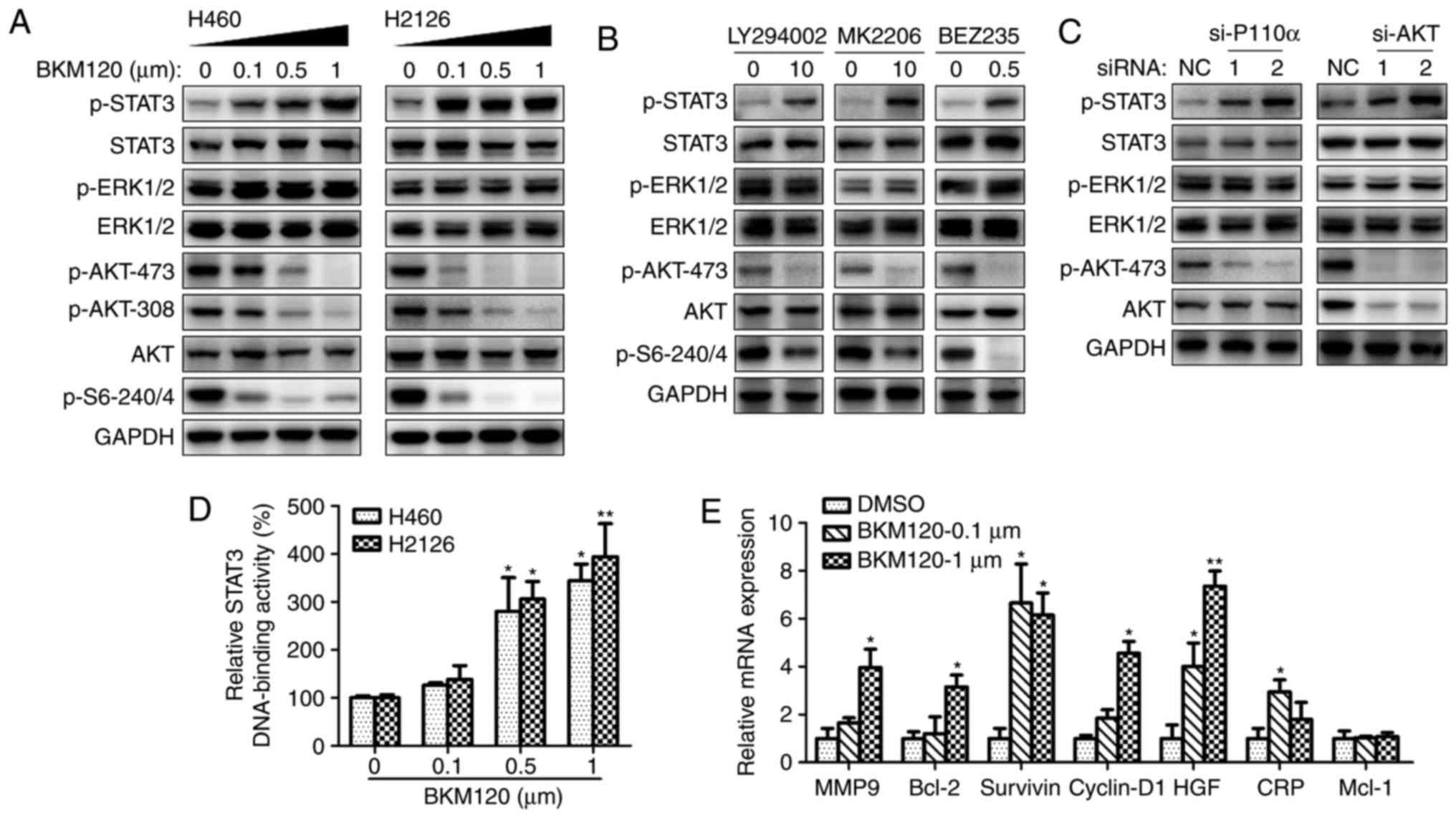
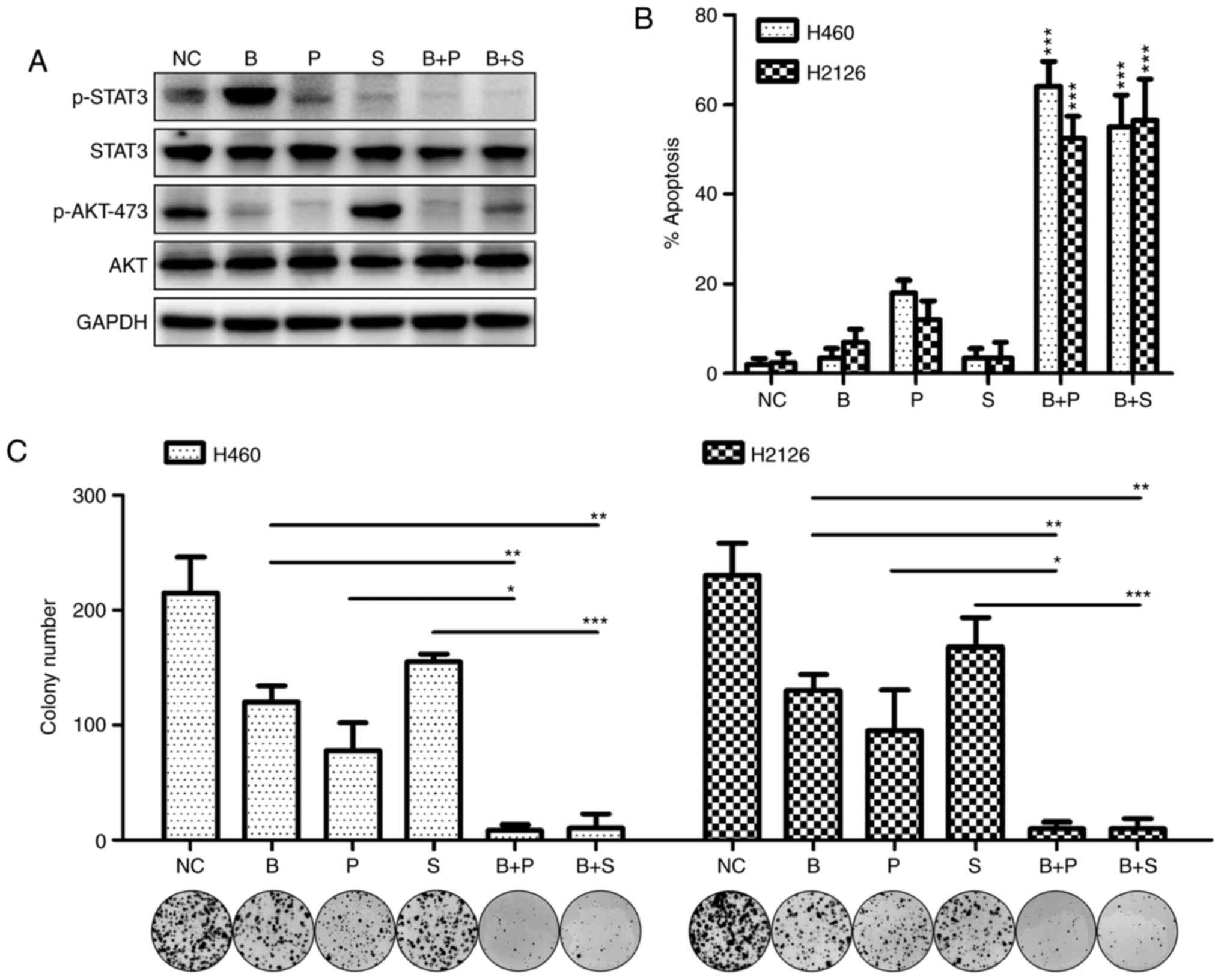
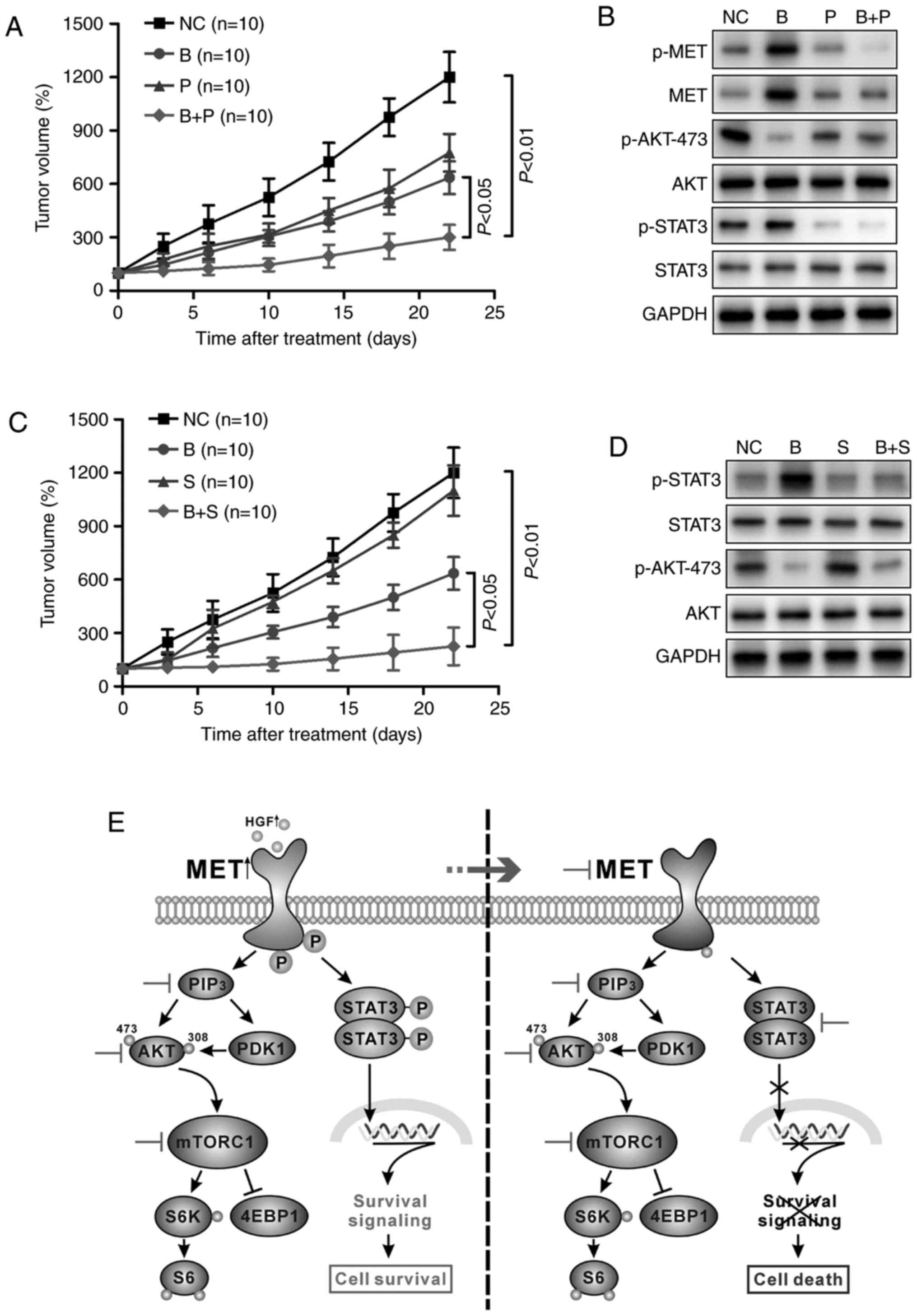
|
1
|
Blanco R, Maestu I, de la Torre MG,
Cassinello A and Nunez I: A review of the management of elderly
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 26:451–463.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Naylor EC, Desani JK and Chung PK:
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy for lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin
N Am. 25:601–609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang L, Li G, Zhao L, Pan F, Qiang J and
Han S: Blocking the PI3K pathway enhances the efficacy of
ALK-targeted therapy in EML4-ALK-positive nonsmall-cell lung
cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:9759–9767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA and
Settleman J: Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer
activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 305:1163–1167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gadepalli VS, Deb SP, Deb S and Rao RR:
Lung cancer stem cells, p53 mutations and MDM2. Subcell Biochem.
85:359–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bild AH, Yao G, Chang JT, Wang Q, Potti A,
Chasse D, Joshi MB, Harpole D, Lancaster JM, Berchuck A, et al:
Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to
targeted therapies. Nature. 439:353–357. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baselga J: Targeting the
phosphoinositide-3 (PI3) kinase pathway in breast cancer.
Oncologist. 16 Suppl 1:S12–S19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Engelman JA: The role of phosphoinositide
3-kinase pathway inhibitors in the treatment of lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:s4637–s4640. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu HG, Ai YW, Yu LL, Zhou XD, Liu J, Li
JH, Xu XM, Liu S, Chen J, Liu F, et al: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase/Akt pathway plays an important role in chemoresistance of
gastric cancer cells against etoposide and doxorubicin induced cell
death. Int J Cancer. 122:433–443. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brana I and Siu LL: Clinical development
of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment.
