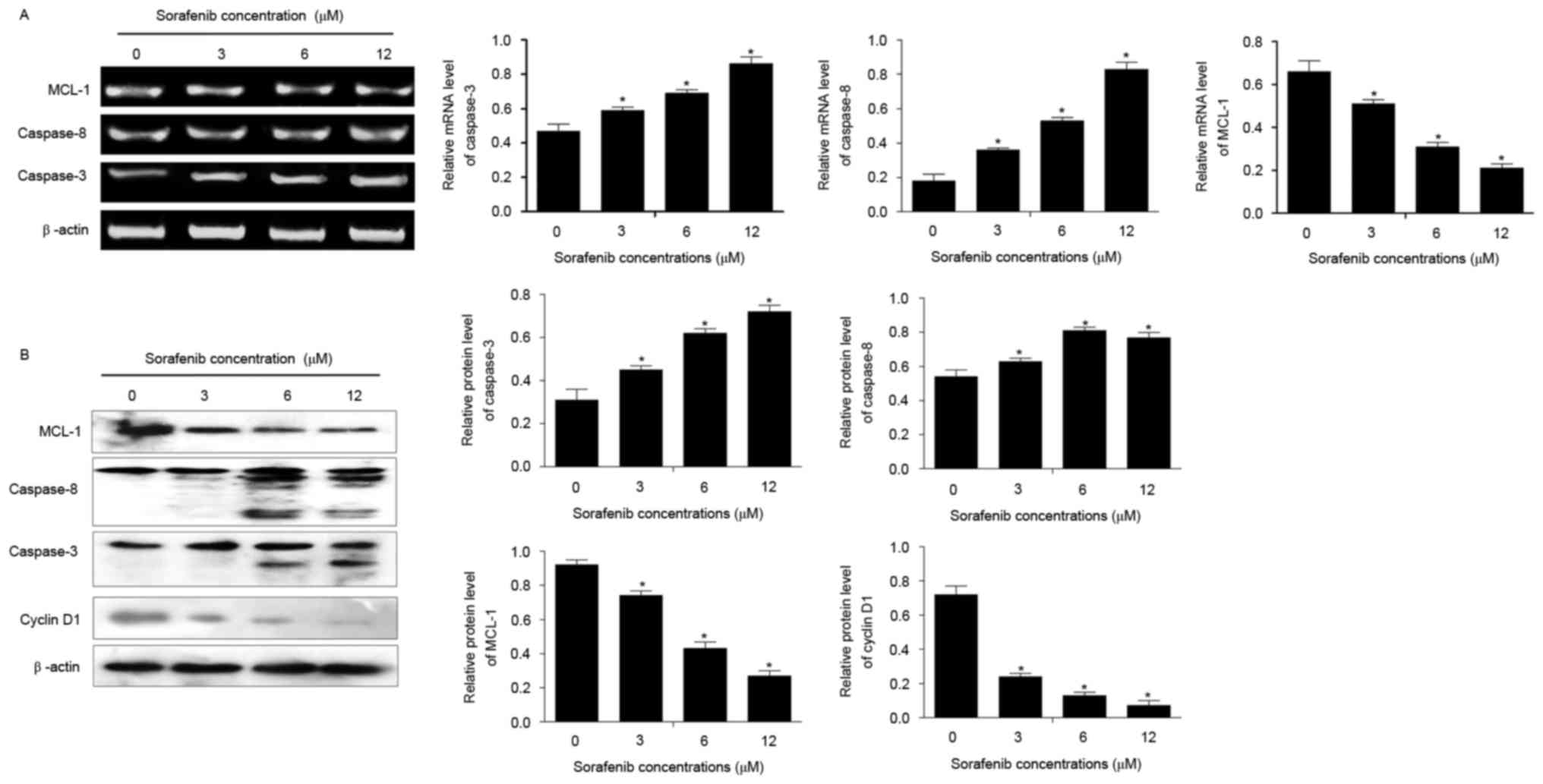
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tallman MS: Acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 27:12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lo-Coco F, Avvisati G, Vignetti M, Thiede
C, Orlando SM, Iacobelli S, Ferrara F, Fazi P, Cicconi L, Di Bona
E, et al: Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide for acute
promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 369:111–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bally C, Fadlallah J, Leverger G, Bertrand
Y, Robert A, Baruchel A, Guerci A, Recher C, Raffoux E, Thomas X,
et al: Outcome of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) in children
and adolescents: An Analysis in two consecutive trials of the
European APL Group. J Clin Oncol. 30:1641–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeshita A, Shigeno K, Shinjo K, Naito K,
Ohnishi K, Hayashi H, Tanimoto M and Ohno R: All-trans retinoic
acid (ATRA) differentiates acute promyelocytic leukemia cells
independently of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) related multidrug
resistance. Leuk Lymphoma. 42:739–746. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adnane L, Trail PA, Taylor I and Wilhelm
SM: Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that
targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases
VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol. 407:597–612.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, Kodama T,
Miyagi T, Hosui A, Tatsumi T, Ishida H, Noda T, Nagano H, et al:
The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and
potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 52:698–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Panka DJ, Wang W, Atkins MB and Mier JW:
The Raf inhibitor BAY 43-9006 (Sorafenib) induces
caspase-independent apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cancer Res.
