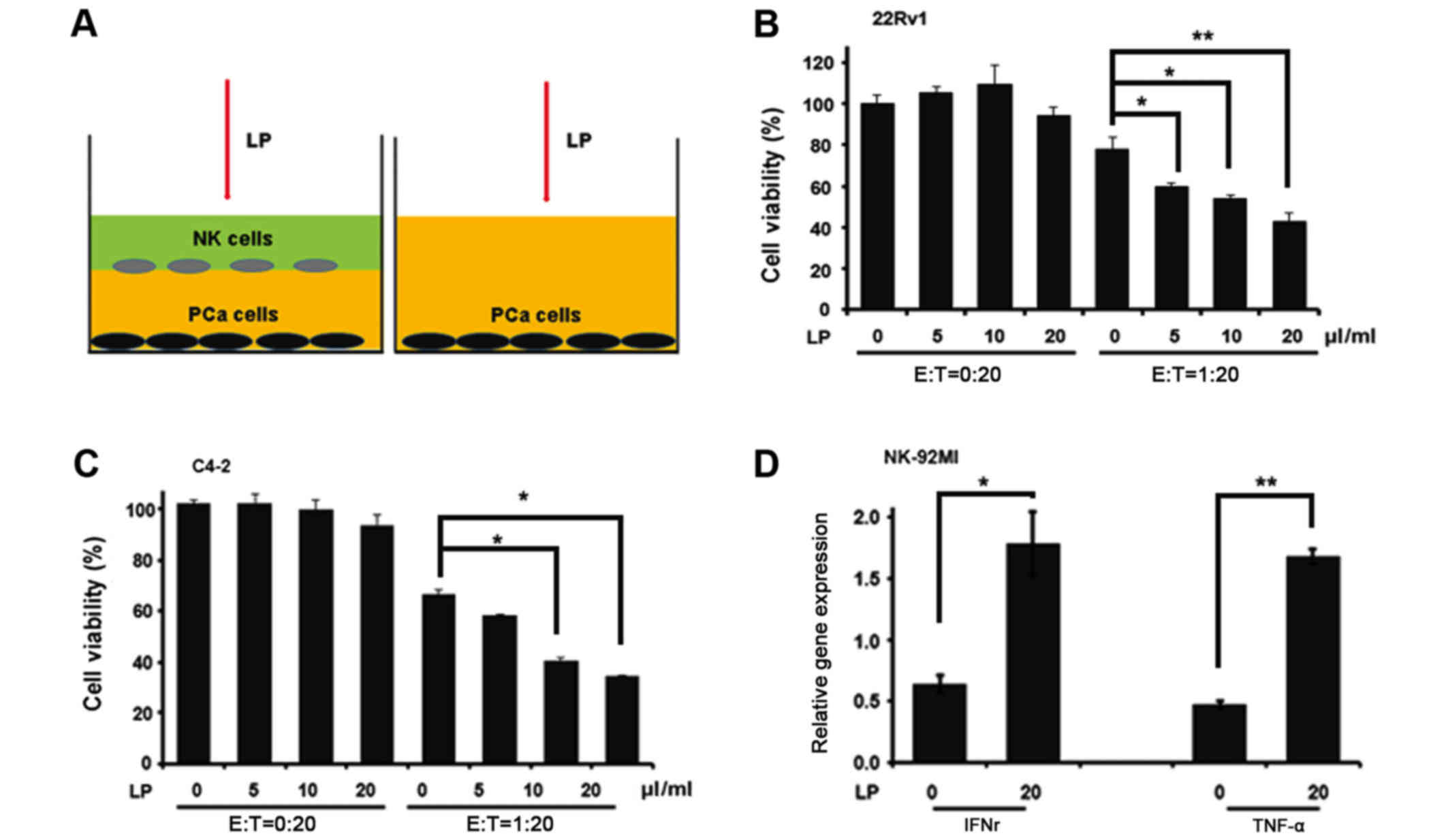
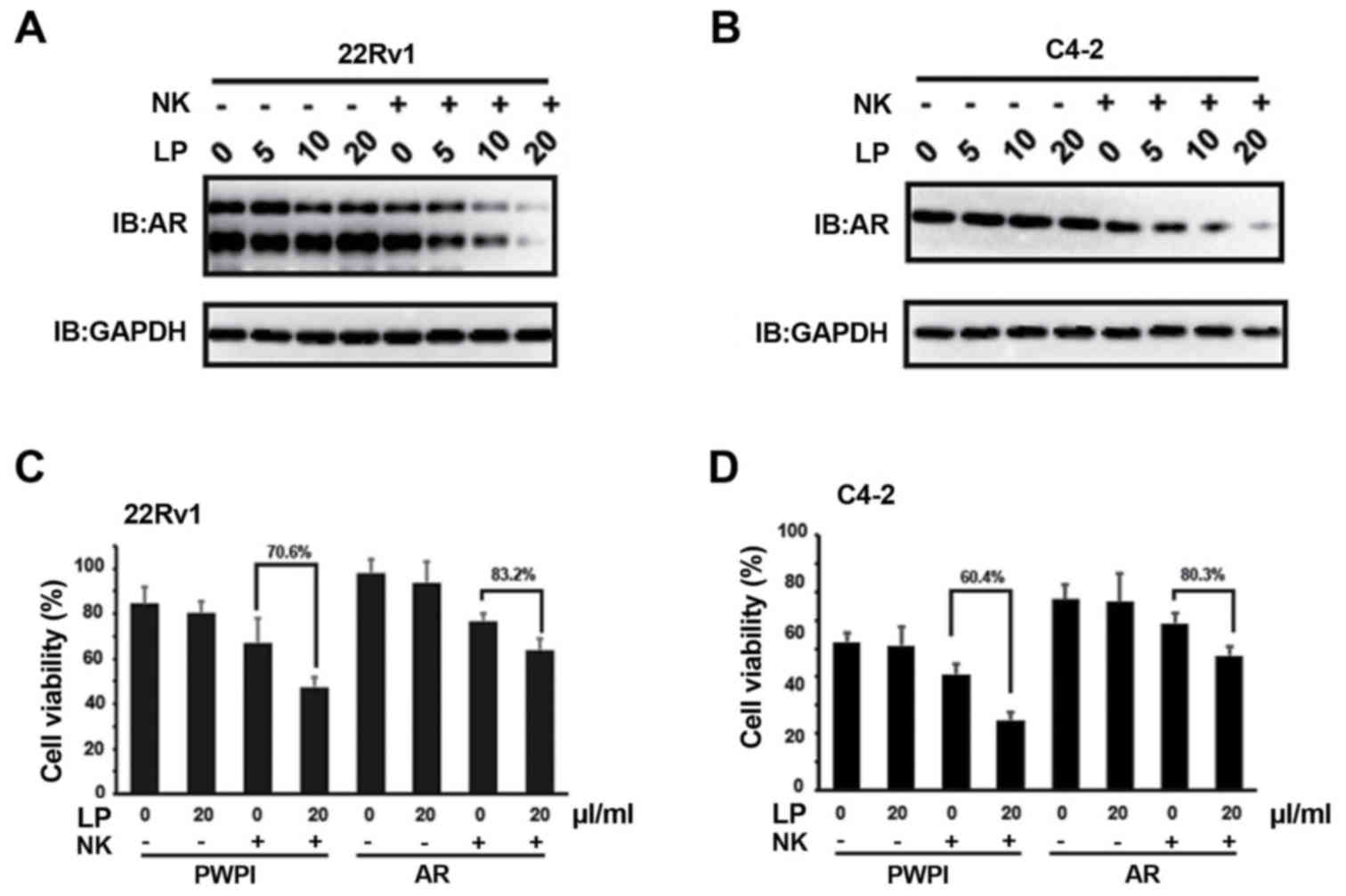
