|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGuire S: World cancer report 2014.
Geneva, Switzerland: World health organization, international
agency for research on cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr.
7:418–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu M, Hu Y, He J and Li B: Prognostic
value of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in lung cancer: A
systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01473742016.
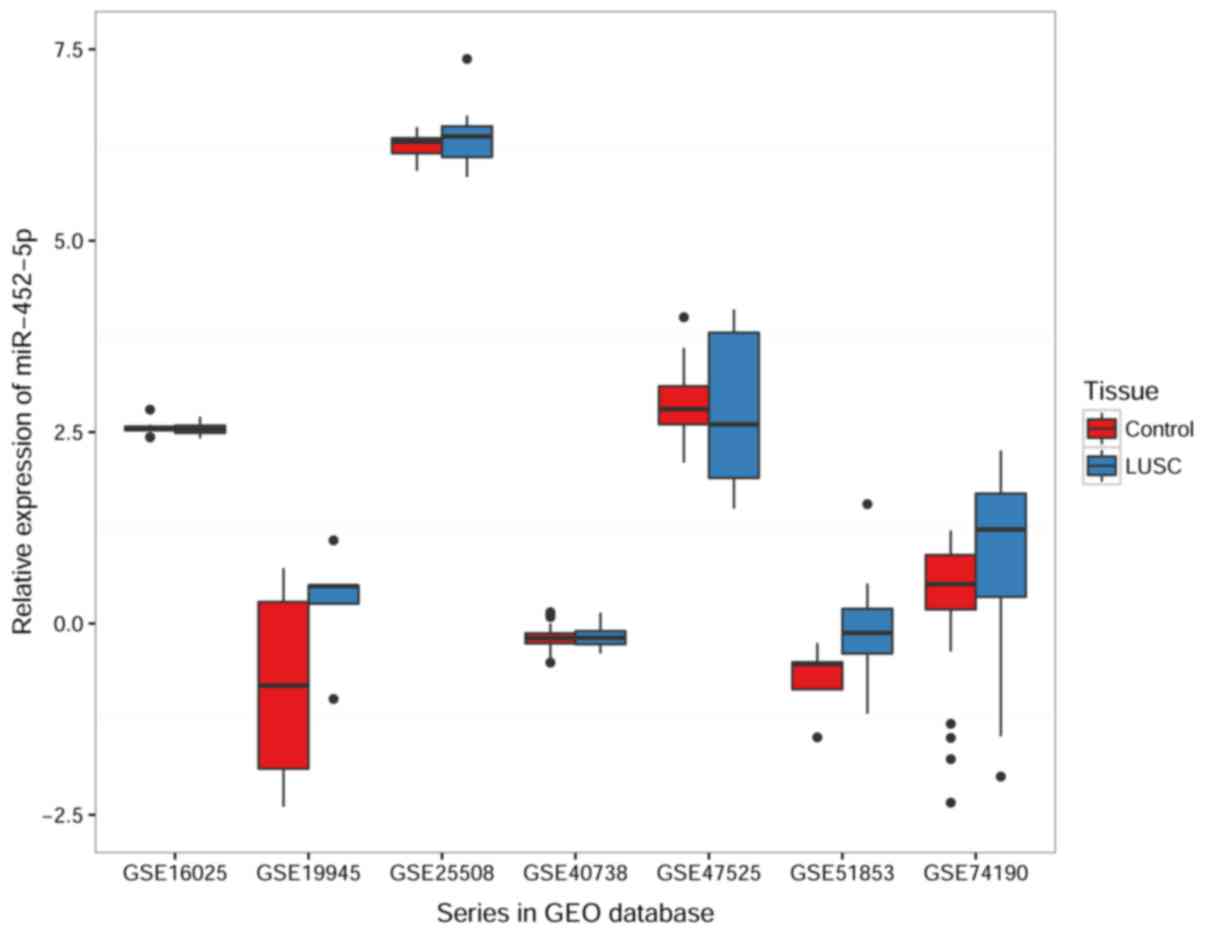
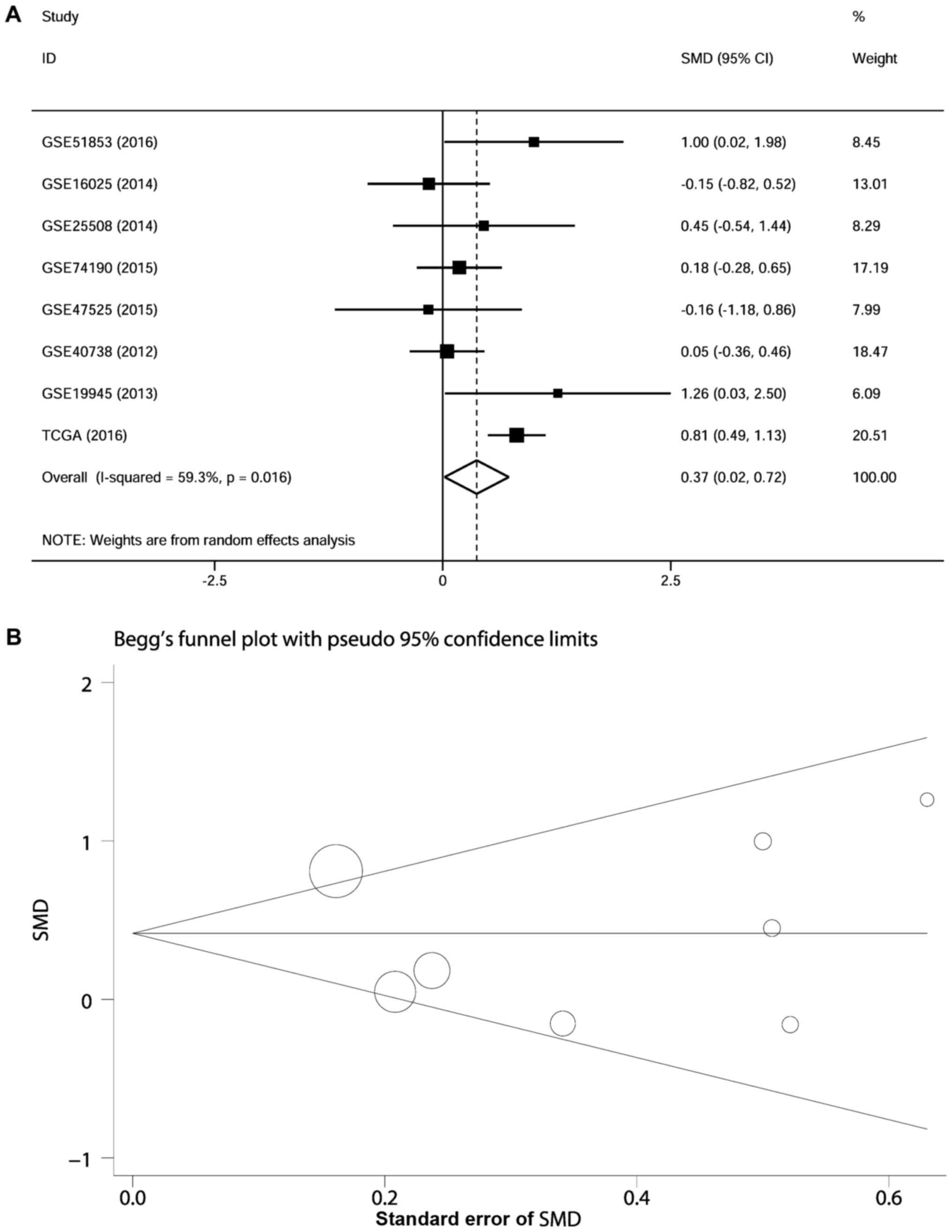
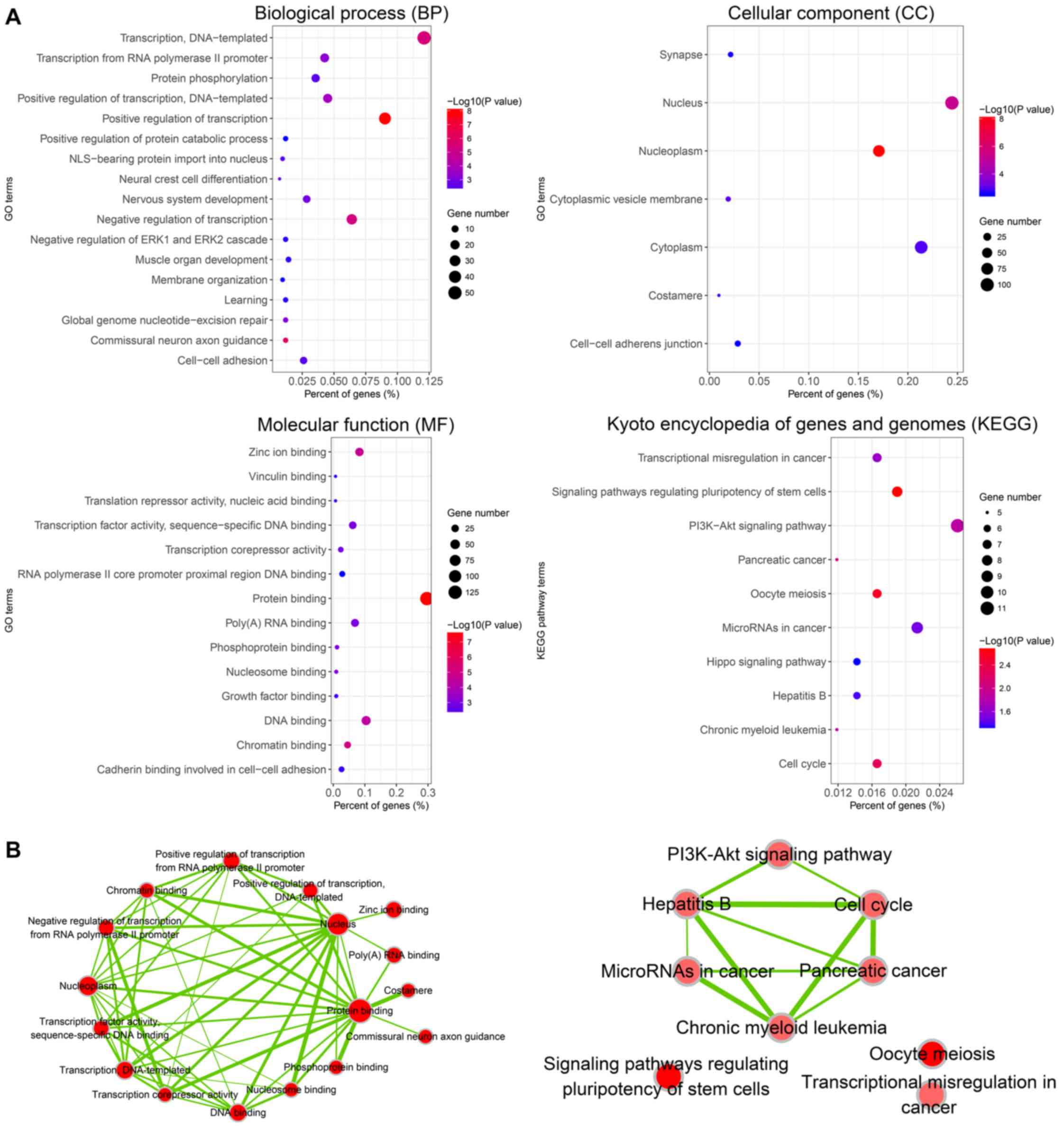
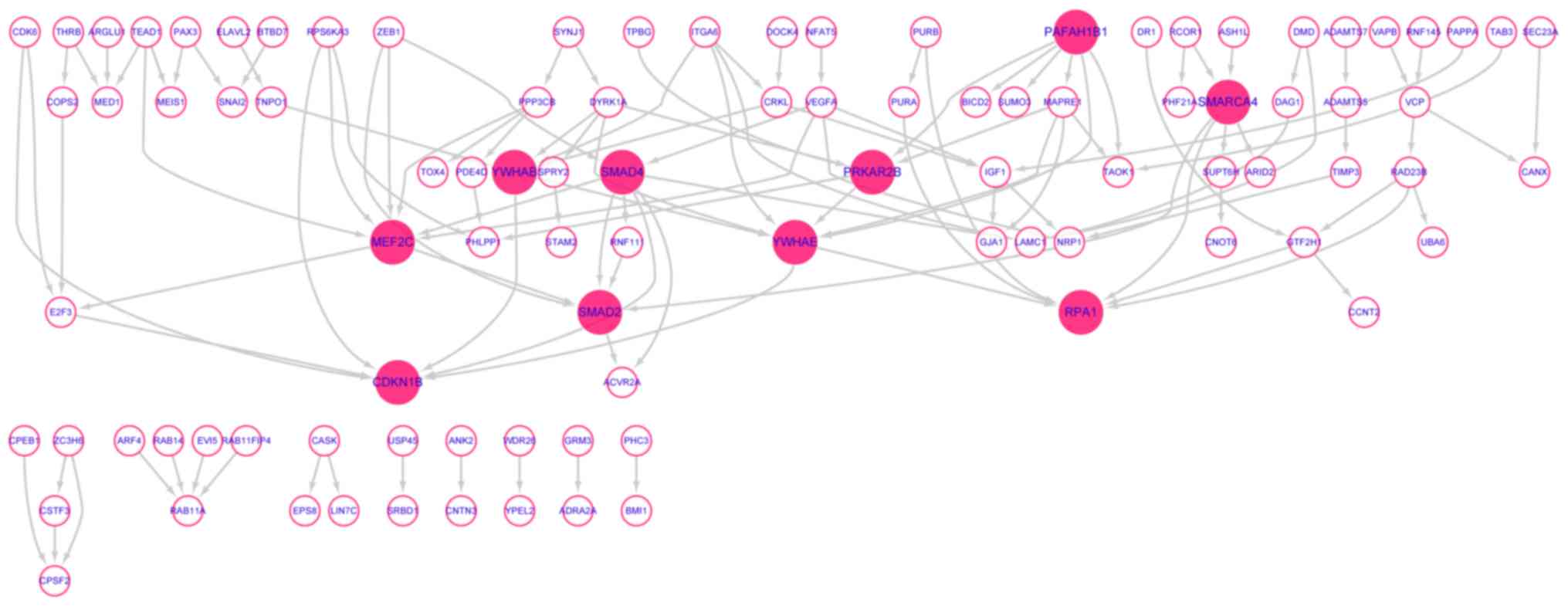
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schmidt B, Beyer J, Dietrich D, Bork I,
Liebenberg V and Fleischhacker M: Quantification of cell-free
mSHOX2 Plasma DNA for therapy monitoring in advanced stage
non-small cell (NSCLC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients.
PLoS One. 10:e01181952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takahashi A, Ishii G, Neri S, Yoshida T,
