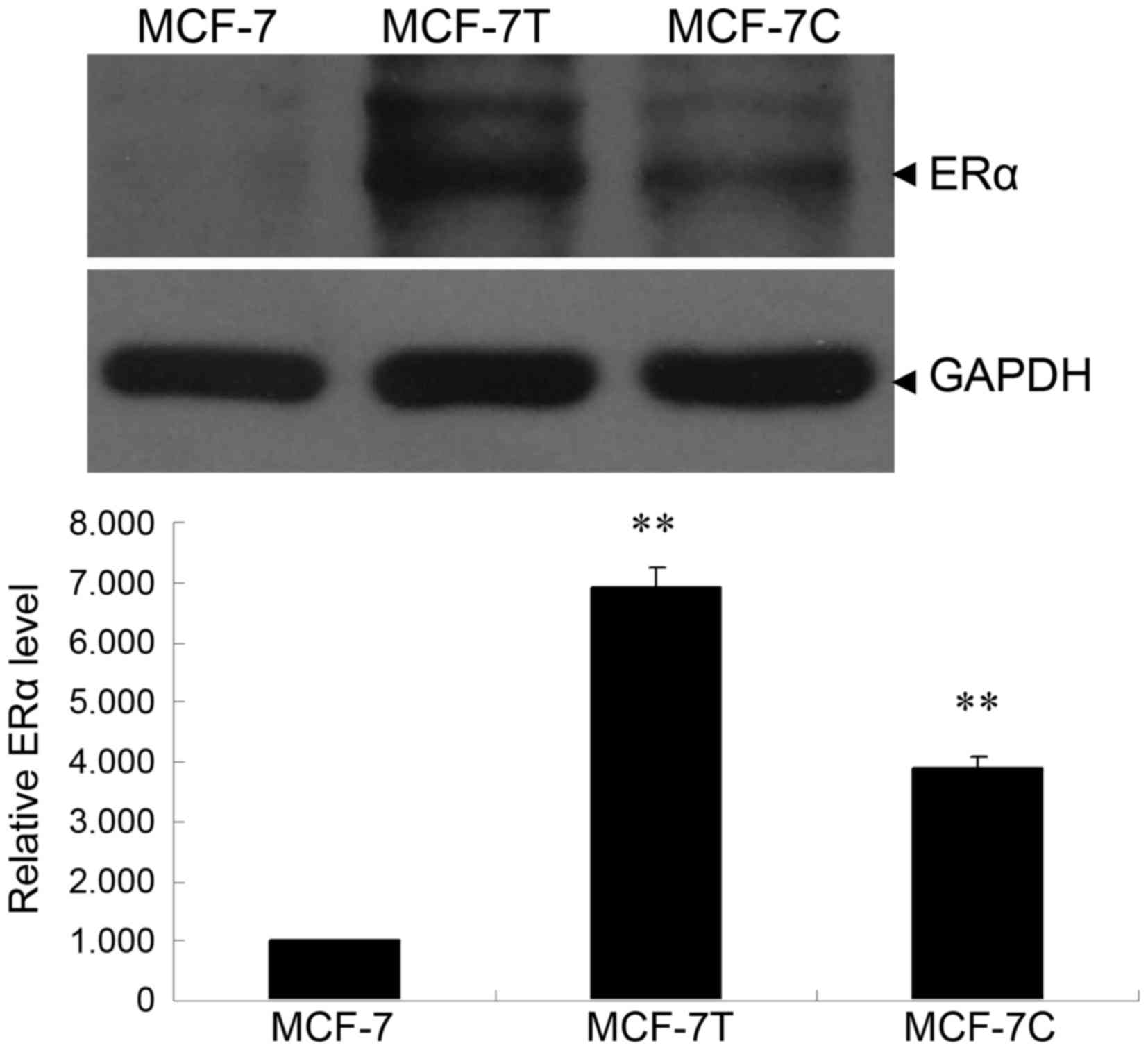
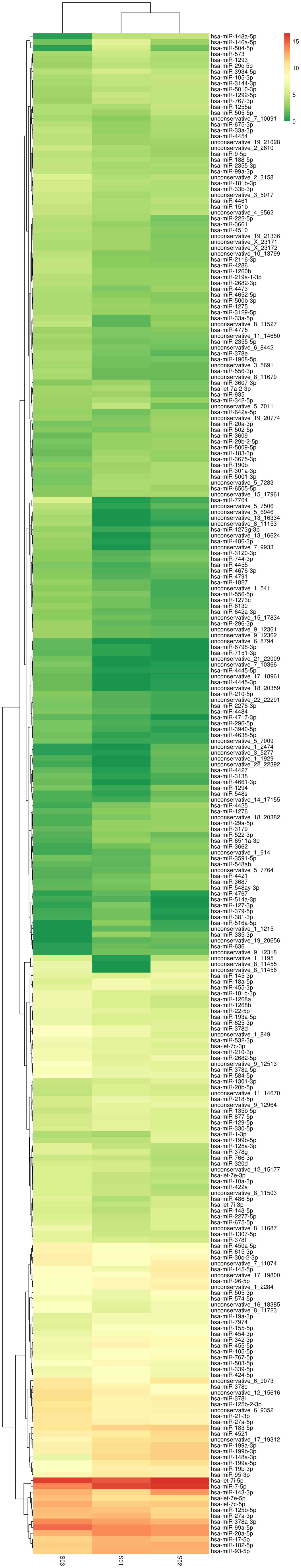
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rao X, Di Leva G, Li M, Fang F, Devlin C,
Hartman-Frey C, Burow ME, Ivan M, Croce CM and Nephew KP:
MicroRNA-221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by
regulating multiple signaling pathways. Oncogene. 30:1082–1097.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wolmark N, Mamounas EP, Baehner FL, Butler
SM, Tang G, Jamshidian F, Sing AP, Shak S and Paik S: Prognostic
impact of the combination of recurrence score and quantitative
estrogen receptor expression (ESR1) on predicting late distant
recurrence risk in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer after 5
years of Tamoxifen: Results from NRG oncology/national surgical
adjuvant breast and bowel project B-28 and B-14. J Clin Oncol.