66:1611–1619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang F, Brown C, Buettner R, Hedvat M,
Starr R, Scuto A, Schroeder A, Jensen M and Jove R: Sorafenib
induces growth arrest and apoptosis of human glioblastoma cells
through the dephosphorylation of signal transducers and activators
of transcription 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:953–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Ruvolo VR, McQueen
T, Evans RL, Bornmann WG, McCubrey J, Cortes J and Andreeff M:
Sorafenib induces apoptosis of AML cells via Bim-mediated
activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leukemia.
22:808–818. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ravandi F, Cortes JE, Jones D, Faderl S,
Garcia-Manero G, Konopleva MY, O'Brien S, Estrov Z, Borthakur G,
Thomas D, et al: Phase I/II study of combination therapy with
sorafenib, idarubicin, and cytarabine in younger patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 28:1856–1862. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pratz KW, Cho E, Levis MJ, Karp JE, Gore
SD, McDevitt M, Stine A, Zhao M, Baker SD, Carducci MA, et al: A
pharmacodynamic study of sorafenib in patients with relapsed and
refractory acute leukemias. Leukemia. 24:1437–1444. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ravandi F, Alattar ML, Grunwald MR, Rudek
MA, Rajkhowa T, Richie MA, Pierce S, Daver N, Garcia-Manero G,
Faderl S, et al: Phase 2 study of azacytidine plus sorafenib in
patients with acute myeloid leukemia and FLT-3 internal tandem
duplication mutation. Blood. 121:4655–4662. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gallagher RE, Moser BK, Racevskis J, Poiré
X, Bloomfield CD, Carroll AJ, Ketterling RP, Roulston D,
Schachter-Tokarz E, Zhou DC, et al: Treatment-influenced
associations of PML-RARα mutations, FLT3 mutations, and additional
chromosome abnormalities in relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Blood. 120:2098–2108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng CL, Guo W, Ji T, Ren T, Yang Y, Li
DS, Qu HY, Li X, Tang S, Yan TQ and Tang XD: Sorafenib induces
growth inhibition and apoptosis in human synovial sarcoma cells via
inhibiting the RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1729–1736. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson DG and Walker CL: Cyclins and cell
cycle checkpoints. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 39:295–312. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou NC, Liu BL, Qi MY, Xu B and Liu X:
Effects of sorafenib on proliferation and apoptosis of human
multiple myeloma cell RPMI 8226. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za
Zhi. 22:1331–1335. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schult C, Dahlhaus M, Ruck S, Sawitzky M,
Amoroso F, Lange S, Etro D, Glass A, Fuellen G, Boldt S, et al: The
multikinase inhibitor Sorafenib displays significant
antiproliferative effects and induces apoptosis via caspase 3, 7
and PARP in B- and T-lymphoblastic cells. BMC cancer. 10:5602010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng XW, Lee SH, Dai H, Loegering D, Yu C,
Flatten K, Schneider P, Dai NT, Kumar SK, Smith BD, et al: Mcl-1 as
a buffer for proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members during TRAIL-induced
apoptosis: A mechanistic basis for sorafenib (bay 43-9006)-induced
TRAIL sensitization. J Biol Chem. 282:29831–29846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang K, Luo C, Li Y, Lu C, Zhou W, Huang H
and Chen X: The study of a novel sorafenib derivative HLC-080 as an
antitumor agent. PLoS One. 9:e1018892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Locatelli SL, Giacomini A, Guidetti A,
Cleris L, Mortarini R, Anichini A, Gianni AM and Carlo-Stella C:
Perifosine and sorafenib combination induces mitochondrial cell
death and antitumor effects in NOD/SCID mice with Hodgkin lymphoma
cell line xenografts. Leukemia. 27:1677–1687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang F, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Lee JT,
Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, Franklin R and McCubrey JA: Regulation of
cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
(Review). Int J Oncol. 22:469–480. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blalock WL, Weinstein-Oppenheimer C, Chang
F, Hoyle PE, Wang XY, Algate PA, Franklin RA, Oberhaus SM, Steelman
LS and McCubrey JA: Signal transduction, cell cycle regulatory, and
anti-apoptotic pathways regulated by IL-3 in hematopoietic cells:
Possible sites for intervention with anti-neoplastic drugs.
Leukemia. 13:1109–1166. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang F and McCubrey JA: P21(Cip1) induced
by Raf is associated with increased Cdk4 activity in hematopoietic
cells. Oncogene. 20:4354–4364. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Malumbres M, Pérez De Castro I, Hernández
MI, Jiménez M, Corral T and Pellicer A: Cellular response to
oncogenic ras involves induction of the Cdk4 and Cdk6 inhibitor
p15(INK4b). Mol Cell Biol. 20:2915–2925. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed
JC, Lainé J and Rivard N: MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the
expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of
human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 79:355–369. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|