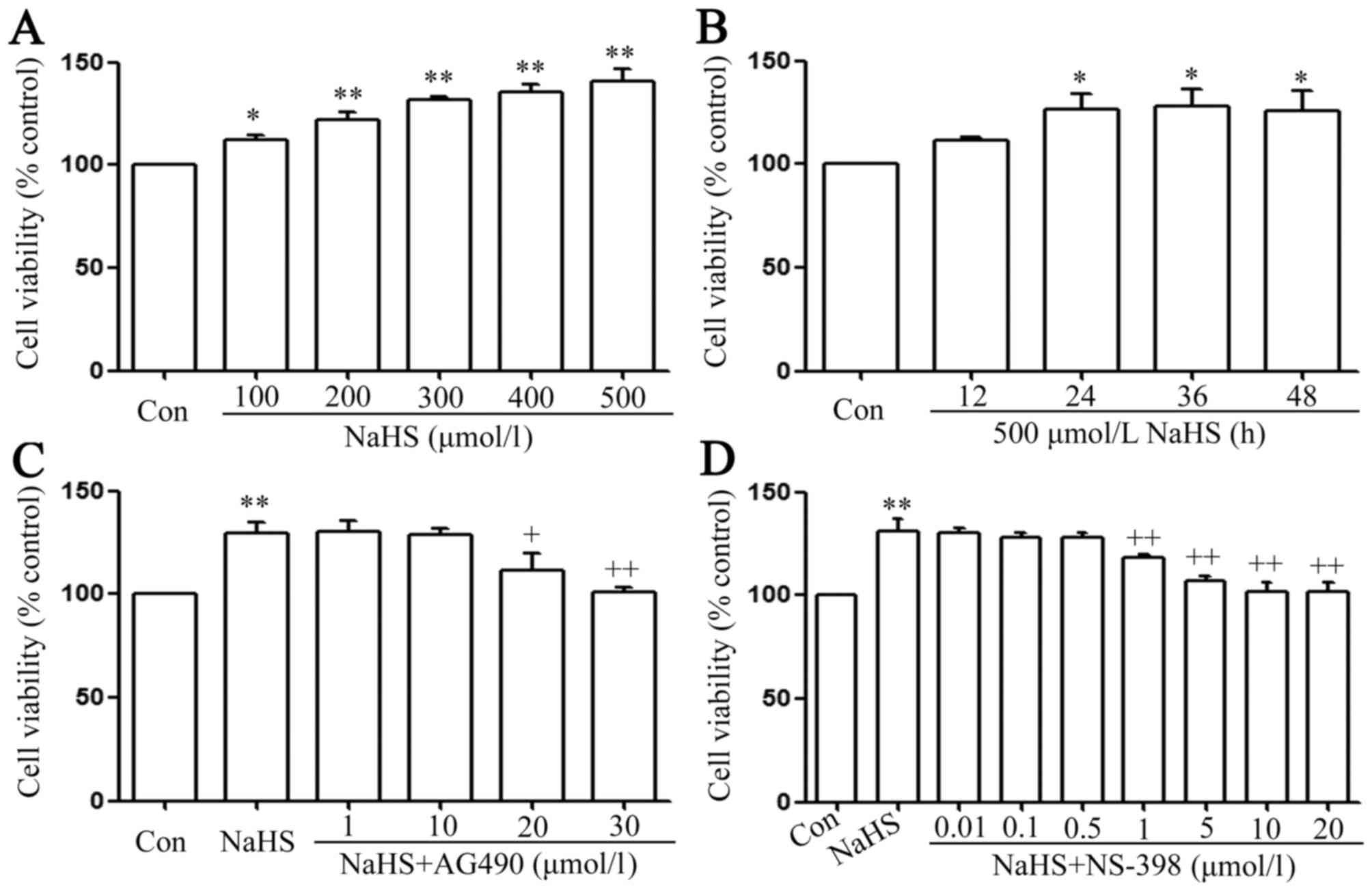
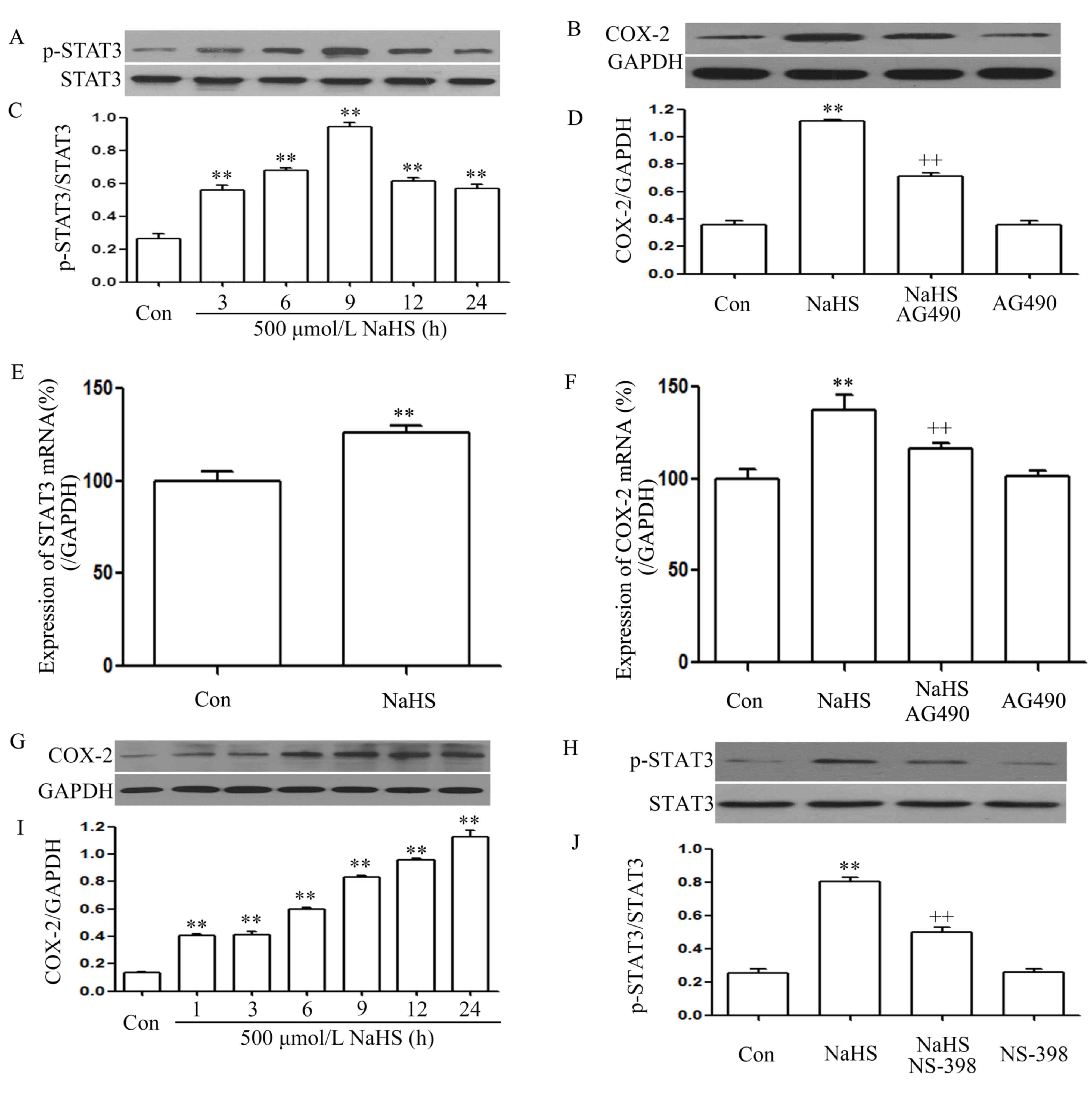
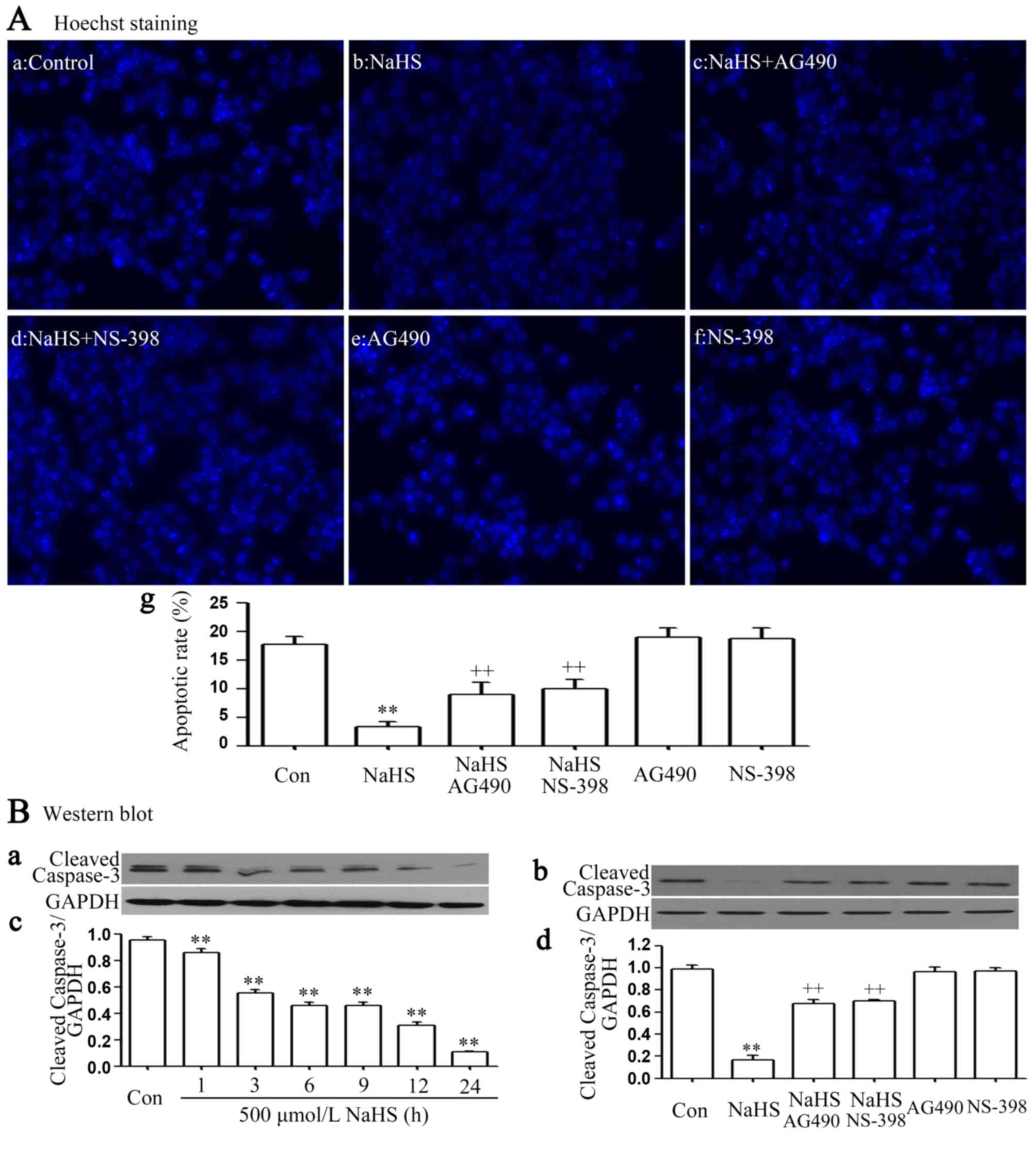
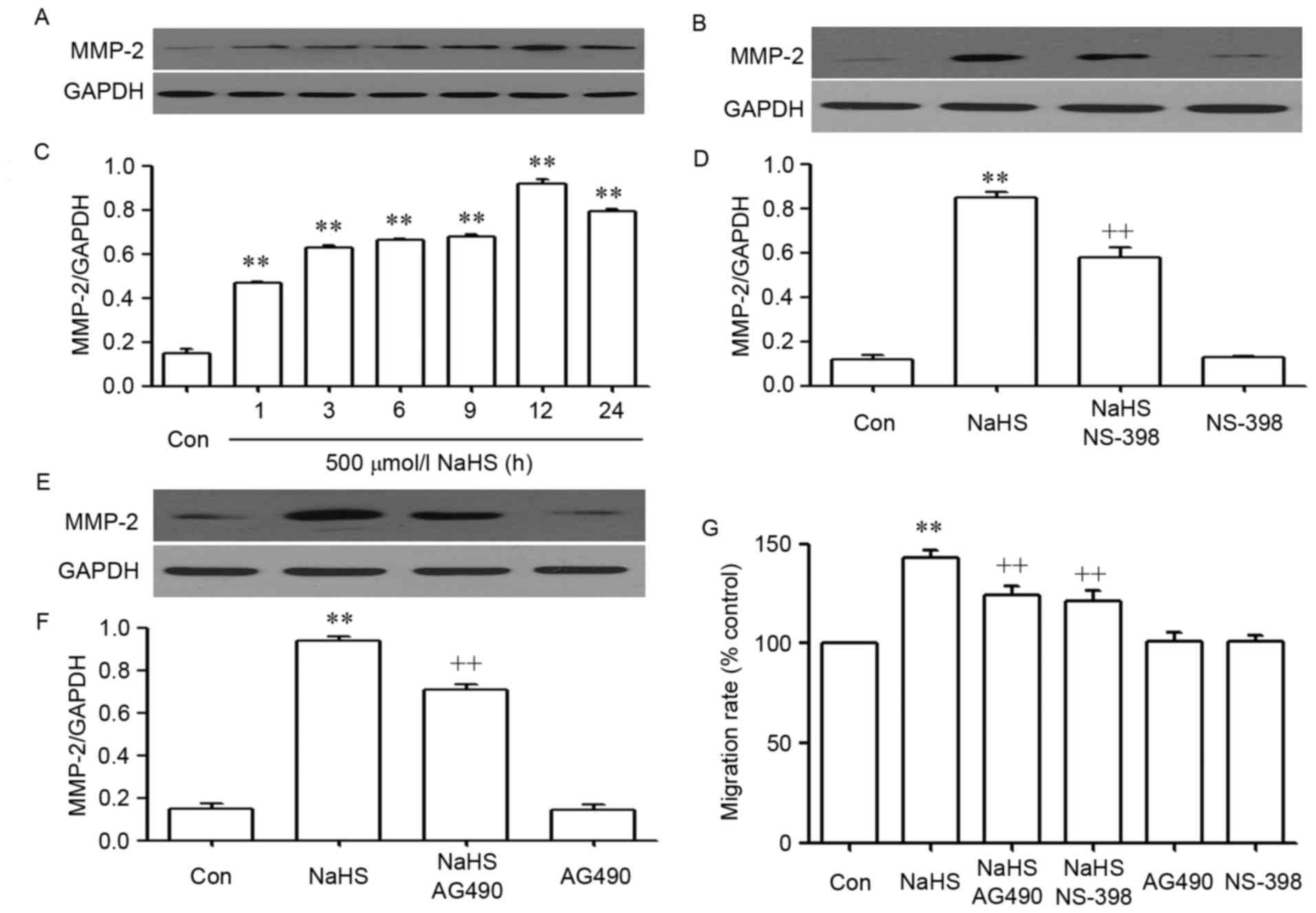
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M and Llovet JM:
Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 5:215–219. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lupberger J and Hildt E: Hepatitis B
virus-induced oncogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:74–81. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verslype C, Van Cutsem E, Dicato M, Arber
N, Berlin JD, Cunningham D, De Gramont A, Diaz-Rubio E, Ducreux M,
Gruenberger T, et al: The management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
current expert opinion and recommendations derived from the 10th
World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer, Barcelona, 2008. Ann
