DC: IAP regulation of metastasis.
Cancer Cell. 17:53–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fulda S and Vucic D: Targeting IAP
proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:109–124. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Altieri DC: New wirings in the survivin
networks. Oncogene. 27:6276–6284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Altieri DC: Survivin-The inconvenient IAP.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 39:91–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dohi T, Beltrami E, Wall NR, Plescia J and
Altieri DC: Mitochondrial survivin inhibits apoptosis and promotes
tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 114:1117–1127. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reed JC and Bischoff JR: BIRinging
chromosomes through cell division-and survivin' the experience.
Cell. 102:545–548. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fulda S: Regulation of cell migration,
invasion and metastasis by IAP proteins and their antagonists.
Oncogene. 33:671–676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dohi T, Okada K, Xia F, Wilford CE, Samuel
T, Welsh K, Marusawa H, Zou H, Armstrong R, Matsuzawa S, et al: An
IAP-IAP complex inhibits apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:34087–34090.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube
SE, Gion M and Clark GM; Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC
Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics, : REporting recommendations
for tumour MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Br J Cancer.
93:387–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmelzle M, Dizdar L, Matthaei H, Baldus
SE, Wolters J, Lindenlauf N, Bruns I, Cadeddu RP, Kröpil F, Topp
SA, et al: Esophageal cancer proliferation is mediated by
cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9). Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
94:25–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dizdar L, Oesterwind KA, Riemer JC, Werner
TA, Mersch S, Möhlendick B, Schutte SC, Verde PE, Raba K, Topp SA,