34:2350–2358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ingle JN: Postmenopausal women with
hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Balancing benefit and
toxicity from aromatase inhibitors. Breast. 22 Suppl 2:S180–S183.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manavalan TT, Teng Y, Appana SN, Datta S,
Kalbfleisch TS, Li Y and Klinge CM: Differential expression of
microRNA expression in tamoxifen-sensitive MCF-7 versus
tamoxifen-resistant LY2 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
313:26–43. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arpino G, Wiechmann L, Osborne CK and
Schiff R: Crosstalk between the estrogen receptor and the HER
tyrosine kinase receptor family: Molecular mechanism and clinical
implications for endocrine therapy resistance. Endocr Rev.
29:217–233. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ciupek A, Rechoum Y, Gu G, Gelsomino L,
Beyer AR, Brusco L, Covington KR, Tsimelzon A and Fuqua SA:
Androgen receptor promotes tamoxifen agonist activity by activation
of EGFR in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
154:225–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karam M, Bièche I, Legay C, Vacher S,
Auclair C and Ricort JM: Protein kinase D1 regulates ERα-positive
breast cancer cell growth response to 17β-estradiol and contributes
to poor prognosis in patients. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2536–2552. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Musgrove EA and Sutherland RL: Biological
determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:631–643. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kondo N, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Fujii Y and
Yamashita H: miR-206 expression is down-regulated in estrogen
receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer. Cancer Res.
68:5004–5008. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adams BD, Furneaux H and White BA: The
micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen
receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and represses ERalpha messenger RNA and
protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol.
21:1132–1147. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B, Roy S,
Datta J, Shapiro CL, Jacob S and Majumder S: MicroRNA-221/222
confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting
p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 283:29897–29903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuan Y, Qin L, Liu D, Wu RC, Mussi P, Zhou
S, Songyang Z and Xu J: Genetic screening reveals an essential role
of p27kip1 in restriction of breast cancer progression.
Cancer Res. 67:8032–8042. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty
SM, Riggs KA, Li Y and Klinge CM: Estradiol downregulates miR-21
expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:2584–2595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Z, Yuan YC, Wang Y, Liu Z, Chan HJ
and Chen S: Down-regulation of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
associated with aromatase inhibitor resistance and a poor prognosis
in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 152:29–39. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang TH, Wu F, Loeb GB, Hsu R,
Heidersbach A, Brincat A, Horiuchi D, Lebbink RJ, Mo YY, Goga A and
McManus MT: Up-regulation of miR-21 by HER2/neu signaling promotes
cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 284:18515–18524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Valeri N, Gasparini P, Braconi C, Paone A,
Lovat F, Fabbri M, Sumani KM, Alder H, Amadori D, Patel T, et al:
MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating
human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp.
21098–21103. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang LY and Trujillo JM: Biological
characterization of multidrug-resistant human colon carcinoma
sublines induced/selected by two methods. Cancer Res. 50:3218–3225.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fahlgren N, Howell MD, Kasschau KD,
Chapman EJ, Sullivan CM, Cumbie JS, Givan SA, Law TF, Grant SR,
Dangl JL and Carrington JC: High-throughput sequencing of
Arabidopsis microRNAs: Evidence for frequent birth and death of
MIRNA genes. PLoS One. 2:e2192007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hammond SM: RNAi, microRNAs, and human
disease. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 58 Suppl 1:S63–S68. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bajan S and Hutvagner G: Regulation of
miRNA processing and miRNA mediated gene repression in cancer.
Microrna. 3:10–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nygaard S, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Eriksen
J, Balslev E, Flyger H, Tolstrup N, Møller S, Krogh A and Litman T:
Identification and analysis of miRNAs in human breast cancer and
teratoma samples using deep sequencing. BMC Med Genomics. 2:352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yahya SM and Elsayed GH: A summary for
molecular regulations of miRNAs in breast cancer. Clin Biochem.
