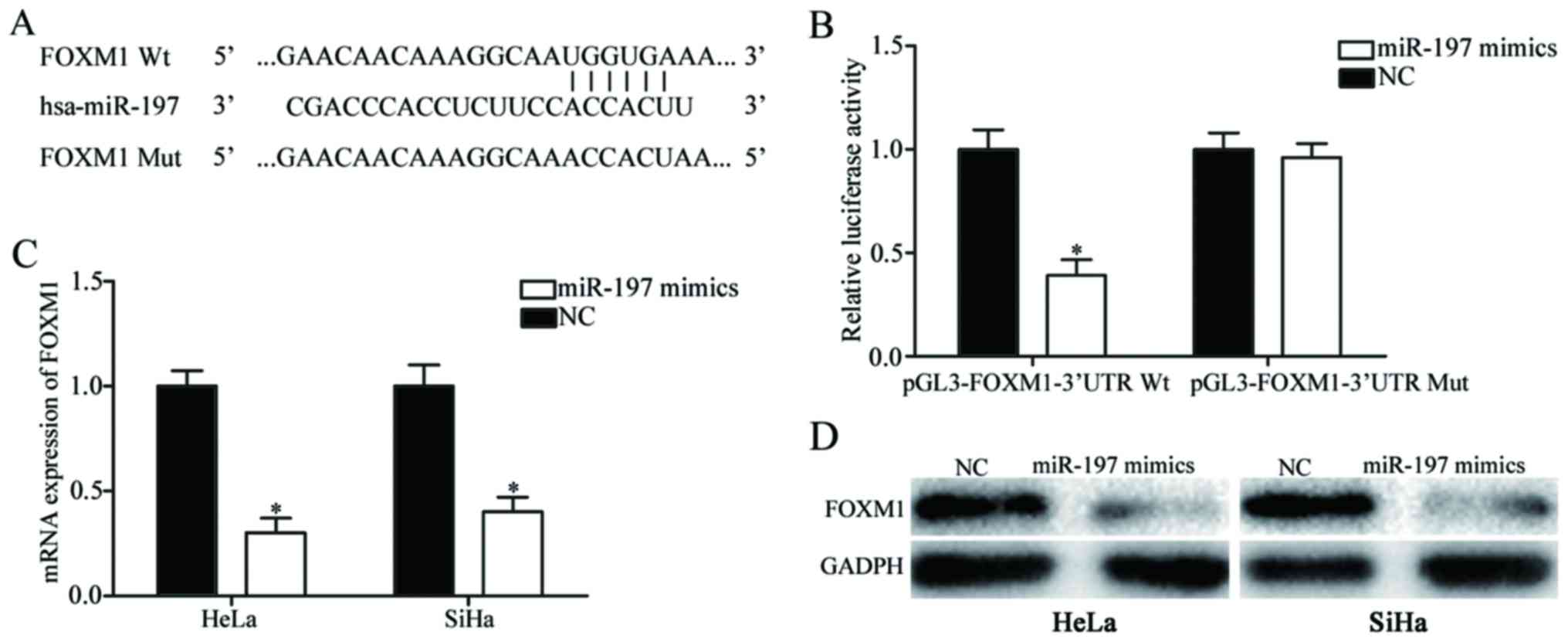
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paradkar PH, Joshi JV, Mertia PN, Agashe
SV and Vaidya RA: Role of cytokines in genesis, progression and
prognosis of cervical cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3851–3864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bosch FX and de Sanjosé S: Chapter 1:
Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer-burden and assessment of
causality. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 3–13. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu Y, Zhang Y and Zhang S: MicroRNA-92
regulates cervical tumorigenesis and its expression is upregulated
by human papillomavirus-16 E6 in cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
6:468–474. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morice P and Castaigne D: Advances in the
surgical management of invasive cervical cancer. Curr Opin Obstet
Gynecol. 17:5–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mayr NA, Huang Z, Wang JZ, Lo SS, Fan JM,
Grecula JC, Sammet S, Sammet CL, Jia G, Zhang J, et al:
Characterizing tumor heterogeneity with functional imaging and
quantifying high-risk tumor volume for early prediction of
treatment outcome: Cervical cancer as a model. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 83:972–979. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carthew RW: Gene regulation by microRNAs.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 16:203–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pereira PM, Marques JP, Soares AR, Carreto
L and Santos MA: MicroRNA expression variability in human cervical
tissues. PLoS One. 5:e117802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun YC, Wang J, Guo CC, Sai K, Wang J,
Chen FR, Yang QY, Chen YS, Wang J, To TS, et al: MiR-181b
sensitizes glioma cells to teniposide by targeting MDM2. BMC
Cancer. 14:6112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang T, Thakur A, Chen T, Yang L, Lei G,
Liang Y, Zhang S, Ren H and Chen M: MicroRNA-15a induces cell
apoptosis and inhibits metastasis by targeting BCL2L2 in non-small
cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:4357–4365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to
mammalian P-bodies. Nat Cell Biol. 7:719–723. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian LQ, Liu EQ, Zhu XD, Wang XG, Li J and
Xu GM: MicroRNA-197 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting GAB2
in glioblastoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:4279–4288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ling J, Jiang L, Zhang C, Dai J, Wu Q and
Tan J: Upregulation of miR-197 inhibits cell proliferation by
directly targeting IGFBP5 in human uterine leiomyoma cells. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 51:835–842. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Y, Li F, Saha MN, Abdi J, Qiu L and
Chang H: miR-137 and miR-197 induce apoptosis and suppress
tumorigenicity by targeting MCL-1 in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:2399–2411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang TY, Liu SG, Zhao BS, Qi B, Qin XG and
Yao WJ: Implications of microRNA-197 downregulated expression in
esophageal cancer with poor prognosis. Genet Mol Res. 13:5574–5581.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mavridis K, Gueugnon F, Petit-Courty A,
Courty Y, Barascu A, Guyetant S and Scorilas A: The oncomiR miR-197
is a novel prognostic indicator for non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 112:1527–1535. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zou D, Wang D, Li R, Tang Y, Yuan L, Long
X and Zhou Q: MiR-197 induces Taxol resistance in human ovarian
cancer cells by regulating NLK. Tumour Biol. 36:6725–6732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai W, Wang C, Wang F, Wang Y, Shen M,
Chen K, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhu R, et al: Anti-miR-197
inhibits migration in HCC cells by targeting KAI 1/CD82. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 446:541–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu X, Ling J, Fu Z, Ji C, Wu J and Xu Q:
Effects of miRNA-197 overexpression on proliferation, apoptosis and
migration in levonorgestrel treated uterine leiomyoma cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 71:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kaestner KH, Knochel W and Martinez DE:
Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription
factors. Genes Dev. 14:142–146. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koo CY, Muir KW and Lam EW: FOXM1: From
cancer initiation to progression and treatment. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1819:28–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He SY, Shen HW, Xu L, Zhao XH, Yuan L, Niu
G, You ZS and Yao SZ: FOXM1 promotes tumor cell invasion and
correlates with poor prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 127:601–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hou Y, Li W, Sheng Y, Li L, Huang Y, Zhang
Z, Zhu T, Peace D, Quigley JG, Wu W, et al: The transcription
factor Foxm1 is essential for the quiescence and maintenance of
hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Immunol. 16:810–818. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|