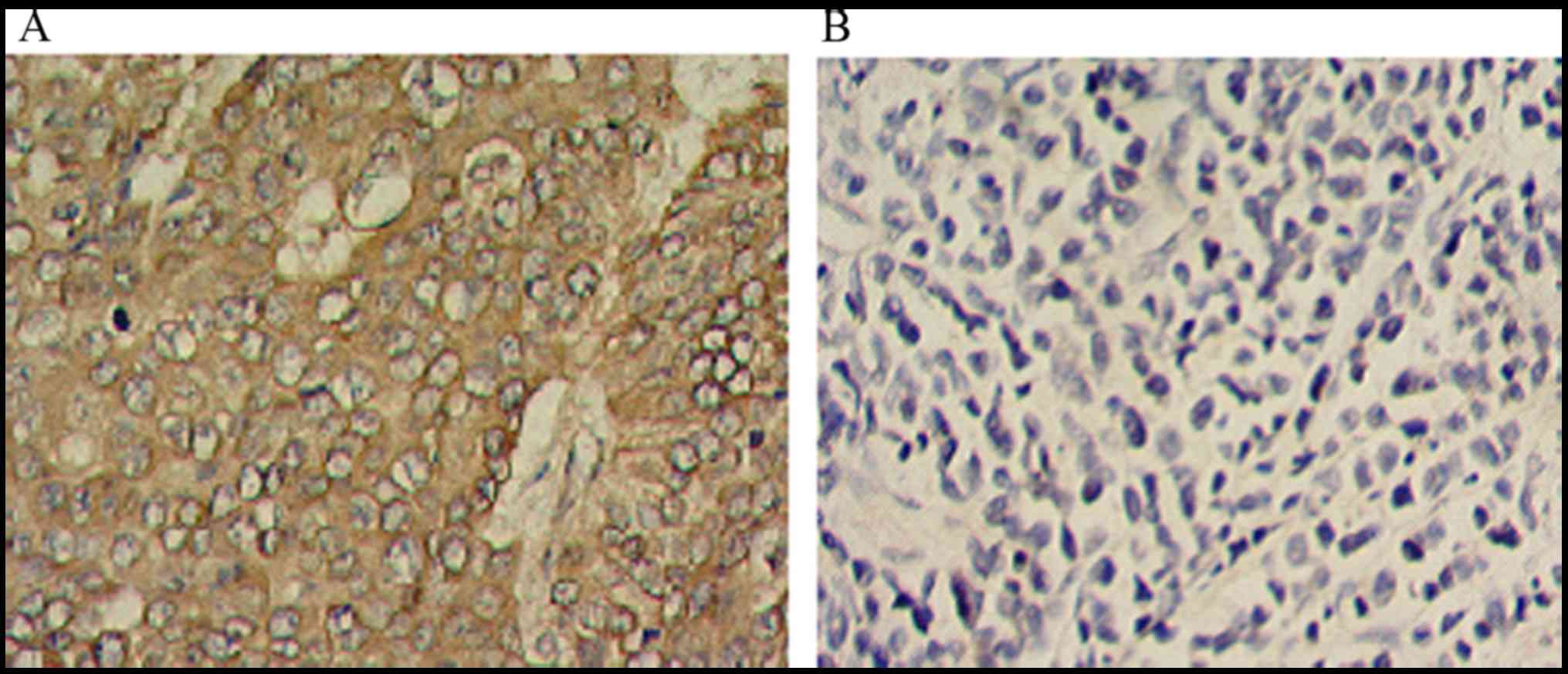
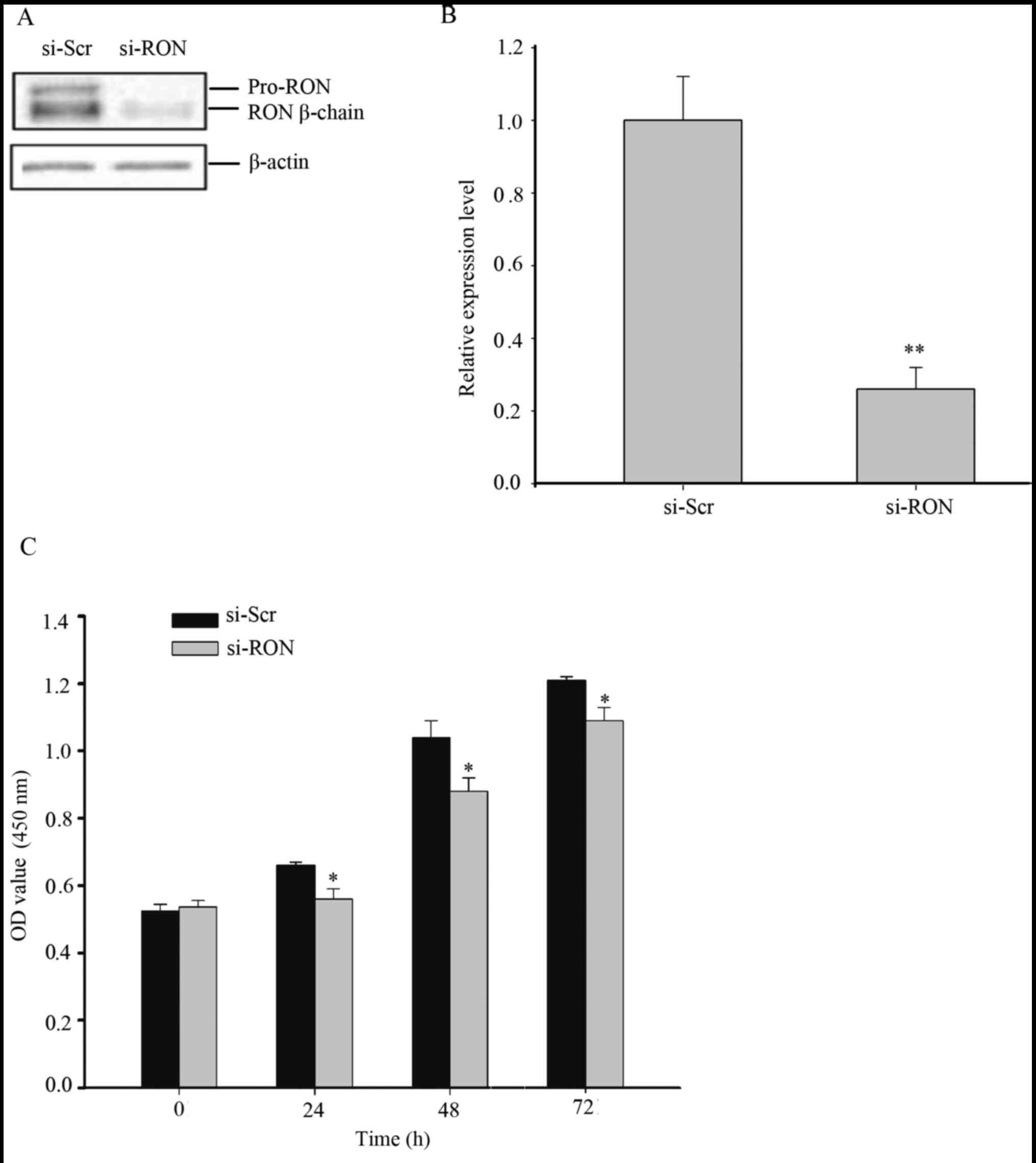
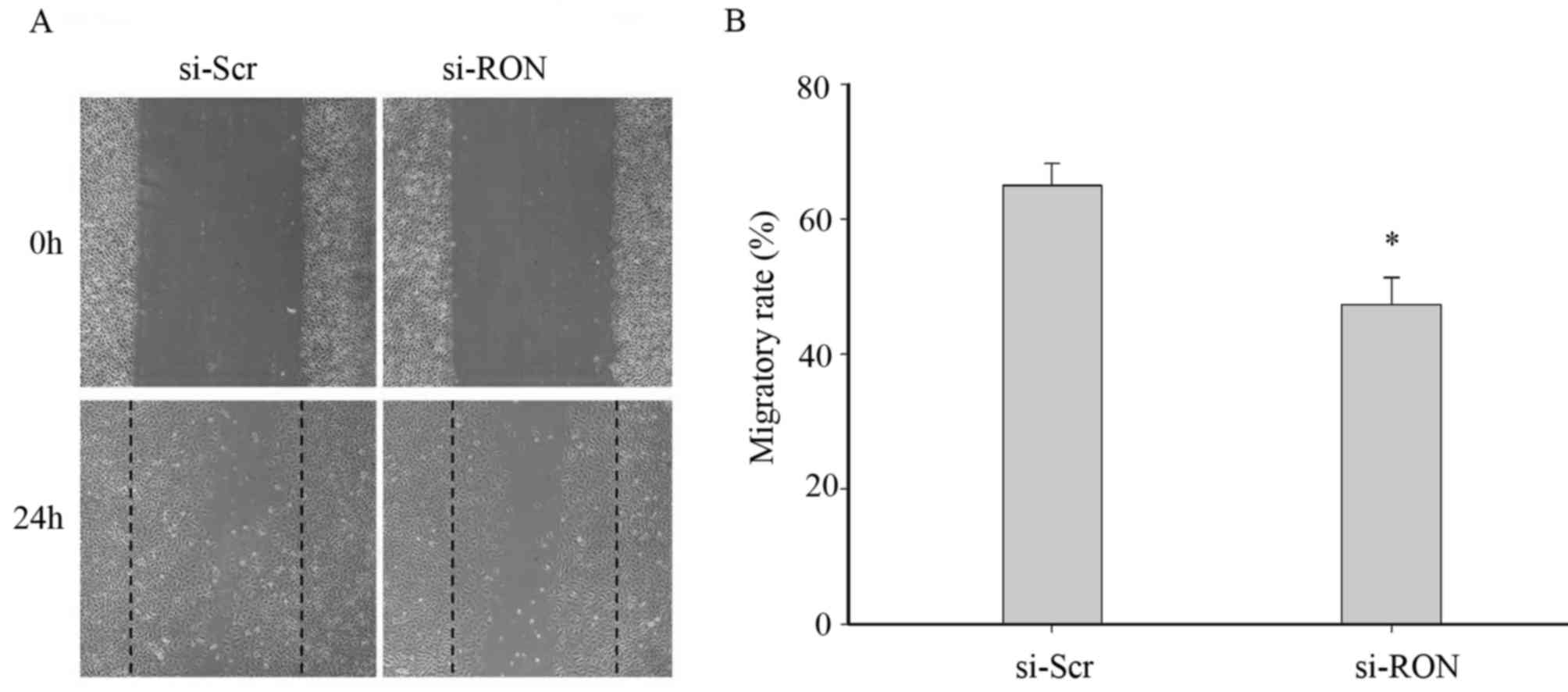
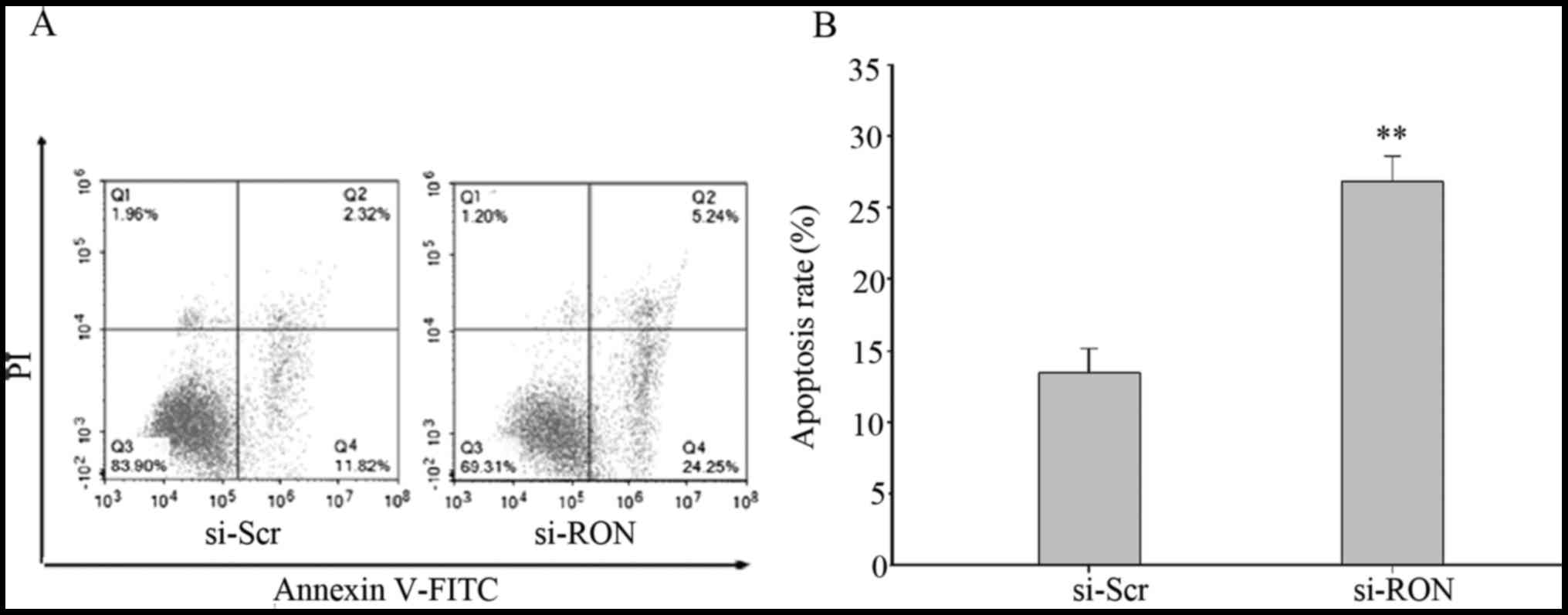
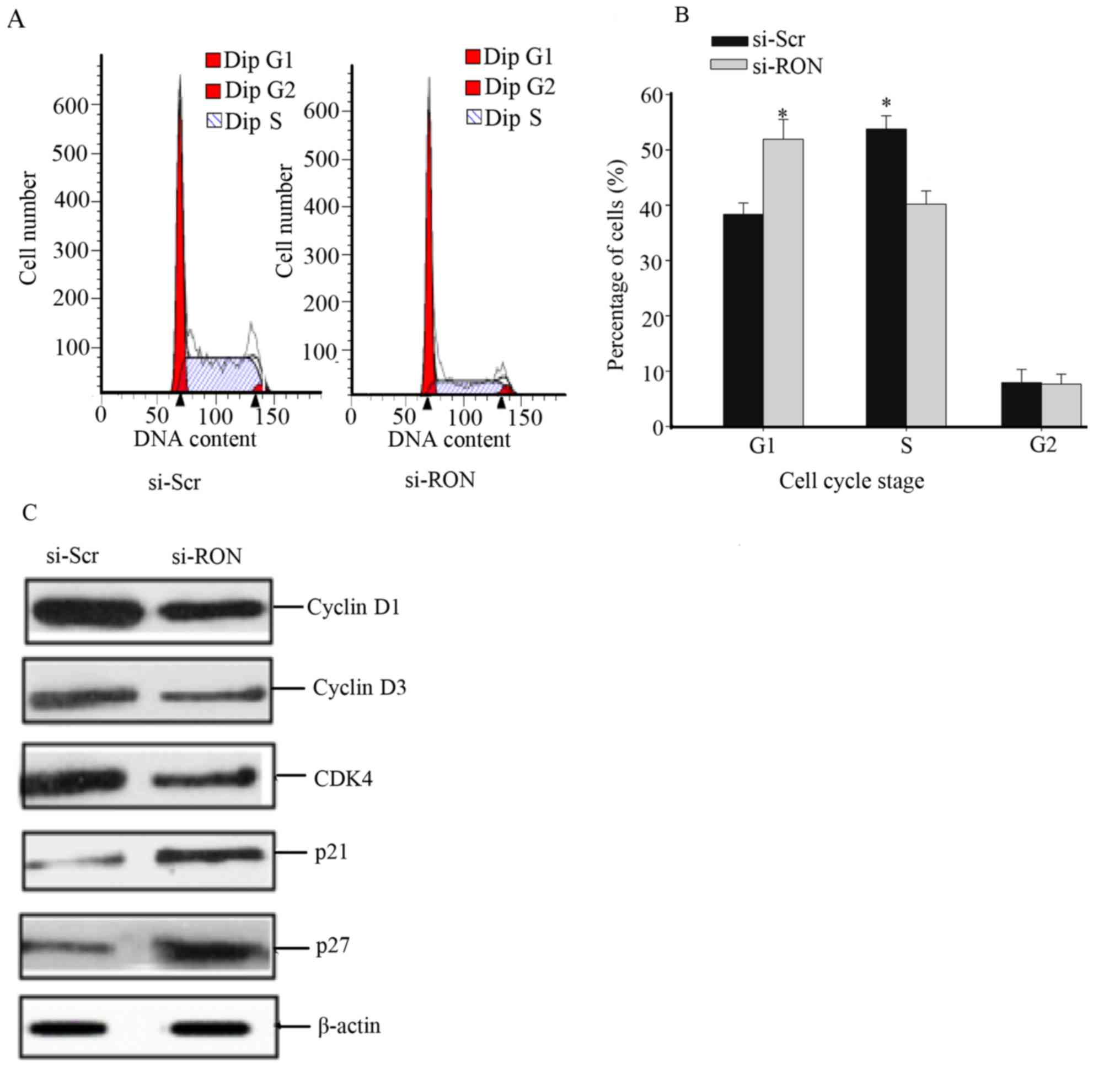
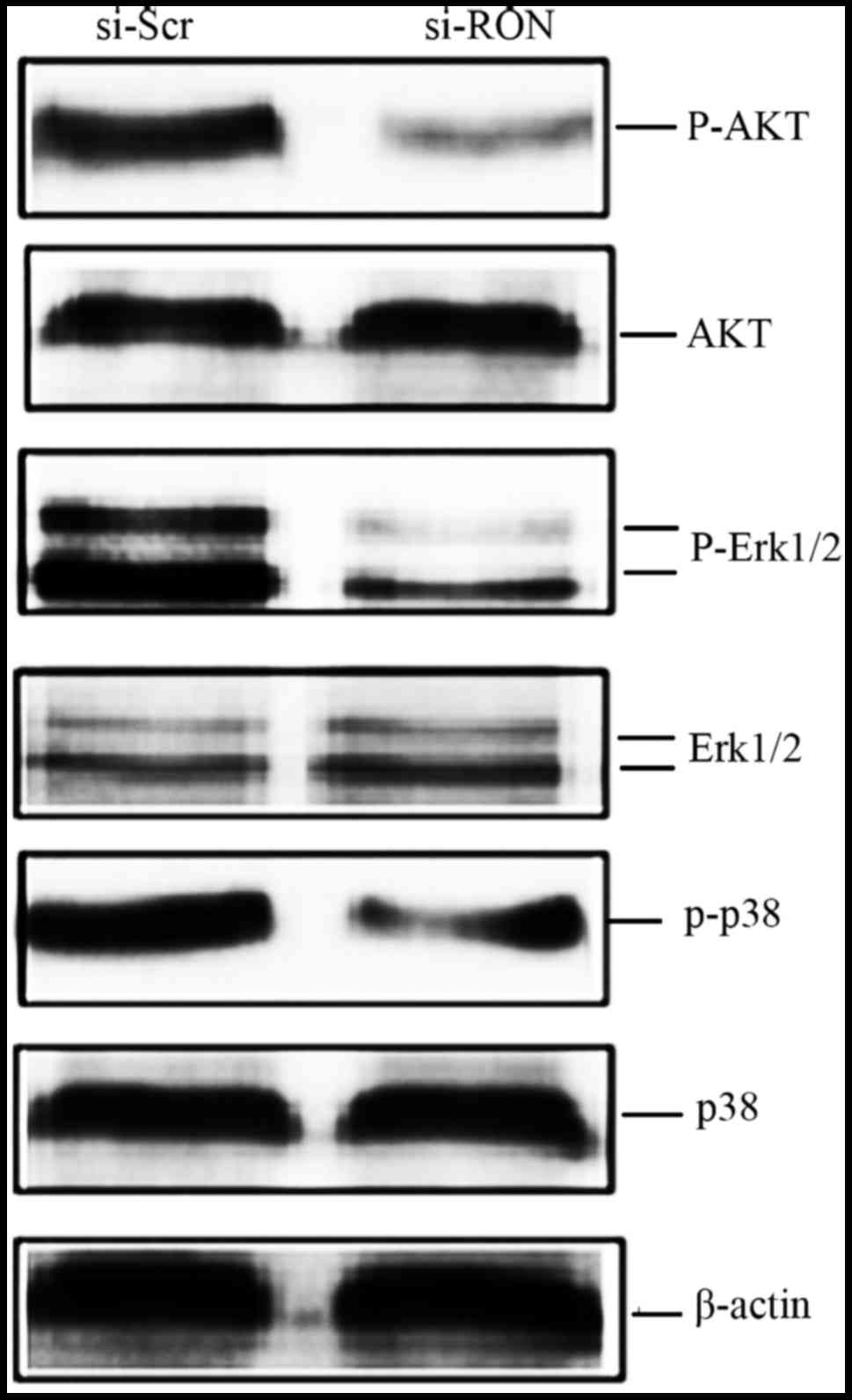
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin-Doyle W and Kwiatkowski DJ:
Molecular biology of bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am.
29:191–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bellmunt J, Powles T and Vogelzang NJ: A
review on the evolution of PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for bladder
cancer: The future is now. Cancer Treat Rev. 54:58–67. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pinto IG: Systemic therapy in bladder
cancer. Indian J Urol. 33:118–126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mohammed AA, El-Tanni H, El-Khatib HM,
Mirza AA, Mirza AA and Alturaifi TH: Urinary bladder cancer:
Biomarkers and target therapy, new era for more attention. Oncol
Rev. 10:3202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang MH, Padhye SS, Guin S, Ma Q and Zhou
YQ: Potential therapeutics specific to c-MET/RON receptor tyrosine
kinases for molecular targeting in cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 31:1181–1188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park YL, Lee GH, Kim KY, Myung E, Kim JS,
Myung DS, Park KJ, Cho SB, Lee WS, Jung YD, et al: Expression of
RON in colorectal cancer and its relationships with tumor cell
behavior and prognosis. Tumori. 98:652–662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feres KJ, Ischenko I and Hayman MJ: The
RON receptor tyrosine kinase promotes MSP-independent cell
spreading and survival in breast epithelial cells. Oncogene.
