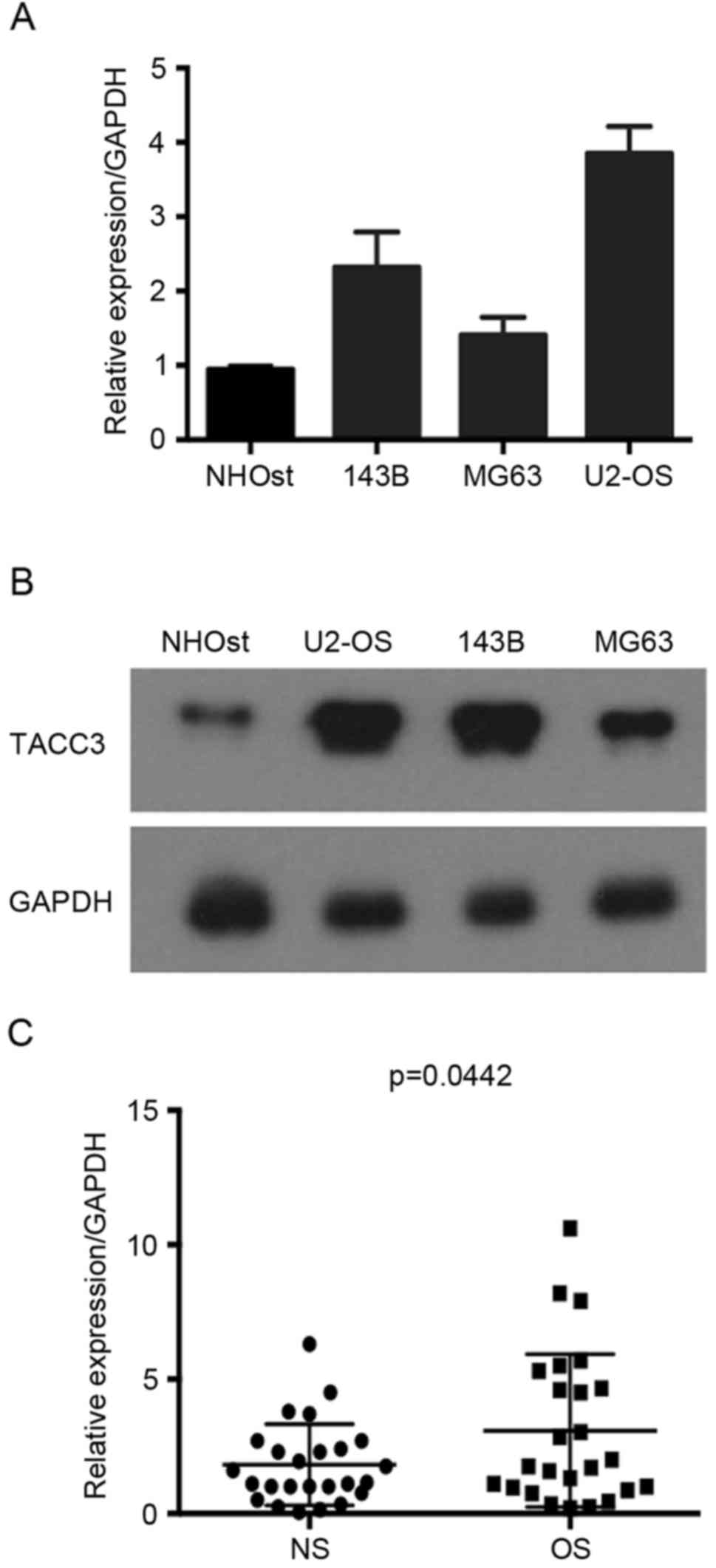
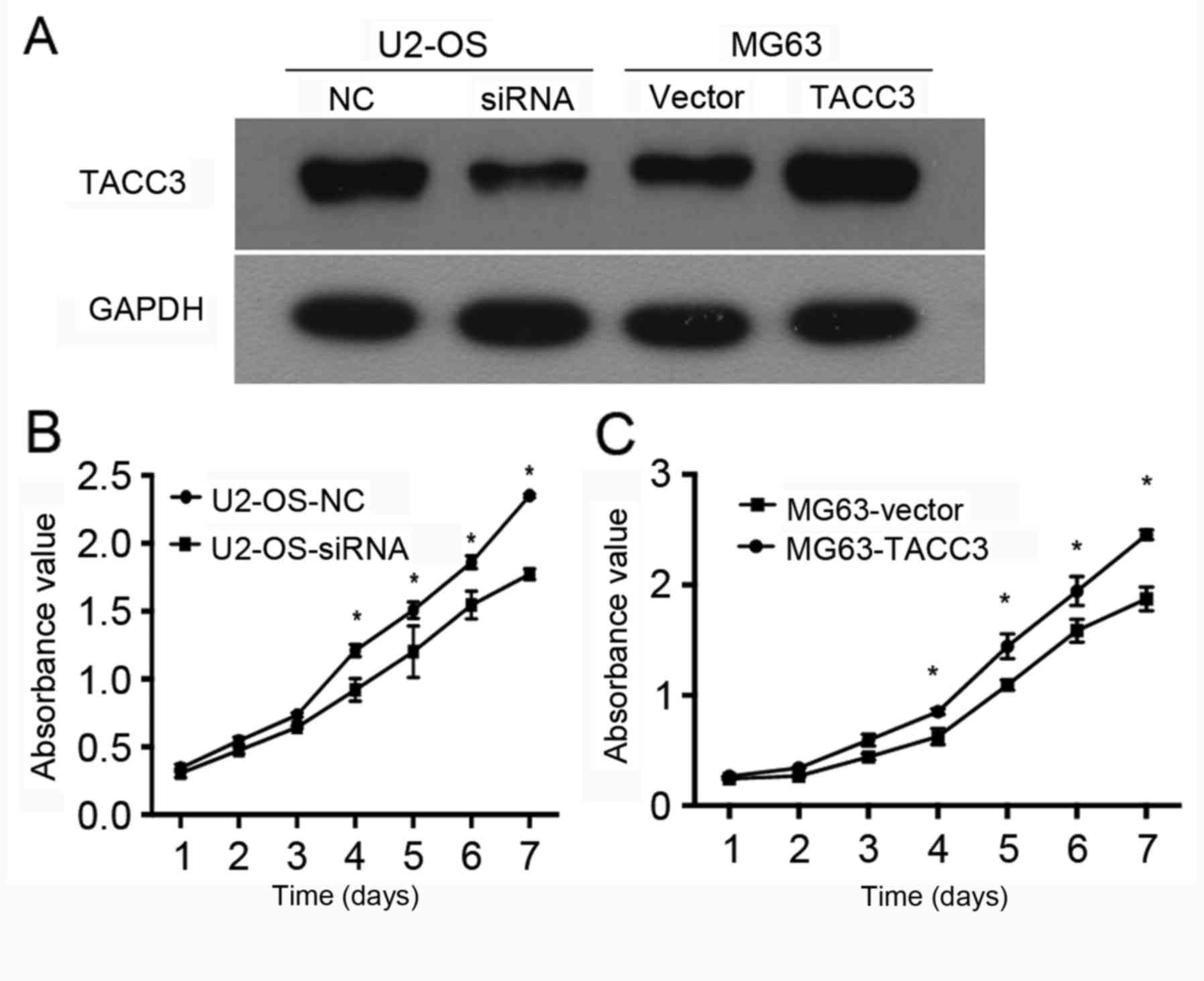
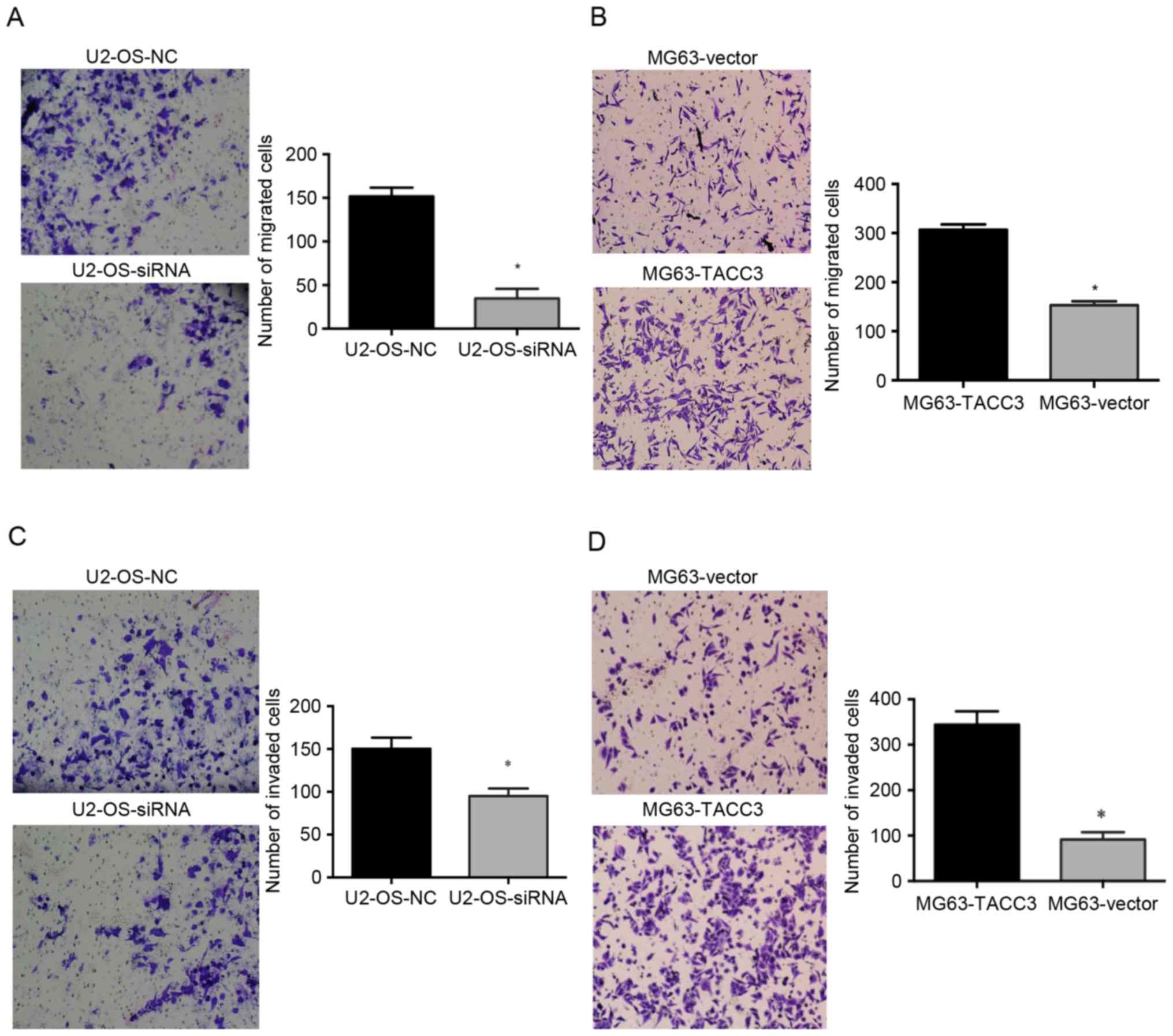
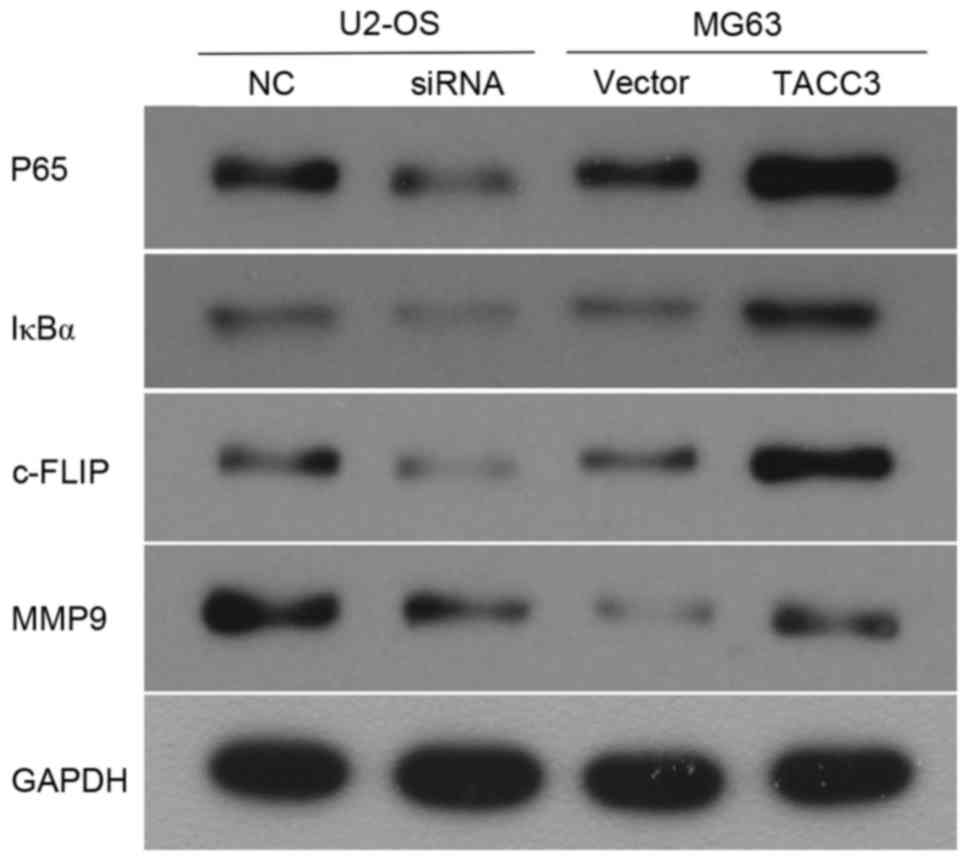
|
1
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrari S, Smeland S, Mercuri M, Bertoni
F, Longhi A, Ruggieri P, Alvegard TA, Picci P, Capanna R, Bernini
G, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with high-dose Ifosfamide,
high-dose methotrexate, cisplatin, and doxorubicin for patients
