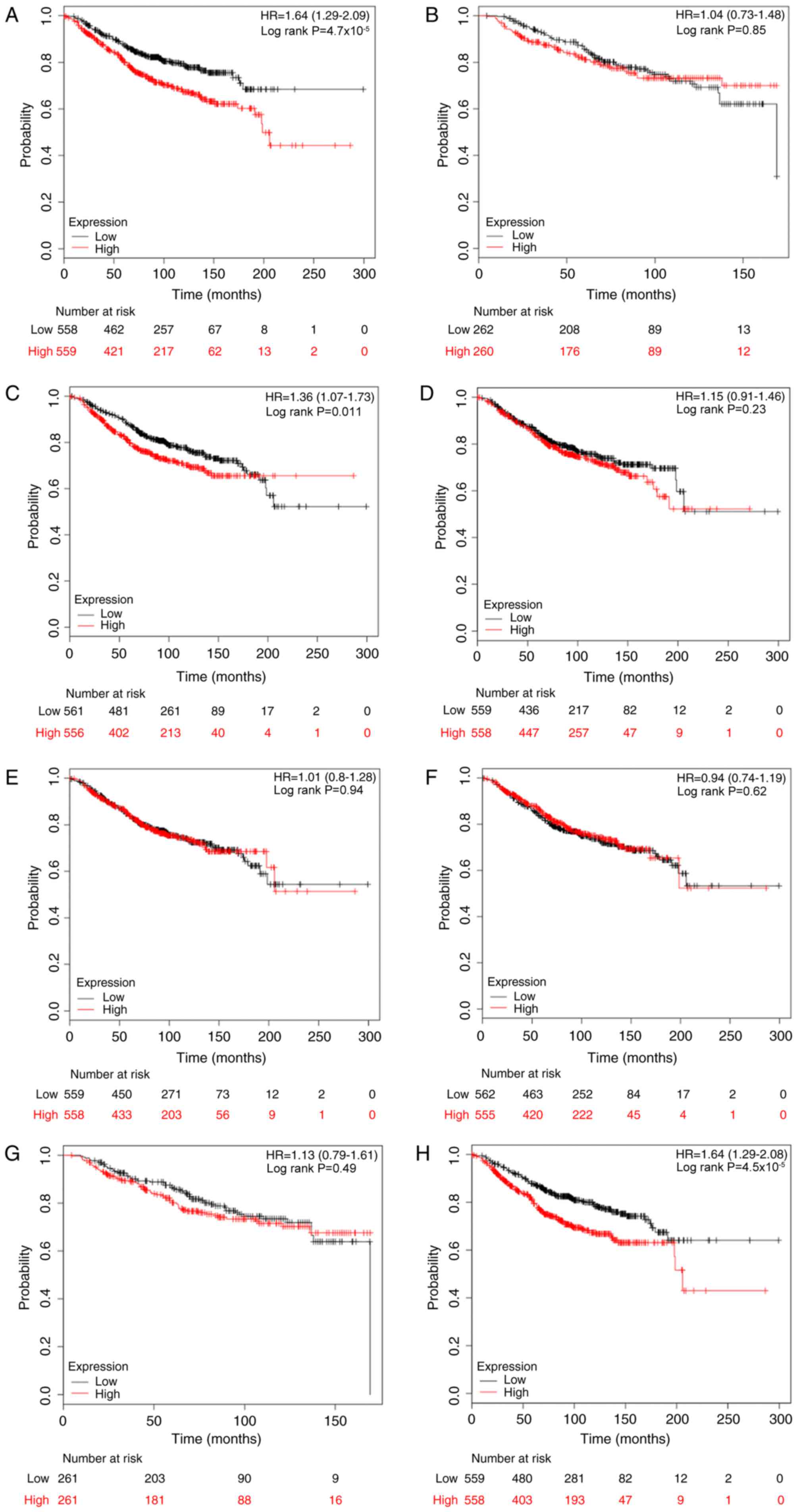
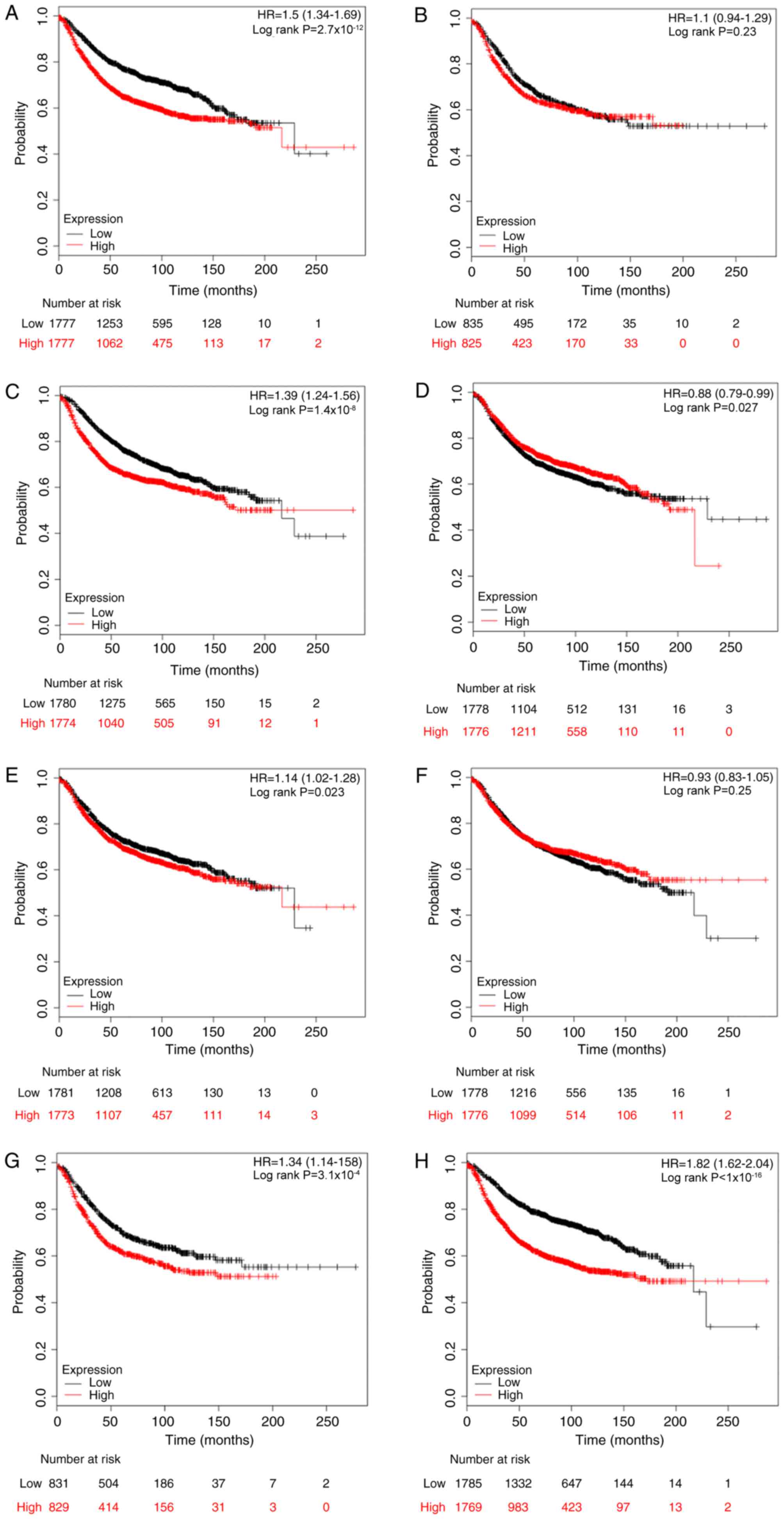
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chlebowski RT, Manson JE, Anderson GL,
Cauley JA, Aragaki AK, Stefanick ML, Lane DS, Johnson KC,
Wactawski-Wende J, Chen C, et al: Estrogen plus progestin and
breast cancer incidence and mortality in the Women's health
initiative observational study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 105:526–535.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Althuis MD, Dozier JM, Anderson WF, Devesa
SS and Brinton LA: Global trends in breast cancer incidence and
mortality 1973–1997. Int J Epidemiol. 34:405–412. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Assi HA, Khoury KE, Dbouk H, Khalil LE,
Mouhieddine TH and El Saghir NS: Epidemiology and prognosis of
breast cancer in young women. J Thorac Dis. 5 Suppl 1:S2–S8.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsantoulis PK and Gorgoulis VG:
Involvement of E2F transcription factor family in cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 41:2403–2414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Attwooll C, Lazzerini Denchi E and Helin
K: The E2F family: Specific functions and overlapping interests.
EMBO J. 23:4709–4716. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bell LA and Ryan KM: Life and death
decisions by E2F-1. Cell Death Differ. 11:137–142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stevens C and La Thangue NB: E2F and cell
cycle control: A double-edged sword. Arch Biochem Biophys.