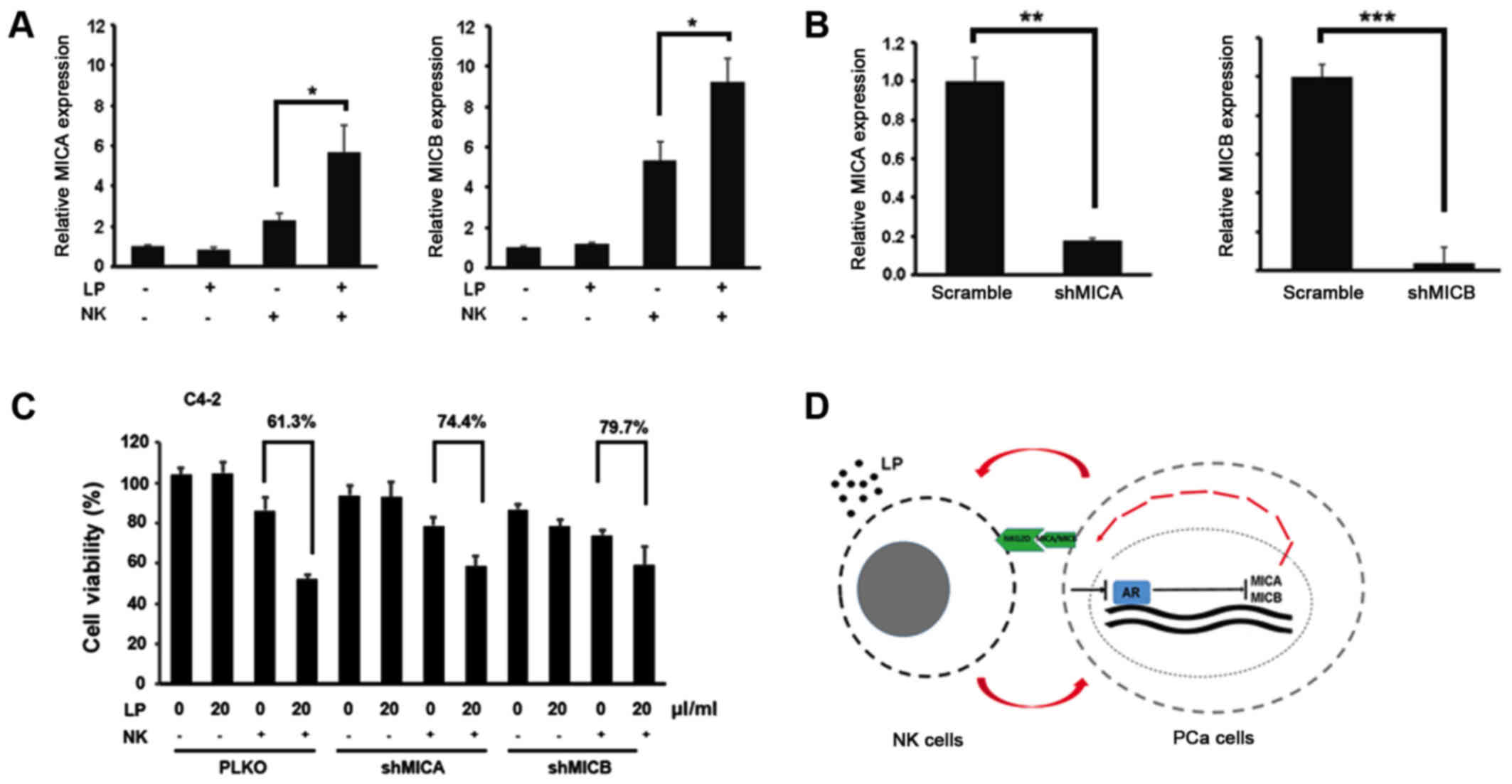
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huggins C: Effect of orchiectomy and
irradiation on cancer of the prostate. Ann Surg. 115:1192–1200.
