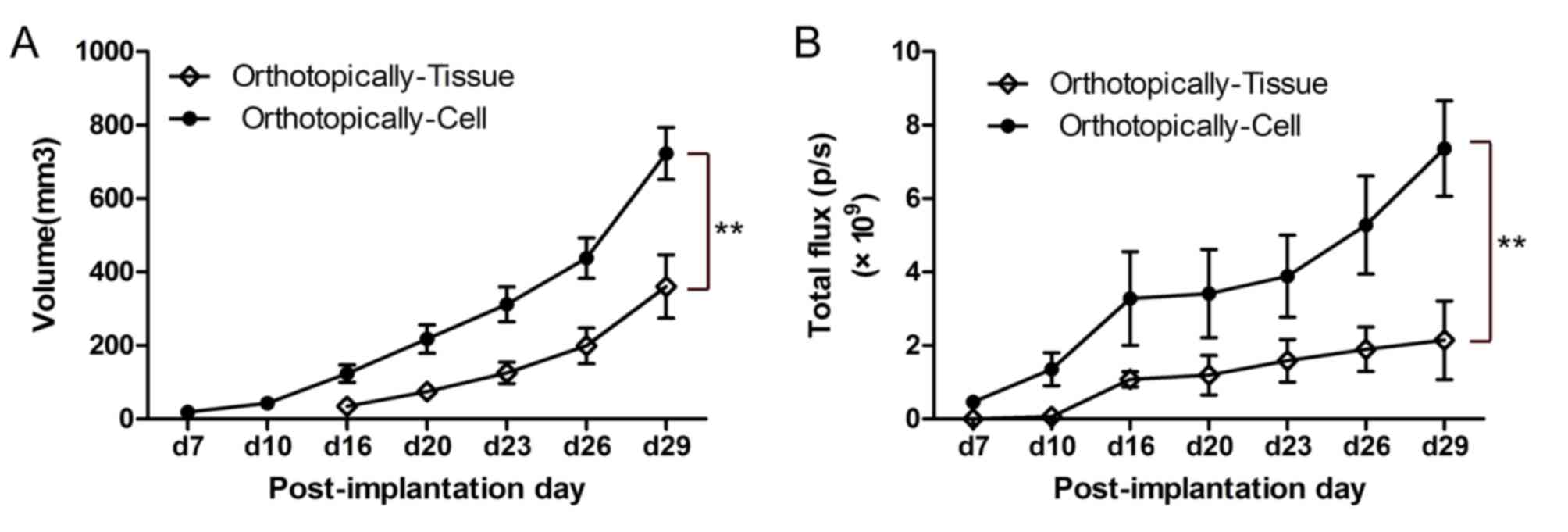
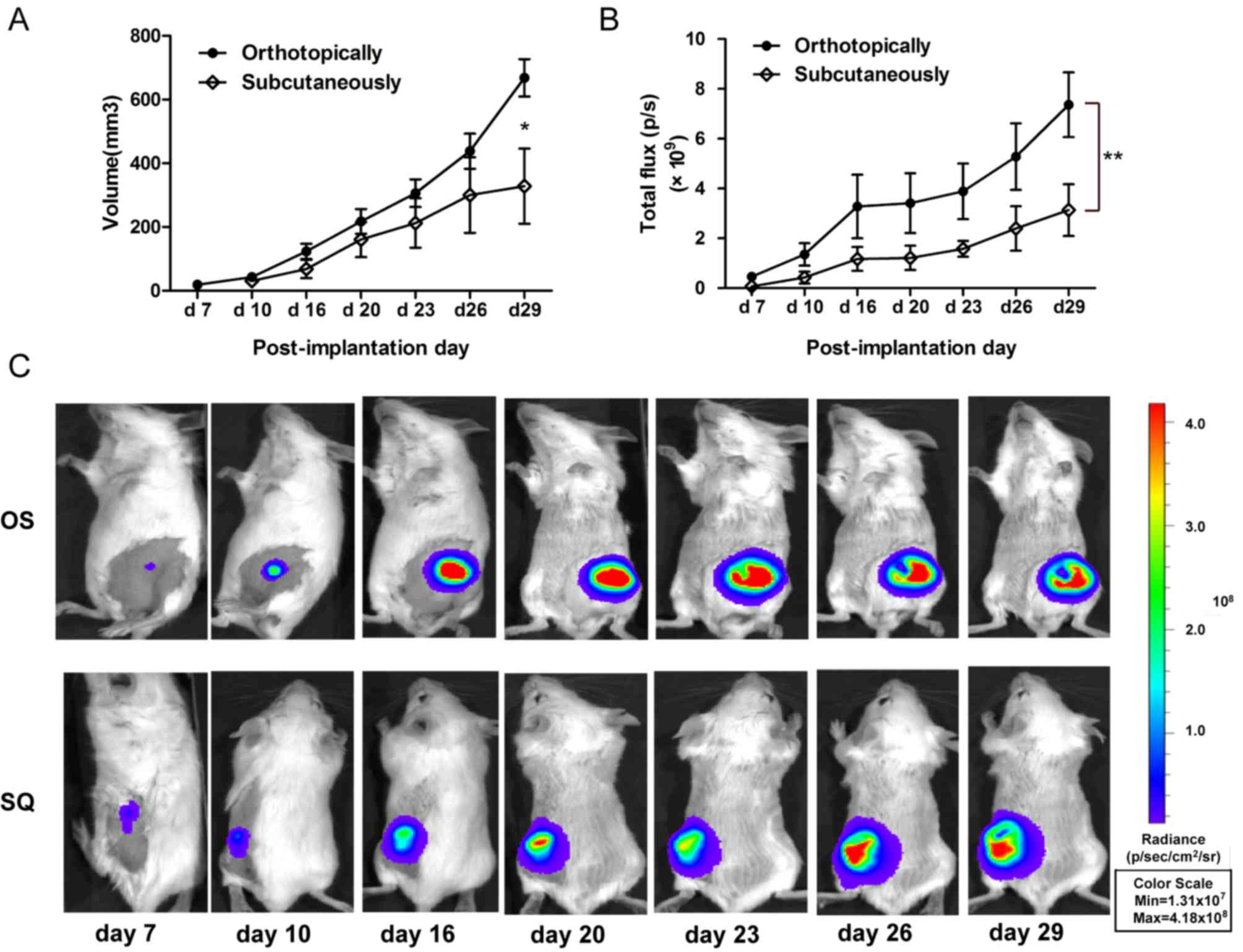
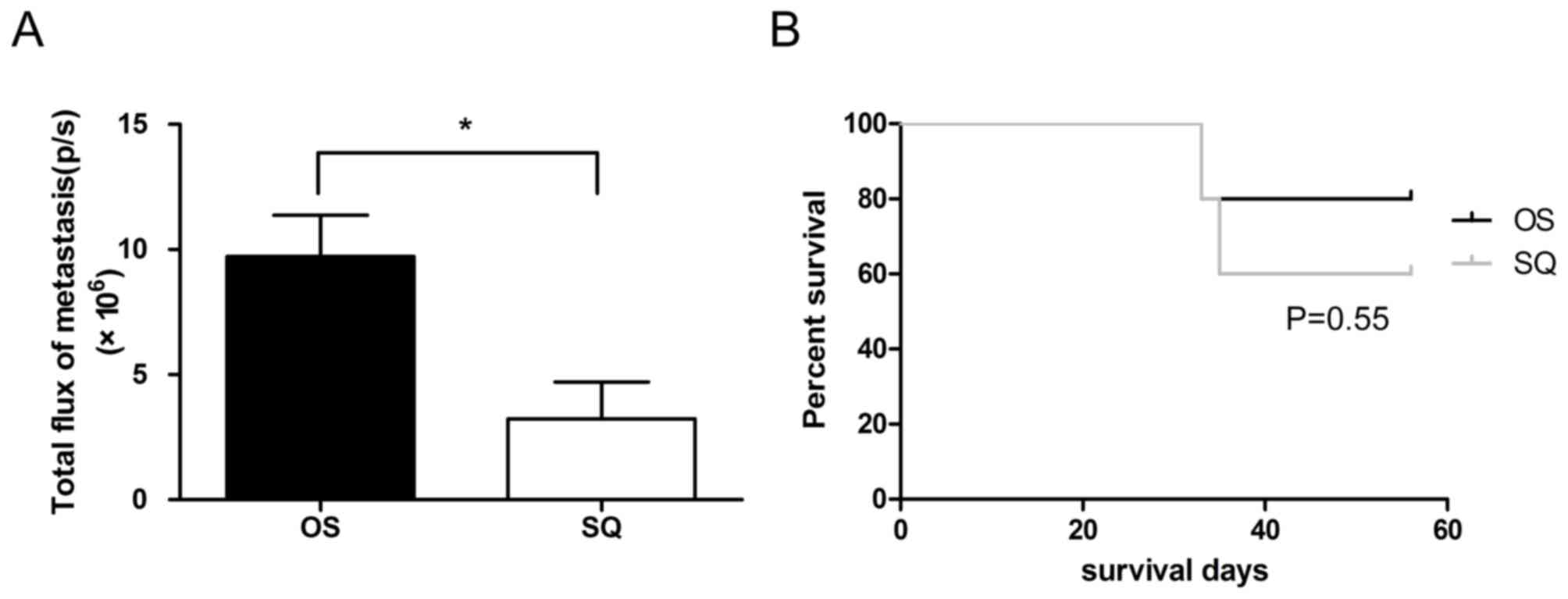
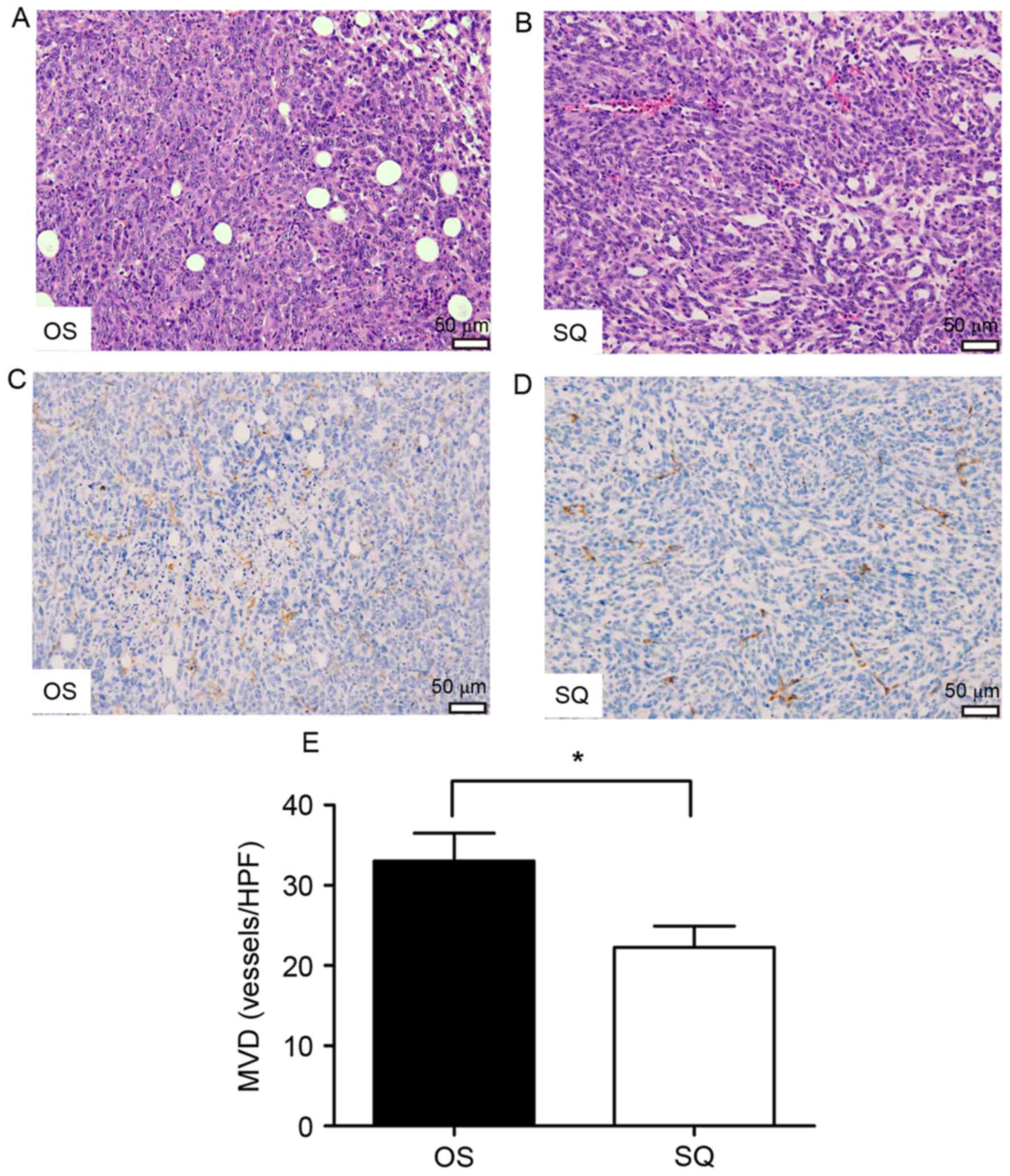
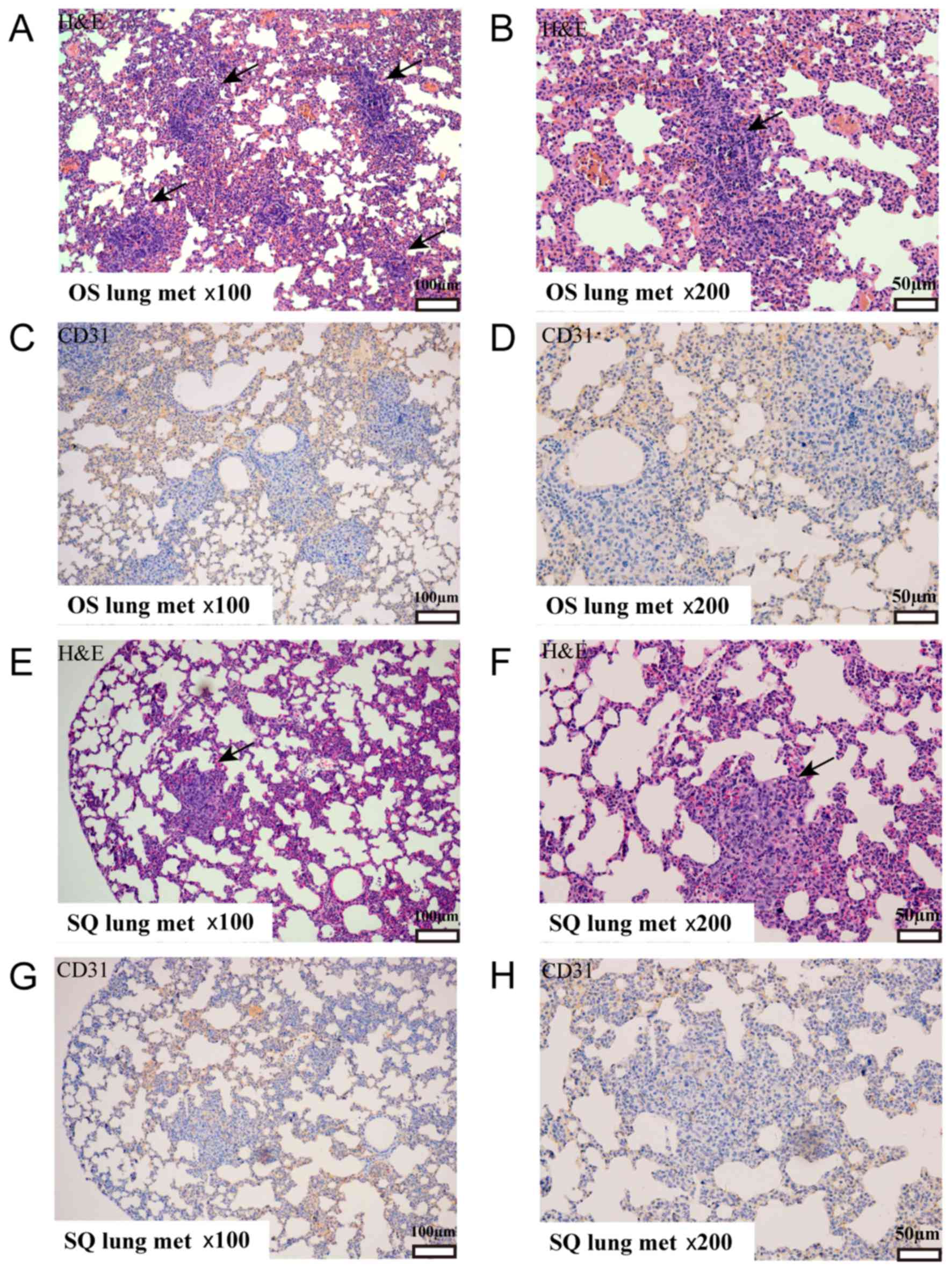
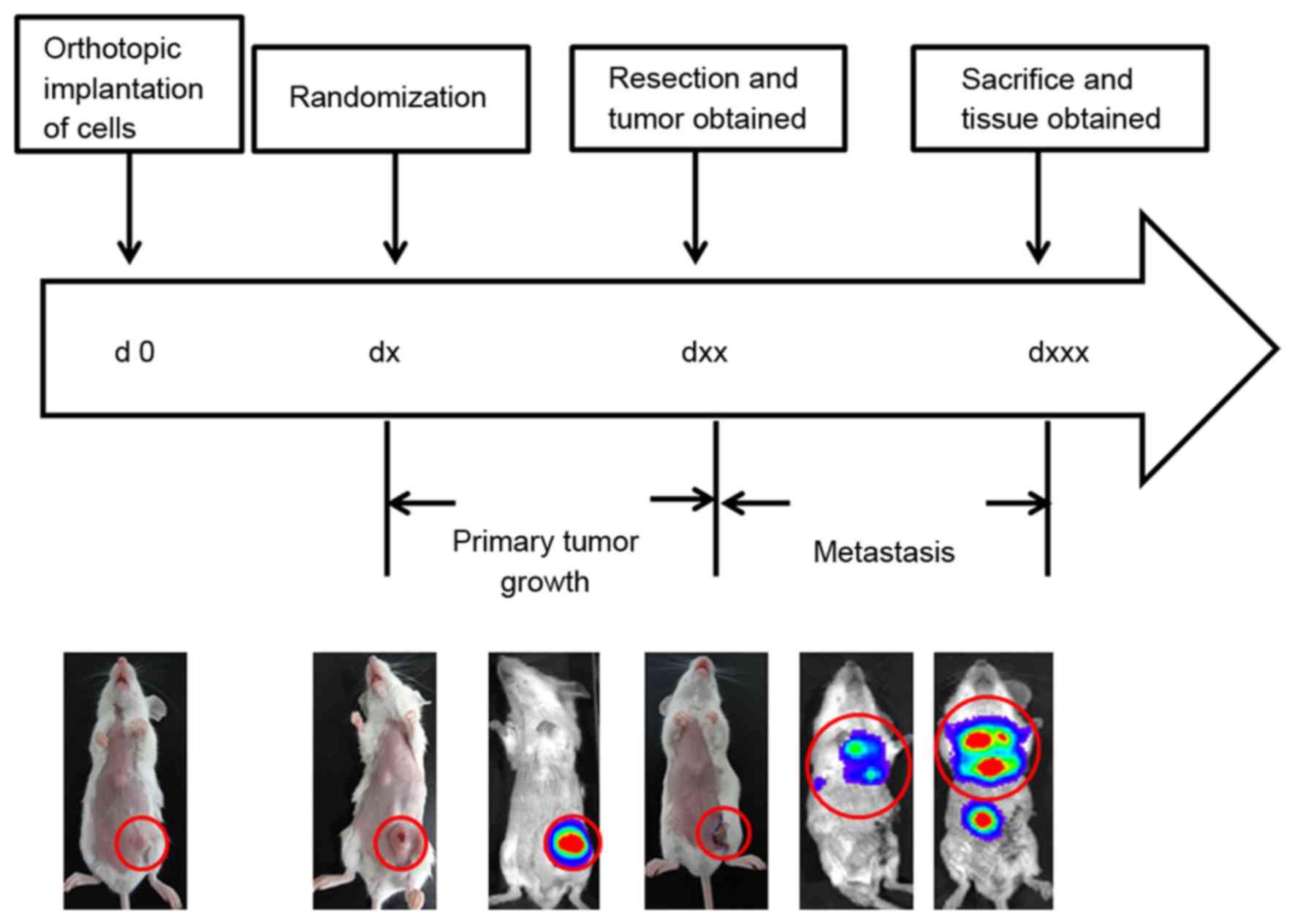
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shi XJ, Au WW, Wu KS, Chen LX and Lin K:
Mortality characteristics and prediction of female breast cancer in
China from 1991 to 2011. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2785–2791.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Light DW: Global drug discovery: Europe is
ahead. Health Aff (Millwood). 28:w969–w977. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ottewell PD, Coleman RE and Holen I: From
genetic abnormality to metastases: Murine models of breast cancer