et al: Preclinical assesement of survivin and XIAP as prognostic
biomarkers and therapeutic targets in gastroenteropancreatic
neuroendocrine neoplasia. Oncotarget. 8:8369–8382. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Werner TA, Tamkan-Ölcek Y, Dizdar L,
Riemer JC, Wolf A, Cupisti K, Verde PE, Knoefel WT and Krieg A:
Survivin and XIAP: Two valuable biomarkers in medullary thyroid
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 114:427–434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
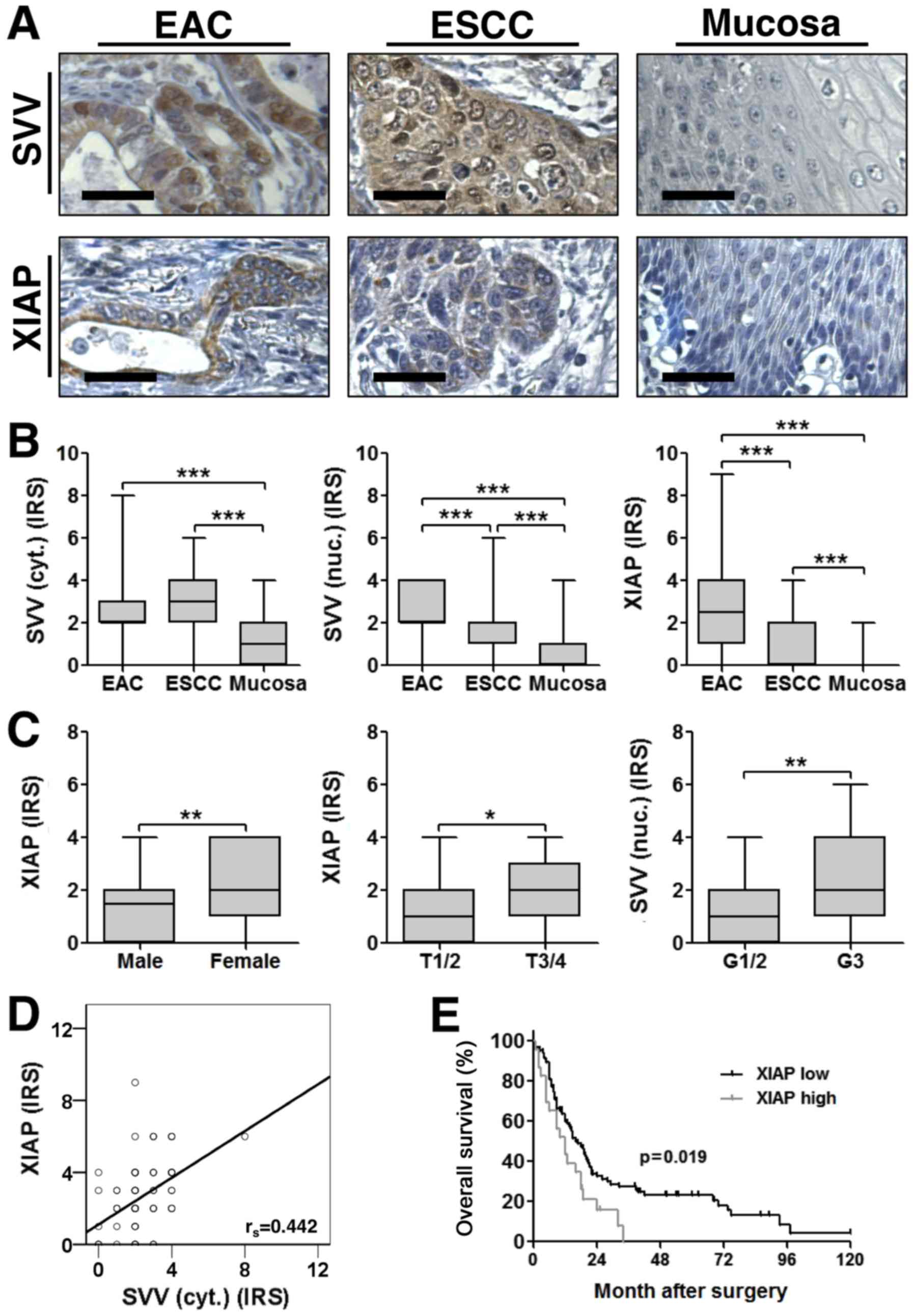
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi
N and Tobe T: Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal
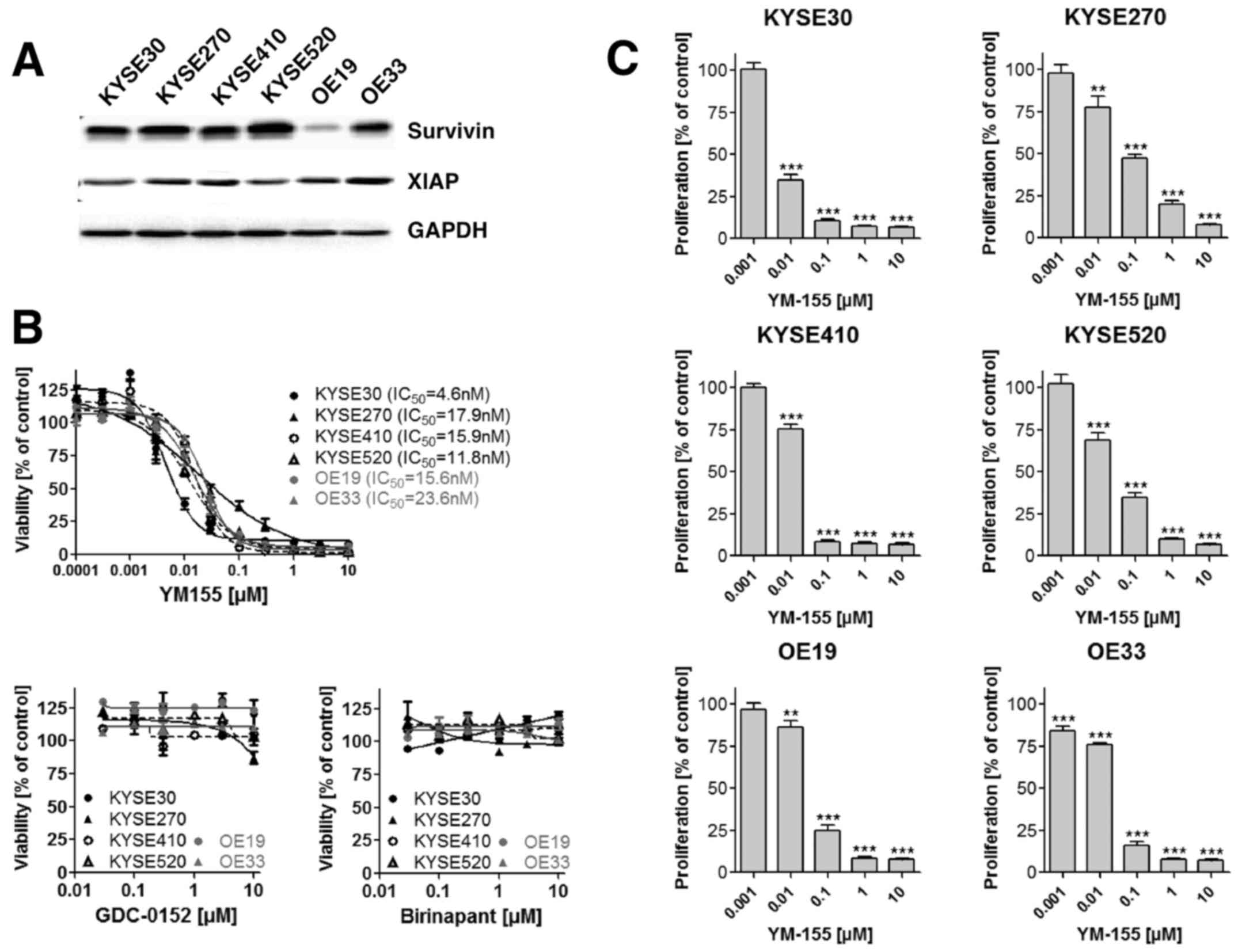
cancer cell lines. Cancer. 69:277–284. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krieg A, Mersch S, Boeck I, Dizdar L,
Weihe E, Hilal Z, Krausch M, Möhlendick B, Topp SA, Piekorz RP, et
al: New model for gastroenteropancreatic large-cell neuroendocrine
carcinoma: Establishment of two clinically relevant cell lines.
PLoS One. 9:e887132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamm I, Richter S, Oltersdorf D, Creutzig
U, Harbott J, Scholz F, Karawajew L, Ludwig WD and Wuchter C: High
expression levels of x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and
survivin correlate with poor overall survival in childhood de novo
acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3737–3744. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rosato A, Pivetta M, Parenti A, Iaderosa
GA, Zoso A, Milan G, Mandruzzato S, Del Bianco P, Ruol A, Zaninotto
G and Zanovello P: Survivin in esophageal cancer: An accurate
prognostic marker for squamous cell carcinoma but not
adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 119:1717–1722. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takeno S, Yamashita S, Takahashi Y, Ono K,
Kamei M, Moroga T and Kawahara K: Survivin expression in
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Its prognostic impact and
splice variant expression. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 37:440–445.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia H, Chen S, Huang H and Ma H: Survivin
