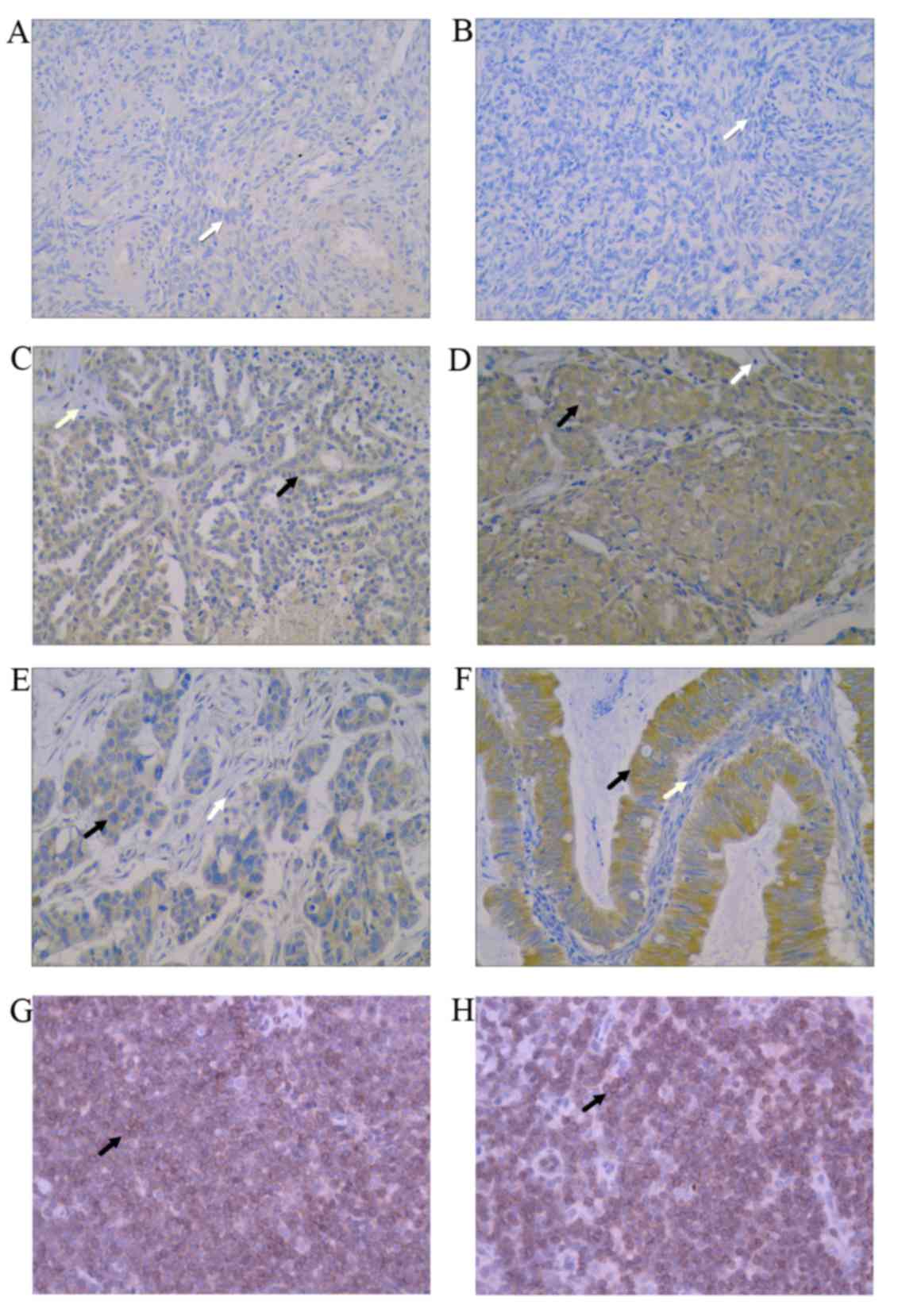
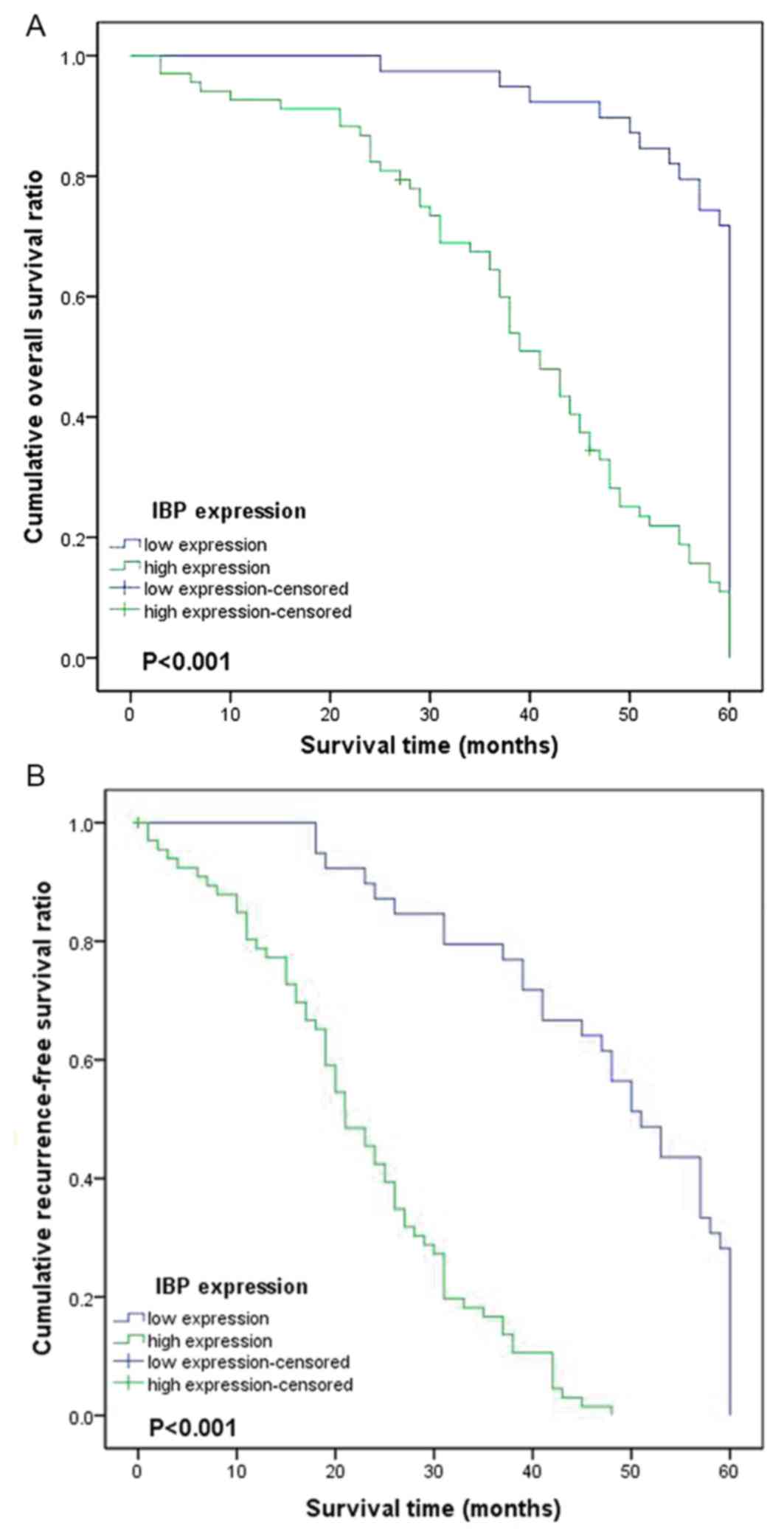
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katso RM, Manek S, Ganjavi H, Biddolph S,
Charnock MF, Bradburn M, Wells M and Ganesan TS: Overexpression of
H-Ryk in epithelial ovarian cancer: Prognostic significance of
receptor expression. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3271–3281. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kolwijck E, Lybol CJ, Bulten J, Vollebergh
JH, Wevers RA and Massuger LF: Prevalence of cysts in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 151:96–100. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gupta S, Fanzo JC, Hu C, Cox D, Jang SY,
Lee AE, Greenberg S and Pernis AB: T cell receptor engagement leads
to the recruitment of IBP, a novel guanine nucleotide exchange
factor, to the immunological synapse. J Biol Chem. 278:541–549.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tanaka Y, Bi K, Kitamura R, Hong S, Altman
Y, Matsumoto A, Tabata H, Lebedeva S, Bushway PJ and Altman A:
SWAP-70-like adapter of T cells, an adapter protein that regulates
early TCR-initiated signaling in Th2 lineage cells. Immunity.