and their use in the development of anticancer therapies. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 96:101–113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rashid OM and Takabe K: Animal models for
exploring the pharmacokinetics of breast cancer therapies. Expert
Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 11:221–230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wagner KU: Models of breast cancer: Quo
vadis, animal modeling? Breast Cancer Res. 6:31–38. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL,
McArthur MJ, Montgomery CA Jr, Butel JS and Bradley A: Mice
deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to
spontaneous tumours. Nature. 356:215–221. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Escobar Galvis ML, Jia J, Zhang X,
Jastrebova N, Spillmann D, Gottfridsson E, van Kuppevelt TH,
Zcharia E, Vlodavsky I, Lindahl U and Li JP: Transgenic or
tumor-induced expression of heparanase upregulates sulfation of
heparan sulfate. Nat Chem Biol. 3:773–778. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matsui Y, Halter SA, Holt JT, Hogan BL and
Coffey RJ: Development of mammary hyperplasia and neoplasia in
MMTV-TGF alpha transgenic mice. Cell. 61:1147–1155. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ursini-Siegel J, Schade B, Cardiff RD and
Muller WJ: Insights from transgenic mouse models of ERBB2-induced
breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:389–397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menezes ME, Das SK, Emdad L, Windle JJ,
Wang XY, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Genetically engineered mice as
experimental tools to dissect the critical events in breast cancer.
Adv Cancer Res. 121:331–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chakravarty G, Mathur A, Mallade P,
Gerlach S, Willis J, Datta A, Srivastav S, Abdel-Mageed AB and
Mondal D: Nelfinavir targets multiple drug resistance mechanisms to
increase the efficacy of doxorubicin in MCF-7/Dox breast cancer
cells. Biochimie. 124:53–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Pan GF, Jiang ZZ, Yang J, Sun LX and
Zhang LY: Triptolide inhibits human breast cancer MCF-7 cell growth
via downregulation of the ERα-mediated signaling pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:606–613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Habu S, Fukui H, Shimamura K, Kasai M,
Nagai Y, Okumura K and Tamaoki N: In vivo effects of anti-asialo
GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted
tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 127:34–38. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marangoni E, Vincent-Salomon A, Auger N,
Degeorges A, Assayag F, de Cremoux P, de Plater L, Guyader C, De
Pinieux G, Judde JG, et al: A new model of patient tumor-derived
breast cancer xenografts for preclinical assays. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3989–3998. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schuh JC: Trials, tribulations, and trends
in tumor modeling in mice. Toxicol Pathol. 32 Suppl 1:S53–S66.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Talmadge JE, Singh RK, Fidler IJ and Raz
A: Murine models to evaluate novel and conventional therapeutic
strategies for cancer. Am J Pathol. 170:793–804. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gravekamp C, Sypniewska R, Gauntt S,
Tarango M, Price P and Reddick R: Behavior of metastatic and
nonmetastatic breast tumors in old mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
229:665–675. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh M, Ramos I, Asafu-Adjei D,
Quispe-Tintaya W, Chandra D, Jahangir A, Zang X, Aggarwal BB and
Gravekamp C: Curcumin improves the therapeutic efficacy of
Listeria(at)-Mage-b vaccine in correlation with improved T-cell
responses in blood of a triple-negative breast cancer model 4T1.
