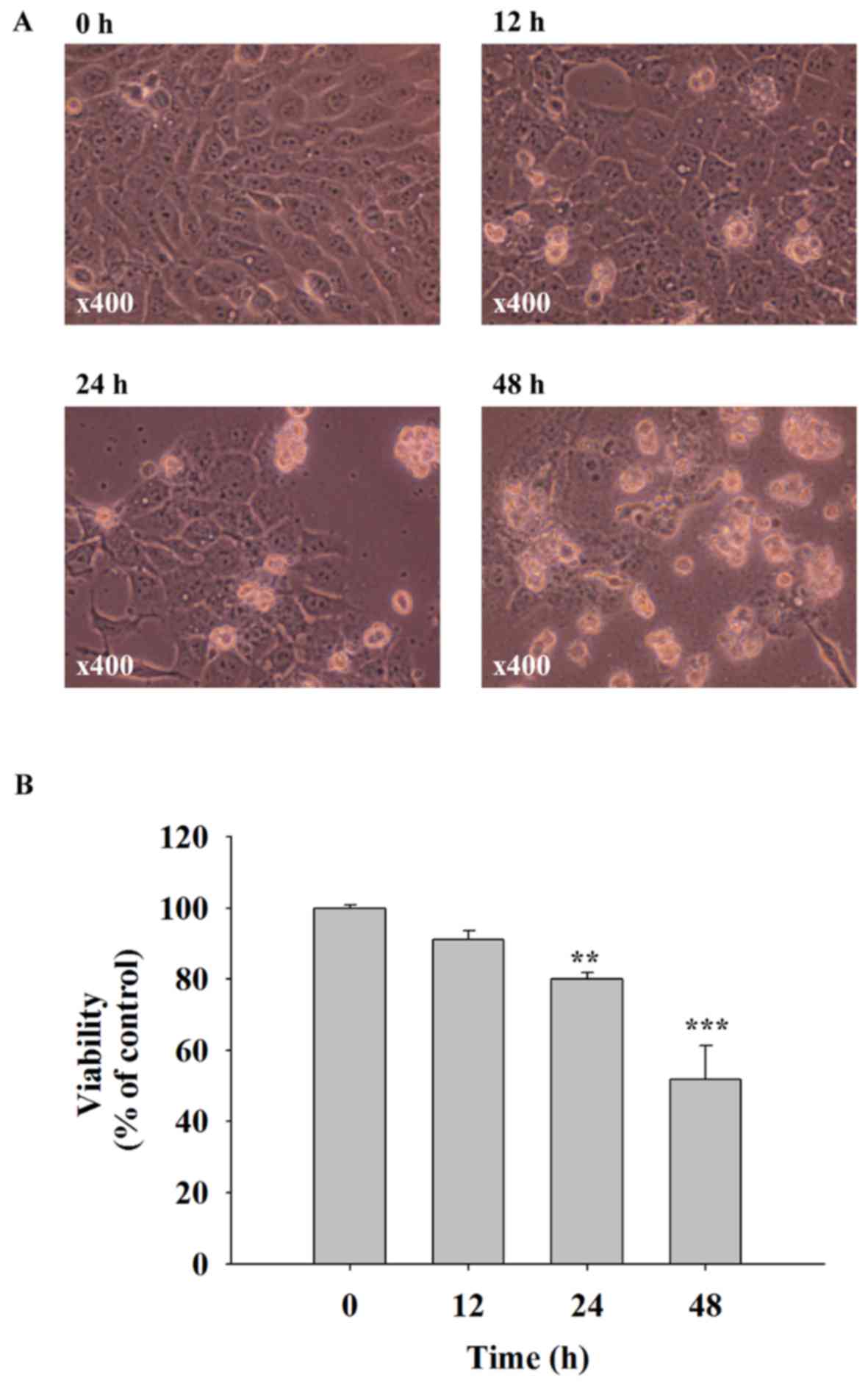
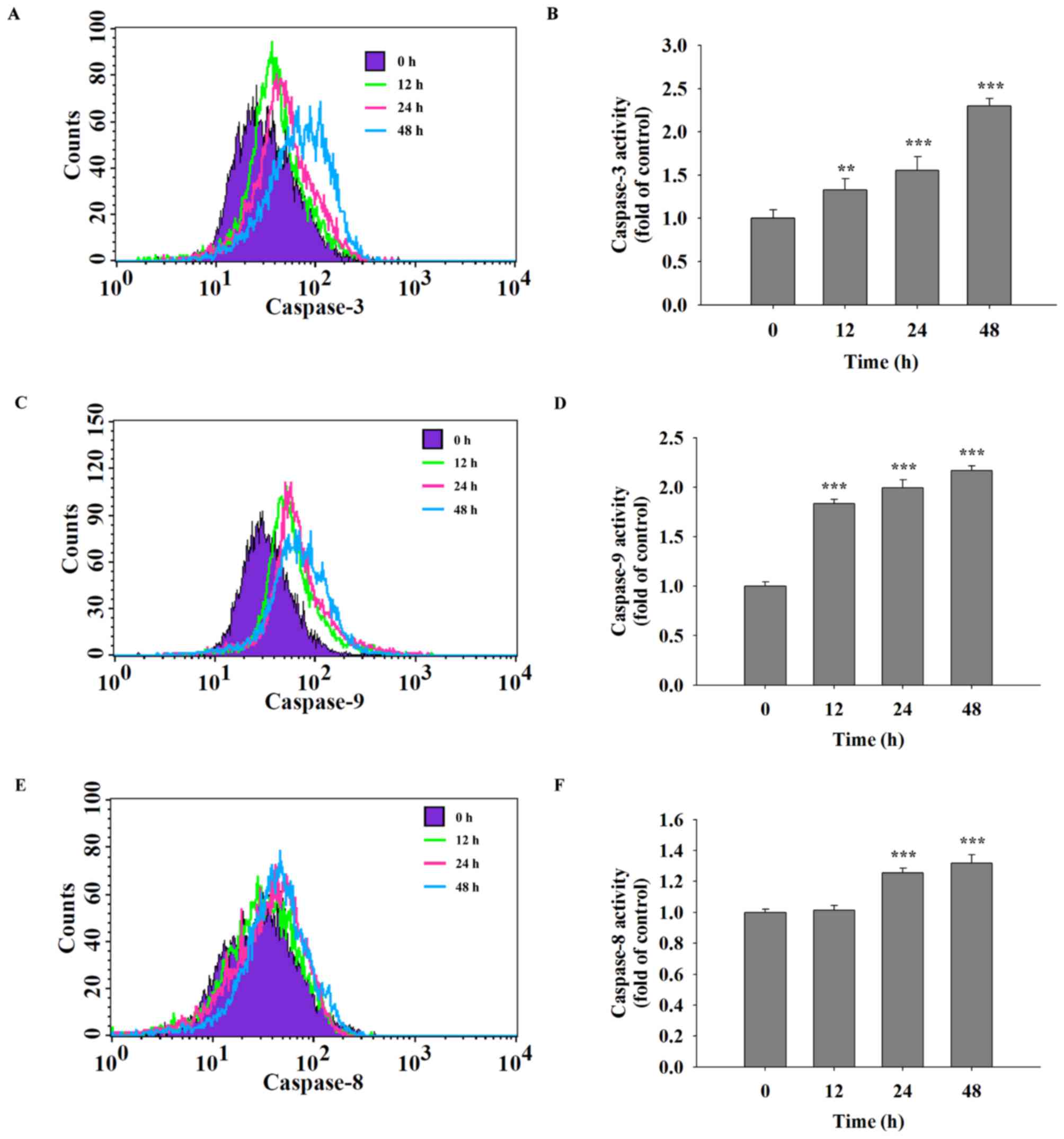
|
1
|
Maleki D, Ghojazadeh M, Mahmoudi SS,
Mahmoudi SM, Pournaghi-Azar F, Torab A, Piri R, Azami-Aghdash S and
Naghavi-Behzad M: Epidemiology of oral cancer in Iran: A systematic
review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:5427–5432. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krishna A, Singh S, Kumar V and Pal US:
Molecular concept in human oral cancer. Natl J Maxillofac Surg.
6:9–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Halboub ES, Al-Anazi YM and Al-Mohaya MA:
Characterization of Yemeni patients treated for oral and pharyngeal
cancers in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 32:1177–1182. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chung TT, Pan MS, Kuo CL, Wong RH, Lin CW,
Chen MK and Yang SF: Impact of RECK gene polymorphisms and
environmental factors on oral cancer susceptibility and
clinicopathologic characteristics in Taiwan. Carcinogenesis.
32:1063–1068. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galbiatti AL, Padovani-Junior JA, Maníglia
JV, Rodrigues CD, Pavarino ÉC and Goloni-Bertollo EM: Head and neck
cancer: Causes, prevention and treatment. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol.