28:279–288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng HL, Liu HS, Lin YJ, Chen HH, Hsu PY,
Chang TY, Ho CL, Tzai TS and Chow NH: Co-expression of RON and MET
is a prognostic indicator for patients with transitional-cell
carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Cancer. 92:1906–1914. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsu PY, Liu HS, Cheng HL, Tzai TS, Guo HR,
Ho CL and Chow NH: Collaboration of RON and epidermal growth factor
receptor in human bladder carcinogenesis. J Urol. 176:2262–2267.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen JF, Yu BX, Yu R, Ma L, Lv XY, Cheng Y
and Ma Q: Monoclonal antibody Zt/g4 targeting RON receptor tyrosine
kinase enhances chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cells to
Epirubicin by promoting G1/S arrest and apoptosis. Oncol Rep.
37:721–728. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao HP, Zhou YQ, Zhang R and Wang MH:
MSP-RON signaling in cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic
potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:466–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thomas RM, Toney K, Fenoglio-Preiser C,
Revelo-Penafiel MP, Hingorani SR, Tuveson DA, Waltz SE and Lowy AM:
The RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediates oncogenic phenotypes in
pancreatic cancer cells and is increasingly expressed during
pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Res. 67:6075–6082. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zarei O, Benvenuti S, Ustun-Alkan F,
Hamzeh-Mivehroud M and Dastmalchi S: Strategies of targeting the
extracellular domain of RON tyrosine kinase receptor for cancer
therapy and drug delivery. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:2429–2446.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang MH, Lee W, Luo YL, Weis MT and Yao
HP: Altered expression of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase in
various epithelial cancers and its contribution to tumorigenic
phenotypes in thyroid cancer cells. J Pathol. 213:402–411. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wagh PK, Peace BE and Waltz SE:
Met-related receptor tyrosine kinase Ron in tumor growth and
metastasis. Adv Cancer Res. 100:1–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Camp ER, Liu W, Fan F, Yang A, Somcio R
and Ellis LM: RON, a tyrosine kinase receptor involved in tumor
progression and metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol. 12:273–281. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang MH, Wang D and Chen YQ: Oncogenic and
invasive potentials of human macrophage-stimulating protein
receptor, the RON receptor tyrosine kinase. Carcinogenesis.
24:1291–1300. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A: Oncogenic
signaling pathways activated by RON receptor tyrosine kinase. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 3:31–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chung CY, Park YL, Song YA, Myung E, Kim
KY, Lee GH, Ki HS, Park KJ, Cho SB, Lee WS, et al: Knockdown of RON
inhibits AP-1 activity and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest
through the modulation of Akt/FoxO signaling in human colorectal
cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci. 57:371–380. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song YA, Park YL, Kim KY, Myung E, Chung
CY, Cho SB, Lee WS, Jung YD, Kweon SS and Joo YE: RON is associated
with tumor progression via the inhibition of apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest in human gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 62:127–136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho SB, Park YL, Song YA, Kim KY, Lee GH,
Cho DH, Myung DS, Park KJ, Lee WS, Chung IJ, et al: Small
interfering RNA-directed targeting of RON alters invasive and
oncogenic phenotypes of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 26:1581–1586. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murray AW and Marks D: Can sequencing shed
light on cell cycling? Nature. 409:844–846. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Connell-Crowley L, Elledge SJ and Harper
JW: G1 cyclin-dependent kinases are sufficient to initiate DNA
synthesis in quiescent human fibroblasts. Curr Biol. 8:65–68. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vermeulen K, van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang Y, Hu J, Zheng J, Li J, Wei T, Zheng
Z and Cheng Y: Down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
and induction of apoptosis in CA46 Burkitt lymphoma cells by
baicalin. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang MH, Zhang R, Zhou YQ and Yao HP:
Pathogenesis of RON receptor tyrosine kinase in cancer cells:
Activation mechanism, functional crosstalk, and signaling
addiction. J Biomed Res. 27:345–356. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu Y, Yao HP and Wang MH: Multiple
variants of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase: Biochemical
properties, tumorigenic activities, and potential drug targets.
Cancer Lett. 257:157–164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|