Oncol. 20 Suppl 7:Svii1–Svii6. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang H and Chen L: Tumor microenviroment
and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28 Suppl 1:S43–S48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Iakova P, Timchenko L and Timchenko NA:
Intracellular signaling and hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer
Biol. 21:28–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Faivre S, Bouattour M and Raymond E: Novel
molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 31
Suppl 1:S151–S160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chuang SC, La Vecchia C and Boffetta P:
Liver cancer: Descriptive epidemiology and risk factors other than
HBV and HCV infection. Cancer Lett. 286:9–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang X, Bi S, Yang W, Wang L, Cui G, Cui
F, Zhang Y, Liu J, Gong X, Chen Y, et al: Epidemiological
serosurvey of hepatitis B in China-declining HBV prevalence due to
hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccine. 27:6550–6557. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng B, Zhu YJ, Wang HY and Chen L:
Gender disparity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Multiple
underlying mechanisms. Sci China Life Sc. 60:575–584. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Levy DE and Darnell JE Jr: Stats:
Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 3:651–662. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar
KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S and Sung B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation and
cancer: How intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1171:59–76. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sandur SK,
Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B and Ichikawa H: Targeting
signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention
and therapy of cancer: modern target but ancient solution. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1091:151–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao T, Ren H, Wang X, Liu P, Yan F, Jiang
W, Li Y, Li J, Gribben JG, Jia L and Hao J: Rituximab-induced HMGB1
release is associated with inhibition of STAT3 activity in human
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 6:27816–27831. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mukthavaram R, Ouyang X, Saklecha R, Jiang
P, Nomura N, Pingle SC, Guo F and Makale M: Effect of the
JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor SAR317461 on human glioblastoma tumorspheres.