BMC Med. 10:1612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Seront E, Rottey S, Filleul B, Glorieux P,
Goeminne JC, Verschaeve V, Vandenbulcke JM, Sautois B, Boegner P,
Gillain A, et al: Phase II study of dual phosphoinositol-3-kinase
(PI3K) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor BEZ235 in
patients with locally advanced or metastatic transitional cell
carcinoma. BJU Int. 118:408–415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bedard PL, Tabernero J, Janku F, Wainberg
ZA, Paz-Ares L, Vansteenkiste J, Van Cutsem E, Pérez-García J,
Stathis A, Britten CD, et al: A phase Ib dose-escalation study of
the oral pan-PI3K inhibitor buparlisib (BKM120) in combination with
the oral MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib (GSK1120212) in patients with
selected advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 21:730–738. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen CL, Loy A, Cen L, Chan C, Hsieh FC,
Cheng G, Wu B, Qualman SJ, Kunisada K, Yamauchi-Takihara K and Lin
J: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is involved
in cell growth and survival of human rhabdomyosarcoma and
osteosarcoma cells. BMC Cancer. 7:1112007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang C, Wang L, Yang X, Lai L, Chen D and
Duan C: Expression of activated signal transducer and activator of
transcription-3 as a predictive and prognostic marker in advanced
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 13:3142015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gritsko T, Williams A, Turkson J, Kaneko
S, Bowman T, Huang M, Nam S, Eweis I, Diaz N, Sullivan D, et al:
Persistent activation of stat3 signaling induces survivin gene
expression and confers resistance to apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:11–19. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Masciocchi D, Gelain A, Villa S,
Meneghetti F and Barlocco D: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 (STAT3): A promising target for anticancer therapy.
Future Med Chem. 3:567–597. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fossey SL, Liao AT, McCleese JK, Bear MD,
Lin J, Li PK, Kisseberth WC and London CA: Characterization of
STAT3 activation and expression in canine and human osteosarcoma.
BMC Cancer. 9:812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carpenter RL and Lo HW: STAT3 target genes
relevant to human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 6:897–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martinez-Marti A and Felip E: PI3K pathway
in NSCLC. Front Oncol. 1:552011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heavey S, O'Byrne KJ and Gately K:
Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:445–456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ando Y, Inada-Inoue M, Mitsuma A, Yoshino
T, Ohtsu A, Suenaga N, Sato M, Kakizume T, Robson M, Quadt C and
Doi T: Phase I dose-escalation study of buparlisib (BKM120), an
oral pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced
solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 105:347–353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Serra V, Scaltriti M, Prudkin L, Eichhorn
PJ, Ibrahim YH, Chandarlapaty S, Markman B, Rodriguez O, Guzman M,
Rodriguez S, et al: PI3K inhibition results in enhanced HER
signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast
cancer. Oncogene. 30:2547–2557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ilic N, Utermark T, Widlund HR and Roberts
TM: PI3K-targeted therapy can be evaded by gene amplification along
the MYC-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) axis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:E699–E708. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tenbaum SP, Ordóñez-Morán P, Puig I,
Chicote I, Arqués O, Landolfi S, Fernández Y, Herance JR, Gispert
JD, Mendizabal L, et al: β-catenin confers resistance to PI3K and
AKT inhibitors and subverts FOXO3a to promote metastasis in colon
cancer. Nat Med. 18:892–901. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Santiago S, Raeder M,
Zhang F, Isabella A, Yang J, Semaan DJ, Chen C, Fox EA, et al:
Oncogenic PIK3CA-driven mammary tumors frequently recur via PI3K
pathway-dependent and PI3K pathway-independent mechanisms. Nat Med.
17:1116–1120. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He L and Hristova K: Quantification of the
effects of mutations on receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activation
in mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1233:81–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Vande Woude GF: Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kubo T, Yamamoto H, Lockwood WW, Valencia
I, Soh J, Peyton M, Jida M, Otani H, Fujii T, Ouchida M, et al: MET
gene amplification or EGFR mutation activate MET in lung cancers
untreated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int J Cancer.
124:1778–1784. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Janbabai G, Oladi Z, Farazmandfar T,
Taghvaei T and Naghshvar F: The prognostic impact of EGFR, ErbB2
and MET gene amplification in human gastric carcinomas as measured
by quantitative Real-Time PCR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:1945–1952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Syed ZA, Yin W, Hughes K, Gill JN, Shi R
and Clifford JL: HGF/c-met/Stat3 signaling during skin tumor cell
invasion: Indications for a positive feedback loop. BMC Cancer.
11:1802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang YW, Wang LM, Jove R and Vande Woude
GF: Requirement of Stat3 signaling for HGF/SF-Met mediated
tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 21:217–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Van Schaeybroeck S, Kalimutho M, Dunne PD,
Carson R, Allen W, Jithesh PV, Redmond KL, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S,
Blayney J, et al: ADAM17-dependent c-MET-STAT3 signaling mediates
resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer. Cell
Rep. 7:1940–1955. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|