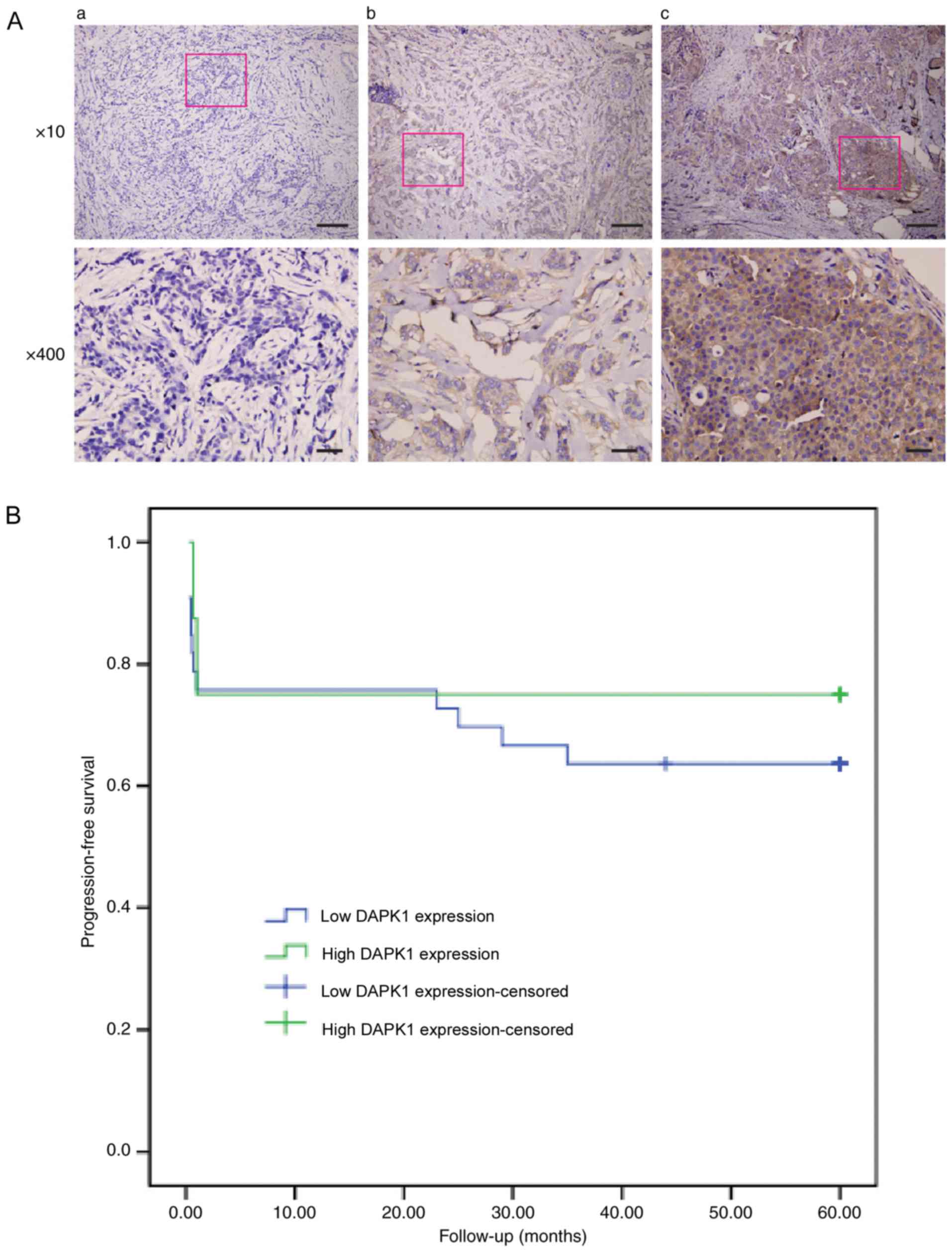
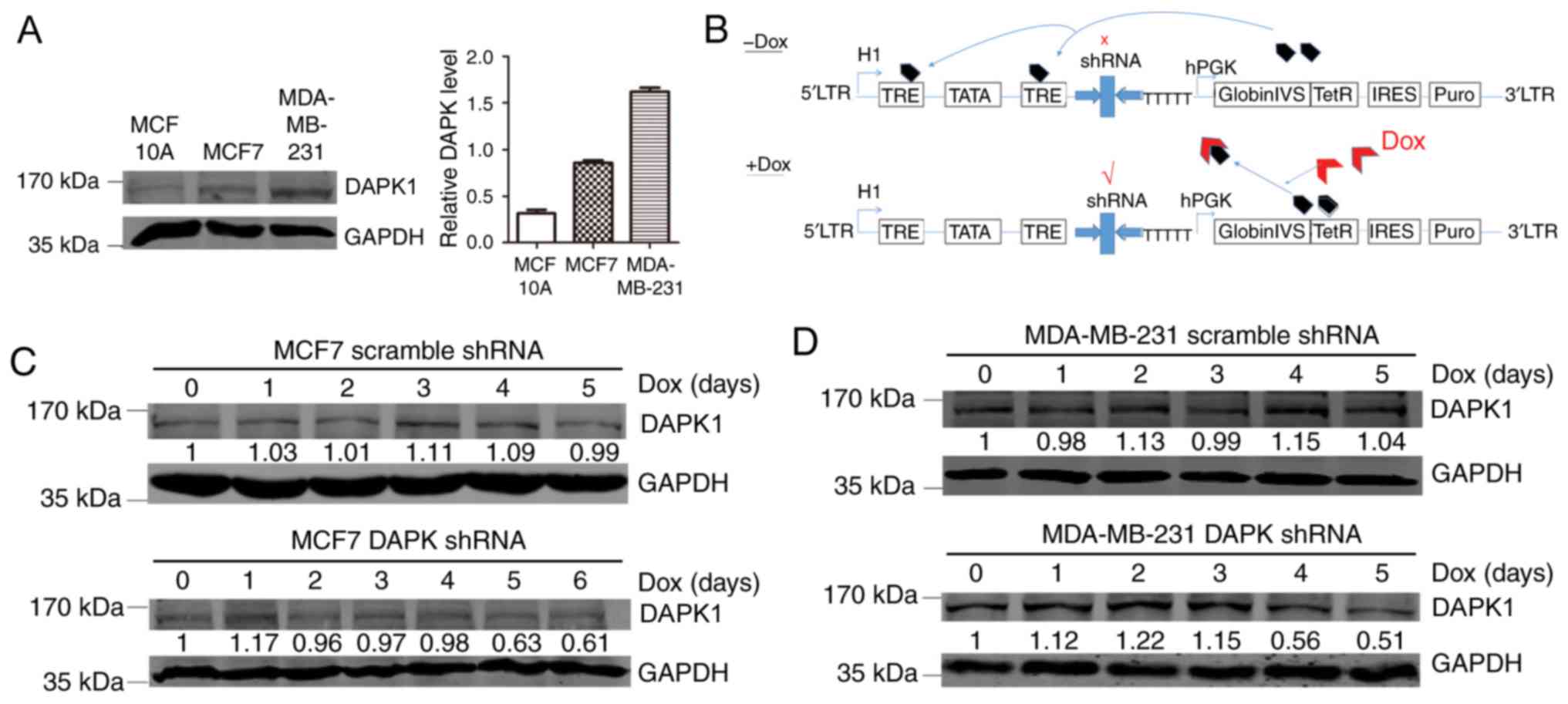
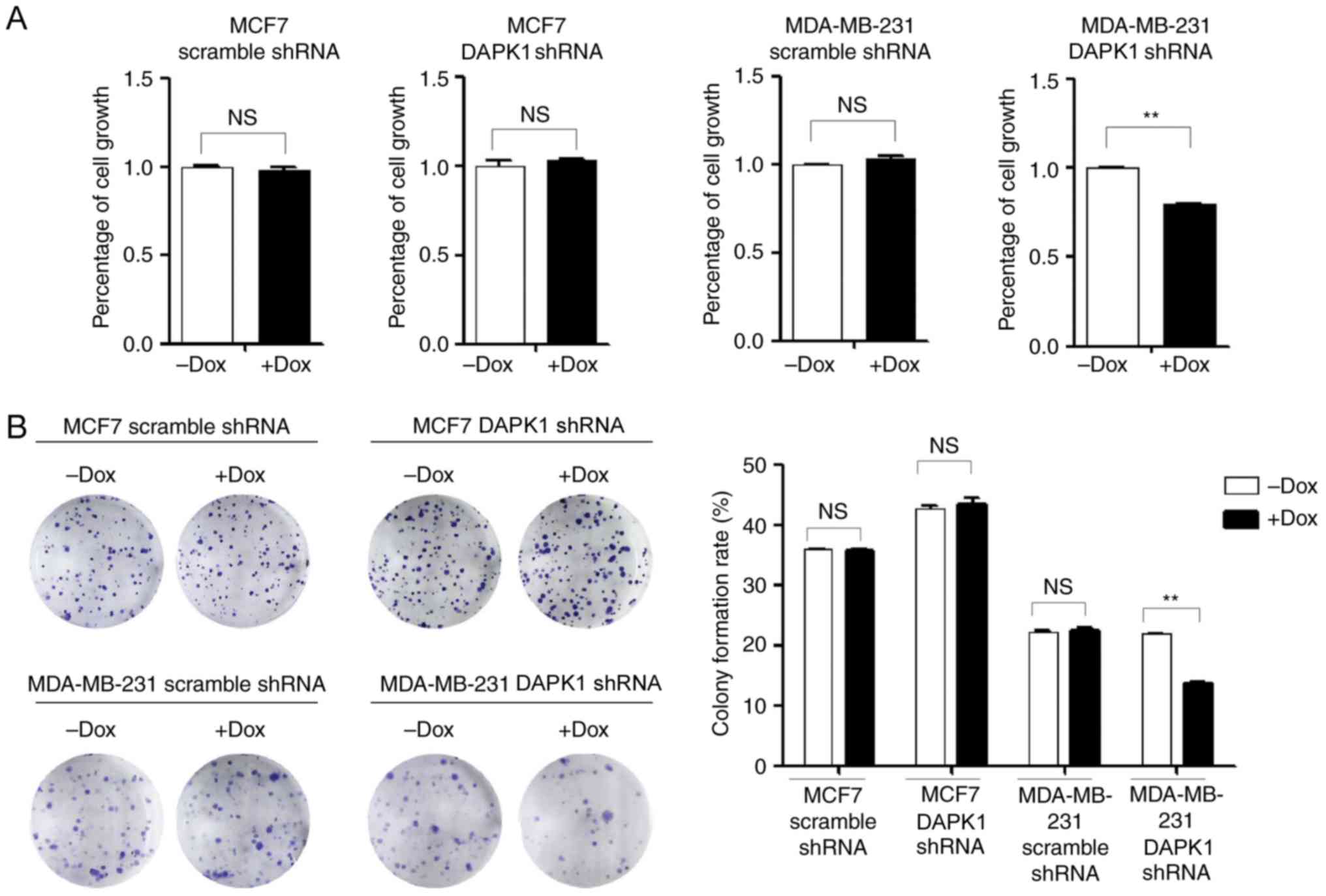
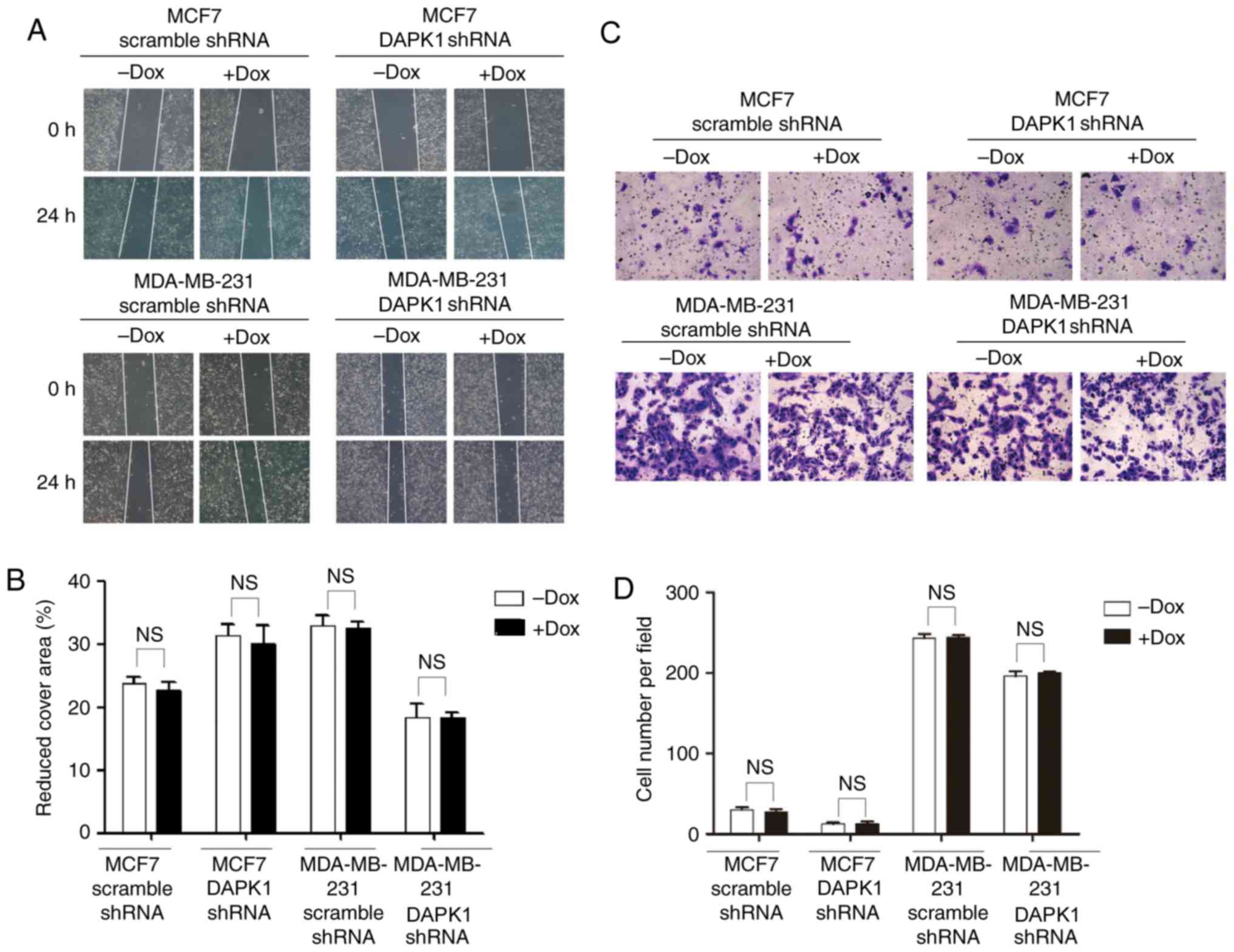
|
1
|
Shiloh R, Bialik S and Kimchi A: The DAPK
family: A structure-function analysis. Apoptosis. 19:286–297. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin Y, Hupp TR and Stevens C:
Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) and signal transduction:
Additional roles beyond cell death. FEBS J. 277:48–57. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin Y, Stevens C, Harrison B, Pathuri S,
Amin E and Hupp TR: The alternative splice variant of DAPK-1,
s-DAPK-1, induces proteasome-independent DAPK-1 destabilization.
Mol Cell Biochem. 328:101–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin Y, Stevens C, Hrstka R, Harrison B,
Fourtouna A, Pathuri S, Vojtesek B and Hupp T: An alternative
transcript from the death-associated protein kinase 1 locus
encoding a small protein selectively mediates membrane blebbing.