with localized osteosarcoma of the extremity: A joint study by the
Italian and Scandinavian Sarcoma Groups. J Clin Oncol.
23:8845–8852. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu J, Song G, Tang Q, Zou C, Han F, Zhao
Z, Yong B, Yin J, Xu H, Xie X, et al: IRX1 hypomethylation promotes
osteosarcoma metastasis via induction of CXCL14/NF-κB signaling. J
Clin Invest. 125:1839–1856. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hou CH, Lin FL, Hou SM and Liu JF: Cyr61
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis of
osteosarcoma by Raf-1/MEK/ERK/Elk-1/TWIST-1 signaling pathway. Mol
Cancer. 13:2362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsai HC, Su HL, Huang CY, Fong YC, Hsu CJ
and Tang CH: CTGF increases matrix metalloproteinases expression
and subsequently promotes tumor metastasis in human osteosarcoma
through down-regulating miR-519d. Oncotarget. 5:3800–3812. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Still IH, Vince P and Cowell JK: The third
member of the transforming acidic coiled coil-containing gene
family, TACC3, maps in 4p16, close to translocation breakpoints in
multiple myeloma, and is upregulated in various cancer cell lines.
Genomics. 58:165–170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kiemeney LA, Sulem P, Besenbacher S,
Vermeulen SH, Sigurdsson A, Thorleifsson G, Gudbjartsson DF, Stacey
SN, Gudmundsson J, Zanon C, et al: A sequence variant at 4p16.3
confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer. Nat Genet.
