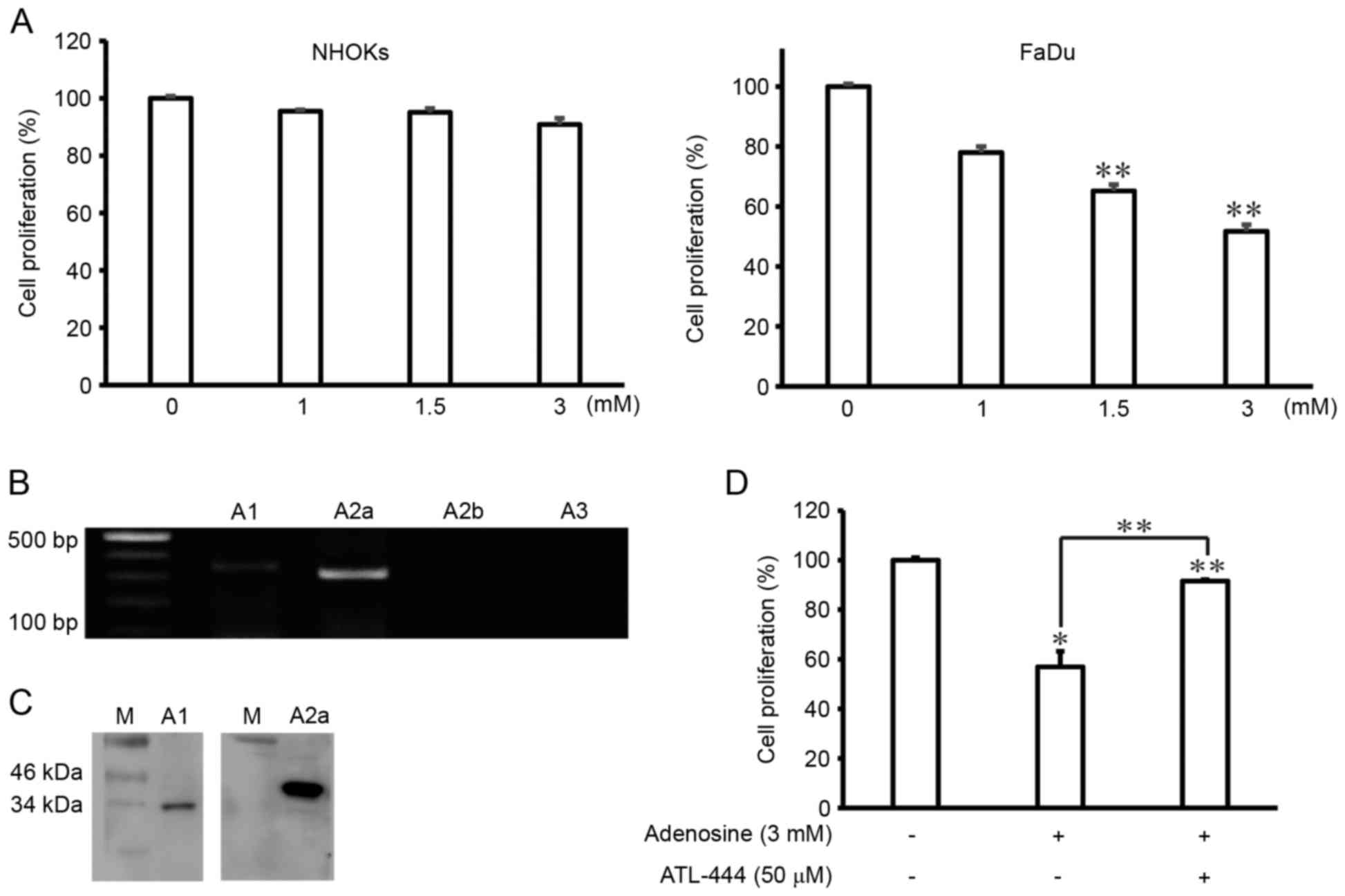
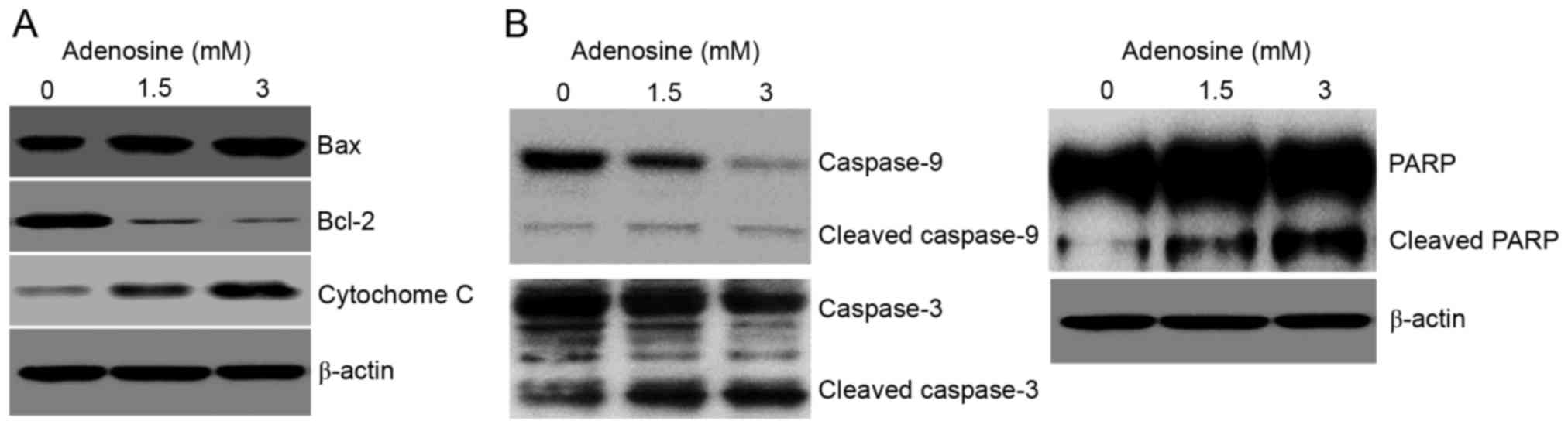
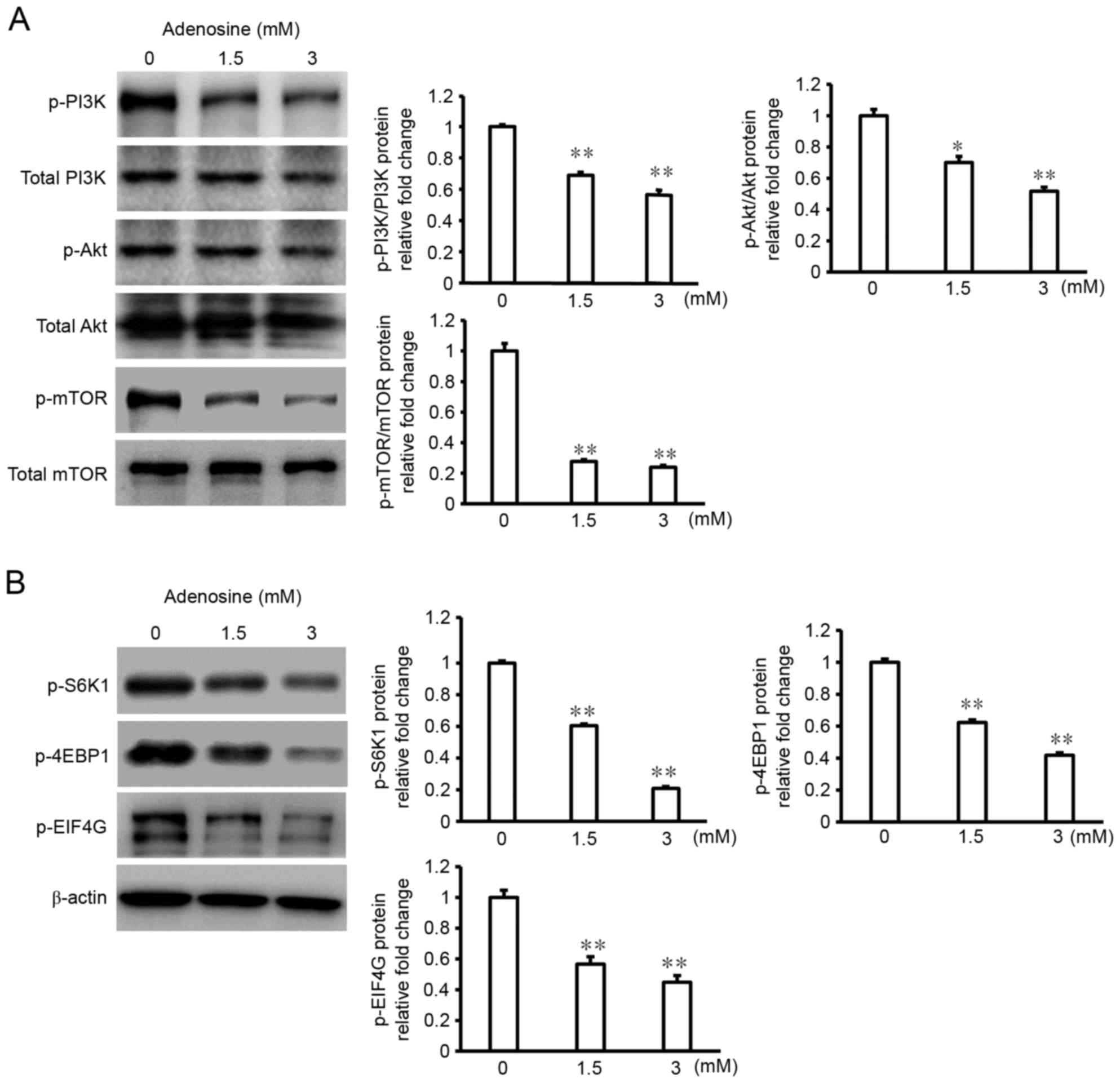
|
1
|
Vigneswaran N and Williams MD:
Epidemiological trends in head and neck cancer and aids in
diagnosis. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 26:123–141. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rothenberg SM and Ellisen LW: The
molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J
Clin Invest. 122:1951–1957. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Whang SN, Filippova M and Duerksen-Hughes
P: Recent progress in therapeutic treatments and screening
strategies for the prevention and treatment of HPV-associated head
and neck cancer. Viruses. 7:5040–5065. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chaturvedi AK, Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM,
Hernandez BY, Xiao W, Kim E, Jiang B, Goodman MT, Sibug-Saber M,
Cozen W, et al: Human papillomavirus and rising oropharyngeal
cancer incidence in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 29:4294–4301.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D and