FEBS J. 275:2574–2584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang Y, Chen L, Guo L, Hupp TR and Lin Y:
Evaluating DAPK as a therapeutic target. Apoptosis. 19:371–386.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao J, Zhao D, Poage GM, Mazumdar A,
Zhang Y, Hill JL, Hartman ZC, Savage MI, Mills GB and Brown PH:
Death-associated protein kinase 1 promotes growth of p53-mutant
cancers. J Clin Invest. 125:2707–2720. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stevens C, Lin Y, Harrison B, Burch L,
Ridgway RA, Sansom O and Hupp T: Peptide combinatorial libraries
identify TSC2 as a death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) death
domain-binding protein and reveal a stimulatory role for DAPK in
mTORC1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:334–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuo JC, Wang WJ, Yao CC, Wu PR and Chen
RH: The tumor suppressor DAPK inhibits cell motility by blocking
the integrin-mediated polarity pathway. J Cell Biol. 172:619–631.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie JW, Chen PC, Zheng CH, Li P, Wang JB,
Lin JX, Lu J, Chen QY, Cao LL, Lin M, et al: Evaluation of the
prognostic value and functional roles of CD44v6 in gastric cancer.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:1809–1817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin Y, Richards FM, Krippendorff BF,
Bramhall JL, Harrington JA, Bapiro TE, Robertson A, Zheleva D and
Jodrell DI: Paclitaxel and CYC3, an aurora kinase A inhibitor,
synergise in pancreatic cancer cells but not bone marrow precursor
cells. Br J Cancer. 107:1692–1701. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lehmann U, Celikkaya G, Hasemeier B,
Langer F and Kreipe H: Promoter hypermethylation of the
death-associated protein kinase gene in breast cancer is associated
with the invasive lobular subtype. Cancer Res. 62:6634–6638.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Christoph F, Kempkensteffen C, Weikert S,
Köllermann J, Krause H, Miller K, Schostak M and Schrader M:
Methylation of tumour suppressor genes APAF-1 and DAPK-1 and in
vitro effects of demethylating agents in bladder and kidney cancer.
Br J Cancer. 95:1701–1707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Satoh A, Toyota M, Itoh F, Kikuchi T,
Obata T, Sasaki Y, Suzuki H, Yawata A, Kusano M, Fujita M, et al:
DNA methylation and histone deacetylation associated with silencing
DAP kinase gene expression in colorectal and gastric cancers. Br J
Cancer. 86:1817–1823. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Y, Henderson P, Pettersson S, Satsangi
J, Hupp T and Stevens C: Tuberous sclerosis-2 (TSC2) regulates the
stability of death-associated protein kinase-1 (DAPK) through a
lysosome-dependent degradation pathway. FEBS J. 278:354–370. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ivanovska J, Zlobec I, Forster S,
Karamitopoulou E, Dawson H, Koelzer VH, Agaimy A, Garreis F, Söder
S, Laqua W, et al: DAPK loss in colon cancer tumor buds:
implications for migration capacity of disseminating tumor cells.
Oncotarget. 6:36774–36788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin Y, Blue EK and Gallagher PJ: Control
of death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) activity by
phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation. J Biol Chem.
281:39033–39040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Nephew KP and Gallagher PJ:
Regulation of death-associated protein kinase. Stabilization by
HSP90 heterocomplexes. J Biol Chem. 282:11795–11804. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee YR, Yuan WC, Ho HC, Chen CH, Shih HM
and Chen RH: The Cullin 3 substrate adaptor KLHL20 mediates DAPK
ubiquitination to control interferon responses. EMBO J.
29:1748–1761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin Y, Stevens C and Hupp T:
Identification of a dominant negative functional domain on DAPK-1
that degrades DAPK-1 protein and stimulates TNFR-1-mediated
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:16792–16802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stevens C, Lin Y, Sanchez M, Amin E,
Copson E, White H, Durston V, Eccles DM and Hupp T: A germ line
mutation in the death domain of DAPK-1 inactivates ERK-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:13791–13803. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CH, Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Tsai HC, Lin JR,
Chang ZF and Chen RH: Bidirectional signals transduced by DAPK-ERK
interaction promote the apoptotic effect of DAPK. EMBO J.
24:294–304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuo JC, Wang WJ, Yao CC, Wu PP and Chen
RH: The tumor suppressor DAPK inhibits cell motility by blocking
the integrin-mediated polarity pathway. J cell Biol. 172:619–631.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|