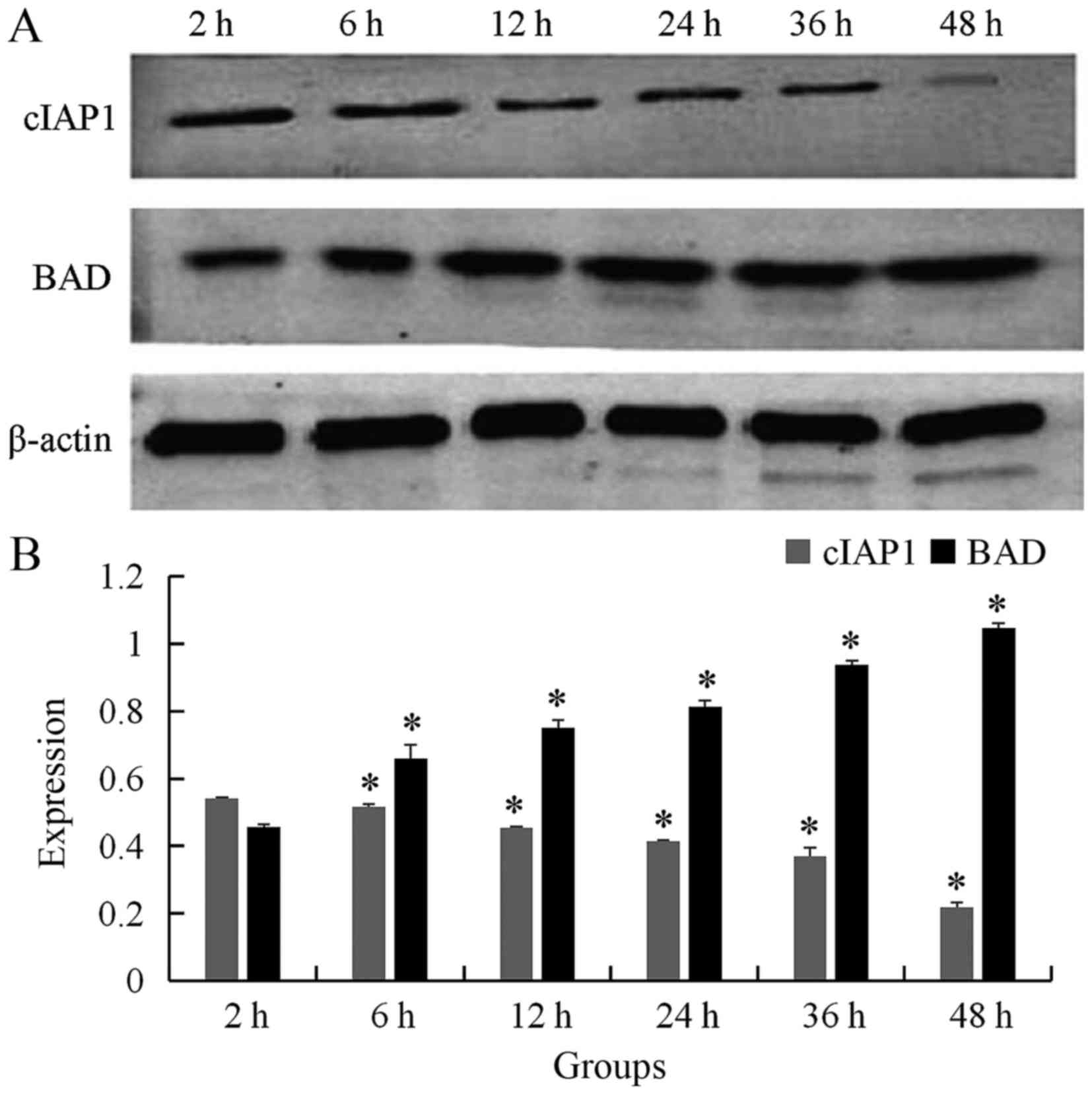
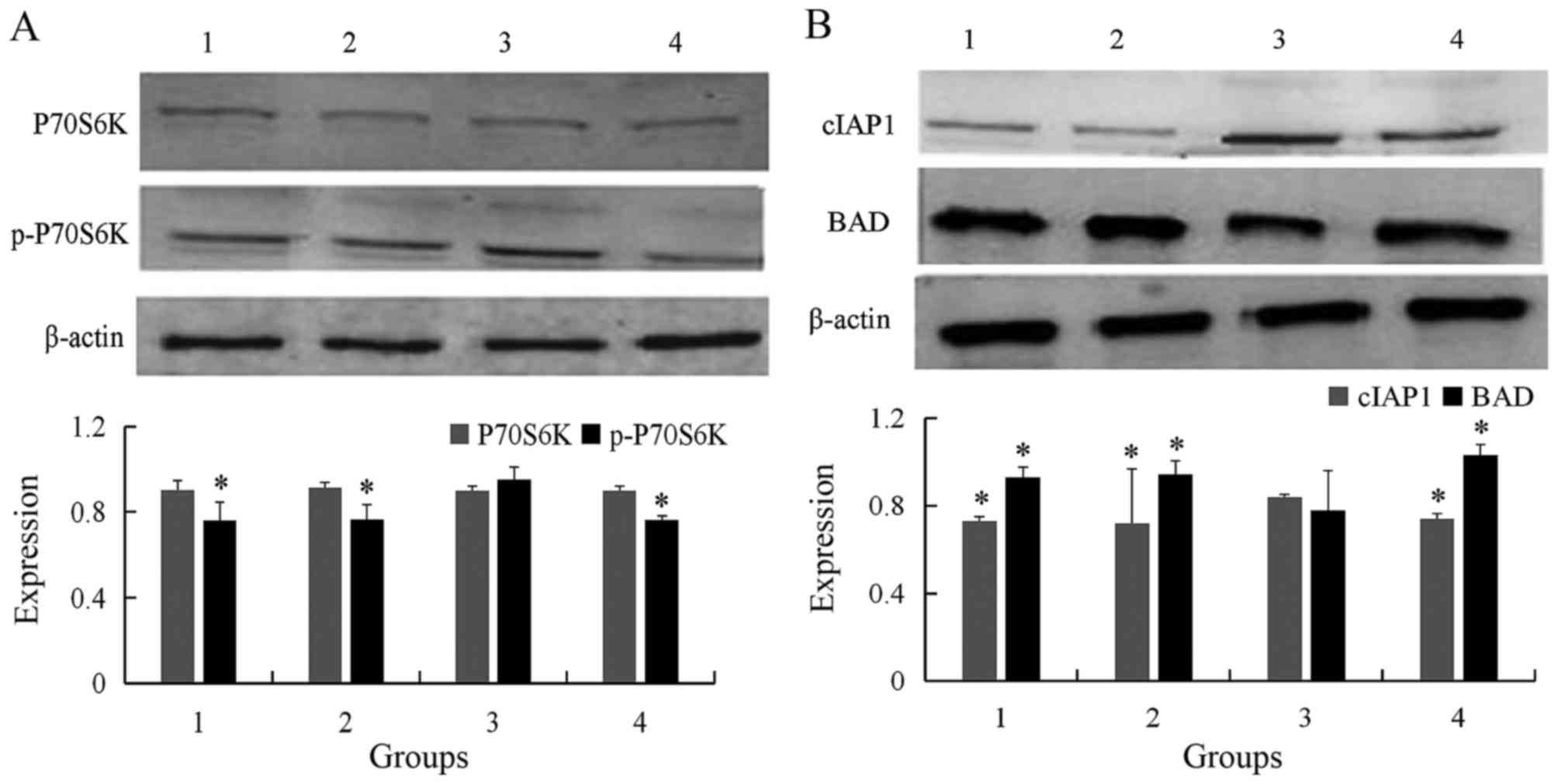
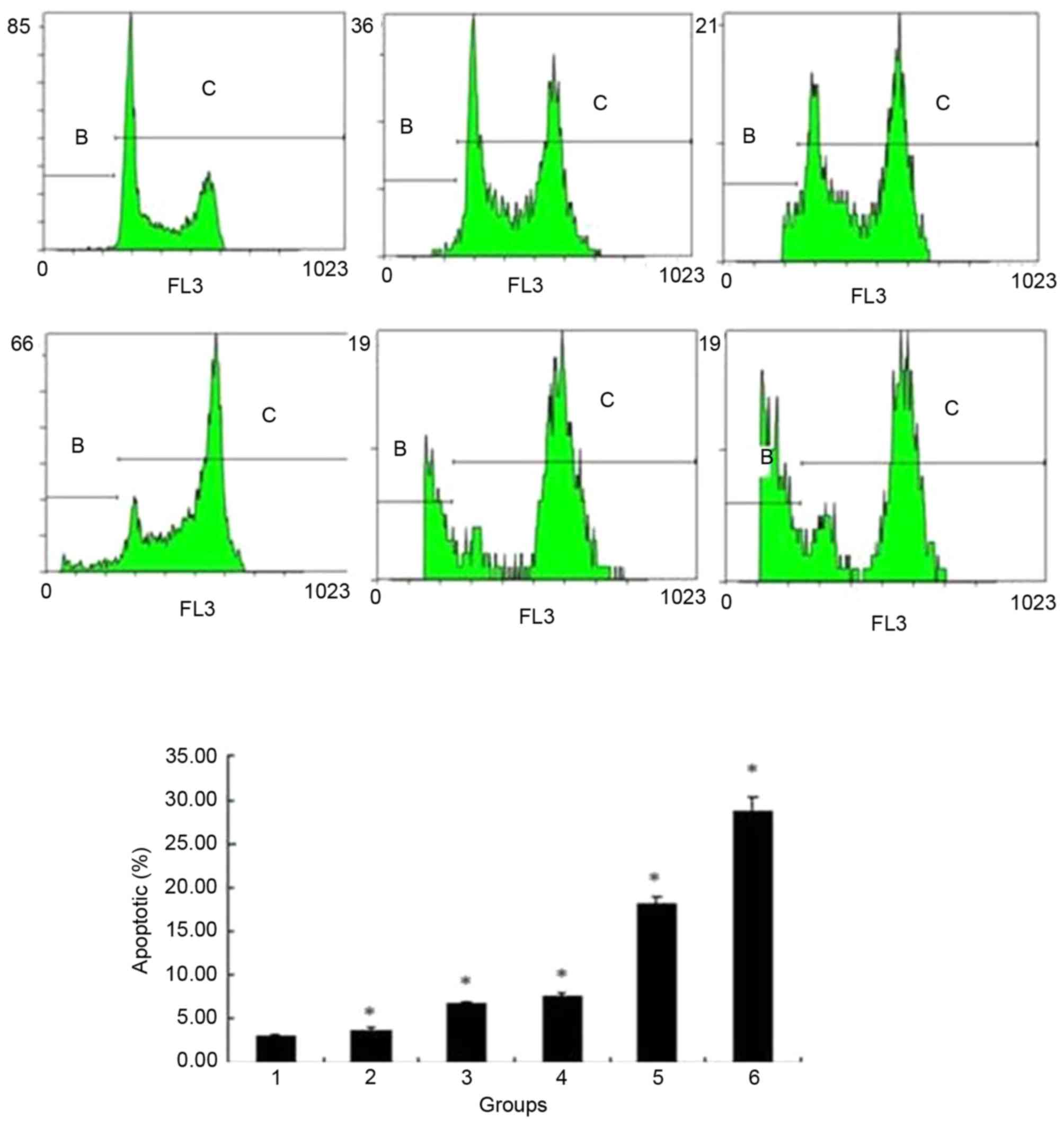
|
1
|
Cai EH, Gao YX, Wei ZZ, Chen WY, Yu P and
Li K: Serum miR-21 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 3:1563–1567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mao WM, Zheng WH and Ling ZQ:
Epidemiologic risk factors for esophageal cancer development. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2461–2466. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Enziger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li B, Li J, Xu WW, Guan XY, Qin YR, Zhang
LY, Law S, Tsao SW and Cheung AL: Suppression of esophageal tumor
growth and chemoresistance by directly targeting the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Oncotarget. 5:11576–11587. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watabe M, Kawazoe N, Masuda Y, Nakajo S
and Nakaya K: Bcl-2 protein inhibits bufalin-induced apoptosis
through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation
in human leukemia U937 cells. Cancer Res. 57:3097–3100.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yeh JY, Huang WJ, Kan SF and Wang PS:
Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen
dependent and independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
54:112–124. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Z, Li E and Liu Y, Gao Y, Sun H, Wang
Y, Wang Z, Liu X, Wang Q and Liu Y: Bufalin induces the apoptosis
of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells via the downregulation of
survivin expression. Acta Heamatol. 128:144–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhu Z, Sun H, Ma G, Wang Z, Li E and Liu Y
and Liu Y: Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the
inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:2025–2035. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng
Y, Zhang J and Liu Y: PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin-induced
apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 20:59–64.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hong SH and Choi YH: Bufalin induces
apoptosis through activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic
pathways in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:114–120.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen YN, Deng HY and Zhang P: Bufalin
Inhibits the Proliferation of human esophageal carcinoma TE13 cells
through down-regulation of ERK. Asian J Pharm Nurs Med Sci.