412:157–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Z, Zheng S and Yu Q: The E2F family and
the role of E2F1 in apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:2389–2397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang H, Martin V, Gomez-Manzano C,
Johnson DG, Alonso M, White E, Xu J, McDonnell TJ, Shinojima N and
Fueyo J: The RB-E2F1 pathway regulates autophagy. Cancer Res.
70:7882–7893. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gorgoulis VG, Zacharatos P, Mariatos G,
Kotsinas A, Bouda M, Kletsas D, Asimacopoulos PJ, Agnantis N,
Kittas C and Papavassiliou AG: Transcription factor E2F-1 acts as a
growth-promoting factor and is associated with adverse prognosis in
non-small cell lung carcinomas. J Pathol. 198:142–156. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang CL, Liu D, Nakano J, Yokomise H,
Ueno M, Kadota K and Wada H: E2F1 overexpression correlates with
thymidylate synthase and survivin gene expressions and tumor
proliferation in non small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:6938–6946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu LX, Jiang HC, Liu ZH, Zhu AL, Zhang
WH, Wu LF, Zhou J, Wang XQ and Wu M: Expression of cell
cycle/growth regulator genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma and
adjacent normal liver tissues. Oncol Rep. 10:1771–1775.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng Q, Wang Q, Zong WY, Zheng DL, Wen YX,
Wang KS, Teng XM, Zhang X, Huang J and Han ZG: E2F8 contributes to
human hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating cell proliferation.
Cancer Res. 70:782–791. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Palaiologou M, Koskinas J, Karanikolas M,
Fatourou E and Tiniakos DG: E2F-1 is overexpressed and
pro-apoptotic in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Virchows Arch.
460:439–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Meyer T, Bijsmans IT, Van de Vijver KK,
Bekaert S, Oosting J, Van Criekinge W, van Engeland M and Sieben
NL: E2Fs mediate a fundamental cell-cycle deregulation in
high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas. J Pathol. 217:14–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reimer D, Sadr S, Wiedemair A, Goebel G,
Concin N, Hofstetter G, Marth C and Zeimet AG: Expression of the
E2F family of transcription factors and its clinical relevance in
ovarian cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1091:270–281. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu KH, Patterson AP, Wang L, Marquez RT,
Atkinson EN, Baggerly KA, Ramoth LR, Rosen DG, Liu J, Hellstrom I,
et al: Selection of potential markers for epithelial ovarian cancer
with gene expression arrays and recursive descent partition
analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3291–3300. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kim
YD and Kim HY: E2F1 expression is related with the poor survival of
lymph node-positive breast cancer patients treated with
fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 82:11–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rakha EA, Pinder SE, Paish EC, Robertson
JF and Ellis IO: Expression of E2F-4 in invasive breast carcinomas
is associated with poor prognosis. J Pathol. 203:754–761. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujiwara K, Yuwanita I, Hollern DP and
Andrechek ER: Prediction and genetic demonstration of a role for
activator E2Fs in Myc-induced tumors. Cancer Res. 71:1924–1932.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szász AM, Lánczky A, Nagy A, Förster S,
Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A and Győrffy B:
Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric
cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget.
7:49322–49333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gluck S, Ross JS, Royce M, McKenna EF Jr,
Perou CM, Avisar E and Wu L: TP53 genomics predict higher clinical
and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer
treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 132:781–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao H, Langerød A, Ji Y, Nowels KW,
Nesland JM, Tibshirani R, Bukholm IK, Kåresen R, Botstein D,
Børresen-Dale AL and Jeffrey SS: Different gene expression patterns
in invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas of the breast. Mol Biol
Cell. 15:2523–2536. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, Lu X,
Brown M, Miron A, Liao X, Iglehart JD, Livingston DM and Ganesan S:
X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer.
