|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yasui W, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Anami K,
Naito Y and Oue N: Molecular pathology of gastric cancer: Research
and practice. Pathol Res Pract. 207:608–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen DL, Zhang DS, Lu YX, Chen LZ, Zeng
ZL, He MM, Wang FH, Li YH, Zhang HZ, Pelicano H, et al:
microRNA-217 inhibits tumor progression and metastasis by
downregulating EZH2 and predicts favorable prognosis in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:10868–10879. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao X, Tang C, Xiao S, Fu C and Yu P:
Enhancement of proliferation and invasion by MicroRNA-590-5p via
targeting PBRM1 in clear cell renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Res.
20:537–544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fernandez-Santiago R, Iranzo A, Gaig C,
Serradell M, Fernández M, Tolosa E, Santamaría J and Ezquerra M:
MicroRNA association with synucleinopathy conversion in rapid eye
movement behavior disorder. Ann Neurol. 77:895–901. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang AM, Huang TT, Hsu KW, Huang KH, Fang
WL, Yang MH, Lo SS, Chi CW, Lin JJ and Yeh TS: Yin Yang 1 is a
target of microRNA-34 family and contributes to gastric
carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 5:5002–5016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, An Y, Hu H, Yin J, Zhang P,
Nie Y, Wu K, Shi Y and Fan D: MiR-19a/b modulate the metastasis of
gastric cancer cells by targeting the tumour suppressor MXD1. Cell
Death Dis. 5:e11442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han TS, Hur K, Xu G, Choi B, Okugawa Y,
Toiyama Y, Oshima H, Oshima M, Lee HJ, Kim VN, et al: MicroRNA-29c
mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting
ITGB1. Gut. 64:203–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gong J, Li J, Wang Y, Liu C, Jia H, Jiang
C, Wang Y, Luo M, Zhao H, Dong L, et al: Characterization of
microRNA-29 family expression and investigation of their
mechanistic roles in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 35:497–506.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Z, Cao Y, Jie Z, Liu Y, Li Y, Li J, Zhu
G, Liu Z, Tu Y, Peng G, et al: miR-495 and miR-551a inhibit the
migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by directly
interacting with PRL-3. Cancer Lett. 323:41–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nishida N, Mimori K, Fabbri M, Yokobori T,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y and Mori M:
MicroRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells
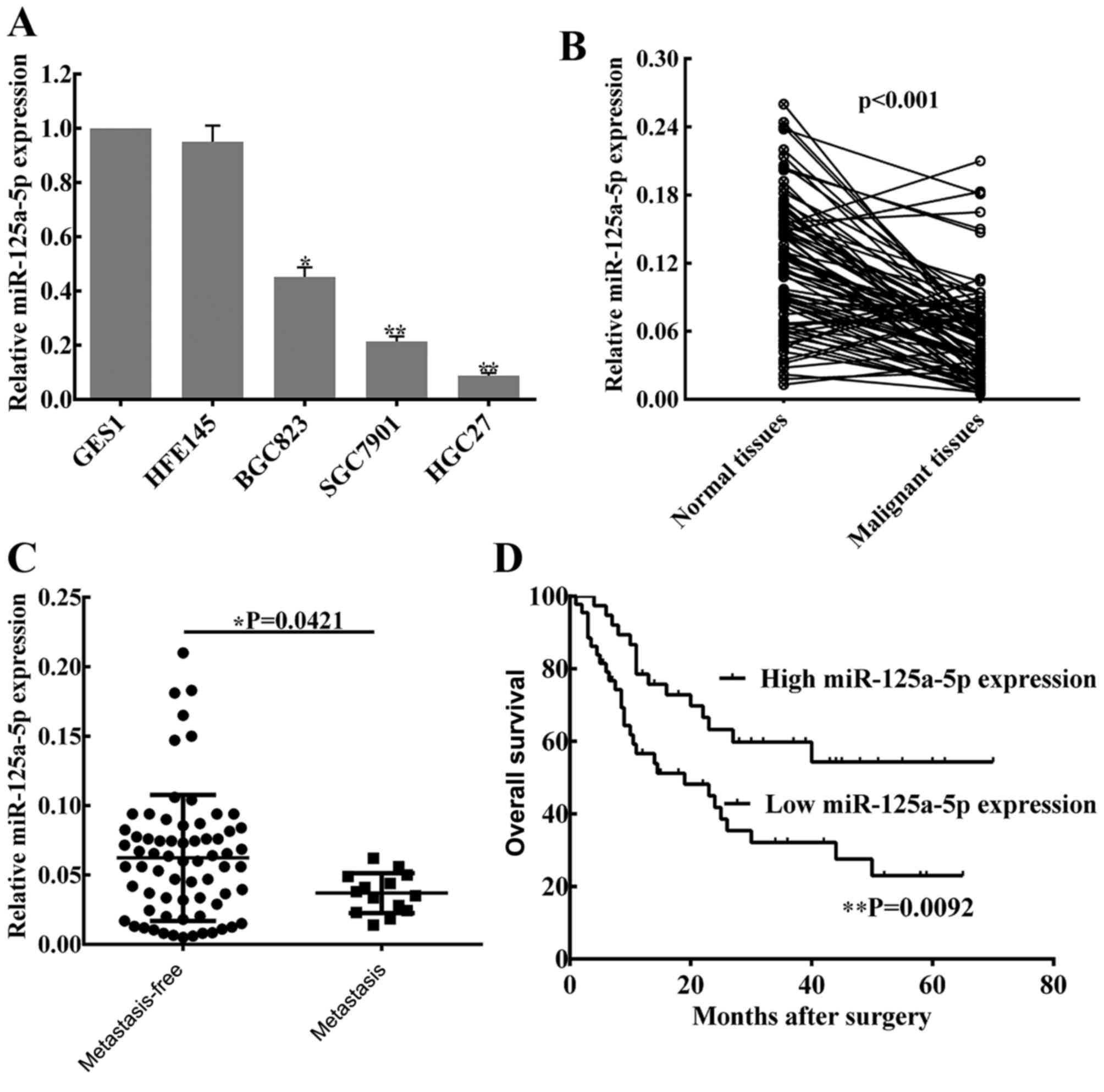
in combination with trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2725–2733.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seraj MJ, Samant RS, Verderame MF and
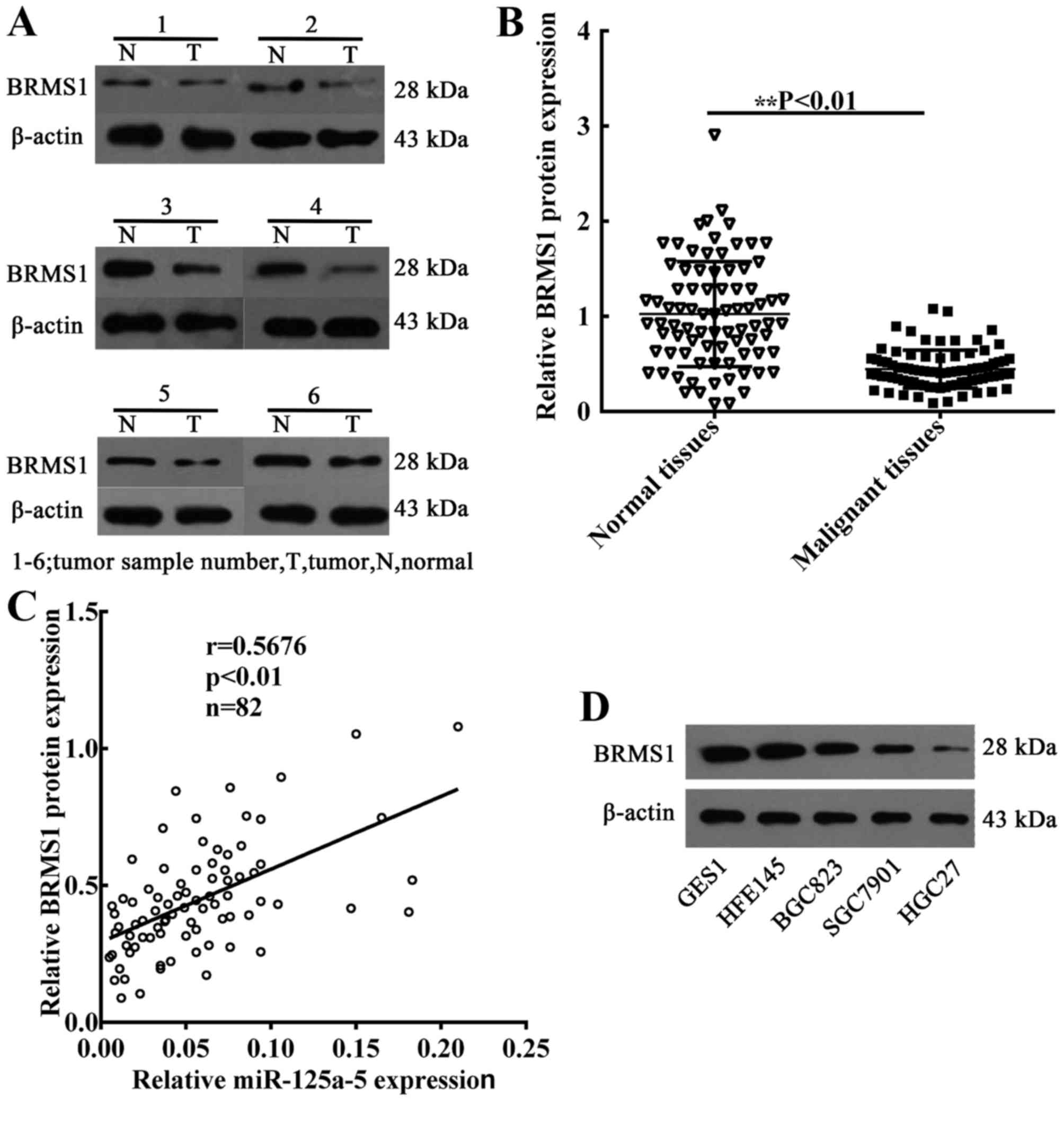