18:403–414. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Canonigo-Balancio AJ, Fos C, Prod'homme T,
Bécart S and Altman A: SLAT/Def6 plays a critical role in the
development of Th17 cell-mediated experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 183:7259–7267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Q, Gupta S and Pernis AB: Regulation
of TLR4-mediated signaling by IBP/Def6, a novel activator of Rho
GTPases. J Leukoc Biol. 85:539–543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fanzo JC, Yang W, Jang SY, Gupta S, Chen
Q, Siddiq A, Greenberg S and Pernis AB: Loss of IRF-4-binding
protein leads to the spontaneous development of systemic
autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. 116:703–714. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Subramanian S, West RB, Marinelli RJ,
Nielsen TO, Rubin BP, Goldblum JR, Patel RM, Zhu S, Montgomery K,
Ng TL, et al: The gene expression profile of extraskeletal myxoid
chondrosarcoma. J Pathol. 206:433–444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gupta S, Lee A, Hu C, Fanzo J, Goldberg I,
Cattoretti G and Pernis AB: Molecular cloning of IBP, a SWAP-70
homologous GEF, which is highly expressed in the immune system. Hum
Immunol. 64:389–401. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lazer G and Katzav S: Guanine nucleotide
exchange factors for RhoGTPases: Good therapeutic targets for
cancer therapy? Cell Signal. 23:969–979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Li P, Zhou Y, Li S, Yi W,
Chen A, Kong P and Hu C: Overexpression of the interferon
regulatory factor 4-binding protein in human colorectal cancer and
its clinical significance. Cancer Epidemiol. 33:130–136. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li P, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Li S, Zhang Y, Bian
X, Chen A and Hu C: The ectopic expression of IFN regulatory factor
4-binding protein is correlated with the malignant behavior of
human breast cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:1002–1009. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jian CX, Yang MZ, Li P, Xiong J, Zhang ZJ,
Li CJ, Chen A, Hu CM, Zhou JX and Li SH: Ectopically expressed IBP
promotes cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Invest. 30:748–756. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pecorelli S: Revised FIGO staging for
carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and endometrium. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 105:103–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tavassoli FA and Devilee P: World health
organization classification of tumor. Histopathology. 30:274–276.
2002.
|
|
17
|
Ioffe OB and Silverberg SG: A universal
grading system for ovarian cancer. Contemporary Ob/gyn. 2000.
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y and Zhang B: D4-GDI, a Rho GTPase
regulator, promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness. Cancer Res.
66:5592–5598. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Raimondi F, Felline A and Fanelli F:
Catching functional modes and structural communication in Dbl
family Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors. J Chem Inf Model.
55:1878–1893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ridley AJ: Rho family proteins:
Coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol. 11:471–477. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bokoch GM: Regulation of cell function by
Rho family GTPases. Immunol Res. 21:139–148. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bar-Sagi D and Hall A: Ras and Rho
GTPases: A family reunion. Cell. 103:227–238. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vega FM and Ridley AJ: Rho GTPases in
cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett. 582:2093–2101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karlsson R, Pedersen ED, Wang Z and
Brakebusch C: Rho GTPase function in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1796:91–98. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin M and van Golen KL: Rho-regulatory
proteins in breast cancer cell motility and invasion. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 84:49–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Banyard J, Anand-Apte B, Symons M and
Zetter BR: Motility and invasion are differentially modulated by
Rho family GTPases. Oncogene. 19:580–591. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saurin JC, Fallavier M, Sordat B, Gevrey
JC, Chayvialle JA and Abello J: Bombesin stimulates invasion and
migration of Isreco1 colon carcinoma cells in a Rho-dependent
manner. Cancer Res. 62:4829–4835. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mavrakis KJ, McKinlay KJ, Jones P and
Sablitzky F: DEF6, a novel PH-DH-like domain protein, is an
upstream activator of the Rho GTPases Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA. Exp
Cell Res. 294:335–344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oka T, Ihara S and Fukui Y: Cooperation of
DEF6 with activated Rac in regulating cell morphology. J Biol Chem.
282:2011–2018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Samson T, Will C, Knoblauch A, Sharek L,
von der Mark K, Burridge K and Wixler V: Def-6, a guanine
nucleotide exchange factor for Rac1, interacts with the skeletal
muscle integrin chain alpha7A and influences myoblast
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 282:15730–15742. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Christophe D, Christophe-Hobertus C and
Pichon B: Nuclear targeting of proteins. How many different
signals? Cell Signal. 12:337–341. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Han Q, Wang X, Yang M, Zhang Z, Li
P, Chen A, Hu C and Li S: IBP-mediated suppression of autophagy
promotes growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells via
activating mTORC2/Akt/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang M, Yuan F, Li P, Chen Z, Chen A, Li S
and Hu C: Interferon regulatory factor 4 binding protein is a novel
p53 target gene and suppresses cisplatin-induced apoptosis of
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 11:542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|