over-expression is correlated with a poor prognosis in esophageal
cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta. 446:82–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Grabowski P, Kühnel T, Mühr-Wilkenshoff F,
Heine B, Stein H, Höpfner M, Germer CT and Scherübl H: Prognostic
value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 88:115–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mega S, Miyamoto M, Li L, Kadoya M,
Takahashi R, Hase R, Kaneko H, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Itoh T, et
al: Immunohistochemical analysis of nuclear survivin expression in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 19:355–359.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu H, Wang Q, Hu C, Zhang W, Quan L, Liu
M, Xu N and Xiao Z: High expression of survivin predicts poor
prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma following
radiotherapy. Tumour Biol. 32:1147–1153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hui MK, Lai KK, Chan KW, Luk JM, Lee NP,
Chung Y, Cheung LC, Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Tang JC and Law S:
Clinical correlation of nuclear survivin in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 29:3009–3016. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hsu KF, Lin CK, Yu CP, Tzao C, Lee SC, Lee
YY, Tsai WC and Jin JS: Cortactin, fascin, and survivin expression
associated with clinicopathological parameters in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 22:402–408. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou S, Ye W, Shao Q, Qi Y, Zhang M and
Liang J: Prognostic significance of XIAP and NF-κB expression in
esophageal carcinoma with postoperative radiotherapy. World J Surg
Oncol. 11:2882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Malhotra U, Zaidi AH, Kosovec JE, Kasi PM,
Komatsu Y, Rotoloni CL, Davison JM, R C, Irvin, Hoppo T, et al:
Prognostic value and targeted inhibition of survivin expression in
esophageal adenocarcinoma and cancer-adjacent squamous epithelium.