Hashimoto H, Suzuki S, Umemura S, Matsumoto S, Yoh K, Niho S, et
al: Podoplanin-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibit
small cell lung cancer growth. Oncotarget. 6:9531–9541. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meza R, Meernik C, Jeon J and Cote ML:
Lung cancer incidence trends by gender, race and histology in the
United States, 1973–2010. PLoS One. 10:e01213232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Han Y, Wang X, Wang W, Wang X, Wen
M, Xia J, Xing H, Li X and Zhang Z: Correlation of EGFR Del 19 with
Fn14/JAK/STAT signaling molecules in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Rep. 36:1030–1040. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CK, Brown C, Gralla RJ, Hirsh V,
Thongprasert S, Tsai CM, Tan EH, Ho JC, Chu da T, Zaatar A, et al:
Impact of EGFR inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer on
progression-free and overall survival: A meta-analysis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 105:595–605. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Drilon A, Rekhtman N, Ladanyi M and Paik
P: Squamous-cell carcinomas of the lung: Emerging biology,
controversies, and the promise of targeted therapy. Lancet Oncol.
13:e418–e426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu C, Li S, Chen T, Hu H, Ding C, Xu Z,
Chen J, Liu Z, Lei Z, Zhang HT, et al: miR-296-5p suppresses cell
viability by directly targeting PLK1 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Rep. 35:497–503. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Miao L, Ni R, Zhang H, Li L, Wang
X, Li X and Wang J: microRNA-520a-3p inhibits proliferation and
cancer stem cell phenotype by targeting HOXD8 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:3529–3535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang D, Ma J, Ji X, Xu F and Wei Y:
miR-141 regulation of EIF4E expression affects docetaxel
chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep.
37:608–616. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou L, Di Q, Sun B, Wang X, Li M and Shi
J: MicroRNA-194 restrains the cell progression of non-small cell
lung cancer by targeting human nuclear distribution protein C.
Oncol Rep. 35:3435–3444. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Wei L and Zhao S: miR-338 inhibits
the metastasis of lung cancer by targeting integrin β3. Oncol Rep.
36:1467–1474. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu X, Liu T, Fang O, Dong W, Zhang F,
Leach L, Hu X and Luo Z: MicroRNA-708-5p acts as a therapeutic
agent against metastatic lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:2417–2432.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li D, Du X, Liu A and Li P: Suppression of
nucleosome-binding protein 1 by miR-326 impedes cell proliferation
and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
35:1117–1124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taylor MA, Wappett M, Delpuech O, Brown H
and Chresta CM: Enhanced MAPK signaling drives ETS1-mediated
induction of miR-29b leading to downregulation of TET1 and changes
in epigenetic modifications in a subset of lung SCC. Oncogene.