42:415–419. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hood FE and Royle SJ: Pulling it together:
The mitotic function of TACC3. Bioarchitecture. 1:105–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sadek CM, Pelto-Huikko M, Tujague M,
Steffensen KR, Wennerholm M and Gustafsson JA: TACC3 expression is
tightly regulated during early differentiation. Gene Expr Patterns.
3:203–211. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao R, Natsume Y and Noda T: TACC3 is
required for the proper mitosis of sclerotome mesenchymal cells
during formation of the axial skeleton. Cancer Sci. 98:555–562.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Capelletti M, Dodge ME, Ercan D, Hammerman
PS, Park SI, Kim J, Sasaki H, Jablons DM, Lipson D, Young L, et al:
Identification of recurrent FGFR3-TACC3 fusion oncogenes from lung
adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6551–6558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou DS, Wang HB, Zhou ZG, Zhang YJ, Zhong
Q, Xu L, Huang YH, Yeung SC, Chen MS and Zeng MS: TACC3 promotes
stemness and is a potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:24163–24177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Wu MS, Zou C, Tang Q, Lu J, Liu D,
Wu Y, Yin J, Xie X, Shen J, et al: Downregulation of MCT1 inhibits
tumor growth, metastasis and enhances chemotherapeutic efficacy in
osteosarcoma through regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett.
342:150–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schon S, Flierman I, Ofner A, Stahringer
A, Holdt LM, Kolligs FT and Herbst A: β-catenin regulates NF-κB
activity via TNFRSF19 in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
135:1800–1811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bera A, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Dey N, Das F,
Kasinath BS, Abboud HE and Choudhury GG: NFκB-mediated cyclin D1
expression by microRNA-21 influences renal cancer cell
proliferation. Cell Signal. 25:2575–2586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shao N, Lu Z, Zhang Y, Wang M, Li W, Hu Z,
Wang S and Lin Y: Interleukin-8 upregulates integrin 3 expression
and promotes estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cell invasion
by activating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett. 364:165–172.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Korber MI, Staribacher A, Ratzenbock I,
Steger G and Mader RM: NFκB-Associated pathways in progression of
chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil in an in vitro model of colonic
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 36:1631–1639. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang QL, Xie XB, Wang J, Chen Q, Han AJ,
Zou CY, Yin JQ, Liu DW, Liang Y, Zhao ZQ, et al: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3, NF-κB signaling, and tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:749–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ha GH, Park JS and Breuer EK: TACC3
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the
activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett.
332:63–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lauffart B, Vaughan MM, Eddy R, Chervinsky
D, DiCioccio RA, Black JD and Still IH: Aberrations of TACC1 and
TACC3 are associated with ovarian cancer. BMC Women's Health.
5:82005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yun M, Rong J, Lin ZR, He YL, Zhang JX,
Peng ZW, Tang LQ, Zeng MS, Zhong Q and Ye S: High expression of
transforming acidic coiled coil-containing protein 3 strongly
correlates with aggressive characteristics and poor prognosis of
gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 34:1397–1405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang F, Kuang B, Que Y, Lin Z, Yuan L,
Xiao W, Peng R and Zhang X and Zhang X: The clinical significance
of transforming acidic coiled-coil protein 3 expression in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:436–446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nahm JH, Kim H, Lee H, Cho JY, Choi YR,
Yoon YS, Han HS and Park YN: Transforming acidic
coiled-coil-containing protein 3 (TACC3) overexpression in
hepatocellular carcinomas is associated with ‘stemness’ and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related marker expression and a
poor prognosis. Tumour Biol. 37:393–403. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang ZL, Lin ZR, Xiao YR, Cao X, Zhu LC,
Zeng MS, Zhong Q and Wen ZS: High expression of TACC3 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis. Oncotarget.
6:6850–6861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ha GH, Kim JL and Breuer EK: TACC3 is
essential for EGF-mediated EMT in cervical cancer. PLoS One.
8:e703532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|