PLoS One. 8:e783432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang S, Ding F, Luo A, Chen A, Yu Z, Ren
S, Liu Z and Zhang L: XIAP is highly expressed in esophageal cancer
and its downregulation by RNAi sensitizes esophageal carcinoma cell
lines to chemotherapeutics. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:973–980. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nemoto T, Kitagawa M, Hasegawa M, Ikeda S,
Akashi T, Takizawa T, Hirokawa K and Koike M: Expression of IAP
family proteins in esophageal cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 76:253–259.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dohi T, Xia F and Altieri DC:
Compartmentalized phosphorylation of IAP by protein kinase A
regulates cytoprotection. Mol Cell. 27:17–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dabrowski A, Filip A, Zgodziński W,
Dabrowska M, Polańska D, Wójcik M, Zinkiewicz K and Wallner G:
Assessment of prognostic significance of cytoplasmic survivin
expression in advanced oesophageal cancer. Folia Histochem
Cytobiol. 42:169–172. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Warnecke-Eberz U, Hokita S, Xi H, Higashi
H, Baldus SE, Metzger R, Brabender J, Bollschweiler E, Mueller RP,
Dienes HP, et al: Overexpression of survivin mRNA is associated
with a favorable prognosis following neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy
in esophageal cancer. Oncol Rep. 13:1241–1246. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamauchi T, Nakamura N, Hiramoto M, Yuri
M, Yokota H, Naitou M, Takeuchi M, Yamanaka K, Kita A, Nakahara T,
et al: Sepantronium bromide (YM155) induces disruption of the
ILF3/p54(nrb) complex, which is required for survivin expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 425:711–716. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheng Q, Ling X, Haller A, Nakahara T,
Yamanaka K, Kita A, Koutoku H, Takeuchi M, Brattain MG and Li F:
Suppression of survivin promoter activity by YM155 involves
disruption of Sp1-DNA interaction in the survivin core promoter.
Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 3:179–197. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qin Q, Cheng H, Lu J, Zhan L, Zheng J, Cai
J, Yang X, Xu L, Zhu H, Zhang C, et al: Small-molecule survivin
inhibitor YM155 enhances radiosensitization in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma by the abrogation of G2 checkpoint and suppression
of homologous recombination repair. J Hematol Oncol. 7:622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao N, Mao Y, Han G, Ju Q, Zhou L, Liu F,