35:4345–4357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Olbromski M, Grzegrzolka J,
Jankowska-Konsur A, Witkiewicz W, Podhorska-Okolow M and Dziegiel
P: MicroRNAs modulate the expression of the SOX18 transcript in
lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 36:2884–2892. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Altuvia Y, Landgraf P, Lithwick G, Elefant
N, Pfeffer S, Aravin A, Brownstein MJ, Tuschl T and Margalit H:
Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:2697–2706. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Veerla S, Lindgren D, Kvist A, Frigyesi A,
Staaf J, Persson H, Liedberg F, Chebil G, Gudjonsson S, Borg A, et
al: MiRNA expression in urothelial carcinomas: Important roles of
miR-10a, miR-222, miR-125b, miR-7 and miR-452 for tumor stage and
metastasis, and frequent homozygous losses of miR-31. Int J Cancer.
124:2236–2242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu SG, Qin XG, Zhao BS, Qi B, Yao WJ,
Wang TY, Li HC and Wu XN: Differential expression of miRNAs in
esophageal cancer tissue. Oncol Lett. 5:1639–1642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng Q, Sheng Q, Jiang C, Shu J, Chen J,
Nie Z, Lv Z and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-452 promotes tumorigenesis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor 1B. Mol Cell Biochem. 389:187–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Q, Gong JP, Li J, Zhong SL, Chen WX,
Zhang JY, Ma TF, Ji H, Lv MM, Zhao JH and Tang JH: Down-regulation
of miRNA-452 is associated with adriamycin-resistance in breast
cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5137–5142. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kristensen H, Haldrup C, Strand S,
Mundbjerg K, Mortensen MM, Thorsen K, Ostenfeld MS, Wild PJ, Arsov
C, Goering W, et al: Hypermethylation of the GABRE~miR-452~miR-224
promoter in prostate cancer predicts biochemical recurrence after
radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2169–2181. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu L, Chen K, Wu J, Shi L, Hu B, Cheng S,
Li M and Song L: Downregulation of miR-452 promotes stem-like
traits and tumorigenicity of gliomas. Clin Cancer Res.
19:3429–3438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Han L, Pang J, Wang Y, Feng F and
Jiang Q: Expression of microRNA-452 via adenoviral vector inhibits
non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation and metastasis.
Tumour Biol. 37:8259–8270. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He Z, Xia Y, Pan C, Ma T, Liu B, Wang J,
Chen L and Chen Y: Up-regulation of MiR-452 inhibits metastasis of
non-small cell lung cancer by regulating BMI1. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 37:387–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He Z, Xia Y, Liu B, Qi X, Li Z, Wang J,
Chen L and Chen Y: Down-regulation of miR-452 is associated with
poor prognosis in the non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis.
8:894–900. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Merico D, Isserlin R, Stueker O, Emili A
and Bader GD: Enrichment map: A network-based method for gene-set
enrichment visualization and interpretation. PLoS One.
5:e139842010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shannon PT, Grimes M, Kutlu B, Bot JJ and
Galas DJ: RCytoscape: Tools for exploratory network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 14:2172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Beckers A, Van Peer G, Carter DR, Mets E,
Althoff K, Cheung BB, Schulte JH, Mestdagh P, Vandesompele J,
Marshall GM, et al: MYCN-targeting miRNAs are predominantly
downregulated during MYCN-driven neuroblastoma tumor formation.
Oncotarget. 6:5204–5216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY,
Huang XR, Lan HY, Sung JJ and Yu J: microRNA-29b prevents liver
fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and
inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
6:7325–7338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zou ZJ, Fan L, Wang L, Xu J, Zhang R, Tian
T, Li JY and Xu W: miR-26a and miR-214 down-regulate expression of
the PTEN gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but not PTEN
mutation or promoter methylation. Oncotarget. 6:1276–1285. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li J, Guan J, Long X, Wang Y and Xiang X:
mir-1-mediated paracrine effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on
lung cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance. Oncol Rep.
35:3523–3531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Peng J, Liu HZ, Zhong J, Deng ZF, Tie CR,
Rao Q, Xu W, You T, Li J, Cai CB, et al: MicroRNA-187 is an
independent prognostic factor in lung cancer and promotes lung
cancer cell invasion via targeting of PTRF. Oncol Rep.
36:2609–2618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fukazawa T, Guo M, Ishida N, Yamatsuji T,
Takaoka M, Yokota E, Haisa M, Miyake N, Ikeda T, Okui T, et al:
SOX2 suppresses CDKN1A to sustain growth of lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:201132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cannell IG, Merrick KA, Morandell S, Zhu
CQ, Braun CJ, Grant RA, Cameron ER, Tsao MS, Hemann MT and Yaffe
MB: A pleiotropic RNA-binding protein controls distinct cell cycle
checkpoints to drive resistance of p53-defective tumors to
chemotherapy. Cancer Cell. 28:623–637. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|