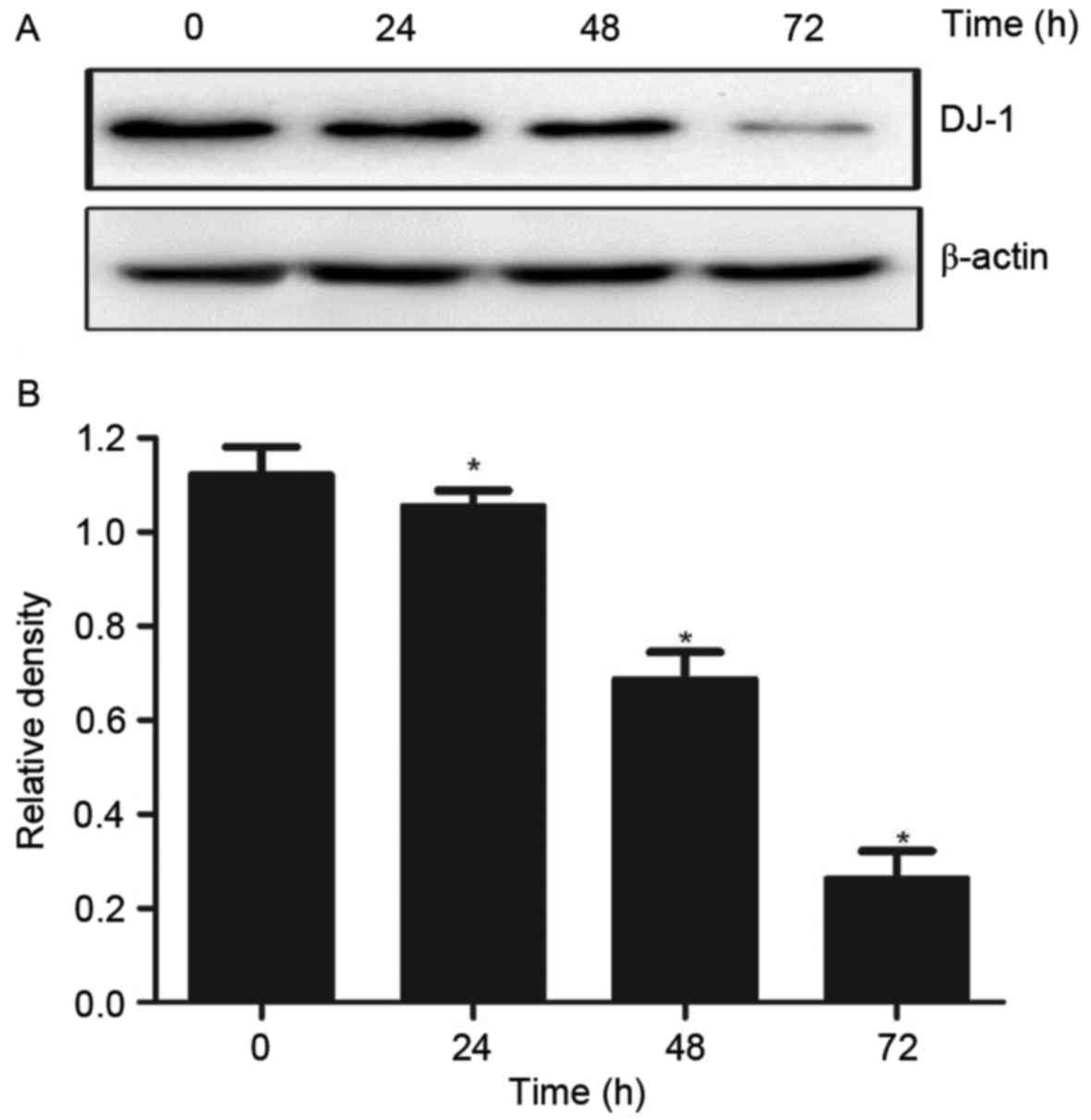
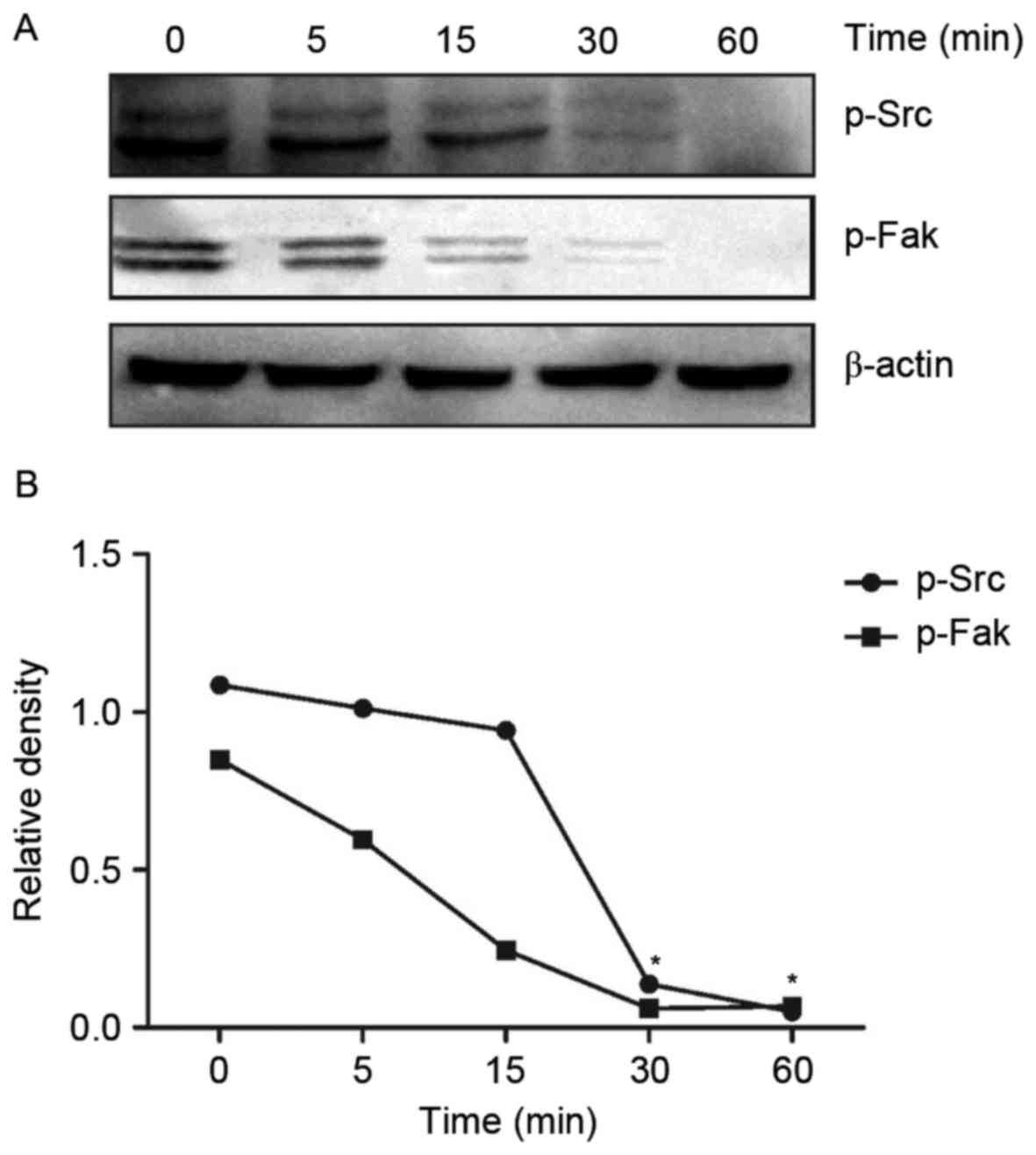
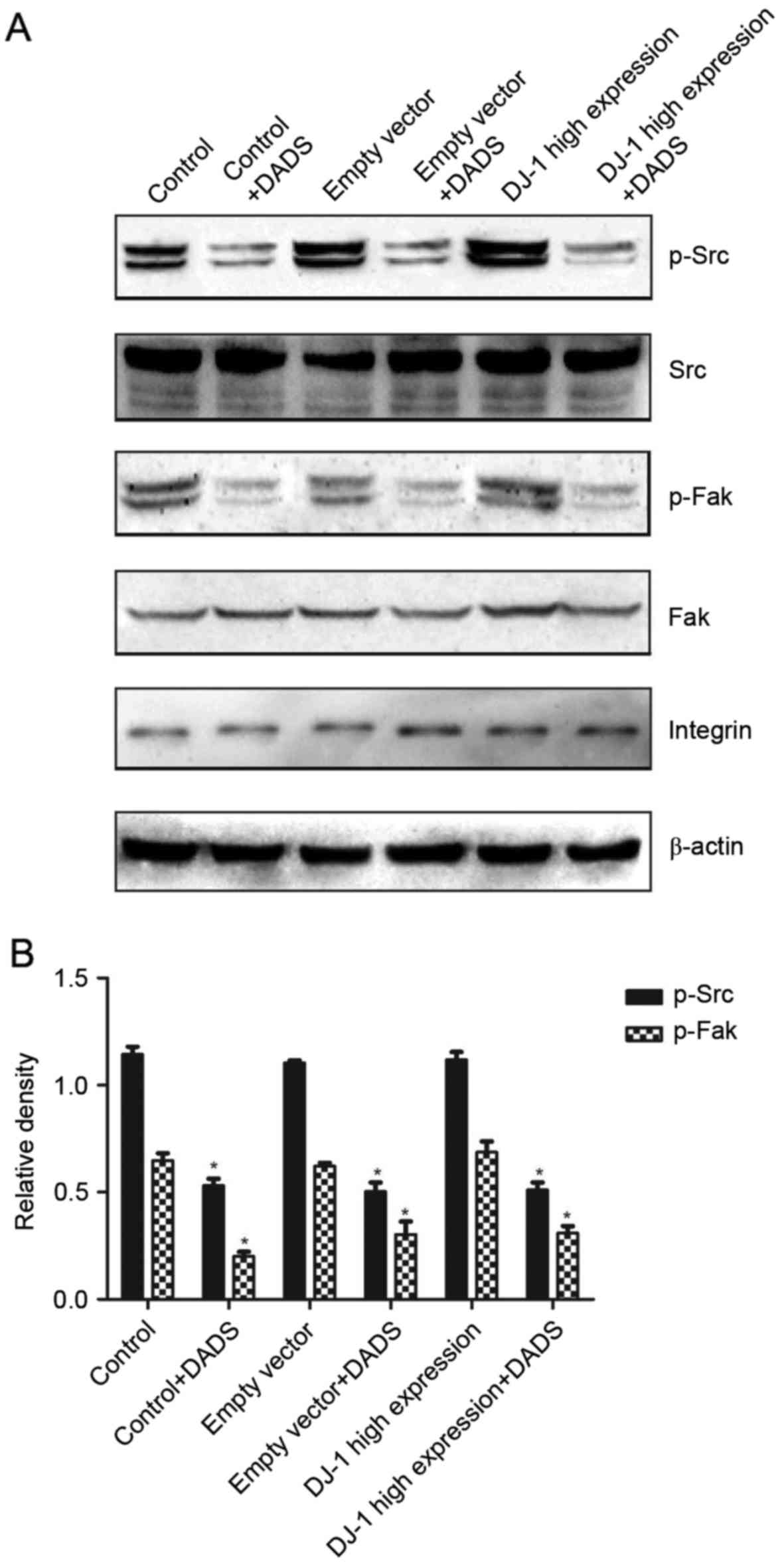
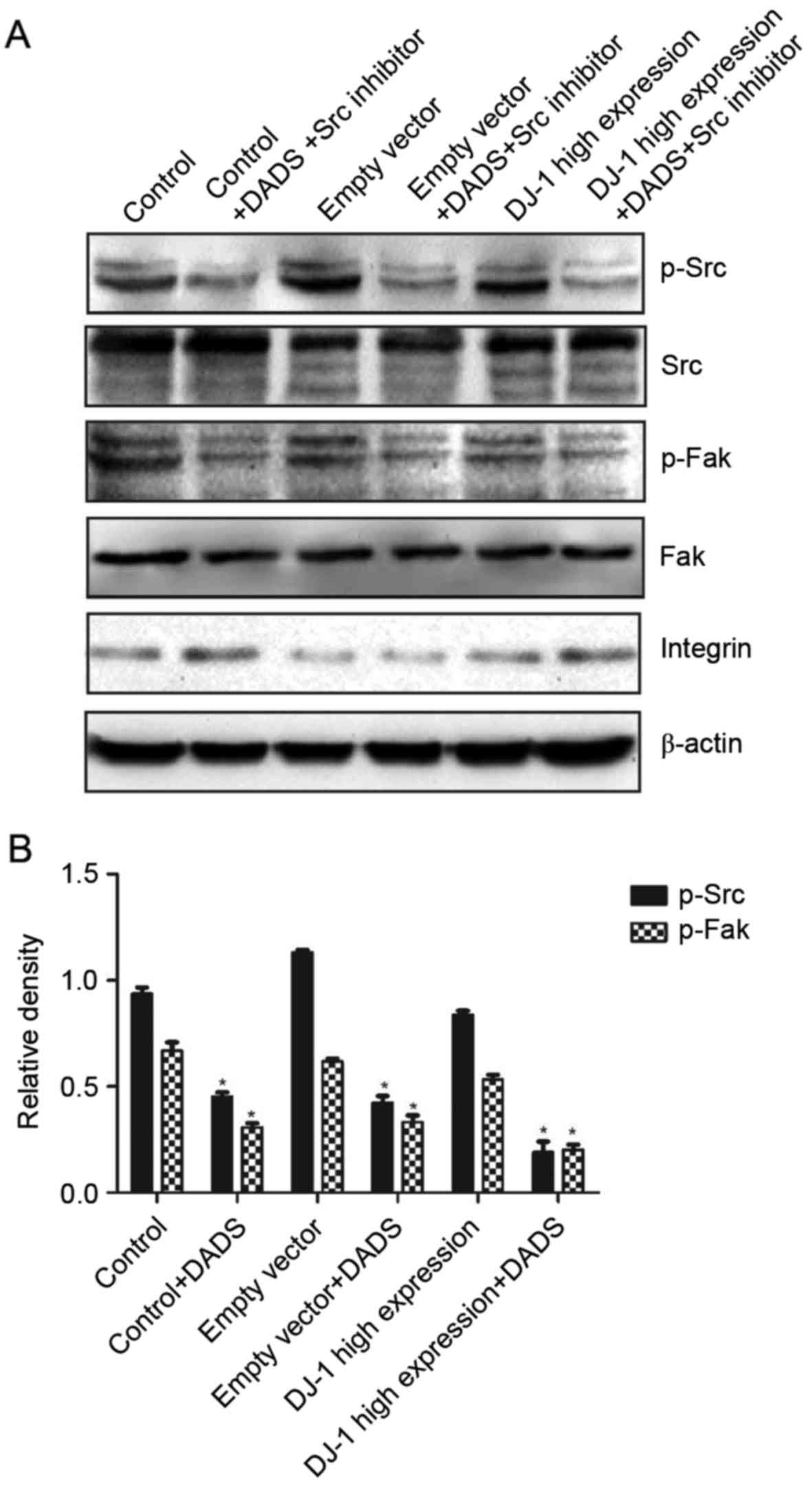
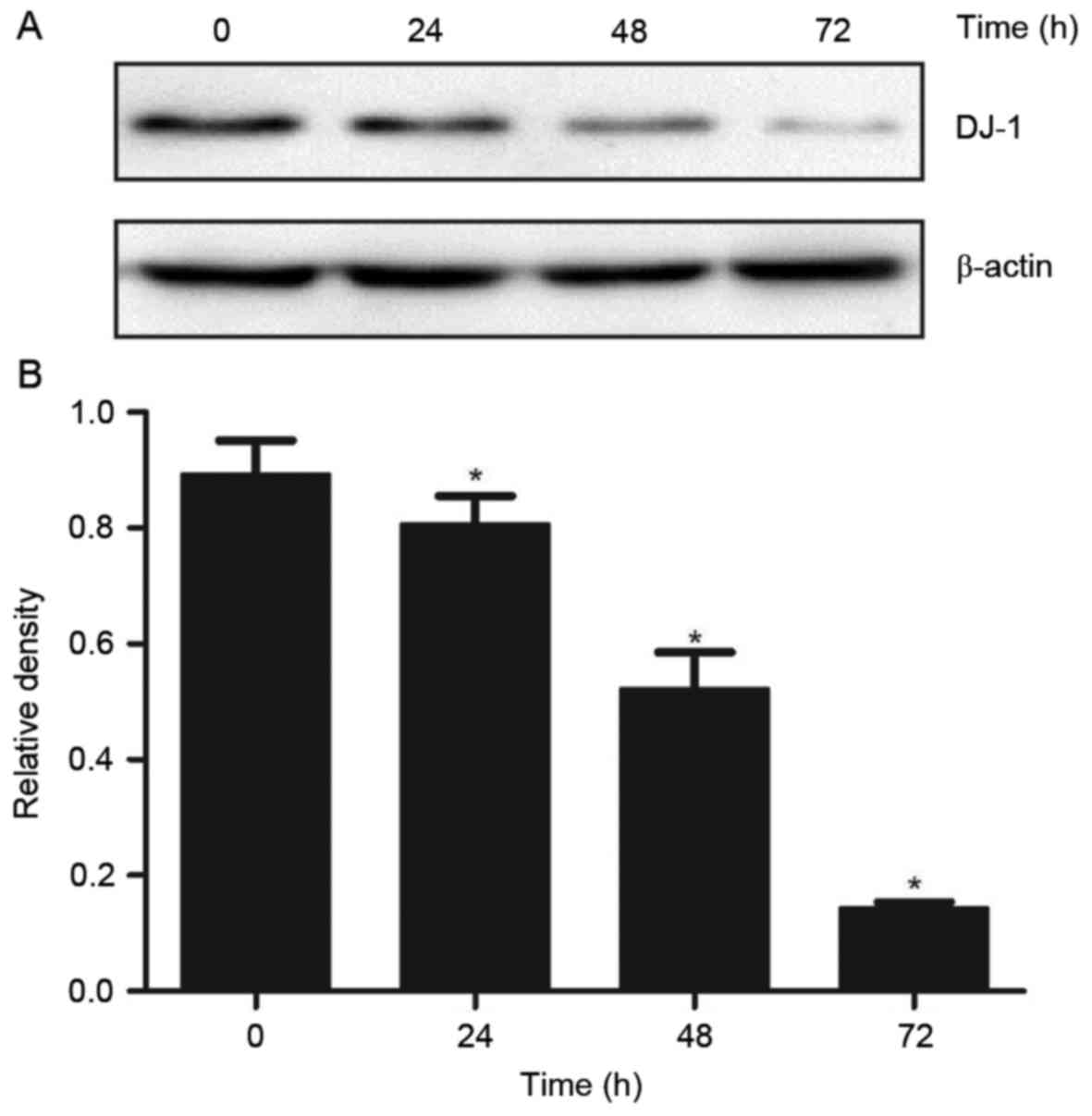
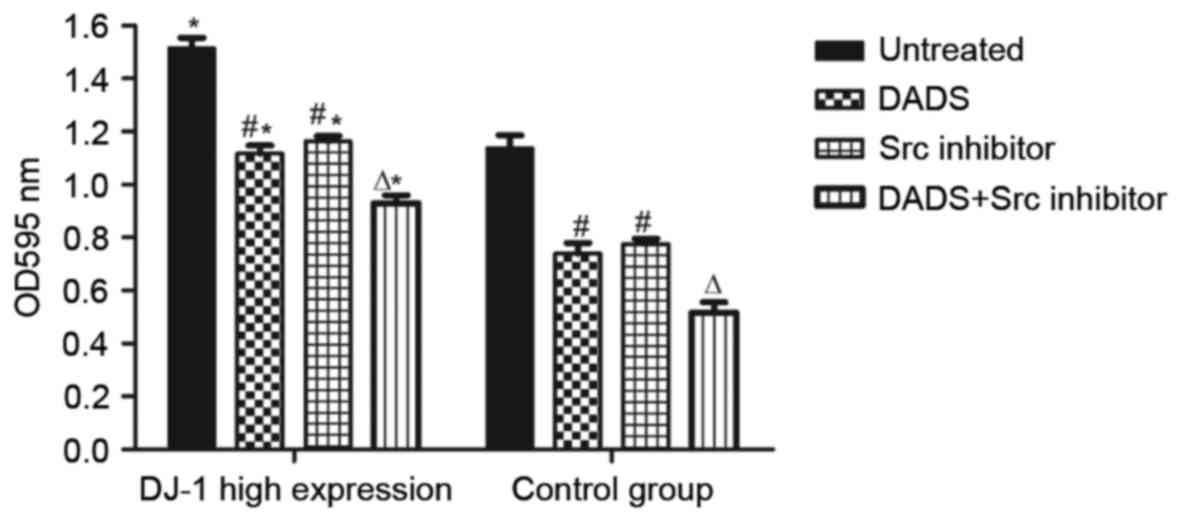
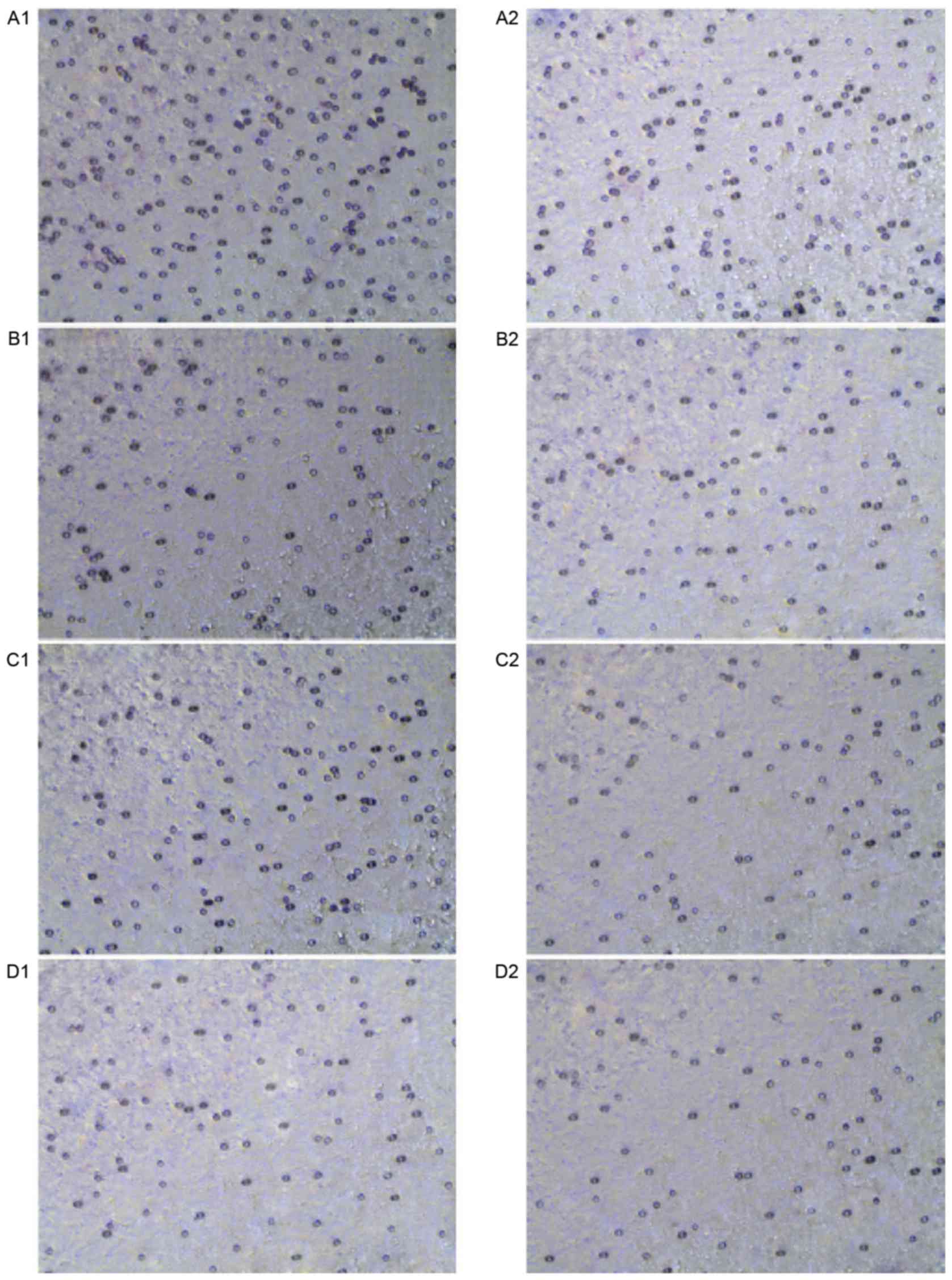
|
1
|
Pratheeshkumar P, Thejass P and Kutan G:
Diallyl disulfide induces caspase-dependent apoptosis via
mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway in B16F-10 melanoma cells
by up-regulating p53, caspase-3 and down-regulating
pro-inflammatory cytokines and nuclear factor-κβ-mediated Bcl-2
activation. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 29:113–125. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Altonsy MO, Habib TN and Andrews SC:
Diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis in a breast-cancer cell line
(MCF-7) may be caused by inhibition of histone deacetylation. Nutr
Cancer. 64:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, Tang Y and Xie X,
Yang L, Su Q and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1
signaling pathway by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer
Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiao X, Chen B, Liu X, Liu P, Zheng G, Ye
F, Tang H and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses SRC/Ras/ERK
signaling-mediated proliferation and metastasis in human breast
cancer by up-regulating miR-34a. PLoS One. 9:e1127202014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Truong D, Hindmarsh W and O'Brien PJ: The
molecular mechanisms of diallyl disulfide and diallyl sulfide
induced hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 180:79–88.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee IC, Kim SH, Baek HS, Moon C, Kim SH,
Kim YB, Yun WK, Kim HC and Kim JC: Protective effects of diallyl
disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity through
activation of Nrf2. Environ Toxicol. 30:538–548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yin X, Zhang J, Li X, Liu D, Feng C, Liang
R, Zhuang K, Cai C, Xue X, Jing F, et al: DADS suppresses human
esophageal xenograft tumors through RAF/MEK/ERK and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12422–12441.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsubura A, Lai YC, Kuwata M, Uehara N and
Yoshizawa K: Anticancer effects of garlic and garlic-derived
compounds for breast cancer control. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
11:249–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jie HE WY and Huang WG: Analysis of
protein expression of cell differentiation induced by HL-60 cells
by two dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Nan Uni (Med Edi).
32:143–6. 2004.
|
|
10
|
Chien CH, Lee MJ, Liou HC, Liou HH and Fu
WM: Local immunosuppressive microenvironment enhances migration of
melanoma cells to lungs in DJ-1 knockout mice. PLoS One.
10:e01158272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan J, Ren H, Jia N, Fei E, Zhou T, Jiang
P, Wu M and Wang G: DJ-1 decreases Bax expression through
repressing p53 transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem.
283:4022–4030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pei XJ, Wu TT, Li B, Tian XY, Li Z and
Yang QX: Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory
factor and DJ-1 contribute to cell invasion and metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 11:106–115. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang B, Qin H, Wang Y, Chen W, Luo J, Zhu
X, Wen W and Lei W: Effect of DJ-1 overexpression on the
proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and migration of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma SNU-46 cells through PI3K/AKT/mTOR. Oncol
Rep. 32:1108–1116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Devine MJ, Plun-Favreau H and Wood NW:
Parkinson's disease and cancer: Two wars, one front. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:812–823. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He X, Zheng Z, Li J, Ben Q, Liu J, Zhang
J, Ji J, Yu B, Chen X, Su L, et al: DJ-1 promotes invasion and
metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells by activating SRC/ERK/uPA.