Xu Y and Zhao X: YM155, a survivin suppressant, triggers
PARP-dependent cell death (parthanatos) and inhibits esophageal
squamous-cell carcinoma xenografts in mice. Oncotarget.
6:18445–18459. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
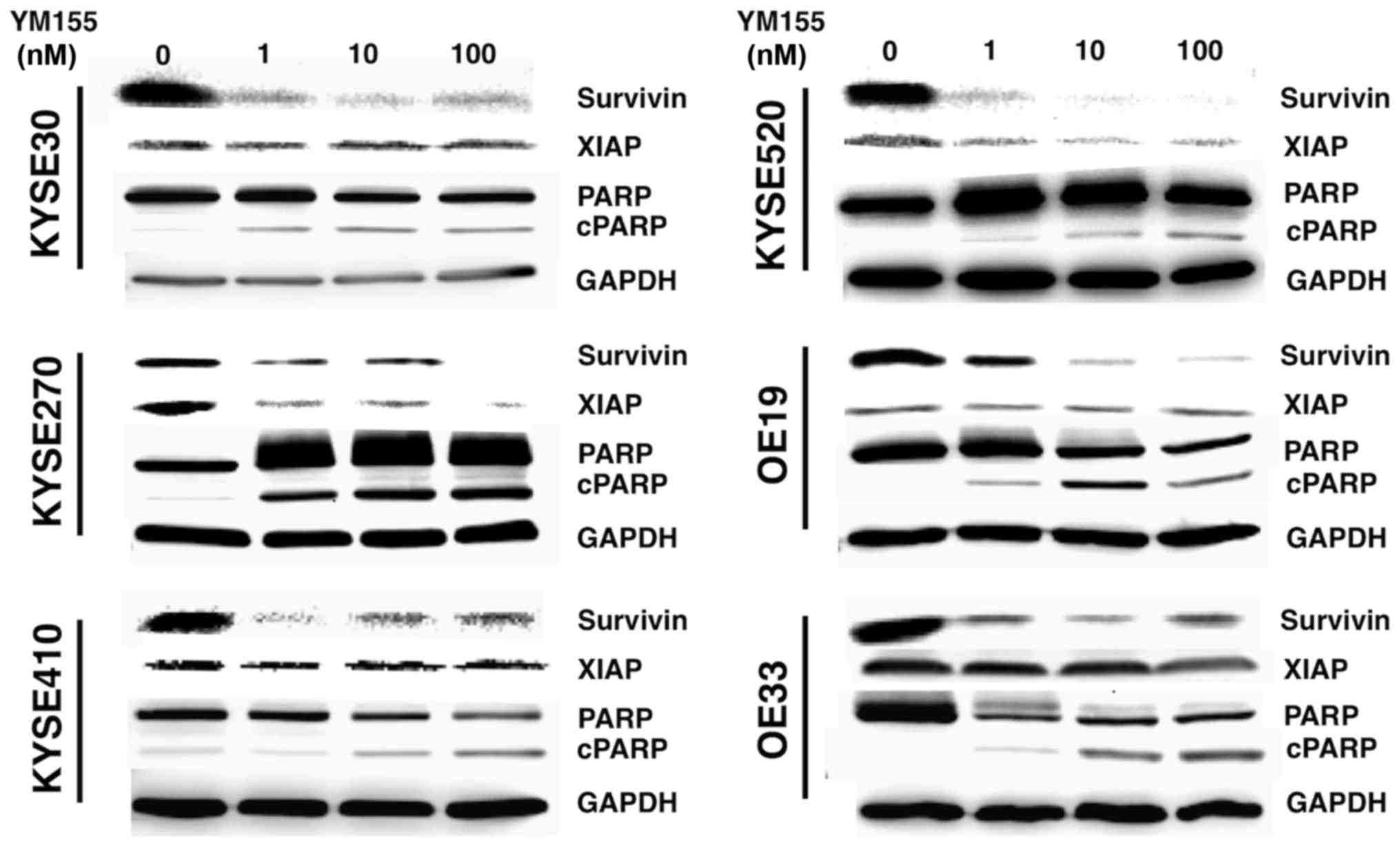
Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y,
Davidson NE and Poirier GG: Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 53:3976–3985. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Benetatos CA, Mitsuuchi Y, Burns JM,
Neiman EM, Condon SM, Yu G, Seipel ME, Kapoor GS, Laporte MG,
Rippin SR, et al: Birinapant (TL32711), a bivalent SMAC mimetic,
targets TRAF2-associated cIAPs, abrogates TNF-induced NF-κB
activation, and is active in patient-derived xenograft models. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:867–879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Flygare JA, Beresini M, Budha N, Chan H,
Chan IT, Cheeti S, Cohen F, Deshayes K, Doerner K, Eckhardt SG, et
al: Discovery of a potent small-molecule antagonist of inhibitor of
apoptosis (IAP) proteins and clinical candidate for the treatment
of cancer (GDC-0152). J Med Chem. 55:4101–4113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu Z, Sun C, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP,
Betz SF, Oost T, Herrmann J, Wu JC and Fesik SW: Structural basis
for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature.
408:1004–1008. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang
X and Shi Y: Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO.
Nature. 408:1008–1012. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fulda S: Smac mimetics as IAP antagonists.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 39:132–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bai L, Smith DC and Wang S: Small-molecule
SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther.
144:82–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Petersen SL, Peyton M, Minna JD and Wang
X: Overcoming cancer cell resistance to Smac mimetic induced
apoptosis by modulating cIAP-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:pp. 11936–11941. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Maas C, Tromp JM, van Laar J, Thijssen R,
Elias JA, Malara A, Krippner-Heidenreich A, Silke J, van Oers MH
and Eldering E: CLL cells are resistant to smac mimetics because of
an inability to form a ripoptosome complex. Cell Death Dis.
4:e7822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|