Cancer Med. 2:571–582. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takahashi K, Nagai N, Ogura K, Tsuneyama
K, Saiki I, Irimura T and Hayakawa Y: Mammary tissue
microenvironment determines T cell-dependent breast
cancer-associated inflammation. Cancer Sci. 106:867–874. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tao K, Fang M, Alroy J and Sahagian GG:
Imagable 4T1 model for the study of late stage breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:2282008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou H, Roy S, Cochran E, Zouaoui R, Chu
CL, Duffner J, Zhao G, Smith S, Galcheva-Gargova Z, Karlgren J, et
al: M402, a novel heparan sulfate mimetic, targets multiple
pathways implicated in tumor progression and metastasis. PLoS One.
6:e211062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee HS, Ha AW and Kim WK: Effect of
resveratrol on the metastasis of 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells in
vitro and in vivo. Nutr Res Pract. 6:294–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mehta RR, Katta H, Kalra A, Patel R, Gupta
A, Alimirah F, Murillo G, Peng X, Unni A, Muzzio M and Mehta RG:
Efficacy and mechanism of action of Deguelin in suppressing
metastasis of 4T1 cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:855–866. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gibson-D'Ambrosio RE, Samuel M and
D'Ambrosio SM: A method for isolating large numbers of viable
disaggregated cells from various human tissues for cell culture
establishment. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 22:529–534. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weigand A, Boos AM, Tasbihi K, Beier JP,
Dalton PD, Schrauder M, Horch RE, Beckmann MW, Strissel PL and
Strick R: Selective isolation and characterization of primary cells
from normal breast and tumors reveal plasticity of adipose derived
stem cells. Breast Cancer Res. 18:322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis-correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jordan VC: Proven value of translational
research with appropriate animal models to advance breast cancer
treatment and save lives: The tamoxifen tale. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
79:254–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clarke R: Animal models of breast cancer:
Their diversity and role in biomedical research. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 39:1–6. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morioka CY, Saito S, Ohzawa K, Asano S,
Hibino Y, Nakada Y, Kita KI and Watanabe A: Subcutaneously
inoculated cells and implanted pancreatic cancer tissue show
different patterns of metastases in Syrian golden hamsters. JOP.
1:183–190. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rao Q, You A, Guo Z, Zuo B, Gao X, Zhang
T, Du Z, Wu C and Yin H: Intrahepatic tissue implantation
represents a favorable approach for establishing orthotopic
transplantation hepatocellular carcinoma mouse models. PLoS One.
11:e1482632016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
de la Cruz-Merino L, Barco-Sánchez A,
Henao Carrasco F, Nogales Fernández E, Vallejo Benítez A, Brugal
Molina J, Martínez Peinado A, Grueso López A, Ruiz Borrego M, Codes
Manuel de Villena M, et al: New insights into the role of the
immune microenvironment in breast carcinoma. Clin Dev Immunol.
2013:7853172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rashid OM, Nagahashi M, Ramachandran S,
Dumur C, Schaum J, Yamada A, Terracina KP, Milstien S, Spiegel S
and Takabe K: An improved syngeneic orthotopic murine model of
human breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
147:501–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rashid OM, Nagahashi M, Ramachandran S,
Dumur CI, Schaum JC, Yamada A, Aoyagi T, Milstien S, Spiegel S and
Takabe K: Is tail vein injection a relevant breast cancer lung
metastasis model? J Thorac Dis. 5:385–392. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bibby MC: Orthotopic models of cancer for
preclinical drug evaluation: Advantages and disadvantages. Eur J
Cancer. 40:852–857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nieman KM, Romero IL, Van Houten B and
Lengyel E: Adipose tissue and adipocytes support tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1533–1541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hammond E, Brandt R and Dredge K: PG545, a
heparan sulfate mimetic, reduces heparanase expression in vivo,
blocks spontaneous metastases and enhances overall survival in the
4T1 breast carcinoma model. PLoS One. 7:e521752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim JB, Urban K, Cochran E, Lee S, Ang A,
Rice B, Bata A, Campbell K, Coffee R, Gorodinsky A, et al:
Non-invasive detection of a small number of bioluminescent cancer
cells in vivo. PLoS One. 5:e93642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|