Welch DR: Functional evidence for a novel human breast carcinoma
metastasis suppressor, BRMS1, encoded at chromosome 11q13. Cancer
Res. 60:2764–2769. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu J, Wang Y, Qiao X, Saiyin H, Zhao S,
Qiao S and Wu Y: Cloning and characterization of a novel human
BRMS1 transcript variant in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 337:266–275. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Mayo MW, Nagji AS, Hall EH, Shock
LS, Xiao A, Stelow EB and Jones DR: BRMS1 suppresses lung cancer
metastases through an E3 ligase function on histone
acetyltransferase p300. Cancer Res. 73:1308–1317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Slipicevic A, Holm R, Emilsen E, Ree
Rosnes AK, Welch DR, Mælandsmo GM and Flørenes VA: Cytoplasmic
BRMS1 expression in malignant melanoma is associated with increased
disease-free survival. BMC Cancer. 12:732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Guan J, Sun Y, Chai J, Zou T,
Gong W, Zhu Z, Liu X, Hou Q and Song X: Effect of BRMS1 on
tumorigenicity and metastasis of human rectal cancer. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 70:505–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsieh TH, Hsu CY, Tsai CF, Long CY, Chai
CY, Hou MF, Lee JN, Wu DC, Wang SC and Tsai EM: miR-125a-5p is a
prognostic biomarker that targets HDAC4 to suppress breast
tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6:494–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang L, Huang Q, Chang J, Wang E and Qiu
X: MicroRNA HSA-miR-125a-5p induces apoptosis by activating p53 in
lung cancer cells. Exp Lung Res. 37:387–398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Washington K: 7th edition of the AJCC
cancer staging manual: Stomach. Ann Surg Oncol. 12:3077–3079. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Jiang W, Wang Y, Wu J, Saiyin H,
Qiao X, Mei X, Guo B, Fang X, Zhang L, et al: Breast cancer
metastasis suppressor 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell
apoptosis via suppressing osteopontin expression. PLoS One.
7:e429762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garofalo M and Croce CM: microRNAs: Master
regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 51:25–43. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB: MicroRNA in
cancer prognosis. N Engl J Med. 359:2720–2722. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Day E and Lal A: MicroRNAs and their
target gene networks in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
12:2012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang L, Huang Q, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Chang
J, Qiu X and Wang E: Hsa-miR-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p are
downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and have inverse