79:239–247. 2013.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Langford R, Bonell CP, Jones HE, Pouliou
T, Murphy SM, Waters E, Komro KA, Gibbs LF, Magnus D and Campbell
R: The WHO Health Promoting School framework for improving the
health and well-being of students and their academic achievement.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD008958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Braun OM, Neumeister B, Neuhold N,
Siebenhandl A, Wimmer M, Holzner JH, Popp W, Strassl H, Dobrowsky W
and Gritzmann N: Histological grading of therapy induced regression
in squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity: A morphological and
immunohistochemical study. Pathol Res Pract. 185:368–372. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D and
Ferris RL: Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 371:1695–1709. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagao T, Chaturvedi P, Shaha A and
Sankaranarayanan R: Prevention and early detection of head and neck
squamous cell cancers. J Oncol. 2011:3181452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Denaro N, Russi EG, Lefebvre JL and
Merlano MC: A systematic review of current and emerging approaches
in the field of larynx preservation. Radiother Oncol. 110:16–24.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El Deen DA, Toson EA and El Morsy SM:
Gemcitabine-based induction chemotherapy and concurrent with
radiation in advanced head and neck cancer. Med Oncol.
29:3367–3373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan
MB and Kromhout D: Dietary flavonoids and cancer risk in the
Zutphen Elderly Study. Nutr Cancer. 22:175–184. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weisburger JH: Mechanisms of action of
antioxidants as exemplified in vegetables, tomatoes and tea. Food
Chem Toxicol. 37:943–948. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baowen Q, Yulin Z, Xin W, Wenjing X, Hao
Z, Zhizhi C, Xingmei D, Xia Z, Yuquan W and Lijuan C: A further
investigation concerning correlation between anti-fibrotic effect
of liposomal quercetin and inflammatory cytokines in pulmonary
fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 642:134–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boots AW, Haenen GR and Bast A: Health
effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur J
Pharmacol. 585:325–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Staedler D, Idrizi E, Kenzaoui BH and
Juillerat-Jeanneret L: Drug combinations with quercetin:
Doxorubicin plus quercetin in human breast cancer cells. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 68:1161–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cincin ZB, Unlu M, Kiran B, Bireller ES,
Baran Y and Cakmakoglu B: Molecular mechanisms of
quercitrin-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Arch
Med Res. 45:445–454. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bhat FA, Sharmila G, Balakrishnan S,
Arunkumar R, Elumalai P, Suganya S, Singh Raja P, Srinivasan N and
Arunakaran J: Quercetin reverses EGF-induced epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and invasiveness in prostate cancer (PC-3)
cell line via EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 25:1132–1139.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu JL, Du J, Fan LL, Liu XY, Gu L and Ge
YB: Effects of quercetin on hyper-proliferation of gastric mucosal
cells in rats treated with chronic oral ethanol through the
reactive oxygen species-nitric oxide pathway. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:3242–3248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee DH and Lee YJ: Quercetin suppresses
hypoxia-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha) through inhibiting protein synthesis. J Cell Biochem.
105:546–553. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tanigawa S, Fujii M and Hou DX:
Stabilization of p53 is involved in quercetin-induced cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
72:797–804. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Priyadarsini Vidya R, Murugan Senthil R,
Maitreyi S, Ramalingam K, Karunagaran D and Nagini S: The flavonoid
quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53
induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:84–91. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Haghiac M and Walle T: Quercetin induces
necrosis and apoptosis in SCC-9 oral cancer cells. Nutr Cancer.
53:220–231. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang JW, Kim JH, Song K, Kim SH, Yoon JH
and Kim KS: Kaempferol and quercetin, components of Ginkgo biloba
extract (EGb 761), induce caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in oral
cavity cancer cells. Phytother Res. 24 Suppl 1:S77–S82. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang CY, Chan CY, Chou IT, Lien CH, Hung
HC and Lee MF: Quercetin induces growth arrest through activation
of FOXO1 transcription factor in EGFR-overexpressing oral cancer
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 24:1596–1603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu KW, Chen JC, Lai TY, Yang JS, Weng SW,
Ma YS, Lin HY, Wu RS, Wu KC, Wood WG and Chung JG: Gypenosides
suppress growth of human oral cancer SAS cells in vitro and in a
murine xenograft model: The role of apoptosis mediated by
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways. Integr Cancer
Ther. 11:129–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang YM, Velmurugan BK, Kuo WW, Chen YS,
Ho TJ, Tsai CT, Ye CX, Tsai CH, Tsai FJ and Huang CY: Inhibitory
effect of alpinate Oxyphyllae fructus extracts on Ang II-induced
cardiac pathological remodeling-related pathways in H9c2
cardiomyoblast cells. BioMed. 3:148–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chiu CH, Chou YC, Lin JP, Kuo CL, Lu HF,
Huang YP, Yu CC, Lin ML and Chung JG: Chloroform extract of solanum
lyratum induced G0/G1 arrest via p21/p16 and induced apoptosis via
reactive oxygen species, caspases and mitochondrial pathways in
human oral cancer cell lines. Am J Chin Med. 43:1453–1469. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsieh WT, Lin HY, Chen JH, Kuo YH, Fan MJ,
Wu RS, Wu KC, Wood WG and Chung JG: Latex of Euphorbia antiquorum
induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells via c-jun
n-terminal kinase activation and reactive oxygen species
production. Nutr Cancer. 63:1339–1347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang SH, Wu LW, Huang AC, Yu CC, Lien JC,
Huang YP, Yang JS, Yang JH, Hsiao YP, Wood WG, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in
human melanoma A375.S2 cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS)
and both mitochondria-dependent and death receptor-mediated
multiple signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 60:665–675. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leung YM, Wong KL, Chen SW, Lu DY, Kuo CS,
Chen YR, Chen YW and Cheng TH: Down-regulation of voltage-gated
Ca2+ channels in Ca2+ store-depleted rat
insulinoma RINm5F cells. BioMed. 3:130–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fesik SW: Promoting apoptosis as a
strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:876–885.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kerr JF, Winterford CM and Harmon BV:
Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer.