1942. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heinlein CA and Chang C: Androgen receptor
in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 25:276–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coutinho I, Day TK, Tilley WD and Selth
LA: Androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate
cancer: A lesson in persistence. Endocr Relat Cancer. 23:T179–T197.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bishop JL, Davies A, Ketola K and Zoubeidi
A: Regulation of tumor cell plasticity by the androgen receptor in
prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:R165–R182. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kaarbø M, Klokk TI and Saatcioglu F:
Androgen signaling and its interactions with other signaling
pathways in prostate cancer. Bioessays. 29:1227–1238. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Efstathiou E, Titus M, Tsavachidou D,
Tzelepi V, Wen S, Hoang A, Molina A, Chieffo N, Smith LA, Karlou M,
et al: Effects of abiraterone acetate on androgen signaling in
castrate-resistant prostate cancer in bone. J Clin Oncol.
30:637–643. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vasaitis TS, Bruno RD and Njar VC: CYP17
inhibitors for prostate cancer therapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
125:23–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ, Chen Y, Watson
PA, Arora V, Wongvipat J, Smith-Jones PM, Yoo D, Kwon A, et al:
Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of
advanced prostate cancer. Science. 324:787–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME,
Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, et
al: Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after
chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 367:1187–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corn PG: The tumor microenvironment in
prostate cancer: Elucidating molecular pathways for therapy
development. Cancer Manag Res. 4:183–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karlou M, Tzelepi V and Efstathiou E:
Therapeutic targeting of the prostate cancer microenvironment. Nat
Rev Urol. 7:494–509. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pasero C, Gravis G, Granjeaud S, Guerin M,
Thomassin-Piana J, Rocchi P, Salem N, Walz J, Moretta A and Olive
D: Highly effective NK cells are associated with good prognosis in
patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
6:14360–14373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang R, Jaw JJ, Stutzman NC, Zou Z and Sun
PD: Natural killer cell-produced IFN-γ and TNF-α induce target cell
cytolysis through up-regulation of ICAM-1. J Leukoc Biol.
91:299–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo Y, Hu Q, Sun C, Gu B, Xu K and Xia G:
Postoperative renormalization of C-reactive protein with adjuvant
lienal polypeptide and its association with tumour recurrence in T1
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 44:620–626. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brett A, Pandey S and Fraizer G: The
Wilms' tumor gene (WT1) regulates E-cadherin expression and
migration of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:32013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin SJ, Chou FJ, Li L, Lin CY, Yeh S and
Chang C: Natural killer cells suppress enzalutamide resistance and
cell invasion in the castration resistant prostate cancer via
targeting the androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (ARv7). Cancer
Lett. 398:62–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nausch N and Cerwenka A: NKG2D ligands in
tumor immunity. Oncogene. 27:5944–5958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koivisto P, Kononen J, Palmberg C, Tammela
T, Hyytinen E, Isola J, Trapman J, Cleutjens K, Noordzij A,
Visakorpi T and Kallioniemi OP: Androgen receptor gene
amplification: A possible molecular mechanism for androgen
deprivation therapy failure in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
57:314–319. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joseph JD, Lu N, Qian J, Sensintaffar J,
Shao G, Brigham D, Moon M, Maneval EC, Chen I, Darimont B and Hager
JH: A clinically relevant androgen receptor mutation confers
resistance to second-generation antiandrogens enzalutamide and
ARN-509. Cancer Discov. 3:1020–1029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dehm SM, Schmidt LJ, Heemers HV, Vessella
RL and Tindall DJ: Splicing of a novel androgen receptor exon
generates a constitutively active androgen receptor that mediates
prostate cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Res. 68:5469–5477. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang R, Sun Y, Li L, Niu Y, Lin W, Lin C,
Antonarakis ES, Luo J, Yeh S and Chang C: Preclinical study using
malat1 small interfering RNA or androgen receptor splicing variant
7 degradation enhancer ASC-J9®to suppress
enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer progression. Eur Urol.
72:835–844. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu JD, Higgins LM, Steinle A, Cosman D,
Haugk K and Plymate SR: Prevalent expression of the
immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related molecule is
counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. J Clin Invest.
114:560–568. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|