Cancer Cell. 9:121–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Radvanyi L, Singh-Sandhu D, Gallichan S,
Lovitt C, Pedyczak A, Mallo G, Gish K, Kwok K, Hanna W, Zubovits J,
et al: The gene associated with trichorhinophalangeal syndrome in
humans is overexpressed in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:11005–11010. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang
MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO and Gelmon K: Metastatic
behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 28:3271–3277.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki T, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Naka K,
Ishikawa T and Tahara E: Expression of the E2F family in human
gastrointestinal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 81:535–538. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu L, Timmers C, Maiti B, Saavedra HI,
Sang L, Chong GT, Nuckolls F, Giangrande P, Wright FA, Field SJ, et
al: The E2F1-3 transcription factors are essential for cellular
proliferation. Nature. 414:457–462. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Muller H, Moroni MC, Vigo E, Petersen BO,
Bartek J and Helin K: Induction of S-phase entry by E2F
transcription factors depends on their nuclear localization. Mol
Cell Biol. 17:5508–5520. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Worku D, Jouhra F, Jiang GW, Patani N,
Newbold RF and Mokbel K: Evidence of a tumour suppressive function
of E2F1 gene in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 28:2135–2139.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ho GH, Calvano JE, Bisogna M and Van Zee
KJ: Expression of E2F-1 and E2F-4 is reduced in primary and
metastatic breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 69:115–122.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vuaroqueaux V, Urban P, Labuhn M,
Delorenzi M, Wirapati P, Benz CC, Flury R, Dieterich H, Spyratos F,
Eppenberger U and Eppenberger-Castori S: Low E2F1 transcript levels
are a strong determinant of favorable breast cancer outcome. Breast
Cancer Res. 9:R332007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Johnson DG and Degregori J: Putting the
oncogenic and tumor suppressive activities of E2F into context.
Curr Mol Med. 6:731–738. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Leone G, Sears R, Huang E, Rempel R,
Nuckolls F, Park CH, Giangrande P, Wu L, Saavedra HI, Field SJ, et
al: Myc requires distinct E2F activities to induce S phase and
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 8:105–113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nguyen-Vu T, Vedin LL, Liu K, Jonsson P,
Lin JZ, Candelaria NR, Candelaria LP, Addanki S, Williams C,
Gustafsson JÅ, et al: Liver × receptor ligands disrupt breast
cancer cell proliferation through an E2F-mediated mechanism. Breast
Cancer Res. 15:R512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pusapati RV, Weaks RL, Rounbehler RJ,
McArthur MJ and Johnson DG: E2F2 suppresses Myc-induced
proliferation and tumorigenesis. Mol Carcinog. 49:152–156.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chong JL, Tsai SY, Sharma N, Opavsky R,
Price R, Wu L, Fernandez SA and Leone G: E2f3a and E2f3b contribute
to the control of cell proliferation and mouse development. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:414–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vimala K, Sundarraj S, Sujitha MV and
Kannan S: Curtailing overexpression of E2F3 in breast cancer using
siRNA (E2F3)-based gene silencing. Arch Med Res. 43:415–422. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dirks PB, Rutka JT, Hubbard SL, Mondal S
and Hamel PA: The E2F-family proteins induce distinct cell cycle
regulatory factors in p16-arrested, U343 astrocytoma cells.
Oncogene. 17:867–876. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Polanowska J, Le Cam L, Orsetti B, Vallés
H, Fabbrizio E, Fajas L, Taviaux S, Theillet C and Sardet C: Human
E2F5 gene is oncogenic in primary rodent cells and is amplified in
human breast tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 28:126–130. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dyson N: The regulation of E2F by
pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12:2245–2262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tian H, Hou L, Xiong YM, Huang JX, Zhang
WH, Pan YY and Song XR: miR-132 targeting E2F5 suppresses cell
proliferation, invasion, migration in ovarian cancer cells. Am J
Transl Res. 8:1492–1501. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Umemura S, Shirane M, Takekoshi S,
Kusakabe T, Itoh J, Egashira N, Tokuda Y, Mori K and Osamura YR:
Overexpression of E2F-5 correlates with a pathological basal
phenotype and a worse clinical outcome. Br J Cancer. 100:764–771.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Trimarchi JM, Fairchild B, Wen J and Lees
JA: The E2F6 transcription factor is a component of the mammalian
Bmi1-containing polycomb complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:1519–1524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lammens T, Li J, Leone G and De Veylder L:
Atypical E2Fs: New players in the E2F transcription factor family.
Trends Cell Biol. 19:111–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Moon NS and Dyson N: E2F7 and E2F8 keep
the E2F family in balance. Dev Cell. 14:1–3. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tang H, Liu P, Yang L and Xie X, Ye F, Wu
M, Liu X, Chen B, Zhang L and Xie X: miR-185 suppresses tumor
proliferation by directly targeting E2F6 and DNMT1 and indirectly
upregulating BRCA1 in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer
Ther. 13:3185–3197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chu J, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Lv X, Wu Y, Hu
P, Su F, Gong C, Song E, et al: E2F7 overexpression leads to
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells by competing with E2F1
at miR-15a/16 promoter. Oncotarget. 6:31944–31957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ye L, Guo L, He Z, Wang X, Lin C, Zhang X,
Wu S, Bao Y, Yang Q, Song L and Lin H: Upregulation of E2F8
promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in breast cancer by
modulating G1/S phase transition. Oncotarget. 7:23757–23771. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|