effects on invasion and migration of lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
10:3182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tong Z, Liu N, Lin L, Guo X, Yang D and
Zhang Q: miR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces
apoptosis in colon cancer via targeting BCL2, BCL2L12 and MCL1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 75:129–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Qian P, Zhang X, Zhang M, Wang H,
Wu M, Kong X, Tan S, Ding K, Perry JK, et al: Autocrine/paracrine
human growth hormone-stimulated microRNA 96-182-183 cluster
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in breast
cancer. J Biol Chem. 290:13812–13829. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hurst DR: Metastasis suppression by BRMS1
associated with SIN3 chromatin remodeling complexes. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 31:641–651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mei P, Bai J, Shi M, Liu Q, Li Z, Fan Y
and Zheng J: BRMS1 suppresses glioma progression by regulating
invasion, migration and adhesion of glioma cells. PLoS One.
9:e985442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
You J, He X, Ding H and Zhang T: BRMS1
regulates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 71:465–472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roberts MR, Hong CC, Edge SB, Yao S,
Bshara W, Higgins MJ, Freudenheim JL and Ambrosone CB: Case-only
analyses of the associations between polymorphisms in the
metastasis-modifying genes BRMS1 and SIPA1 and breast tumor
characteristics, lymph node metastasis, and survival. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 139:873–885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q,
Park SJ, Shin WC, Yang HD, Park M, Park WS, et al: MicroRNA-31
functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:8089–8102. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Wang T, Cao Z, Huang H, Li J, Liu W,
Liu S, You L, Zhou L, Zhang T and Zhao Y: MiR-497 downregulation
contributes to the malignancy of pancreatic cancer and associates
with a poor prognosis. Oncotarget. 5:6983–6993. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Q, Huang Z, Guo W, Ni S, Xiao X, Wang
L, Huang D, Tan C, Xu Q, Zha R, et al: microRNA-202-3p inhibits
cell proliferation by targeting ADP-ribosylation factor-like 5A in
human colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1146–1157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Orom UA, Nielsen FC and Lund AH:
MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and
enhances their translation. Mol Cell. 30:460–471. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsai NP, Lin YL and Wei LN: MicroRNA
mir-346 targets the 5′-untranslated region of receptor-interacting
protein 140 (RIP140) mRNA and up-regulates its protein expression.
Biochem J. 424:411–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|