Carcinogenesis. 33:555–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Che P, Yang Y, Han X, Hu M, Sellers JC,
Londono-Joshi AI, Cai GQ, Buchsbaum DJ, Christein JD, Tang Q, et
al: S100A4 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through a dual
signaling pathway mediated by Src and focal adhesion kinase. Sci
Rep. 5:84532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ku MJ, Kim JH, Lee J, Cho JY, Chun T and
Lee SY: Maclurin suppresses migration and invasion of human
non-small-cell lung cancer cells via anti-oxidative activity and
inhibition of the Src/FAK-ERK-β-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
402:243–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fang XQ, Liu XF, Yao L, Chen CQ, Lin JF,
Gu ZD, Ni PH, Zheng XM and Fan QS: Focal adhesion kinase regulates
the phosphorylation protein tyrosine phosphatase-α at Tyr789 in
breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:4303–4308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Altonsy MO, Habib TN and Andrews SC:
Diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis in a breast-cancer cell line
(MCF-7) may be caused by inhibition of histone deacetylation. Nutr
Cancer. 64:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kwon KB, Yoo SJ, Ryu DG, Yang JY, Rho HW,
Kim JS, Park JW, Kim HR and Park BH: Induction of apoptosis by
diallyl disulfide through activation of caspase-3 in human leukemia
HL-60 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 63:41–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jakubíková J and Sedlák J: Garlic-derived
organosulfides induce cytotoxicity, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest
and oxidative stress in human colon carcinoma cell lines.
Neoplasma. 53:191–199. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu XJ, Kassie F and Mersch-Sundermann V:
The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production on diallyl
disulfide (DADS) induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human
A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mutat Res. 579:115–124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakagawa H, Tsuta K, Kiuchi K, Senzaki H,
Tanaka K, Hioki K and Tsubura A: Growth inhibition effects of
diallyl disulfide on human breast cancer cell lines.
Carcinogenesis. 22:891–897. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shin DY, Kim GY, Lee JH, Choi BT, Yoo YH
and Choi YH: Apoptosis induction of human prostate carcinoma DU145
cells by diallyl disulfide via modulation of JNK and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 13:14158–14171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsubura A, Lai YC, Kuwata M, Uehara N and
Yoshizawa K: Anticancer effects of garlic and garlic-derived
compounds for breast cancer control. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
11:249–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carpinteiro A, Becker KA, Japtok L,
Hessler G, Keitsch S, Požgajovà M, Schmid KW, Adams C, Müller S,
Kleuser B, et al: Regulation of hematogenous tumor metastasis by
acid sphingomyelinase. EMBO Mol Med. 7:714–734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu MH TL, Li LP, Huang WG and Su Q: Effect
of growth inhibition and differentiation of HL-60 cell induced by
diallyl disulfide. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 25:300–2. 2004.
|
|
28
|
He J SQ, Huang WG, Xie HL, Liang SP, Song
Y and Xie JY: Proteomic initial Analysis of differentiation of
human myeloid leukemia cells induced by diallyl disulfide. FEBS J.
272 Suppl 1:4402005.
|
|
29
|
Zhang HY, Wang HQ, Liu HM, Guan Y and Du
ZX: Regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand-induced apoptosis by DJ-1 in thyroid cancer cells. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 15:535–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu F, Liang YQ and Huang ZM: The
expression of DJ-1 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its
relationship with tumor invasion and metastasis. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 17:203–206. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu XL, Wen WP, Lei WB, Chai LP, Hou WJ,
Wen YH and Wang XR: DJ-1 expression in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma and its relationship with tumor recurrence and
metastasis. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
45:497–501. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei W, Tang C, Zhan X, Yi H and Li C:
Effect of DJ-1 siRNA on biological behavior of human lung squamous
carcinoma SK-MES-1 cells. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
38:7–13. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Junn E, Jang WH, Zhao X, Jeong BS and
Mouradian MM: Mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 leads to enhanced
neuroprotection. J Neurosci Res. 87:123–129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hao LY, Giasson BI and Bonini NM: DJ-1 is
critical for mitochondrial function and rescues PINK1 loss of
function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:9747–9752. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Junn E, Taniguchi H, Jeong BS, Zhao X,
Ichijo H and Mouradian MM: Interaction of DJ-1 with Daxx inhibits
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 activity and cell death. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:9691–9696. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hwang S, Song S, Hong YK, Choi G, Suh YS,
Han SY, Lee M, Park SH, Lee JH, Lee S, et al: Drosophila DJ-1
decreases neural sensitivity to stress by negatively regulating
Daxx-like protein through dFOXO. PLoS Genet. 9:e10034122013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
JuanWang, Jing yY, Qing Yuxian, Tang
Qingye, Li Qi and Hui Su Tan: DADS inhibits proliferation and
differentiation of human leukemia HL60 cells by down regulated.
Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin. 416–20. 2015.
|
|
38
|
Fang M, Zhong XY, Du B, Lin CL, Luo F,
Tang LJ and Chen J: Role of DJ-1-induced PTEN down-regulation in
migration and invasion of human glioma cells. Chin J Cancer.
29:988–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ismail IA, Kang HS, Lee HJ, Kim JK and
Hong SH: DJ-1 upregulates breast cancer cell invasion by repressing
KLF17 expression. Br J Cancer. 110:1298–1306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu ZM, Li ZR, Huang Y, Yu HH, Huang XS,
Yan YF, Shao JH and Chen HP: DJ-1 is involved in the peritoneal
metastasis of gastric cancer through activation of the Akt
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 31:1489–1497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Cui J, Zhang CH, Yang DJ, Chen JH,
Zan WH, Li B, Li Z and He YL: High-expression of DJ-1 and loss of
PTEN associated with tumor metastasis and correlated with poor
prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 10:1689–1697. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gupta A and Dey CS: PTEN, a widely known
negative regulator of insulin/PI3K signaling, positively regulates
neuronal insulin resistance. Mol Biol Cell. 23:3882–3898. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McNally RS, Davis BK, Clements CM,
Accavitti-Loper MA, Mak TW and Ting JP: DJ-1 enhances cell survival
through the binding of Cezanne, a negative regulator of NF-kappaB.
J Biol Chem. 286:4098–4106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ismail IA, Shakor Abdel AB and Hong SH:
DJ-1 protects breast cancer cells against
2′-benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde-induced oxidative stress independent of
Nrf2. J Cell Physiol. 230:2262–2269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He X, Zheng Z, Li J, Ben Q, Liu J, Zhang
J, Ji J, Yu B, Chen X, Su L, et al: DJ-1 promotes invasion and
metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells by activating SRC/ERK/uPA.
Carcinogenesis. 33:555–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chang AY and Wang M: Molecular mechanisms
of action and potential biomarkers of growth inhibition of
dasatinib (BMS-354825) on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC
Cancer. 13:2672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li Y, Drabsch Y, Pujuguet P, Ren J, van
Laar T, Zhang L, van Dam H, Clément-Lacroix P and Ten Dijke P:
Genetic depletion and pharmacological targeting of αv integrin in
breast cancer cells impairs metastasis in zebrafish and mouse
xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. 17:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim SA, Kwon SM, Kim JA, Kang KW, Yoon JH
and Ahn SG: 5′-Nitro-indirubinoxime, an indirubin derivative,
suppresses metastatic ability of human head and neck cancer cells
through the inhibition of Integrin β1/FAK/Akt signaling. Cancer
Lett. 306:197–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Q, Tang Y, Qin J, Yi L, Yang Y, Wang J,
He J, Su Q and Tan H: Subcellular localization of DJ-1 in human
HL-60 leukemia cells in response to diallyl disulfide treatment.
Mol Med Rep. 14:4666–4672. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ceppi P, Papotti M, Monica V, Lo Iacono M,
Saviozzi S, Pautasso M, Novello S, Mussino S, Bracco E, Volante M
and Scagliotti GV: Effects of Src kinase inhibition induced by
dasatinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines treated with
cisplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:3066–3074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sánchez-Bailón MP, Calcabrini A,
Gómez-Domínguez D, Morte B, Martin-Forero E, Gómez-López G,
Molinari A, Wagner KU and Martín-Pérez J: Src kinases catalytic
activity regulates proliferation, migration and invasiveness of
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 24:1276–1286. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Koppikar P, Choi SH, Egloff AM, Cai Q,
Suzuki S, Freilino M, Nozawa H, Thomas SM, Gooding WE, Siegfried JM
and Grandis JR: Combined inhibition of c-Src and epidermal growth
factor receptor abrogates growth and invasion of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4284–4291. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang SE, Xiang B, Zent R, Quaranta V,
Pozzi A and Arteaga CL: Transforming growth factor beta induces
clustering of HER2 and integrins by activating Src-focal adhesion
kinase and receptor association to the cytoskeleton. Cancer Res.
69:475–482. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun B, Meng J, Xiang T, Chen Z, Li Y, Lu
L, Zhang S and Chen X: Jianpijiedu fang improves survival of
hepatocarcinoma mice by affecting phosphatase and tensin homolog,
phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and focal adhesion kinase. J Tradit Chin
Med. 33:479–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|