Ferris RL: Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 371:1695–1709. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Z, Kapoian T, Shepard M and Lianos
EA: Adenosine-induced apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells.
Kidney Int. 61:1276–1285. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saitoh M, Nagai K, Nakagawa K, Yamamura T,
Yamamoto S and Nishizaki T: Adenosine induces apoptosis in the
human gastric cancer cells via an intrinsic pathway relevant to
activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem Pharmacol.
67:2005–2011. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Panjehpour M and Karami-Tehrani F:
Adenosine modulates cell growth in the human breast cancer cells
via adenosine receptors. Oncol Res. 16:575–585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gessi S, Merighi S, Varani K, Cattabriga
E, Benini A, Mirandola P, Leung E, Mac Lennan S, Feo C, Baraldi S
and Borea PA: Adenosine receptors in colon carcinoma tissues and
colon tumoral cell lines: Focus on the A(3) adenosine subtype. J
Cell Physiol. 211:826–836. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tanaka Y, Yoshihara K, Tsuyuki M and
Kamiya T: Apoptosis induced by adenosine in human leukemia HL-60
cells. Exp Cell Res. 213:242–252. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Merighi S, Mirandola P, Milani D, Varani
K, Gessi S, Klotz KN, Leung E, Baraldi PG and Borea PA: Adenosine
receptors as mediators of both cell proliferation and cell death of
cultured human melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 119:923–933.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Slee EA, Adrain C and Martin SJ:
Executioner caspase-3, −6 and −7 perform distinct, non-redundant
roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
276:7320–7326. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, Gaffney
PR, Reese CB, Painter GF, Holmes AB, McCormick F and Hawkins PT:
Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the
activation of protein kinase B. Science. 277:567–570. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartholomeusz C and Gonzalez-Angulo AM:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Exp Opin
Ther Targets. 16:121–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K,
Niu B, Lu C, Lu C, Xie M, Zhang Q, McMichael JF, et al: Mutational
landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature.