J Transl Med. 13:2692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liao XH, Zheng L, He HP, Zheng DL, Wei ZQ,
Wang N, Dong J, Ma WJ and Zhang TC: STAT3 regulated ATR via
microRNA-383 to control DNA damage to affect apoptosis in A431
cells. Cell Signal. 27:2285–2295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He S, Lu G, Hou H, Zhao Z, Zhu Z, Lu X,
Chen J and Wang Z: Saikosaponin-d suppresses the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 through the phospho-signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:2556–2562. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Loncle C, Bonjoch L, Folch-Puy E,
Lopez-Millan MB, Lac S, Molejon MI, Chuluyan E, Cordelier P, Dubus
P, Lomberk G, et al: IL-17 functions through the novel
REG3β-JAK2-STAT3 inflammatory pathway to promote the transition
from chronic pancreatitis to pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
75:4852–4862. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG and Hermeking H:
lnflammation-induced epigenetic switches in cancer. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 73:23–39. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choudhari SR, Khan MA, Harris G, Picker D,
Jacob GS, Block T and Shailubhai K: Deactivation of Akt and STAT3
signaling promotes apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and enhances
the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to an anticancer
agent, Atiprimod. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:112–121. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kilburn KH, Thrasher JD and Gray MR:
Low-level hydrogen sulfide and central nervous system dysfunction.
Toxicol Ind Health. 26:387–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kamoun P: Endogenous production of
hydrogen sulfide in mammals. Amino Acids. 26:243–254. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhen Y, Pan W, Hu F, Wu H, Feng J, Zhang Y
and Chen J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide exerts
proliferation/anti-apoptosis/angiogenesis/migration effects via
amplifying the activation of NF-κB pathway in PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 46:2194–2204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu D, Si W, Wang M, Lv S, Ji A and Li Y:
Hydrogen sulfide in cancer: Friend or foe? Nitric Oxide. 50:38–45.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee ZW and Deng LW: Role of H2S donors in
cancer biology. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 230:243–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hellmich MR and Szabo C: Hydrogen sulfide
and cancer. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 230:233–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szabo C, Coletta C, Chao C, Módis K,
Szczesny B, Papapetropoulos A and Hellmich MR: Tumor-derived
hydrogen sulfide, produced by cystathionine-β-synthase, stimulates
bioenergetics, cell proliferation and angiogenesis in colon cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:12474–12479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
DU SX, Xiao J, Guan F, Sun LM, Wu WS, Tang
H, DU JB, Tang CS and Jin HF: Predictive role of cerebrospinal
fluid hydrogen sulfide in central nervous system leukemia. Chin Med
J (Engl). 124:3450–3454. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rose P, Moore PK, Ming SH, Nam OC,
Armstrong JS and Whiteman M: Hydrogen sulfide protects colon cancer
cells from chemopreventative agent betaphenylethyl isothiocyanate
induced apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3990–3997. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai WJ, Wang MJ, Ju LH, Wang C and Zhu YC:
Hydrogen sulfide induces human colon cancer cell proliferation:
Role of Akt, ERK and p21. Cell Biol Int. 34:565–572. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhen Y, Zhang W, Liu C, He J, Lu Y, Guo R,
Feng J, Zhang Y and Chen J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide promotes C6
glioma cell growth through activation of the p38 MAPK/ERK1/2-COX-2
pathways. Oncol Rep. 34:2413–2422. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luan HF, Zhao ZB, Zhao QH, Zhu P, Xiu MY
and Ji Y: Hydrogen sulfide postconditioning protects isolated rat
hearts against ischemia and reperfusion injury mediated by the
JAK2/STAT3 survival pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 45:898–905. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu A, Huang JJ, Jin XJ, Li JP, Tang YJ,