73:2013–2026. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwai-Kanai E, Hasegawa K, Araki M, Kakita
T, Morimoto T and Sasayama S: alpha- and beta-adrenergic pathways
differentially regulate cell type-specific apoptosis in rat cardiac
myocytes. Circulation. 100:305–311. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li L, Zhu Z, Joshi B, Porter AT and Tang
DG: A novel hydroxamic acid compound, BMD188, demonstrates
anti-prostate cancer effects by inducing apoptosis. I: In vitro
studies. Anticancer Res. 19:51–60. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li H, Hui L, Xu W, Shen H, Chen Q, Long L
and Zhu X: Modulation of P-glycoprotein expression by triptolide in
adriamycin-resistant K562/A02 cells. Oncol Lett. 3:485–489. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sendrowski K, Rusak M, Sobaniec P, Iłendo
E, Dąbrowska M, Boćkowski L, Koput A and Sobaniec W: Study of the
protective effect of calcium channel blockers against neuronal
damage induced by glutamate in cultured hippocampal neurons.
Pharmacol Rep. 65:730–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Looi CY, Arya A, Cheah FK, Muharram B,
Leong KH, Mohamad K, Wong WF, Rai N and Mustafa MR: Induction of
apoptosis in human breast cancer cells via caspase pathway by
vernodalin isolated from Centratherum anthelminticum (L.) seeds.
PLoS One. 8:e566432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, He QY, Sun RW, Che CM and Chiu JF:
GoldIII porphyrin 1a induced apoptosis by mitochondrial death
pathways related to reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res.
65:11553–11564. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang J, Li TZ, Xu GH, Luo BB, Chen YX and
Zhang T: Low-concentration capsaicin promotes colorectal cancer
metastasis by triggering ROS production and modulating Akt/mTOR and
STAT-3 pathways. Neoplasma. 60:364–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takenokuchi M, Miyamoto K, Saigo K and
Taniguchi T: Bortezomib causes ER stress-related death of acute
promyelocytic leukemia cells through excessive accumulation of
PML-RARA. Anticancer Res. 35:3307–3316. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Harashima N, Minami T, Uemura H and Harada
M: Transfection of poly(I:C) can induce reactive oxygen
species-triggered apoptosis and interferon-β-mediated growth arrest
in human renal cell carcinoma cells via innate adjuvant receptors
and the 2–5A system. Mol Cancer. 13:2172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hsu YC, Chiang JH, Yu CS, Hsia TC, Wu RS,
Lien JC, Lai KC, Yu FS and Chung JG: Antitumor effects of deguelin
on H460 human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo: Roles of
apoptotic cell death and H460 tumor xenografts model. Environ
Toxicol. 32:84–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Senft D, Weber A, Saathoff F, Berking C,
Heppt MV, Kammerbauer C, Rothenfusser S, Kellner S, Kurgyis Z,
Besch R and Häcker G: In non-transformed cells Bak activates upon
loss of anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL and Mcl-1 but in the absence of
active BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Dis. 6:e19962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ahsan H, Reagan-Shaw S, Breur J and Ahmad
N: Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma
AsPC-1 and BxPC-3 cells via modulations in Bcl-2 family proteins.
Cancer Lett. 249:198–208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mao Q, Zhang PH, Wang Q and Li SL:
Ginsenoside F(2) induces apoptosis in humor gastric carcinoma cells
through reactive oxygen species-mitochondria pathway and modulation
of ASK-1/JNK signaling cascade in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine.
21:515–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|