2:90–98. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Ponnurangam S, Standing D, Rangarajan P
and Subramaniam D: Tandutinib inhibits the Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway to inhibit colon cancer growth. Mol Cancer Ther.
12:598–609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meng Q, Xia C, Fang J, Rojanasakul Y and
Jiang BH: Role of PI3K and AKT specific isoforms in ovarian cancer
cell migration, invasion and proliferation through the p70S6K1
pathway. Cell Signal. 18:2262–2271. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ji J and Zheng PS: Activation of mTOR
signaling pathway contributes to survival of cervical cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 117:103–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Wang X, Jia Y and Liu Y: Effects of
bufalin on the mTOR/p70S6K pathway and apoptosis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma in nude mice. Int J Mol Med. 40:357–366.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 14:5598–5606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Engels K, Knauer S K, Metzler D, Simf C,
Struschka O, Bier C, Mann W, Kovács AF and Stauber RH: Dynamic
intracellular survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Underlying
molecular mechanism and potential as an early prognostic marker. J
Pathol. 211:532–540. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li W, Wang J, Jiang HR, Xu XL, Zhang J,
Liu ML and Zhai LY: Combined effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and
cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on ovarian carcinoma in vivo.
Int J Mol Sci. 12:668–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Khoo BY, Chua SL and Balaram P: Apoptotic
effects of chrysin in human cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci.
11:2188–2199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen A, Yu J, Zhang L, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Guo
H, Zhou Y, Mitchelson K and Cheng J: Microarray and biochemical
analysis of bufalin-induced apoptosis of HL-60 cells. Biotechnol
Lett. 31:487–494. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takai N, Ueda T, Nishida M, Nasu K and
Narahara H: Bufalin induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Mol Med. 21:637–643. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, Zhao J and Cheng
CH: Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon
cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK
activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1365–1375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ding L, Huang Y, Dai M, Zhao X, Du Q, Dong
F, Wang L, Huo R, Zhang W, Xu X and Tong D: Transmissible
gastroenteritis virus infection induces cell cycle arrest at S and
G2/M phases via p53-dependent pathway. 178:241–251. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Jing Y, Watabe M, Hashimoto S, Nakajo S
and Nakaya K: Cell cycle arrest and protein kinase modulating
effect of bufalin on human leukemia ML1 cells. Anticancer Res.
14:1193–11198. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nasu K, Nishida M, Ueda T, Takai N, Bing
S, Narahara H and Miyakawa I: Bufalin induces apoptosis and the
G0/G1 cell cycle arrest of endometriotic stromal cells: A promising
agent for the treatment of endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod.
11:817–823. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Koeffler HP
and Yokoyama A: Blockade of mTOR Signaling potentiates the ability
of histone deacetylase inhibitor to induce growth arre stand
differentiation of acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia.
22:2159–2168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin HJ, Hsieh FC, Song H and Lin J:
Elevated phosphorylation and activation of PDK-1/AKT pathway in
human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 93:1372–1381. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsurutani J, West KA, Sayyah J, Gills JJ
and Dennis PA: Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway but not the
WTMTOR/p70S6K pathway attenuates laminin-mediated small cell lung
cancer cellular survival and resistance to imatinib mesylate or
chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 65:8423–8432. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fenton TR, Gwalter J, Cramer R and Gout
IT: S6K1 is acetylated at lysine 516 in response to growth factor
stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:400–405. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Darb-Esfahani S, Faggad A, Noske A,
Weichert W, Buckendahl AC, Müller B, Budczies J, Röske A, Dietel M
and Denkert C: Phospho-mTOR and phospho-4EBP1 in endometrial
adenocarcinoma: association with stage and grade in vivo and link
with response to rapamycin treatment in vitro. Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 135:933–941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sutherland S: Several therapies may
prevent or reduce the severity of oral mueositis associated with
cancer treatment. Evid Based Dent. 7:104–105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|