48:388–396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rai G, Rai R, Saeidian AH and Rai M:
Microarray to deep sequencing: Transcriptome and miRNA profiling to
elucidate molecular pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Immunol Res. 64:14–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M,
Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dahiya N, Sherman-Baust CA, Wang TL,
Davidson B, Shih IeM, Zhang Y, Wood W III, Becker KG and Morin PJ:
MicroRNA expression and identification of putative miRNA targets in
ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 3:e24362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin B, Wang W, Meng XX, Du G, Li J, Zhang
SZ, Zhou BH and Fu ZH: Let-7 inhibits self-renewal of
hepatocellular cancer stem-like cells through regulating the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Wnt signaling pathway.
BMC Cancer. 16:8632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR, Schickel R,
Kistner EO, Jewell DA, Feig C, Lengyel E and Peter ME: Let-7
expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 11400–11405. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun X, Fan C, Hu LJ, Du N, Xu CW and Ren
H: Role of let-7 in maintaining characteristics of breast cancer
stem cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:789–792.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barekati Z, Radpour R, Lu Q, Bitzer J,
Zheng H, Toniolo P, Lenner P and Zhong XY: Methylation signature of
lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer.
12:2442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao Y, Deng C, Lu W, Xiao J, Ma D, Guo M,
Recker RR, Gatalica Z, Wang Z and Xiao GG: let-7 microRNAs induce
tamoxifen sensitivity by downregulation of estrogen receptor α
signaling in breast cancer. Mol Med. 17:1233–1241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qi L, Bart J, Tan LP, Platteel I, Sluis
Tv, Huitema S, Harms G, Fu L, Hollema H and Berg Av: Expression of
miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia
of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:1632009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S,
Park JK, Dai Z, Liu CG, Schmittgen TD, Reinhold WC, Croce CM, et
al: MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang ZX, Lu BB, Wang H, Cheng ZX and Yin
YM: MicroRNA-21 modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells
to doxorubicin by targeting PTEN. Arch Med Res. 42:281–290. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee JA, Lee HY, Lee ES, Kim I and Bae JW:
Prognostic implications of microRNA-21 overexpression in invasive
ductal carcinomas of the breast. J Breast Cancer. 14:269–275. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ota D, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Iwatsuki M,
Kataoka A, Masuda N, Ishii H, Ohno S and Mori M: Identification of
recurrence-related microRNAs in the bone marrow of breast cancer
patients. Int J Oncol. 38:955–962. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian F, Shen Y, Chen Z, Li R, Lu J and Ge
Q: Aberrant miR-181b-5p and miR-486-5p expression in serum and
tissue of non-small cell lung cancer. Gene. 591:338–343. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shindo Y, Hazama S, Nakamura Y, Inoue Y,
Kanekiyo S, Suzuki N, Takenouchi H, Tsunedomi R, Nakajima M, Ueno
T, et al: miR-196b, miR-378a and miR-486 are predictive biomarkers
for the efficacy of vaccine treatment in colorectal cancer. Oncol
Lett. 14:1355–1362. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ren C, Chen H, Han C, Fu D, Zhou L, Jin G,
Wang F, Wang D, Chen Y, Ma L, et al: miR-486-5p expression pattern
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric cancer and its
prognostic value. Oncotarget. 7:15840–15853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Cui G, Wang X and Yang Z:
MicroRNA-486-5p targeting PIM-1 suppresses cell proliferation in
breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 35:11137–11145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rusca N and Monticelli S: MiR-146a in
immunity and disease. Mol Biol Int. 2011:4373012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Madhala-Levy D, Williams VC, Hughes SM,
Reshef R and Halevy O: Cooperation between Shh and IGF-I in
promoting myogenic proliferation and differentiation via the
MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways requires Smo activity. J Cell
Physiol. 227:1455–1464. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Deng X, Zeng X and Peng X: The role
of mir-148a in cancer. J Cancer. 7:1233–1241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cittelly DM, Das PM, Spoelstra NS,
Edgerton SM, Richer JK, Thor AD and Jones FE: Downregulation of
miR-342 is associated with tamoxifen resistant breast tumors. Mol
Cancer. 9:3172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Farmer P, Bonnefoi H, Becette V,
Tubiana-Hulin M, Fumoleau P, Larsimont D, Macgrogan G, Bergh J,
Cameron D, Goldstein D, et al: Identification of molecular apocrine
breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene. 24:4660–4671.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jordan MA and Wilson L: Microtubules as a
target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:253–265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Feng D: Screening and functional studies
of miRNAs associated with drug-resistance and relapse in leukemia.
Journal. 2011.
|
|
54
|
Nam S, Long X, Kwon C, Kim S and Nephew
KP: An integrative analysis of cellular contexts, miRNAs and mRNAs
reveals network clusters associated with antiestrogen-resistant
breast cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 13:7322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu MX, Siu MK, Liu SS, Yam JW, Ngan HY
and Chan DW: Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-199b-5p is associated
with acquired chemoresistance via activation of JAG1-Notch1
signaling in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 5:944–958. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|