Huang XF, Cui HJ, Xu WH and Sun GB: Curcumin suppresses
invasiveness and vasculogenic mimicry of squamous cell carcinoma of
the larynx through the inhibition of JAK-2/STAT-3 signaling
pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 5:278–288. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu YY, Guo M, Yang LQ, Zhou F, Yu C, Wang
A, Pang TH, Wu HY, Zou XP, Zhang WJ, et al: Regulation of CD44v6
expression in gastric carcinoma by the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway
and its clinical significance. Oncotarget. 8:45848–45861.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zeng L, Zhen Y, Chen Y, Zou L, Zhang Y, Hu
F, Feng J, Shen J and Wei B: Naringin inhibits growth and induces
apoptosis by a mechanism dependent on reduced activation of
NF-κB/COX-2-caspase-1 pathway in HeLa cervical cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 45:1929–1936. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu W, Chen J, Lin J, Liu D, Mo L, Pan W,
Feng J, Wu W and Zheng D: Exogenous H2S protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury and inflammation by inhibiting
the activation of the NF-κB and IL-1β pathways. Int J Mol Med.
35:177–186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Coletta C, Papapetropoulos A, Erdelyi K,
Olah G, Módis K, Panopoulos P, Asimakopoulou A, Gerö D, Sharina I,
Martin E and Szabo C: Hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide are
mutually dependent in the regulation of angiogenesis and
endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:9161–9166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide: From brain to
gut. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1111–1123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang X, Gao Y, Qin J and Lu S: The role
of miR-34a in the hepatoprotective effect of hydrogen sulfide on
ischemia/reperfusion injury in young and old rats. PLoS One.
9:e1133052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
You Q, Wu Z, Wu B, Liu C, Huang R, Yang L,
Guo R, Wu K and Chen J: Naringin protects cardiomyocytes against
hyperglycemia-induced injuries in vitro and in vivo. J Endocrinol.
230:197–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Israr E,
Gühring H, Brune K, Euchenhofer C, Grösch S and Geisslinger G:
Inhibition of NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation by R- and
S-flurbiprofen. FASEB J. 15:2–4. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Seo KW, Coh YR, Rebhun RB, Ahn JO, Han SM,
Lee HW and Youn HY: Antitumor effects of celecoxib in COX-2
expressing and non-expressing canine melanoma cell lines. Res Vet
Sci. 96:482–486. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wu X, Cai M, Ji F and Lou LM: The impact
of COX-2 on invasion of osteosarcoma cell and its mechanism of
regulation. Cancer Cell Int. 14:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao J, Tian J, Lv Y, Shi F, Kong F, Shi H
and Zhao L: Leptin induces functional activation of
cyclooxygenase-2 through JAK2/STAT3, MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways
in human endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 100:389–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu W, Chen GS, Shao Y, Li XL, Xu HC, Zhang
H, Zhu GQ, Zhou YC, He XP and Sun WH: Gastrin acting on the
cholecystokinin2 receptor induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression
through JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/Akt pathway in human gastric cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 332:11–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gong J, Xie J, Bedolla R, Rivas P,
Chakravarthy D, Freeman JW, Reddick R, Kopetz S, Peterson A, Wang
H, et al: Combined targeting of STAT3/NF-κB/COX-2/EP4 for effective
management of pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1259–1273.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu X, Ji Q, Ye N, Sui H, Zhou L, Zhu H,
Fan Z, Cai J and Li Q: Berberine inhibits invasion and metastasis
of colorectal cancer cells via COX-2/PGE2 mediated JAK2/STAT3
Signaling pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01234782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xiong H, Du W, Sun TT, Lin YW, Wang JL,
Hong J and Fang JY: A positive feedback loop between STAT3 and
cyclooxygenase-2 gene may contribute to Helicobacter
pylori-associated human gastric tumorigenesis. Int J Cancer.
134:2030–2040. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|