502:333–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moral M and Paramio JM: Akt pathway as a
target for therapeutic intervention in HNSCC. Histol Histopathol.
23:1269–1278. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Díaz-Ruiz C, Montaner B and Pérez-Tomás R:
Prodigiosin induces cell death and morphological changes indicative
of apoptosis in gastric cancer cell line HGT-1. Histol Histopathol.
16:415–421. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohana G, Bar-Yehuda S, Barer F and Fishman
P: Differential effect of adenosine on tumor and normal cell
growth: Focus on the A3 adenosine receptor. J Cell Physiol.
186:19–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gessi S, Merighi S, Sacchetto V, Simioni C
and Borea PA: Adenosine receptors and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1808:1400–1412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Synowitz M,
Powell JD, Klotz KN, Gessi S and Borea PA: Adenosine receptors and
cancer. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 193:399–441, 209. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Thakur S, Du J, Hourani S, Ledent C and Li
JM: Inactivation of adenosine A2A receptor attenuates basal and
angiotensin II-induced ROS production by Nox2 in endothelial Cells.
J Biol Chem. 285:40104–40113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma Y, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Chen P, Yu S, Liu
H, Liu F, Song C, Yang D and Liu J: Adenosine induces apoptosis in
human liver cancer cells through ROS production and mitochondrial
dysfunction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 448:8–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shirali S, Aghaei M, Shabani M, Fathi M,
Sohrabi M and Moeinifard M: Adenosine induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis via cyclinD1/Cdk4 and Bcl-2/Bax pathways in human ovarian
cancer cell line OVCAR-3. Tumour Biol. 34:1085–1095. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yasuda Y, Saito M, Yamamura T, Yaguchi T
and Nishizaki T: Extracellular adenosine induces apoptosis in
Caco-2 human colonic cancer cells by activating caspase-9/-3 via
A2a adenosine receptors. J Gastroenterol. 44:56–65. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saito M, Yaguchi T, Yasuda Y, Nakano T and
Nishizaki T: Adenosine suppresses CW2 human colonic cancer growth
by inducing apoptosis via A1 adenosine receptors. Cancer let.
290:211–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gao W, Li JZ, Chan JY, Ho WK and Wong TS:
mTOR pathway and mTOR inhibitors in head and neck cancer. ISRN
Otolaryngol. 2012:9530892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kundu SK and Nestor M: Targeted therapy in
head and neck cancer. Tumour Biol. 33:707–721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Machiels JP and Schmitz S: New advances in
targeted therapies for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck. Anticancer Drugs. 22:626–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Amornphimoltham P, Sriuranpong V, Patel V,
Benavides F, Conti CJ, Sauk J, Sausville EA, Molinolo AA and
Gutkind JS: Persistent activation of the Akt pathway in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: A potential target for UCN-01. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:4029–4037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Merighi S, Mirandola P, Varani K, Gessi S,
Leung E, Baraldi PG, Tabrizi MA and Borea PA: A glance at adenosine
receptors: Novel target for antitumor therapy. Pharmacol Ther.
100:31–48. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vanhaesebroeck B and Waterfield MD:
Signaling by distinct classes of phosphoinositide 3-kiness. Exp
Cell Res. 253:239–254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Altomare DA and Khaled AR: Homeostasis and
the importance for a balance between AKT/mTOR activity and
intracellular signaling. Curr Med Chem. 19:3748–3762. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|